Biochem Exam 2: Muscle Contractions
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Actin microfilaments
plays a part in changing cell shape, cell division, endocytosis, small molecule transport
ATP Hydrolysis
major role in muscle movement
ex) separation of chromosomes, beating of flagella, cell migration, muscular contraction
Amoeboid motion
ATP-G binds both F-actin ends (ATP-G has great affinity for + end)
Binding activates F-actin subunits to hydrolyze ATP
ADP-F-actin conformation change → leads to lower affinity for neighboring subunits
Rate of ATP hydrolysis by F-actin is lower than rate of polymerization → polymer grows as ATP-actin subunits added to + end (pushing force)
Treadmilling
when rate of association of new G-actin molecules in the + end equals rate of disassociation from - end
Voluntary muscles
striated appearance under light microscopy
consist of long, multinucleated cells (muscle fibers)
muscle fibers contain parallel bundles of myofibrils
Sarcomere
myofibril repetitive unit
included between 2 Z disks
contains A bands (thick filaments) + I bands (thin filaments) which are linked via cross bridges
contractions reduce the length of I band and H zone
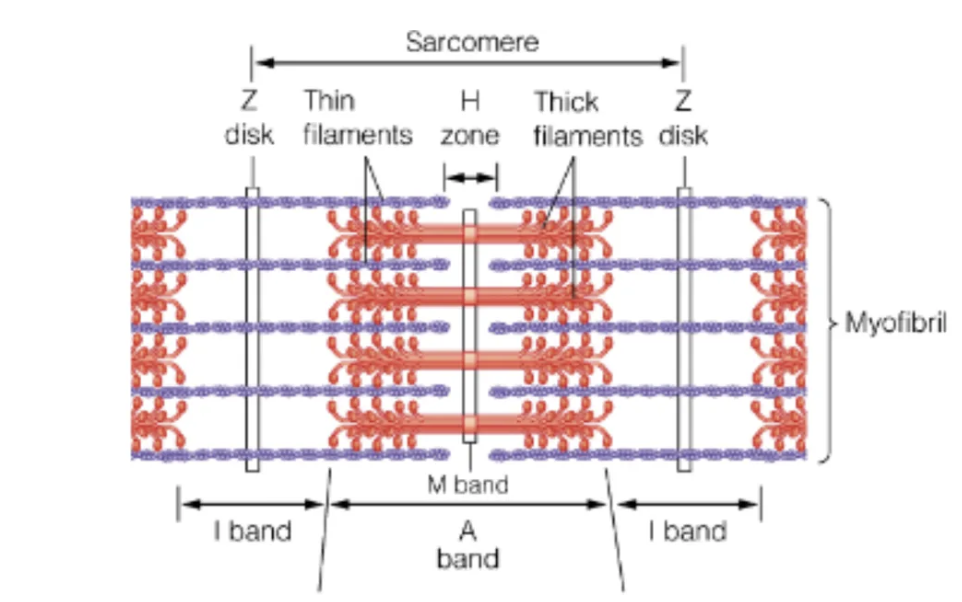
Sliding filament model (Hugh Huxley)
observations where overlapping thick (A bands) & thin filaments (I bands) slid past each other
thick filaments consist of Myosin
thin filaments mainly Actin and a little Tropomyosin + Troponin
Myosin
consists of 6 polypeptide chains
two heavy chains: each w/ N-term globular head (where ATP hydrolysis and interactions w/ actin occur) and a-helix tail → form left-handed coil
tail sequence: 7 AA repeat w/ hydrophobic residues at position 1 + 4
ELC + RLC binds each heavy chain
Myosin under physiological conditions…
several hundred myosin aggregate to form thick filaments
the heads (have ATPase activity) form cross bridges w/ the thin filaments
Actin
part of the thin filaments
exists as 375 AA long monomer (G-actin) or polymer F-actin
each subunit has binding sites for ATP, Ca2+, Mg2+
+ end binds w/ Z disk
ATPase and Ca2+ binding are NOT relevant to muscle contraction
Tropomyosin
homodimer w/ 284 residues
contains several a-helices → fold into parallel coiled coil which masks myosin binding site of actin
Troponin
composed of TnC (Ca2+ binding protein), TnI, TnT
Ca2+ displaces myosin binding site in actin
Dystrophin
reduces stress of muscle membrane upon contraction
if mutated → Duchenne muscular dystrophy and Becker muscular dystrophy
Ca2+ Mechanism
Nerve impulse stimulates myofibril → releases Ca2+ (from sarcoplasmic reticulum)
Ca2+ induces conformation change in tropomyosin-troponin complex → exposes site of actin for myosin binding
Ca2+ pumped back → tro-tro complex resumes resting conformation → blocks myosin binding to actin (muscle relaxation)
IgM (antibody)
most effective against microorganisms; 1st to be secreted
IgA (antibody)
present in intestines; blocks adhesion of pathogens to epithelia
IgG (antibody)
most common; equally present in blood and extravascular fluid
IgE (antibody)
protects against parasites, allergic rxns
IgD (antibody)
unknown function
Antigens
small foreign, non-self molecules that activate immune system
recognized by immunoglobulins
Antibodies (IgG) and antigens
each antibody (IgG) binds 2 identical antigens (divalent molecules) → leads to formation of antibodies cross-linked to antigens
Antibody structure
Ig contains 2 identical light chains + 2 identical heavy chains
subunits connected via di-S bonds
Strength of antibody-antigen interactions determined by:
van der Waals
hydrophobic interactions
h-bonding
ionic interactions
Immunoglobulin fold
sandwich of three-four-stranded antiparallel B-sheets linked by di-S bond
has 3 hypervariable loops → to recognize multiple antigens
Somatic hypermutation
permits fine tuning of antigen specificity of antibody