Dunn M&C - Beyond Mendel
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sex linkage, pedigrees, etc.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
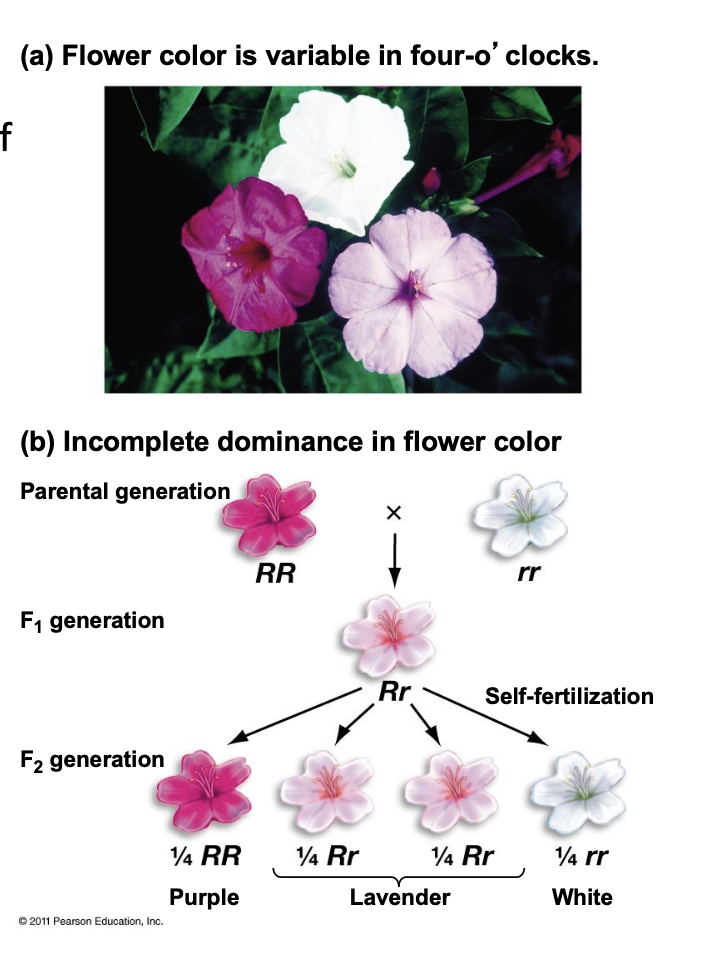
incomplete dominance
looks like the blending hypothesis of inheritance.
e.g, the deep purple/pink allele of the flower color gene is incompletely dominant over the white allele
codominance
occurs when two alleles are phenotypically expressed simultaneously; in other words, heterozygotes express both phenotypes
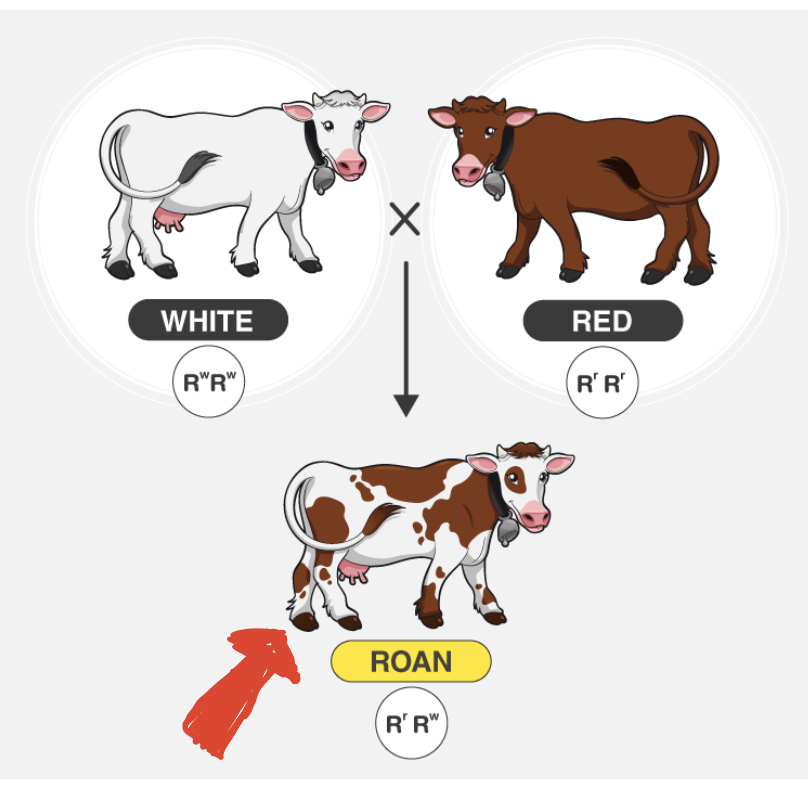
Codominance
occurs when two alleles are phenotypically expressed in equal measure; in other words, heterozygotes express both phenotypes
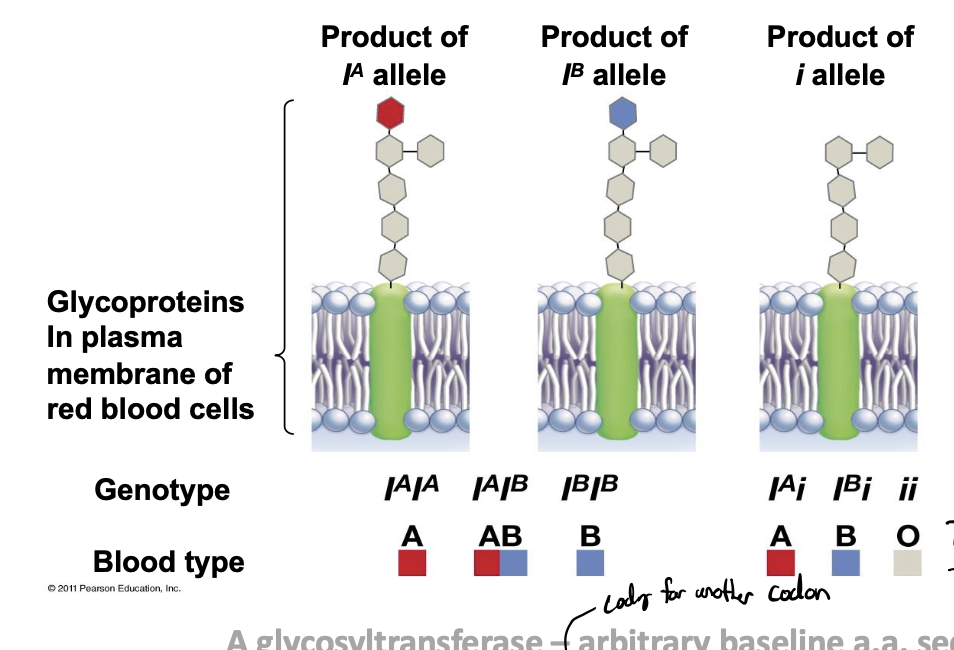
APO blood groups
illustrates multiple alleles, IA, IB, i allele
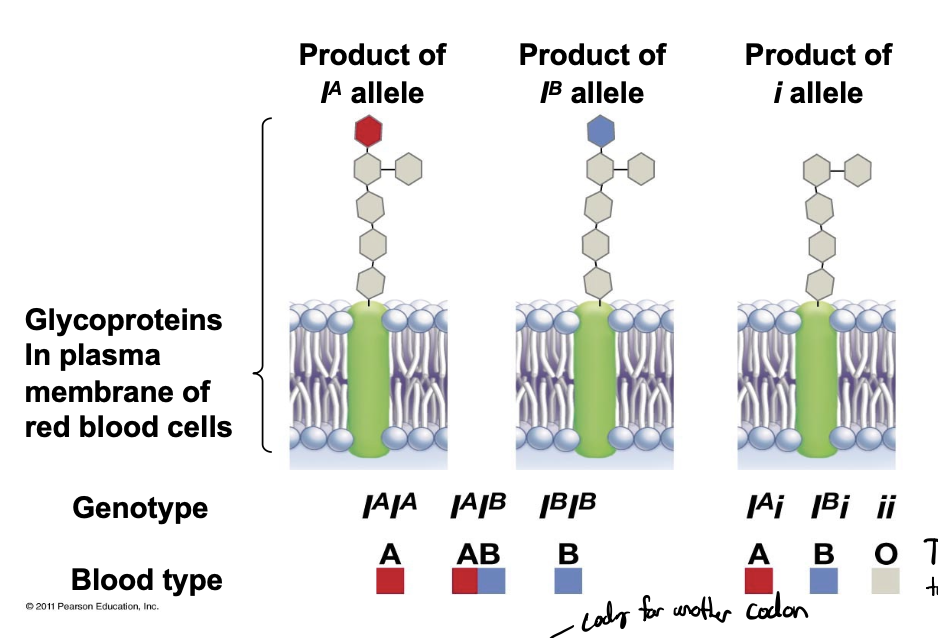
IA allele
causes the surface glycoprotein to be modified by a red sugar
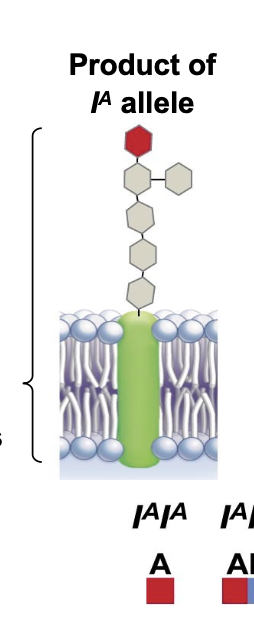
IB allele
causes the surface glycoprotein to be modified by a blue sugar
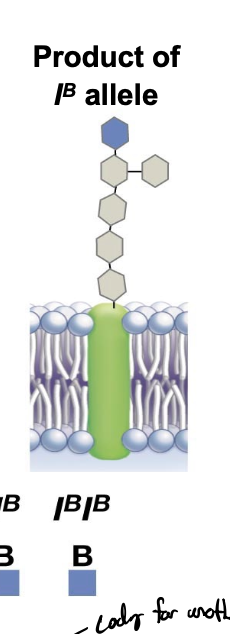
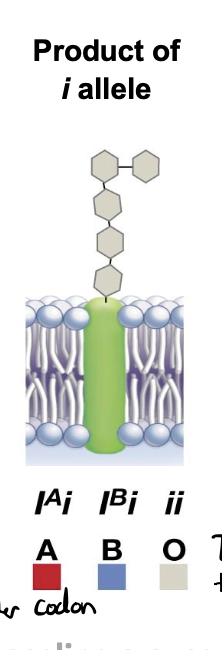
i allele
does not cause any modification (not blue or red sugar added)
polygenic traits
those determined by two or more genes
e.g, hair color, skin color, eye color, height
most considered complex, influenced by environmental factors such as diet.
autosomes
non-sex chromosomes
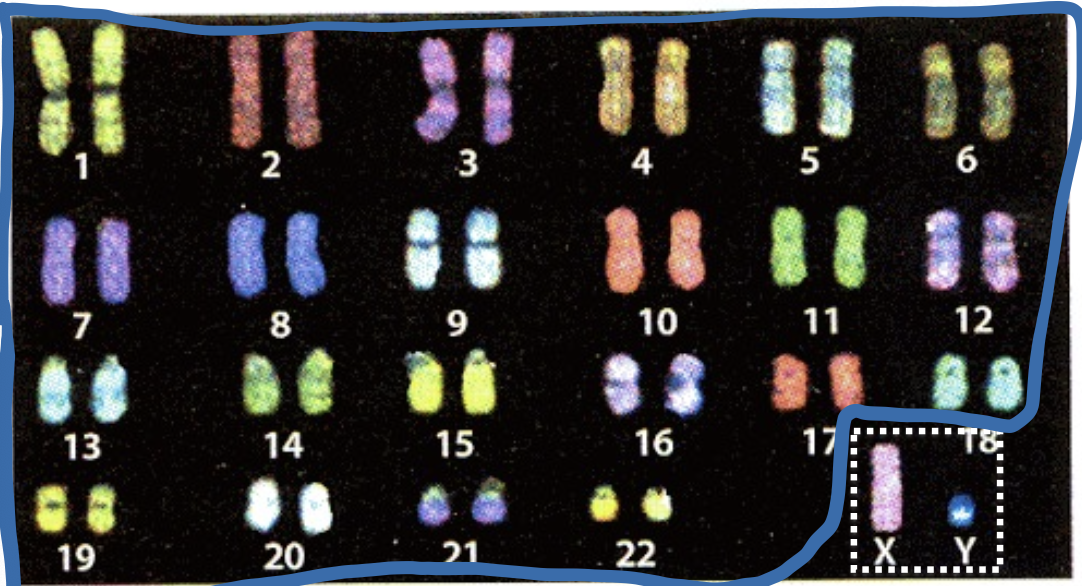
normal human karyotype
44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes
X & Y chromosome during meiosis
act as homologous pairs
50% of sperm contain X and 50% of sperm contains Y chromosomes
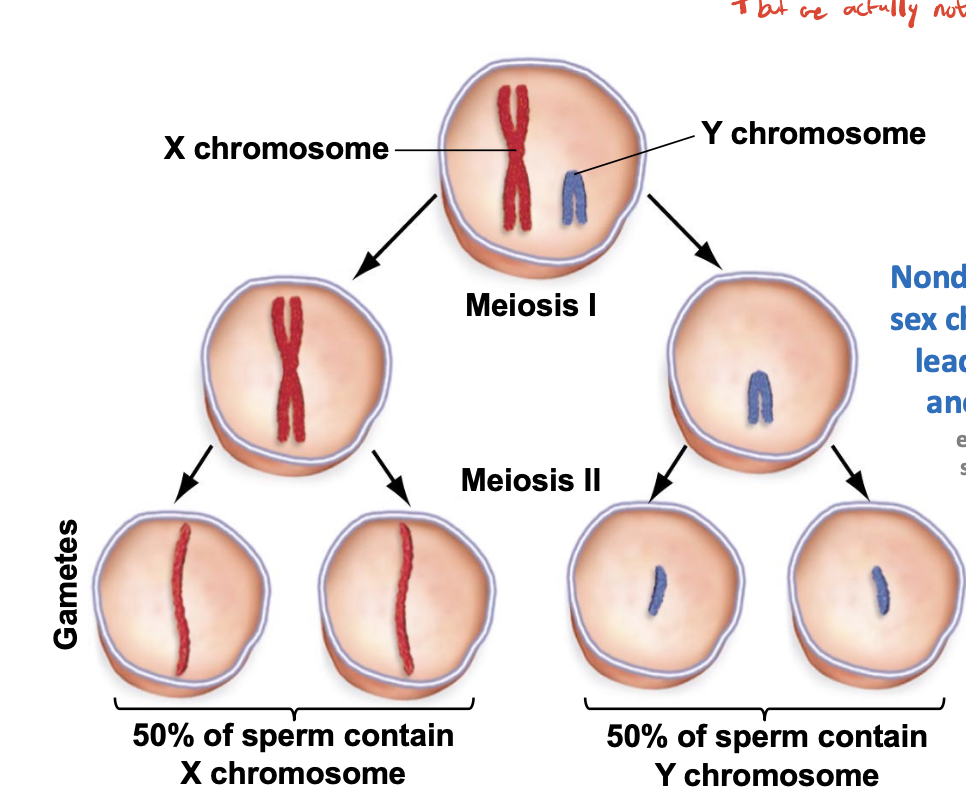
nondisjunction of sex chromosomes
leads to viable aneuploidies
aneuploidy
The occurrence of one or more extra or missing chromosomes in a cell or organism
reciprocal crosses
a cross in one in which you switch the sex of the parent affected by a phenotype.
sex-linked inheritance patterns can be observed by different outcomes of this
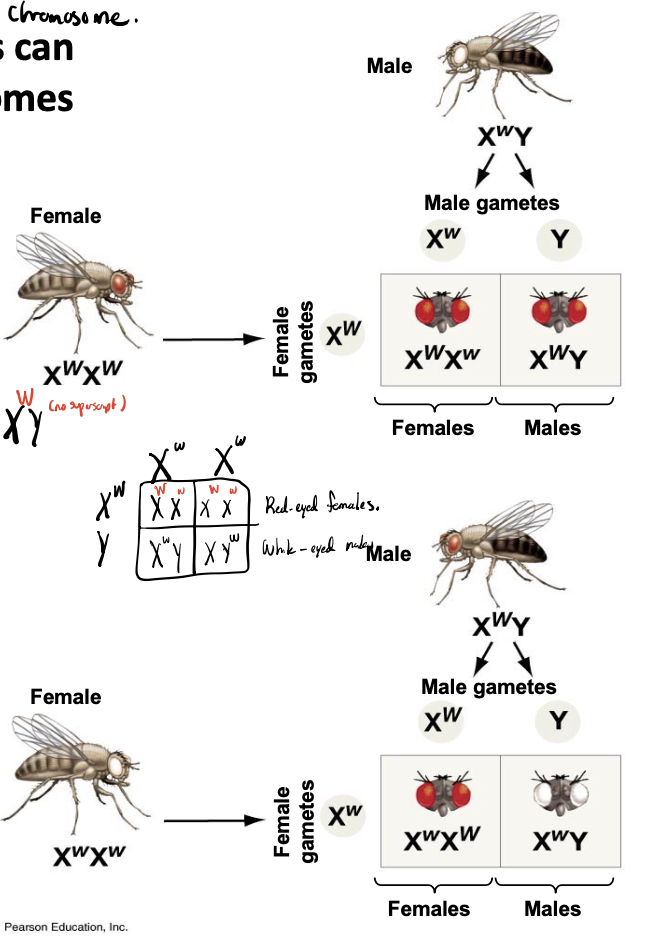
mutations in x-linked genes
results in predominantly male diseases (X-linked diseases)
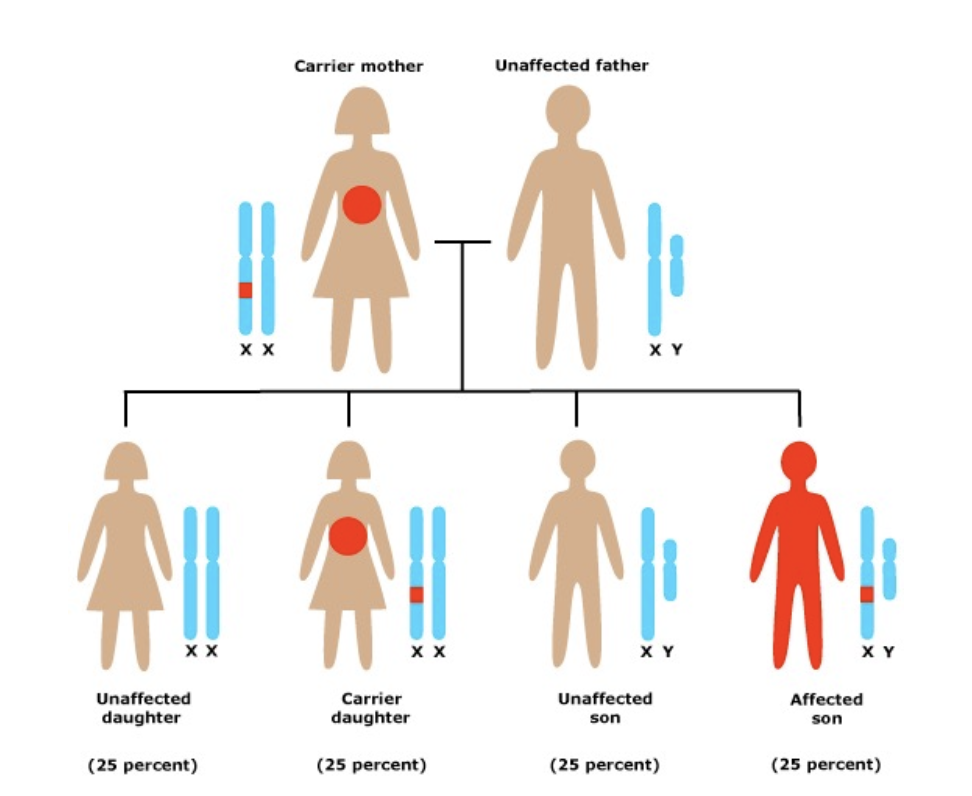
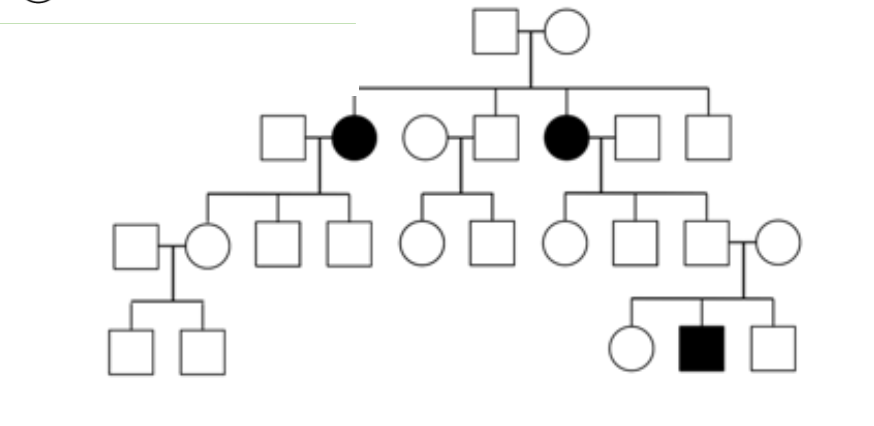
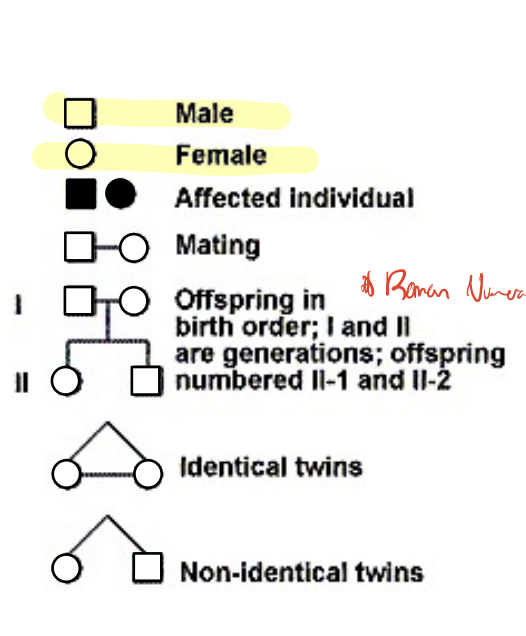
pedigrees
document the inheritance of traits in human families
squares are males, circles are females
lines between people mean that they mated
filled square/circle = affected with a particular phenotype like a disease
patterns of inheritance
describe how traits are passed from parents to offspring, with common patterns including autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and X-linked inheritance.
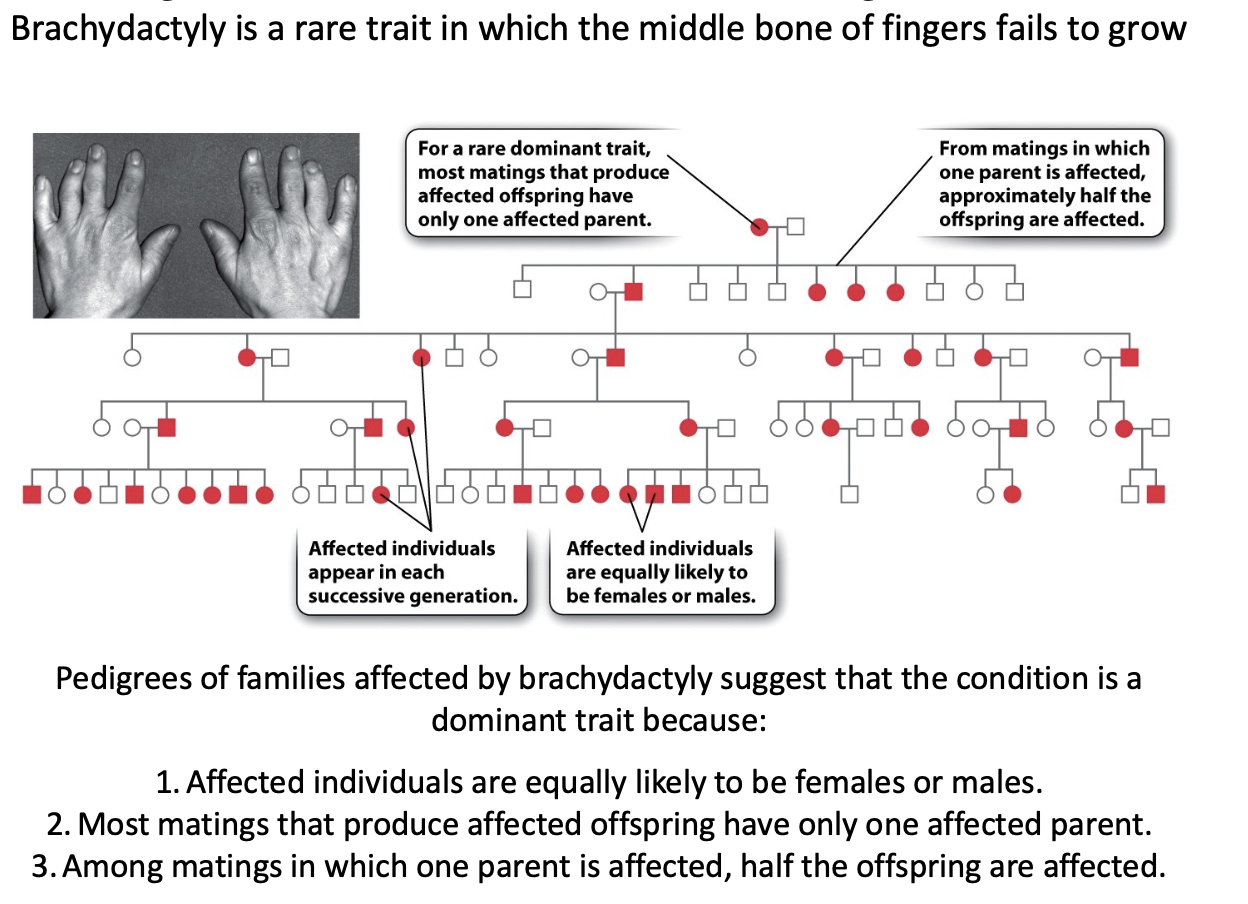
Pedigree of an autosomal dominant allele causing a disease trait
brachydactyly example
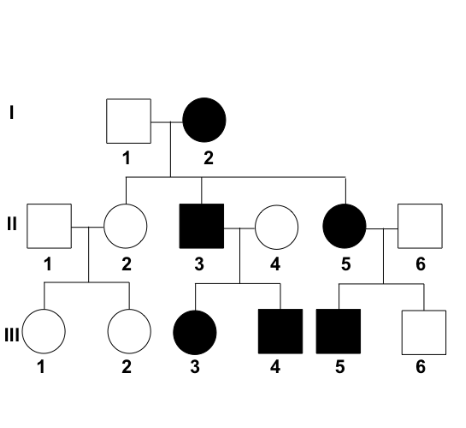
pedigree of an autosomal receessive allele causing a disease trait
albinism is autosomal
the trait may skip one or more generations
females and males are equally likely to be affected.
Individuals may have unaffected parents.
Affected individuals often result from mating between relatives, typically first cousins.
X-linked recessive traits
observed virtually exclusively in males and are often passed through unaffected females
autosomal dominant example
autosomal recessive example