Intro and Math Review
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
How many basic forces are there and what are they
4 basic forces: Electromagnetism, Strong Nuclear, Weak Nuclear, and Gravitation
What holds the nucleus together (despite the like charges on the protons repelling each other?)
Strong Nuclear Force
What causes radioactive to split? (fission)
Repulsive Weak Nuclear Forces
Range of Electromagnetism importance
from atomic level (holds atom together) to the astronomical scale (where gravitation takes over)
Kinematics
the branch of physics that studies the effects of interactions, irrespective of what causes them
Dynamics
Branch of physics that study the laws that govern how/why these interactions are the way they are
How is Physics different from math?
Math studies what it does (ex. numbers or geometric shapes) for its own sake, Physics uses math as an essential tool
To Divide Fractions..
Multiply by the reciprocal of the 2nd term
Order of Operations
Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication/Division, Addition/Subtraction
Linear Equations
Doing the opposite operation on the other side to solve for x
For coordinates,
the order in which you proceed is important (x then y!)
General Linear Function
mx + c, where c is the y-int and x-ints are the solutions of mx+c = 0
m (slope)
positive = increasing function (more positive = increasing at a quicker rate); negative = decreasing function (more negative = decreasing at a quicker rate)
Square Root
Opposite of Square; always the non-negative root
General Quadratic Equation/ Polynomial Graph
where c is a pure number and graph points either upward (positive) or downward depending on a and x-intercepts are zeroes of the equation
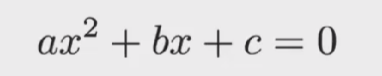
Quadratic Formula
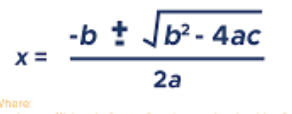
Triangle Trigonometry
based on a right triangle
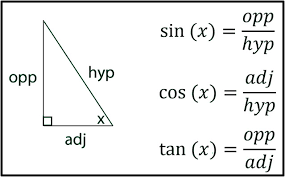
Circle Trigonometry
Based on “unit circle” (radius = 1)
Cosine Graph
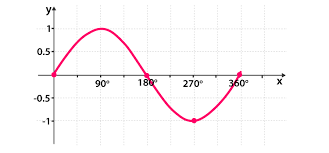
Sine Graph
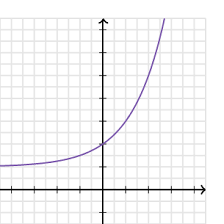
Exponential Function
one of the type ax where a>0 is a fixed number;
e
a number that is composed of a completely random sequence of decimal places
Logarithmic Functions
“opposites” (inverse functions) of exponential functions
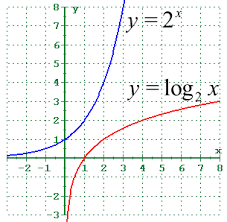
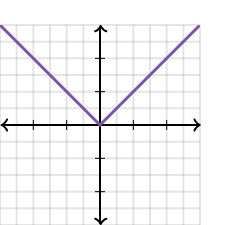
absolute value graph
square root graph
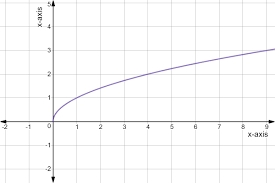
x to fractional power graph
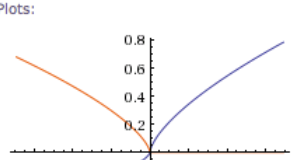
Multiplying by Powers of 10..
Add powers
Dividing by powers of 10…
Subtract powers
Powers of 10
used to express quantity along with the metric system and decimals
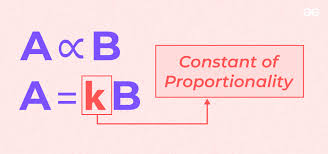
Proportionality
one variable is a multiple of the other variable
Inverse Proportion
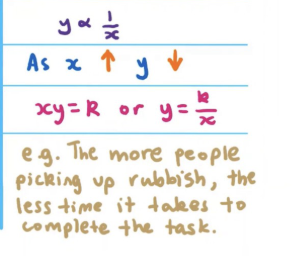
Giga (G)
109; Billion
Mega (M)
106; Milliion
Kilo (K)
103; Thousand
Centi ©
10-2; hundredth
Milli (m)
10-3; Thousandth
Micro (u)
10-6; millionth
Nano (n)
10-9; billionth
more decimal places..
more accurate and greater precision fora measurement
significant figures
number of reliably known digits in a number
Multiplying or Dividing Sig Figs
answer should have no more digits than the numerical value with the fewest significant figures
Adding or Subtracting Sig Figs
final result should have no more decimal places than the number with the fewest decimal places
Volume of a Cylinder
V = 2pir x h where h is easier to measure than r (1/2d)