Bio 102: Theme 3- Evolution: Change Over Time
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Evolution
change over time in frequencies in a population
Population
group of individuals of the same species that interbreed
What does evolution do?
changes populations
What is frequency equivalent to?
Proportion
What is the equation for solving population numbers?
part / whole = count of target / count of all
Gene Pool
set of alleles in a population
High Genetic Diversity
population with large gene pool (many alleles)
Heritable
passed down from parents has a genetic basis
Populations evolve through:
natural selection
genetic drift
gene flow
mutation
Natural selection
individuals with better phenotypes tend to produce more offspring because of the phenotypes
Genetic Drift
Fitness differences in individuals because some individuals are luckier than others
Gene Flow
alleles move between populations that can cause change in a population
Mutation
new alleles can arise from mistakes in DNA replication
Fitness
ability to survive and produce surviving offspring
survival of the alleles/genetic combination
What does SURVIVAL of the FITTEST mean?
Survival= specific alleles persist
Fittest= tend to produce more offspring
Normal Distribution
curve that’s symmetrical around the mean
individual with mean value are most common
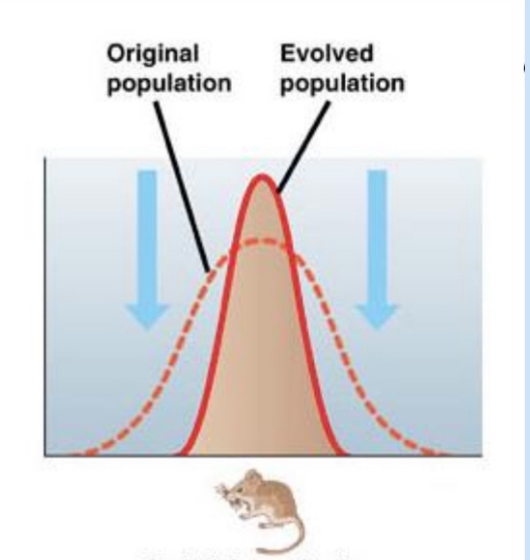
Stabilizing selection
narrowing
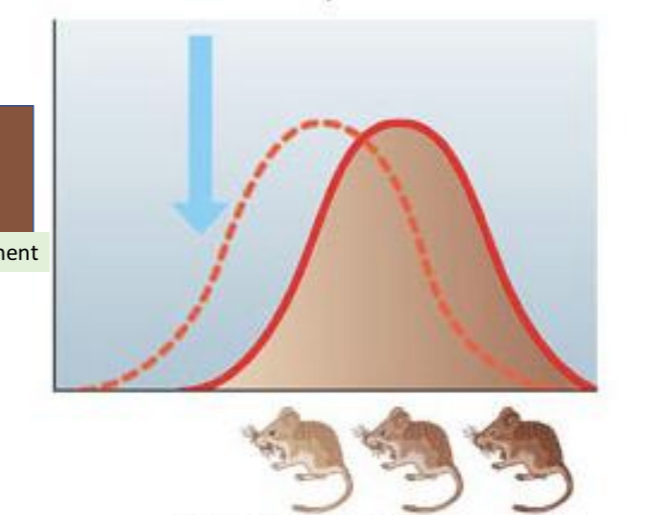
Directional selection
population phenotype becomes more like an extreme
shifts right or left
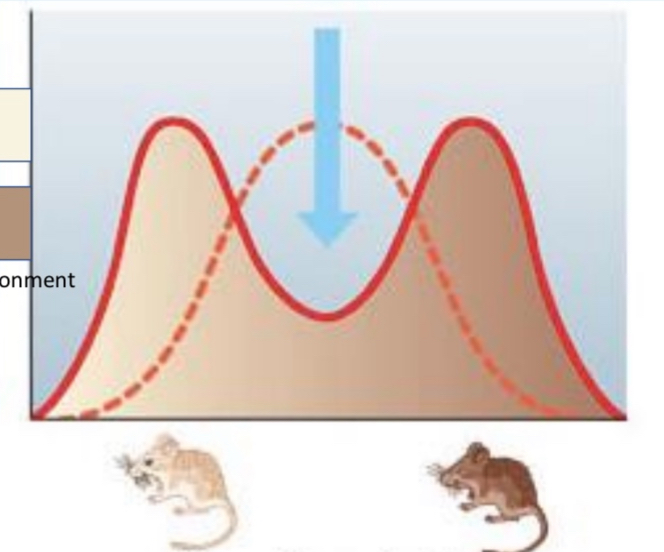
Disruptive selection
disrupts how selection works
Adaptation
natural selection makes populations better adapted
Sexual Dimorphism
males and females have different phenotypes
Sexual selection
individuals with certain inherited traits produce more surviving offspring
there is strong selection pressure for traits that produce the most surviving offspring
Intersexual selection
opposite sex is the “selector”
Intrasexual selection
selection happens between same sex
Ex: moose (male to male)
How can a trait evolve by sexual selection?
if it increases the individual’s fitness
Artificial Selection
breeders select the individuals with desirable traits and use them to create the next generation
Meiosis
creates diversity without adding new alleles
How does meiosis create diversity?
Crossing over
Independent assortment
combinations are new, but the parts aren’t new
How is mutation important?
Adds new alleles to the deck
How much of our genome is uniquely our own?
approximately 30%
What are most mutations?
Mostly neutral with no effect
What happens when a mutation does have an effect?
They are mostly harmful, but sometimes beneficial
What does random mean?
All possible are equally likely
an alleles is jut as likely to become more common than less common
Bottleneck event
random population change due to a disaster
Founder effect
few individuals “found” (create) a new population, and new population’s genetic make-up is a random subset of initial population
Which patterns of evolution cause fitness differences?
(Natural) selection
Genetic Drift
Gene Flow
new alleles come along with migrating individuals
What patterns of evolution cause new alleles
Mutation
Gene Flow
Dispersal
movement from one place to another
sometimes over very, very long distances
Does evolution have a goal?
No, it has no goal. It is random.
Which patterns of evolution increase genetic diversity?
Gene Flow
Mutation
Which patterns of evolution decrease genetic diversity?
Natural Selection
Genetic Drift