Hematopoietic System: Part 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
palpation - assessmet
enlargement of
lymph nodes
spleen
liver
inspection - assessment
petechiae - pinpoint hemorrhages skin/mucosal
nosebleeds
ecchymosis (bruising) - large areas of hemorrhage into skin
diagnostic testing
biopsy of bone marrow/lymph node
analysis of blood cells
special test for specific diseases
biopsy of bone marrow/lymph node - diagnostic testing
bone marrow = dx hematopoietic cancers + other diseases
lymph = ± lymphoma
analysis of blood cells - diagnostic testing
Hct, Hgb, RBC blood smears = presence/absence of anemia
low = anemia
Hct = volume of RBC to % of blood volume (g/dL)
RBC = cells in small chamber/cubic mm
size/Hb concentration = microscope
WBC % + platelet count
retic count = % immature RBC
>2% = increase production of RBC
special test for specific diseases - diagnostic testing
Hgb electrophoresis = genetic abnormalities of Hgb
serum ferritin - indirect measure Fe stores
flow cytometry = determine diseases result of antibodies against RBC/WBC
hemostasis
prevents excessive bleeding after injury
interaction of
blood vessels
platelets
chemical coagulation factors in plasma
endothelial injury - whats happening?
blood vessels undergo spastic contraction
blood shunted to non-injured vessels
platelets
physically obstruct BF
promote vasoconstriction
release chemical = further hemostatic process
fibrinogen → fibrin monomer
polymerizes = thrombus = clotting cascade (from liver)
inhibitors slow rxn
cascade designated by roman numerals
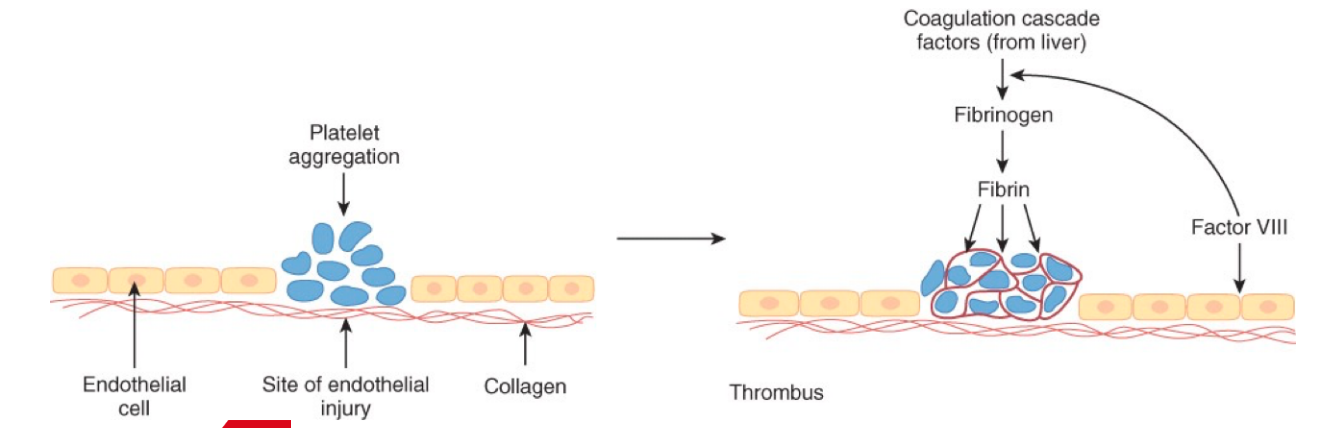
coagulation cascade
thrombosis
formation of blood clot through interaction of tissue, platelets, plasma proteins = coagulation factors
fibrin formation
enzymatic steps = coagulation/clotting cascade
thrombus
blood clot in blood vessel caused by fibrin (polymerized to block vessel)
organized thrombus
thrombus converted into granulation tissue/scar
fibrin
fibrin monomers (plasma proteins) bind = form stringy, strong, insoluble protein (mesh)
plasmin
breaks down insoluble fibrin clot into soluble fragments during repair of tissue after clot formation
causes of hemorrhage
trauma - most common
injury to larger vessels = sig med treatment
spontaneous bleeding
platelet count <10,000/mL
platelets defective
hereditary coagulation disorders
hemophilia
thrombocytopenia
decreased # circulating platelets
caused by
bone marrow failure
peripheral destruction of platelets
temporary platelet deficiency treated with platelet transfusion
acquired coagulation disorders
associated with other diseases/drugs in susceptible individuals
virchow’s triad
conditions leading to thrombosis
endothelial cell injury
stasis or turbulence of blood flow
hypercoagulable state
endothelial cell injury - virchow’s triad
trauma
vasculitis
cig smoke
radiation
atherosclerosis (plaque arteries)
infarction
turbulent BF
bacterial endotoxins
stasis/turbulence of blood flow - virchow’s triad
bifurcation of arteries
atherosclerosis (plaque arteries)
aneurysm
venous stasis (incompetent valves, bed rest)
hypercoagulable state - virchow’s triad
increased estrogen (birth control, preg)
trauma
surgery
inherited coagulopathy
cancer
obesity
diathesis vs coagulopathy
hemorrhagic diathesis = tendency to bleed
coagulopathy = abnormality in coagulation mechanism = excessive bleeding/clotting
platelet decrease/deficiency cause…
petechiae
epistaxis
hematuria = blood urine
hematochezia = blood from anus
menorrhagia = heavy/prolonged menstrual bleeding
increased bleeding following delivery
hematomas = tissue bleeding
joints, soft tissues, brain
purpura - large collections of blood in skin (many petechiae)
platelet count - diagnostic test
do not ID platelet abnormalities
platelet function analyzer - diagnostic test
PFA-100
measure platelet dependent coagulation under flow conditions
activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) - diagnostic test
test for deficiencies in intrinsic pathway of coagulation mech
prothrobin time (PT) - diagnostic test
assess disorder of extrinsic pathway of coagulation
expressed in International normalized ratio (INR)
fibrinogen assay - diagnostic test
measure fibrinogen levels
measure fibrin degradation products/d-dimer reflects fibrinolysis
hemophilia
most common hereditary coagulation disorder
common in 2 forms of X genes = affecting males
females = 2 defective genes to manifest = less common
hemophilia A
hemophilia B
dx = coag factor defect (Plt ct, aPTT, PT), factors VIII and IX
hemophilia A
classic
deficiency of factor VIII
hemophilia B
christmas disease
20% NOT hereditary = new mutants
deficiency of factor IX
bleeding joints, muscles, soft tissues
bleed excessively from minor injury/surgery
spontaneous thrombosis
rare hereditary deficiencies of
antithrombin III
protein C
protein S
The factor V Leiden mutation - spontaneous thrombosis
coagulant factors increased after trauma, operations, childbirth
Pathogenesis
small thrombi > obstruction of blood flow > ischemic injury to tissue supplied by that vessel
infarct - Spontaneous thrombosis
large thrombi in larger arteries, though may not cause complete blockage, can be pathological if bits of thrombi (called EMBOLI) is chipped off it, and travel in the blood stream, causing INFARCTS
Cerebral infarct - stroke
Myocardial Infact - heart attack
Splenic infarct - Spleen
Renal infact - Kidney
Pulmonary embolism - Lungs
coagulation modifier drugs
anticoagulants
antiplatelets
thrombolytics
antifibrinolytics
anticoagulants
warfarin sodium (PO)
unfractionated heparin, low-molecular weight heparin = Enoxaparin (SC)
argatroban, bivalirudin, dabigatran etexilate mesylate
fondaparinux rivaroxaban
warfarin sodium (PO)
anticoagulant
subclass = coumadin
MOA = inhibits vit k-dependent clotting factors
Indi = atrial fibrillation, thrombus prevention, prosthetic heart valve
Contra = allergy, acute bleeding, thrombocytopenia, preg
AE = bleeding, thethargy, muscle pain, purple toes
Nursing = VS, s/s of bleeding, PT/INR, natural health products (result in increased bleeding (dong quai, garlic, ginkgo, st john wort))
TA
onset = 24-72hrs
half-life = 0.4-3 days
[peak plasma] = 4hrs
duration of action = 2-5 days
NOTE = dose cut in half
inhibits vit-k dependent clot factors, foods high in vit k may reduce warfarin ability to prevent clots
leafy greens = food-drug interaction
maintenance warfarin dose established = eat greens, but consistent with intake (affect INR)
unfractionated heparin, low-molecular weight heparin = Enoxaparin (SC)
anticoagulant
subclass = heparins
MOA =LMWH - greater affinity factor Xa
Indi = thromboprophylaxis in surgery, higher dose in DVT/PE treatment
Contra = LMWH - indwelling epidural catheter (given 2hrs after removed)
AE = bleeding, hematoma, nausea, anemia, thrombocytopenia, fever, edema
Nursing = ensure Heparin + LMWH ordered at same time
TA =
LMWH: Onset: 3-5 hrs Half-life: 4-5 H
Peak Plasma Conc: 4-5 H
Duration of action: 12 H
Heparin: Onset: 20-30min Half-life: 1-2 H
Peak Plasma Conc: 2-4 H
Duration of action: 8-12 H
argatroban, bivalirudin, dabigatran etexilate mesylate
anticoagulant
subclass = Direct Thrombin Inhibitors
MOA = PO - prevent stroke/thrombosis
Indi = non-valcular atrial fibrillation
AE = bleeding, dizzy, SOB, fever, urticaria (hives)
Nursing = NO antidote, no BW monitoring, s/s bleeding
TA
onset = 24-72hrs
half-life = 0.4-3
[peak plasma] = 4hrs
duration of action = 2-5 days
NOTE = activated in liver, reversibly binds to free and clot-bound thrombin
excreted in kidneys = dose dependent on kidney function
normal does = 150mg BID, reduced to 75mg DIB if creatine clearance <30mL/min
fondaparinux rivaroxaban
anticoagulant
subclass = Selective Factor Xa Inhibitors
Indi = DVT or pulmonary Edema
Contra = allergy, creatinine clearance of less than 30/min or body wt <50kg
AE = bleeding, hematoma, dizzy, rash, GI, distress, anemia, thrombocytopenia
Nursing = NO antidote
TA
onset = 2hrs
half-life = 17-21 hrs
[peak plasma] = 2-3hrs
duration of action = 24hrs
antiplatelets
Aspirin (PO)
eptifibatide (Integrilin)
Clopidogrel
Aspirin (PO)
antiplatelet
subclass = Salicylate antiplatelet
MOA = acetylates/inhibits cyclooxygenase in platelet irreversibly so platelet cannot regenerate enzymes
Indi = stoke prevention, dual anti-platelet therapy
Contra = allergy, thrombocytopenia, active bleeding, leukemia, trauma, GI ulcer vi K deficiency, recent stroke
AE = drowsy, dizzy, confusion, flushing, N/V, GI bleeding, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, neutropenia, hemolytic, anemia, bleeding
Nursing = VS, s/s bleeding, PT/INR, natural health products (result in increased bleeding (dong quai, garlic, ginkgo, st john wort))
TA
onset = 15-30 min
half-life = 2-3hrs
[peak plasma] = 0.25 - 2 hrs
duration action = 4-6 hrs
eptifibatide (Integrilin)
antiplatelet
subclass = GP Iib/Iiia inhibitors
MOA = block receptor protein by name that occurs in the platelet wall membranes
Indi = acute unstable angina and MI, endovascular procedure, coronary angioplasty
Contra = allergy, thrombocytopenia, active bleeding, leukemia, trauma, GI ulcer vi K deficiency, recent stroke
AE = bradycardia, hypotension, edema, dizzy, bleeding, thrombocytopenia
Nursing = ensure Heparin and LMWH NOT ordered at same time
TA
onst = 1 hr
half-life = 2-2.5hrs
duration action = 4hrs
Clopidogrel
antiplatelet
subclass = ADP inhibitor
MOA = inhibits platelet aggregation by altering platelet membrane = no longer receive signal to aggregate/form clot
Indi = reduce risk of fetal/nonfatal thrombotic stroke, prophylaxis of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), post MI prevention of thrombosis
Contra = allergy, thrombocytopenia, active bleeding, leukemia, trauma, GI ulcer vi K deficiency, recent stroke
AE = chest pain, edema, flu s/s, headache, dizzy, fatigue, abdo pain, diarrhea, nausea, epistaxis, rash, pruritus
Nursing = NO antidote, no BW monitoring, monitor for s/s bleeding
TA
onset = 1-2 hrs
half-life = 8hrs
[peak plasma] = 1hr
duration action = 7-10 days
thrombolytics
Alteplase (Activase)
Tenecteplase (TNKase)
NOTE = substances that form clots destroyed by plasmin
mimic body own process of clot destruction
Alteplase (Activase)
Thrombolytics
subclass = t-PA
MOA = activates conversion of plasminogen to plasmin = breaks down/lyse thrombus
Indi = acute MI, arterial thrombosis, DVT, occlusion of sunts/catheters, PE, acute ischemic stroke
Contra = drug allergy, concurrent drugs that alter clotting, hx of surgery, trauma, bleeding
AE = internal/intracranial/superficial bleeding, hypersensitivity, anaphylactoid rxn, N/V, hypotension, cardiac dysrhythmias
Nursing = VS, s/s bleeding
TA
onset = intermideiat
half-life = 5 min
[peak plasma] = 60 min
duration action = depends on duration of infusion
Tenecteplase (TNKase)
Thrombolytics
subclass = t-PA
MOA = activates conversion of plasminogen to plasmin = breaks down/lyse thrombus
Indi = lysis of suspected occlusive coronary artery thrombi with MI specific to TNK + indications for Alteplase
Contra = drug allergy, concurrent drugs that alter clotting, hx of surgery, trauma, bleeding
AE = internal/intracranial/superficial bleeding, hypersensitivity, anaphylactoid rxn, N/V, hypotension, cardiac dysrhythmias
Nursing = VS, s/s bleeding
antifibrinolytics
Aprotinin (Artiss Trasylol)
tranexamic acid (Cyklokapron)
desmopressin acetate (DDAVP) - injectables, PO, intranasal
NOTE = all prevent lysis of fibrin
fibrin = help platelet plug insoluble and anchors clot to the damaged blood vessel
drug PROMOTE clot formation = hemostatic drugs = OPPOSITE anticoagulants (prevent clot formation)
Aprotinin (Artiss Trasylol)
antifibrinolytic
subclass = Natural antifibrinolytic
MOA = inhibits proteolytic enzyme trypsin, plasmin, kallikrein which lyses proteins that destroy fibrin clots. inhibiting enzymes = aprotinin prevent degradation of fibrin clot + inhibit action of complement systems
Indi = prevention/treat excessive bleeding from systemic hyperfibrinolysis/surgical complication
Contra = allergy, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
AE = dysrhythmias, ortho hypo, bradycardia, headache, dizzy, fatigues, hallucinations, convulsions, N/V, abdo cramp, diarrhea
Nursing = assessment, VS, s/s bleeding in skin/oral mucosa/gums/urine/stool, PTT, PT, INR
TA
onset = 15-30 min
half life = 2-3hrs
[peak plasma] = 0.25-4hrs
duration action = 4-6hrs
tranexamic acid (Cyklokapron)
antifibrinolytic
subclass = Synthetic Antifibrinolytic
MOA =reversible complex with plasminogen + plasmin = ind tp lysine site of plasminogen, tranexamic acid displeased plasminogen from surface of fibrinin = prevent plasma from lysing fibrin clot = ONLY WORK IF CLOT FORMED
Indi = prevention/treat excessive bleeding from systemic hyperfibrinolysis/surgical complication
Contra = allergy, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
AE = dysrhythmias, ortho hypo, bradycardia, headache, dizzy, fatigues, hallucinations, convulsions, N/V, abdo cramp, diarrhea
Nursing = assessment, VS, s/s bleeding in skin/oral mucosa/gums/urine/stool, PTT, PT, INR
TA
onset = 1hr
half-life = 2-2.5hrs
duration action = 4hrs
desmopressin acetate (DDAVP) - injectables, PO, intranasal
antifibrinolytic
subclass = Synthetic Antifibrinolytic
MOA = increasing Willebrand factor (anchodrs platelets to damaged velsselvvia GP Ilb platelet receptor)
Indi = surgical/postoperative homeostasis + management of bleeding in pt with hemophilia A or type I Willebrand disease
Contra = allergy, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) + nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
AE = dysrhythmias, ortho hypo, bradycardia, headache, dizzy, fatigues, hallucinations, convulsions, N/V, abdo cramp, diarrhea
Nursing = assessment, VS, s/s bleeding in skin/oral mucosa/gums/urine/stool, PTT, PT, INR
TA
onset = 1-2hr
half-life = 8hrs
[peak plasma]= 1hr
duration action = 7-10 days
24yr pt MVA = above knee aputation + bedridden 2wks. pt has TROUBLE BREATHING. pt developed…?
pulmonary embolism
Virchow’s triad
pt injured
stasis of blood b/c bedridden
hypercoagulability b/c surgery
pt high risk for thrombus formation
deox blood flow to small arteries in pulmonary system (blocked by thrombus) = ineffective O2 exchange = less O2 in blood = SOB
24yr pt MVA = above knee aputation + bedridden 2wks. pt has TROUBLE BREATHING = Pulmonary Embolism. what coagulation modifier + adverse rxn?
drug = Alteplase (Activase) (Thrombolytic)
AE = internal/intracranial/superficial bleeding, hypersensitivity, anaphylactoid rxn, N/V, hypotension, dysrhythmias
disorders of WBC
blood infections
blood cancers
NOTE = secondary effects of other diseases generally
most infections cause leukocytosis (increase # WBC)
blood infection - disorders of WBC
malaria
endemic (Americas, Asia, Africa) kills 1-3 mil/yr
parasite causes infects/destroys RBC
HIV
pandemic, 3mil/yr
infects lymphocytes/destroys rate faster than replaced
pt die from infection
blood cancers - disorders of WBC
leukemia
cancer of WBC
subclassified to particular lineage involved
lymphoma
WBC cancer via involvement of sites OTHER THAN bone marrow/blood
multiple myeloma
cancer of plasma cells
leukemia - neoplasm
WBC disorder
NO TUMOR
interspersed in lymphatic/circulatory system = interfere with normal function
malignant WBC neoplasms that
originate/spread diffusely in BONE MARROW
produce high WBC in PERIPHERAL blood
classified via
type of WBC
chronicity of disease
degree of differentiation relates to duration
acute = poorly differentiated cells = rapid course
chronic = well-differentiation = slow course
dx via blood smear/bone marrow exam
acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
most common childhood leukemia
rapidly fatal unless treated aggressively
successful therapy = long-term survival and cure
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
older adults
prolonged course
diagnostics of leukemia
blood smear
bone marrow exam
treatments of leukemia
chemo
radiation
bone marrow transplant
manifestations of leukemia
weakness
anemia
bleeding
infection
leukemic cells in blood/bone marrow
lymphoma - neoplasm
several types of malignant neoplasms of lymphocytes + histiocytes
originated in lymphoid tissues OUTSIDE of bone marrow
produce mass lesions
DO NO release malignant cells into blood
class = cell type
Hodgkin = Reed-Sternberg cell
non-Hodgkin
cell size
immunologic markers
histological pattern
details of cell structure
cancer treatment
surgery
radiation
targeted drug therapy
biologic therapy
chemo (antineoplastic agents)
cell-cycle nonspecific drugs = cytotoxic (cell kill at ANY phase)
cell-cycle specific drugs = cytotoxic during SPECIFIC cell cycle
cancer drugs (TI/AE)
LOW therapeutic index (TI)
AE = rapidly dividing cells
hair follicle = hair loss
GI tract = N/V = EMETIC POTENTIAL
bone marrow = toxicity
fertility reduction in postpubertal age
CANNOT discriminate against normal/cancer cells
if GI/Bone marrow effects = NO increase dose
contraindications
weakened stat of pt
low WBC, infection, nutritional comp, dehydration, decrease liver/kidney function
antineoplastics
class = cell cycle non-specific
MOA = cytotoxic ANY phase
Indi = part of complex, frequent revision by oncology, low TI
Contra = preg, liver disease (HBV/HCV)
AE = hair loss, N/V, bone marrow toxicity
Nursing = VS, bloodwork, preg test reproductive age
TA
[peak plasma] = 1-4hrs
pain management/transfusion - antineoplastics
class = cell cycle-specific
MOA = cytotoxic at SPECIFIC cell cycle phase
Indi = part of complex, frequent revision by oncology, low TI
AE = hair loss, N/V, myelosuppression (decreased RBC production from bone marrow), diarrhea, toxicity
Nursing = VS, blood work, PE, nut/hydration