Thẻ ghi nhớ: ECO121 Dan Chu Be | Quizlet
1/426
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
427 Terms
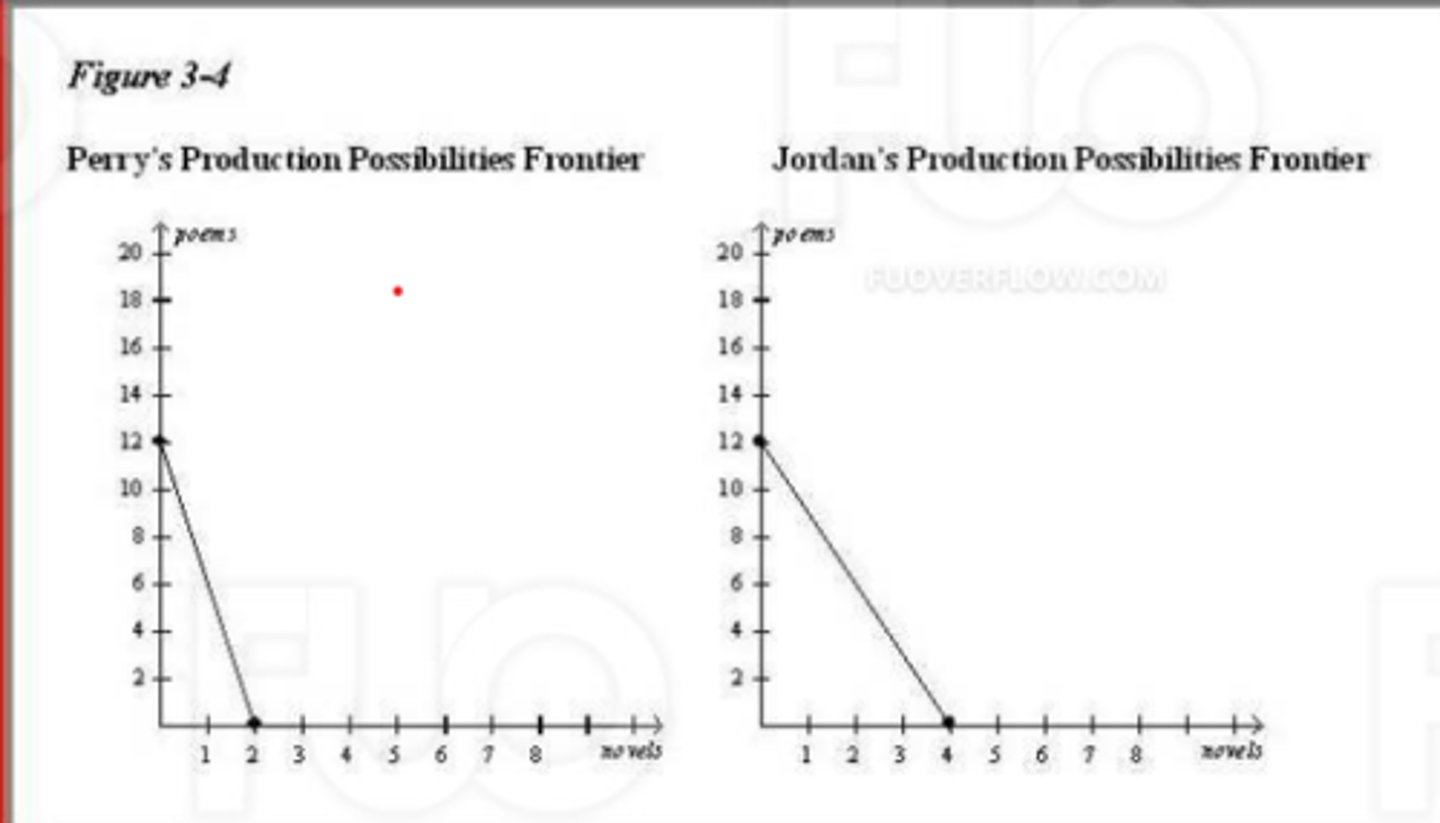
(17741) Refer to Figure 3-4. The opportunity cost of 1 novel for Jordan is
A. 1/3 poem.
8. 12 poems.
C. 4 poems.
D. 3 poems.
D. 3 poems
(17834)
Human capital is the
A. knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience.
B. stock of equipment and structures that is used to produce goods and services.
C. total number of hours worked in an economy.
D. same thing as technological knowledge.
A. knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience.
QN=253 (17968) Suppose that the nominal exchange rate is 120 yen per dollar, that the price of a basket of goods in the U.S. is $500 and the price of a basket of goods in Japan is 50,000 yen. Suppose that these values change to 100 yen per dollar, $600, and 70,000 yen. Then the real exchange rate would
a. appreciate which by itself would make U.S. net exports fall.
b. appreciate which by itself would make U.S. net exports rise.
c. depreciate which by itself would make U.S. net exports fall.
d. depreciate which by itself would make U.S. net exports rise.
d. depreciate which by itself would make U.S. net exports rise.
(17920)
If an economy used gold as money, its money would be
A. commodity money, but not fiat money.
B. fiat money, but not commodity money.
C. both fiat and commodity money.
D. functioning as a store of value and as a unit of account, but not as a medium of exchange
a. commodity money, but not fiat money.
(17870)
If the goverment's expenditures exceeded its receipts, it would tikely
A. lend money to a bank or other financial intermediary.
B. borrow money from a bank or other financial intermediary.
C. buy bonds directly from the public.
D. sell bonds directly to the public.
D. sell bonds directly to the public.
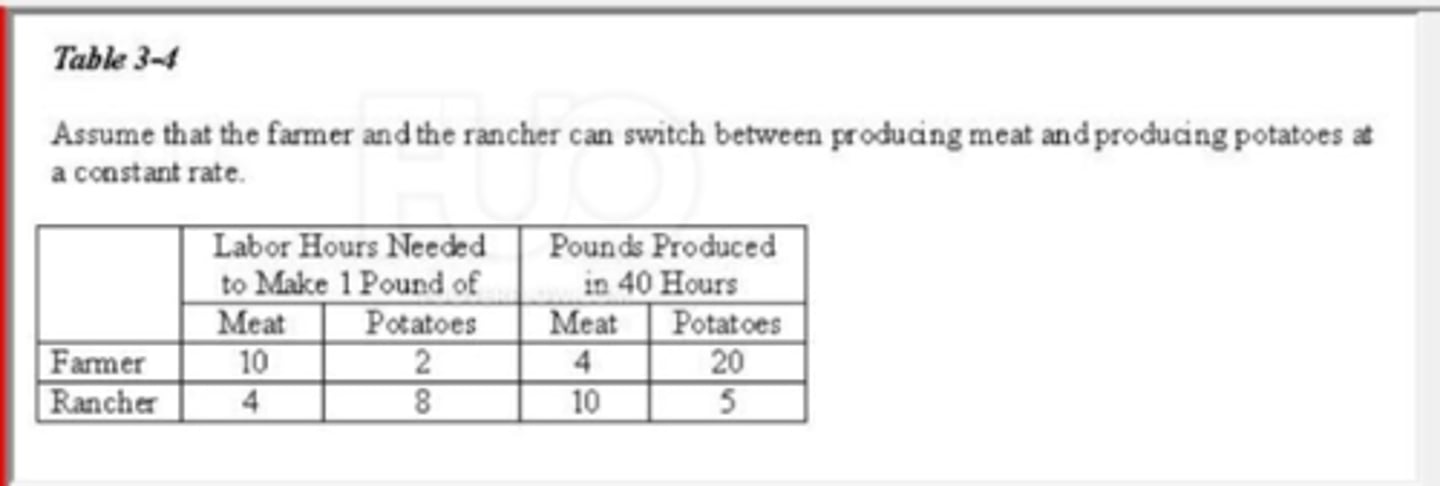
(17749) Refer to Table 3-4. The opportunity cost of 1 pound of potatoes for the farmer is
A. 1/5 pound of meat.
B. 5 pounds of meat.
C. 5 hours of labor.
D. 2 hours of labor.
A. 1/5 pound of meat.
QN=121 (17846) The Peapod Restaurant uses all of the following to produce vegetarian meals. Which of them is an example of physical capital?
a. the owner's knowledge of how to prepare vegetarian entrees
b. the money in the owner's account at the bank from which she borrowed money
c. the tables and chairs in the restaurant
d. the land the restaurant was built on
c. the tables and chairs in the restaurant
(17726) Which famous economist developed the principle of comparative advantage as we know it today?
A. Adam Smith
B. David Ricardo
C. John Maynard Keynes
D. Milton Friedman
B. David Ricardo
(18037)
As the price level rises,
A. the real exchange rate falls, so net exports fall.
B. the real exchange rate falls, so net exports rise.
C. the real exchange rate rises, so net exports fall.
D. the real exchange rate rises, so net exports rise.
C. the real exchange rate rises, so net exports fall.
In order to maintain stable prices, a central bank must
A. maintain low interest rates.
B. keep unemployment low.
C. tightly control the money supply.
D. sell indexed bonds.
C. tightly control the money supply.
(17793)
In the CPI, goods and services are weighted according to
A. how long a market has existed for each good or service.
B. the extent to which each good or service is regarded by the government as a necessity.
C. how much consumers buy of each good or service.
D. the number of firms that produce and sell each good or service.
C. how much consumers buy of each good or service.
(17811)
The consumer price index is used to
A. monitor changes in the level of wholesale prices in the economy.
B. monitor changes in the cost of living over time.
C. monitor changes in the level of real GDP over time.
D. monitor changes in the stock market.
B. monitor changes in the cost of living over time.
QN=126 (17848) Given that a country's real output has increased, in which of the following cases can we be sure that its productivity also has increased?
a. (i) The total number of hours worked rose.
b. (ii) The total number of hours worked stayed the same.
c. (iii) The total number of hours worked fell.
d. Both (ii) and (iii) are correct.
d. Both (ii) and (iii) are correct.
(18056)The theory of liquidity preference assumes that the nominal supply of money is
A. level of real output only .
B. interest rate only.
C. level of real output and by the interest rate.
D. Federal Reserve.
D. Federal Reserve.
(17938)If M = 3,000, P = 2, and Y = 12,000, what is velocity?
A. 1/2
B. 2
C. 4
D. 8
D. 8
QN=249 (17986)
Suppose that more British decide to vacation in the U.S. and that the British purchase more U.S. Treasury bonds. Ignoring how payments are made for these purchases,
a.the first action by itself raises U.S. net exports, the second action by itself raises U.S. net capital outflow.
b.the first action by itself raises U.S. net exports, the second action by itself lowers U.S. net capital outflow.
c.the first action by itself lowers U.S. net exports, the second action by itself raises U.S. net capital outflow.
d.the first action by itself lowers U.S. net exports, the second action by itself lowers U.S. net capital outflow.
b.the first action by itself raises U.S. net exports, the second action by itself lowers U.S. net capital outflow.
QN=26 (17722) Which of the following is not correct?
a. The producer who requires a smaller quantity of inputs to produce a good is said to have an absolute advantage in producing that good.
b. The producer who gives up less of other goods to produce Good X has the smaller opportunity cost of producing Good X.
c. The producer who has the smaller opportunity cost of producing a good is said to have a comparative advantage in producing that good.
d. The gains from specialization and trade are based not on comparative advantage but on absolute advantage.
d. The gains from specialization and trade are based not on comparative advantage but on absolute advantage.
If national saving in a closed economy is greater than zero, which of the following must be true?
a) Either public saving or private saving must be greater than zero.
b) Investment is positive.
c) Y -C -G > 0
d) All answers are correct
d) All answers are correct
(17728) By definition, imports are
A. people who work in foreign countries.
B. goods in which a country has an absolute advantage.
C. limits placed on the quantity of goods leaving a country.
D. goods produced abroad and sold domestically.
D. goods produced abroad and sold domestically.
Last year a country had 800 workers who worked an average of 8 hours and produced 12,800 units. This year the same country had 1000 workers who worked an average of 8 hours and produced 14,000 units. This country's productivity was
a.higher this year than last year. A possible source of this change in productivity is a change in the size of the capital stock.
b.higher this year than last year. A change in the size of the capital stock does not affect productivity.
c.lower this year than last year. A possible source of this change in productivity is a change in the size of the capital stock.
d.lower this year than last year. A change in the size of the capital stock does not affect productivity.
c.lower this year than last year. A possible source of this change in productivity is a change in the size of the capital stock.
In 1949, Sycamore, Illinois built a hospital for about $500,000. In 1987, the county restored the courthouse for about $2.4 million. A price index for nonresidential construction was 14 in 1949, 92 in 1987, and 114.5 in 2000. According to these numbers, the hospital cost about
a.$4.1 million in 2000 dollars, which is less than the cost of the courthouse restoration in 2000 dollars.
b.$4.1 million in 2000 dollars, which is more than the cost of the courthouse restoration in 2000 dollars.
c.$3.6 million in 2000 dollars, which is less than the cost of the courthouse restoration in 2000 dollars.
d.$3.6 million in 2000 dollars, which is more than the cost of the courthouse restoration in 2000 dollars.
b.$4.1 million in 2000 dollars, which is more than the cost of the courthouse restoration in 2000 dollars.
QN=241 (17939)
Suppose one year ago the price index was 120 and Mark purchased $20,000 worth of bonds. One year later the price index is 126. Mark redeems his bonds for $22,250 and is in a 40 percent tax bracket. What is Mark's real after-tax rate of interest to the nearest tenth of a percent?
a.4.3 percent
b.3.1 percent
c.1.8 percent
d.1.2 percent
c.1.8 percent
QN=157 (17885) Suppose some country had an adult population of about 50 million, a labor-force participation rate of 60 percent, and an unemployment rate of 5 percent. How many people were unemployed?
a. 1.425 million
b. 1.5 million
c. 2.5 million
d. 5 million
b. 1.5 million
(17983)
If Saudi Arabia had positive net exports last year, then it
A. sold more abroad than it purchased abroad and had a trade surplus.
B. sold more abroad than it purchased abroad and had a trade deficit.
C. bought more abroad than it sold abroad and had a trade surplus.
D. bought more abroad than it sold abroad and had a trade deficit.
A. sold more abroad than it purchased abroad and had a trade surplus.
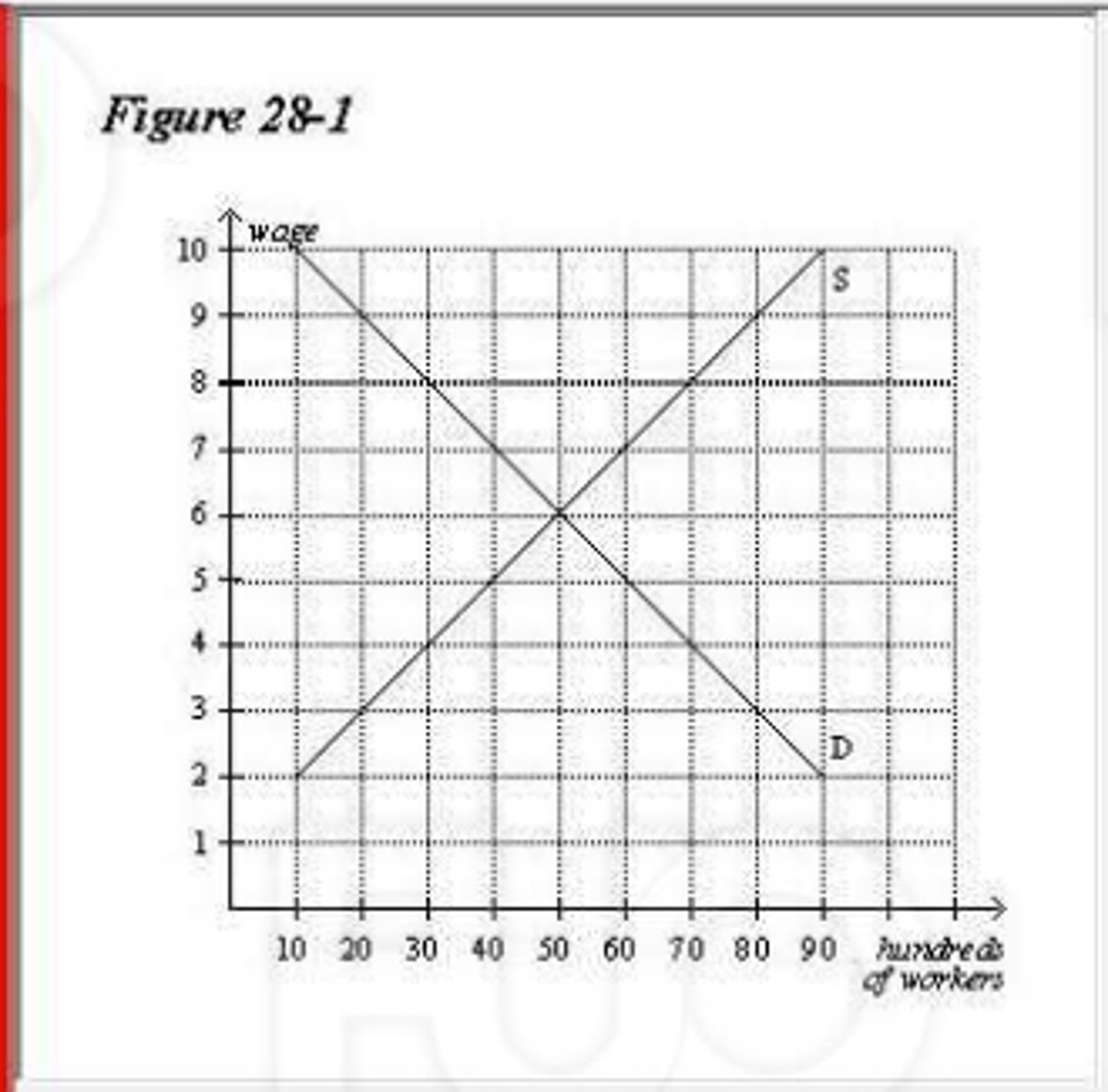
(17893) Refer to Figure 28-1. If the goverment imposes a minimum wage of $4, then how many workers
will be employed?
A. 3000
B. 4000
C. 7000
D. 5000
D. 5000
QN=154 (17872) A change in the tax laws that increases the supply of loanable funds will have a bigger effect on investment when
a. the demand for loanable funds is more elastic and the supply of loanable funds is more inelastic.
b. the demand for loanable funds is more inelastic and the supply of loanable funds is more elastic.
c. both the demand for and supply of loanable funds are more elastic.
d. both the demand for and supply of loanable funds are more inelastic.
a. the demand for loanable funds is more elastic and the supply of loanable funds is more inelastic.
(17783)
Which of the following items is counted as part of governmei purchases?
A. (i) The federal government pays the salary of a Navy officer.
B. (ii) The state of Nevada pays a private firm to repair a Nevada state highway.
C. (ii) The city of Las Vegas, Nevada pays a private firm to collect garbage in that city.
D. All (i), (ii), and (iii) are correct.
D. All (i), (ii), and (iii) are correct.
Assume the MPC is 0.75. Assume there is a multiplier effect and that the total crowding-out effect is $6 billion. An increase in government purchases of $10 billion will shift aggregate demand to the
A. left by $24 billion.
B. left by $36 billion.
C. right by $34 billion.
D. right by $36 billion.
C. right by $34 billion.
(18015)When Mexico suffered from capital flight in 1994, Mexico's r® capital outflow
A. and net exports decreased.
B. and net exports increased
C. increased while net exports decreased.
D. decreased while net exports increased.
B. and net exports increased
QN=6 (17764) Gross domestic product is defined as
a. (i) the quantity of all final goods and services demanded within a country in a given period of time.
b. (ii) the quantity of all final goods and services supplied within a country in a given period of time.
c. (iii) the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time.
d. Both (i) and (ii) are correct.
c. (iii) the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time.
(17988)Other things the same, an increase in the U.S. interest rate Causes the quantity.... supplied to
A. rise because net capital outflow and domestic investment rise.
B. rise because national saving rises.
C. fall because net capital outflow and domestic investment rise.
D. fall because national saving falls.
B. rise because national saving rises.
(17787) The value of the housing services provided by the economy's owner-occupied houses is
A.included in GDP, and the estimated rental values of the houses are used to place a value on these housing services.
В.included in GDP, and the actual mortgage payments made on the houses are used to es
these rental services.
C. excluded from GDP since these services are not sold in any market.
D.excluded from GDP since the value of these housing services cannot be estimated with a
precision
A.included in GDP, and the estimated rental values of the houses are used to place a value on these housing services.
(17748) Refer to Table 3-3. Assume that Zimbabwe and Portugal each has 180 machine minutes
available. If each country divides its time equally between the production of toothbrushes and hairbrushes.
then total production is
A. 48 toothbrushes and 24 hairbrushes.
B. 720 toothbrushes and 1440 hairbrushes.
C. 96 toothbrushes and 48 hairbrushes.
D. 24 toothbrushes and 12 hairbrushes.
A. 48 toothbrushes and 24 hairbrushes.
QN=166 (17896) 1. If all workers and all jobs were the same such that all workers were equally well suited for all jobs, then there would be no
a. cyclical unemployment
.b. frictional unemployment
.c. natural rate of unemployment.
d. structural unemployment.
.b. frictional unemployment
(17757) Refer to Figure 3-3. If Enid must work 0.25 hour to produce each taco, then her production possibilities frontier is based on how many hours of work?
A. 400 hours
B. 100 hours
C. 1600 hours
D. 40 hours
B. 100 hours
QN=215 (17956)
Suppose each good costs $5 per unit and Megan holds $40. What is the real value of the money she holds?
a.$40. If the price of goods rises, to maintain the real value of her money holdings she needs to hold more dollars.
b.8 units of goods. If the price of goods rises, to maintain the real value of her money holdings she needs to hold more dollars.
c.$40. If the price of goods rises, to maintain the real value of her money holdings she needs to hold fewer dollars.
d.8 units of goods. If the price of goods rises, to maintain the real value of her money holdings she needs to hold fewer dollars.
b.8 units of goods. If the price of goods rises, to maintain the real value of her money holdings she needs to hold more dollars.
QN=1 (17730) Assume for Namibia that the opportunity cost of each hut is 200 bowls. Then which of these pairs of points could be on Namibia's production possibilities frontier?
a. (200 huts, 30,000 bowls) and (150 huts, 35,000 bowls)
b. (200 huts, 40,000 bowls) and (150 huts, 30,000 bowls)
c. (300 huts, 50,000 bowl) and (200 huts, 60,000 bowls)
d. (300 huts, 60,000 bowls) and (200 huts, 80,000 bowls)
d. (300 huts, 60,000 bowls) and (200 huts, 80,000 bowls)
(18021)
Recessions in China and India would cause
A. the U.S. price level and real GDP to rise.
B. the U.S. price level and real GDP to fall.
C. the U.S. price level to rise and real GDP to fall.
D. the U.S. price level to fall and real GDP to rise.
B. the U.S. price level and real GDP to fall.
(17954)
An increase in the price level makes the value of money
A. increase, so people want to hold more of it.
B. increase, so people want to hold less of it.
C. decrease, so people want to hold more of it.
D. decrease, so people want to hold less of it.
C. decrease, so people want to hold more of it.
(17829)
Which of the following is a determinant of productivity?
A. (i) human capital per worker
B. (ii) physical capital per worker
C. (ii) natural resources per worker
D. All of (i), (il), and (il are correct.
D. All of (i), (il), and (il are correct.
(17903)
In a system of 100-percent-reserve banking, the purpose of bank is to
A. make loans to households.
B. influence the money supply.
C. give depositors a safe place to keep their money.
D. buy and sell gold.
C. give depositors a safe place to keep their money.
(17908)
An increase in the money supply might indicate that the Fed had
A. purchased bonds in an attempt to increase the federal funds rate.
B. purchased bonds in an attempt to reduce the federal funds rate.
C. sold bonds in an attempt to increase the federal funds rate.
D. sold bonds in an attempt to reduce the federal funds rate.
B. purchased bonds in an attempt to reduce the federal funds rate.
QN=93 (17815)
The CPI was 120 in 2000 and 132 in 2001. Dorgan borrowed money in 2000 and repaid the loan in 2001. If the nominal interest rate on the loan was 12 percent, then the real interest rate was
a.2 percent.
b.10 percent.
c.12 percent.
d.22 percent.
a.2 percent.
(17805)
Economists use the term inflation to describe a situation in vich
A. some prices are rising faster than others.
B. the economy's overall price level is rising.
C. the economy's overall price level is high, but not necessarily rising.
D. the economy's overall output of goods and services is rising faster than the economy's o
B. the economy's overall price level is rising.
(17889)
Unemployment that results because the number of jobs available in some labor insufficient to give a job to everyone who wants one is called
A. the natural rate of unemployment.
B. cyclical unemployment.
C. structural unemployment.
D. frictional unemployment.
C. structural unemployment.
(17799)
The economy's inflation rate is the
A. price level in the current period.
B. absolute change in the price level from the previous period.
C. change in the gross domestic product from the previous period.
D. percentage change in the price level from the previous period.
D. percentage change in the price level from the previous period.
(17945)
The term hyperinflation refers to
A. the spread of inflation from one country to others.
B. a decrease in the inflation rate.
C. a period of very high inflation.
D.inflation accompanied by a recession.
C. a period of very high inflation.
(17927)If the public decides to hold more currency and fewer deposits in banks, bank reserves
A. decrease and the money supply eventually decreases.
B. decrease but the money supply does not change.
C. increase and the money supply eventually increases.
D. increase but the money supply does not change.
A. decrease and the money supply eventually decreases.
(17819)
Scenario 24-3
Grant Gant was a doctor in 1944 and earned $12,000 that year. His daughter, Gretta Gant, is a doctor today and she earned $210,000 in 2005. The price index was 17.6 in 1944 and 184 in 2005.
Refer to Scenario 24-3. Grant Gant's 1944 income in 2005 dollars is
A. $1,147.83.
B. $113,454.55.
C. $125,454.55.
D. $1,996,800.00.
C. $125,454.55.
(17936)
According to the quantity theory of money, a 2 percent increase in the money supply
A. causes the price level to fall by 2 percent.
B. leaves the price level unchanged.
C. causes the price level to rise by less than 2 percent.
D. causes the price level to rise by 2 percent.
D. causes the price level to rise by 2 percent.
(17786)
If you buy a burger and fries at your favorite fast food restaurant,
A.then neither GDP nor consumption will be affected because you would have eaten at home had you not bought the meal at the restaurant.
B. then GDP will be higher, but consumption spending will be unchanged.
C. then GDP will be unchanged, but consumption spending will be higher.
D. then both GDP and consumption spending will be higher.
D. then both GDP and consumption spending will be higher.
(17898)
Public policy
A. can reduce both frictional unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
B. can reduce frictional unemployment, but it cannot reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
C. cannot reduce frictional unemployment, but it can reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
D. cannot reduce either frictional unemployment or the natural rate of unemployment.
A. can reduce both frictional unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
(17843)
Rapid population growtn
A. was hailed by Thomas Robert Malthus as the key to future economic growth.
B. tends to lead to higher levels of educational attainment.
C. is the main reason that less developed nations are poor.
D. may depress economic prosperity by reducing the amount of capital which each worker has to work with.
D. may depress economic prosperity by reducing the amount of capital which each worker has to work with.
(17953)
High and unexpected inflation has a greater cost
A. for those who save than for those who borrow.
B. for those who hold a little money than for those who hold a lot of money.
C. for those whose wages increase by as much as inflation, than those who are paid a fixed nominal wage.
D. for savers in low income tax brackets than for savers in high income tax brackets.
A. for those who save than for those who borrow.
(17824)An understanding of the best ways to produce goods and services is called
A. human capital.
B. physical capital.
C. technology.
D. productivity.
C. technology.
(Choose 1 answer)
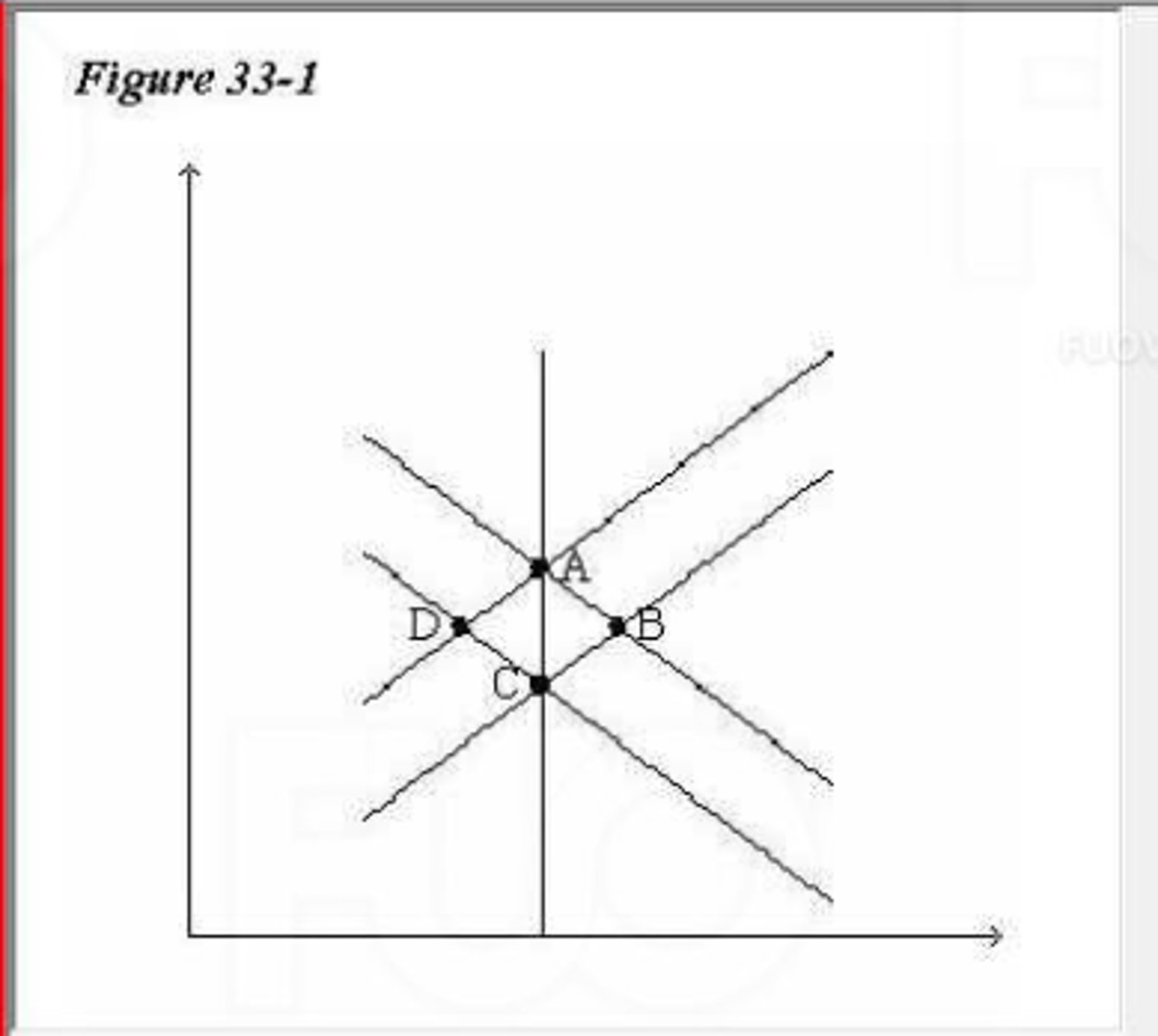
(18040) Refer to Figure 33-1. If the economy is in long-run
equilibrium, then an adverse shift in aggregate supply would move
the economy from
A. C to D.
B. A to B.
C. D to C.
D. B to A.
A. C to D.
(17745) Absolute advantage is found by comparing different producers'
A. opportunity costs.
B. payments to land, labor, and capital.
C. input requirements per unit of output.
D. locational and logistical circumstances.
C. input requirements per unit of output.
(17862)
Suppose that in a closed economy GDP is equal to 11,000, taxes are equal to 2,500 consumption equals 7,500 and government purchases equal 2,000. What are private saving, public saving, and national
saving?
A. 0) 1,500, 1,000, and 500, respectively
B. (ii) 1,000, 500, and 1,500, respectively
C. (il) 500, 1,500, and 1,000, respectively
D. None of (i), (ii), and (ii) is correct.
B. (ii) 1,000, 500, and 1,500, respectively
(17996)
Which of the following will decrease U.S. net capital outflow?
A. (i) capital flight from the United States
B .(ii) the government budget deficit increases
C. (ii) the U.S. imposes import quotas
D.None of (i), (ii), and (iii) is correct.
B .(ii) the government budget deficit increases
(Choose 1 answer)
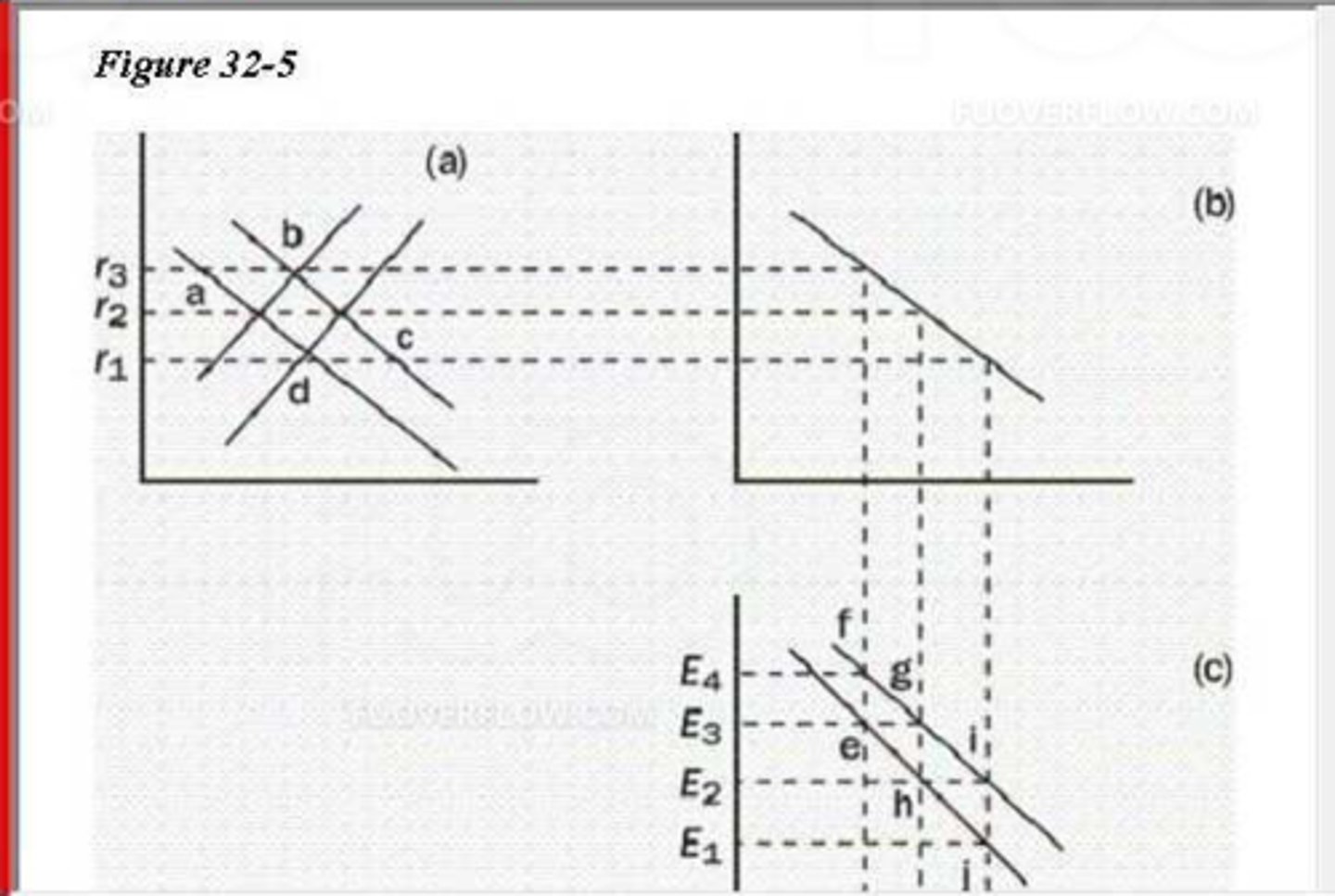
(18001) Referto Figure 32-5. Starting from 12 and E3. an increase in the budget deficit can be illustrated as a move to
A. r1 and E2
B. 13 and E2
C. 13 and E4.
D. r1 and E4.
A. r1 and E2
(17977)
If purchasing power party holds, the price level in the U.S. is 120, and the price level in Canada is 140, which of the following is true for the US dollar?
A. the real exchange rate is 120/140.
B. the real exchange rate is 140/120.
C. the nominal exchange rate is 120/140
D. the nominal exchange rate is 140/120
D. the nominal exchange rate is 140/120
(17725)
Adam Smith
A. and David Ricardo both opposed free trade.
B. opposed free trade, but David Ricardo supported it.
C. supported free trade, but David Ricardo opposed it.
D. and David Ricardo both supported free trade.
D. and David Ricardo both supported free trade.
(17774)
Household spending on education is counted in which component or subcomponent of GDP?
A. consumption of durable goods
B. consumption of nondurable goods
C. consumption of services
D. investment
C. consumption of services
(18065)
Initially, the economy is in long-run equilibrium. The aggregate demand curve then shifts $80 billion to the left. The government wants to change spending to offset this decrease in demand. The MPC is 0.75.
Suppose the effect on aggregate demand of a tax change is 3/4 as strong as the effect of a change in government expenditure. There is no crowding out and no accelerator effect. What should the goverment do
if it wants to offset the decrease in real GDP?
A. Raise both taxes and expenditures by $80 billion dollars.
B. Raise both taxes and expenditures by $10 billion dollars.
C. Reduce both taxes and expenditures by $80 billion dollars.
D. Reduce both taxes and expenditures by $10 billion dollars.
A. Raise both taxes and expenditures by $80 billion dollars.
(17854)
Two of the economy's most important financial intermediaries are
A. suppliers of funds and demanders of funds.
B. banks and the bond market.
C. the stock market and the bond market.
D. banks and mutual funds.
D. banks and mutual funds.
(18034)
The long-run aggregate supply curve would shift right if immigration from abroad
A. increased or Congress made a substantial increase in the minimum wage.
B. decreased or Congress abolished the minimum wage.
C. increased or Congress abolished the minimum wage.
D. decreased or Congress made a substantial increase in the minimum wage.
C. increased or Congress abolished the minimum wage.
(17895)A firm may pay efficiency wages in an attempt to
A. (i) reduce incentives to shirk.
B. (ii) reduce turnover.
C. (iii) attract a well-qualified pool of applicants.
D. All of (i), (ii), and (iii) are correct.
D. All of (i), (ii), and (iii) are correct.
(17823)
One of the Ten Principles of Economics in Chapter 1 is that people face tradeoffs. The growththat arises from capital accumulation is not a free lunch. It requires that society
A. (i) conserve resources for future generations.
B. (ii) sacrifice consumption goods and services now in order to enjoy more consumption in the future.
C. (iii) recycle resources so that future generations can produce goods and services with the accumulated capital.
D. None of (i), (ii), and (iii) is correct.
B. (ii) sacrifice consumption goods and services now in order to enjoy more consumption in the future.
(17832)
In the past there have been violent protests against the World Bank and the World Trade Organization. The protesters argued that these institutions promote free trade and also encourage corporations in rich countries to invest in poor countries. The protesters contended that these practices make rich countries richer and poor countries poorer. An economist would
A. disagree with the protesters because these practices will help make both rich and poor countries richer.
B. disagree with the protesters about free trade, but would agree with the protesters about corporate investment.
C. disagree with the protesters about corporate investment, but would agree with the protesters about free trade.
D. agree with the protesters.
A. disagree with the protesters because these practices will help make both rich and poor countries richer.
(17721) The opportunity cost of an item is
A. the number of hours that one must work in order to buy one unit of the item.
B. what you give up to get that item.
C. always less than the dollar value of the item.
D. always greater than the cost of producing the item.
B. what you give up to get that item.
(17957)
The classical dichotomy argues that changes in the money supply
A. affect both nominal and real variables.
B. affect neither nominal nor real variables.
C. affect nominal variables, but not real variables.
D. do not affect nominal variables, but do affect real variables.
C. affect nominal variables, but not real variables.
(18045)
In the long run, fiscal policy primarily affects
A.aggregate demand. In the short run, it affects primarily aggregate supply-
B.aggregate supply. In the short run, it affects primarily saving, investment, and growth.
C. saving, investment, and growth. In the short run, it affects primarily aggregate demand.
D. saving, investment, and growth. In the short run, it affects primarily aggregate supply.
C. saving, investment, and growth. In the short run, it affects primarily aggregate demand.
(17911)Suppose a bank's reserve ratio is 6.5 percent and the bank has $1,950 in reserve. Its deposits amount to
A. $62.25.
B. $126.75.
C. $22,500.00
D. $30,000.00.
D. $30,000.00.
(17956)
Suppose each good costs 55 per unit and Megan holds $40. What is the real value of the money
A. $40. If the price of goods rises, to maintain the real value of her money holdings she needs to hold more dollars.
B. 8 units of goods. If the price of goods rises, to maintain the real value of her money holdings she needs to hold more dollars.
C. $40. If the price of goods rises, to maintain the real value of her money holdings she needs to hold fewer dollars.
D.8 units of goods. If the price of goods rises, to maintain the real value of her money holdings she needs to hold fewer dollars.
B. 8 units of goods. If the price of goods rises, to maintain the real value of her money holdings she needs to hold more dollars.
(18046)In the long run, changes in the money supply affect
A. (i) prices.
B. (ii) output.
C. (iii) unemployment rates.
D. All of (i), (il), and (il).
A. (i) prices.
(17871) Which of the following lists correctly identifies the four expenditure categories of GDP?
A. consumption, government purchases, investment, net-exports
B. consumption, investment, depreciation, net-exports
C. consumption, saving, investment, depreciation,
D. consumption, government purchases, investment, savings
A. consumption, government purchases, investment, net-exports
(17724)
Two people can benefit from specialization and trade by obtaining a good at a price that is
A. lower than his or her opportunity cost of that good.
B. the same as his or her opportunity cost of that good.
C. higher than his or her opportunity cost of that good.
D. different than his or her opportunity cost of that good.
A. lower than his or her opportunity cost of that good.
(17847)
A barber shop produces 96 haircuts a day. Each barber in the shop works 8 hours per day and produces the same number of haircuts per hour. If the shop's productivity is 3 haircuts per hour of labor, then how many barbers does the shop employ?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 6
C. 4
(17765)
The consumption component of GDP includes spending on
A. durable goods and nondurable goods, but not spending on services.
B. durable goods and services, but not spending on nondurable goods.
C. nondurable goods and services, but not spending on durable goods.
D. durable goods, nondurable goods, and services.
D. durable goods, nondurable goods, and services.
(17790)
Net exports equal
A. exports plus imports.
B. exports minus imports.
C. imports minus exports.
D. GDP minus imports.
B. exports minus imports.
(Choose 1 answer)
(17744) If the production possibilities frontier is bowed outward, then "?" could be
A. 100.
B. 125.
C. 75
D. 50.
B. 125.

(17881)
The labor force equals the
A. number of people employed
B. number of people unemployed.
C. number of people employed plus the number of people unemployed.
D. adult population.
C. number of people employed plus the number of people unemployed.
(17820)
Scenario 24-4
Quinn has job offers in Wrexington and across the country in Charlieville. The Wrexington job would pay a salary of $50,000 per year, and the Charlieville job would pay a salary of $40,000 per year. The CPI in Wrexington is 150, and the CP| in Charlieville is 90.Refer to Scenario 24-4. If Quinn only cares about maximizing her purchasing power, then she should
A. take the Charlieville job.
B. take the Wrexington job.
C. take either job because they both have the same purchasing power.
D. The answer cannot be determined from the information given because a salary is not the same as purchasing power.
A. take the Charlieville job.
(17880)
The labor-force participation rate measures the percentage of the
A. total adult population that is in the labor force.
B. total adult population that is employed.
C. labor force that is employed.
D. labor force that is either employed or unemployed.
A. total adult population that is in the labor force.
(17891)
The amount of unemployment that an economy normally experiences is called the
A. average rate of unemployment.
B. natural rate of unemployment.
C. cyclical rate of unemployment.
D. typical rate of unemployment.
B. natural rate of unemployment.
(Choose 1 answer)
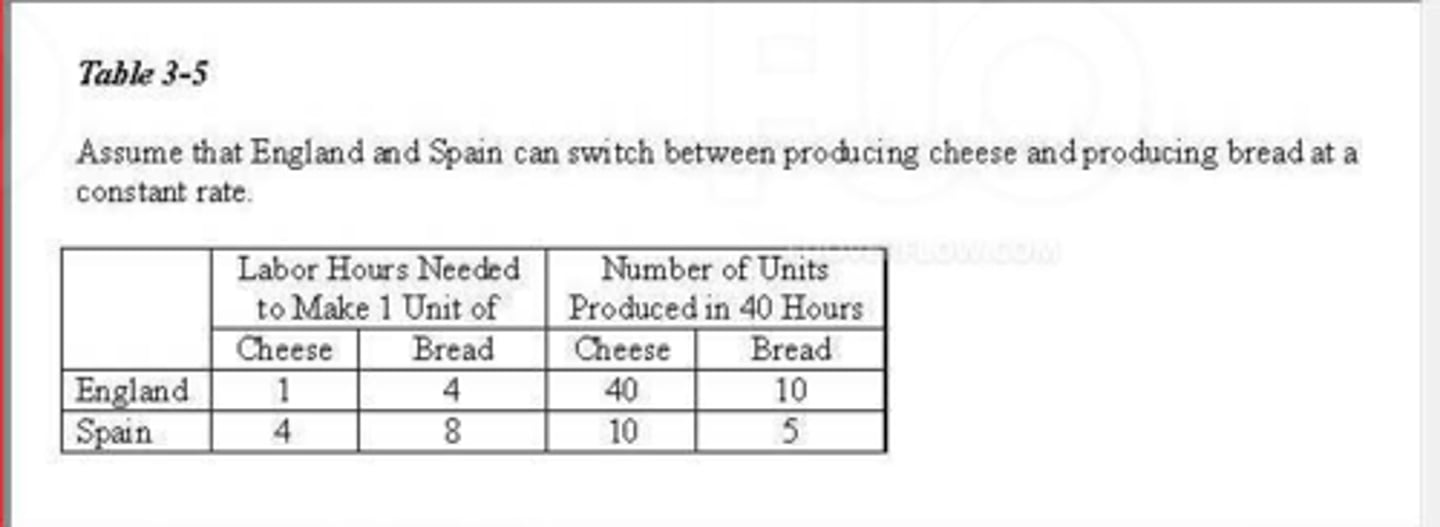
(17750) Refer to Table 3-5. The opportunity cost of 1 unit of cheese for Spain is
A. 2 units of bread.
B. 4 hours of labor.
C. 1/2 unit of bread.
D. 2 hours of labor.
C. 1/2 unit of bread.
(17778)
Which of the following topics are more likely to be studied by a macroeconomist than by a microeconomist?
A. the effect of taxes on the prices of airline tickets, the profitability of automobile-manufacturing firms, and employment trends in the food-service industry
B. the price of beef, wage differences between genders, and antitrust laws
C. how consumers maximize utility, and how prices are established in markets for agricultural products
D. the percentage of the labor force that is out of work, and differences in average income from country to country
D. the percentage of the labor force that is out of work, and differences in average income from country to country
(17899)Which of the following does not help reduce frictional unemployment?
A. (i) Government-run employment agencies
B. (ii) public training programs
C. (iii) unemployment insurance
D. All of (i), (ii), and (iii) help reduce frictional unemployment.
C. (iii) unemployment insurance
(17840)
Which of the following is correct?
A. Although levels of real GDP per person vary substantially from country to country, the growth rate of real GDP per person is similar across countries.
B. Productivity is not closely linked to government policies.
C. The level of real GDP per person is a good gauge of economic prosperity, and the growth rate of real GDP per person is a good gauge of economic progress.
D. Productivity may be measured by the growth rate of real GDP per person.
C.The level of real GDP per person is a good gauge of economic prosperity, and the growth rate of real GDP
In an imaginary economy, consumers buy only sandwiches and magazines. The fixed basket a sandiot 20st 55 The base year is 2008 , the intaiton rate in 200% was 10 percent, then how much did a magazine cost in 2007?
A. $1.87
B. $2.08
C. $2.32
D. $3.00
B. $2.08
(Choose 1 answer)
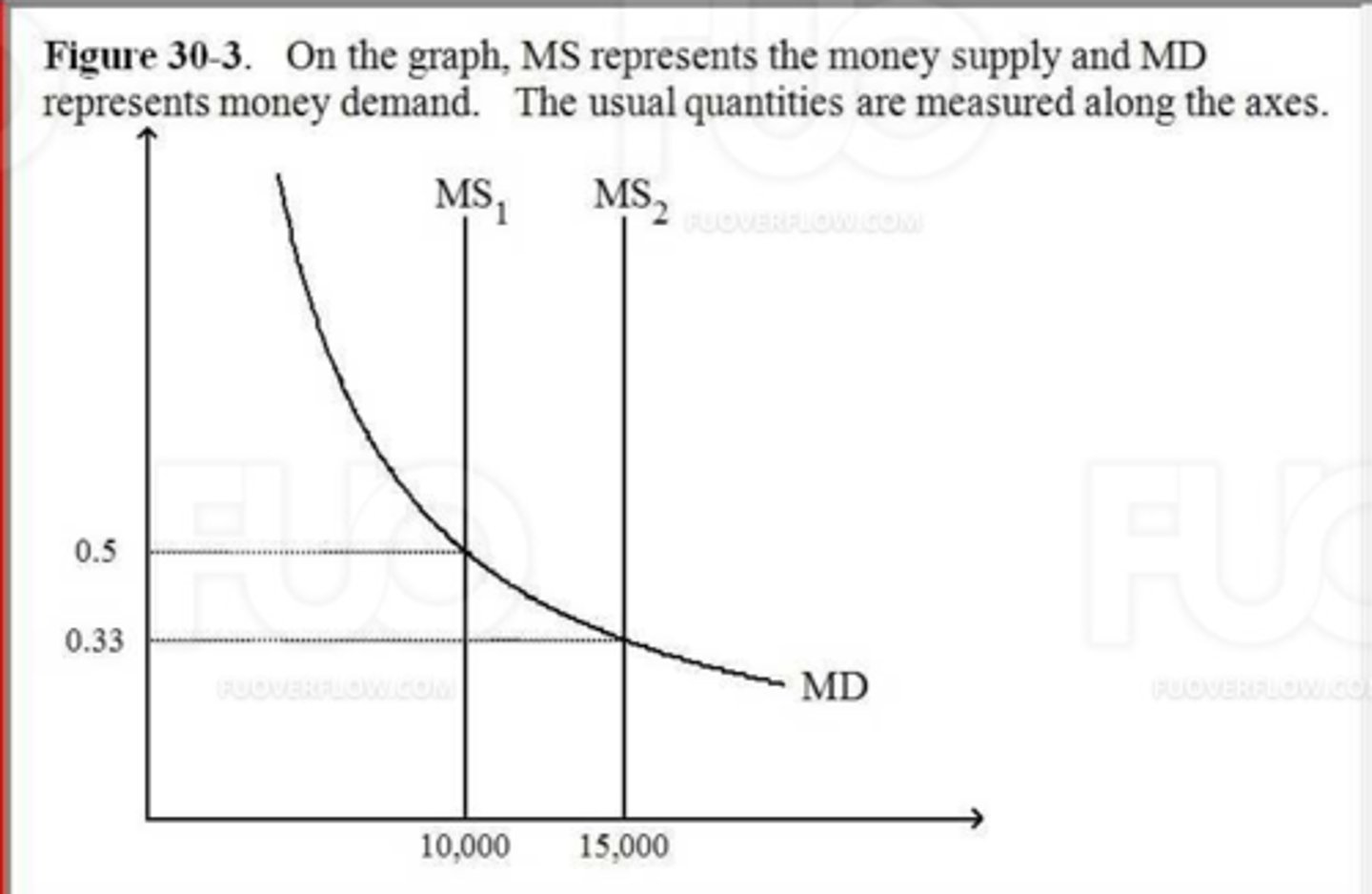
(17932) Referto Figure 30-3. What quantity is measured along the vertical axis?
A. the price level
B. the value of money
C. the velocity of money
D. the quantity of money
B. the value of money
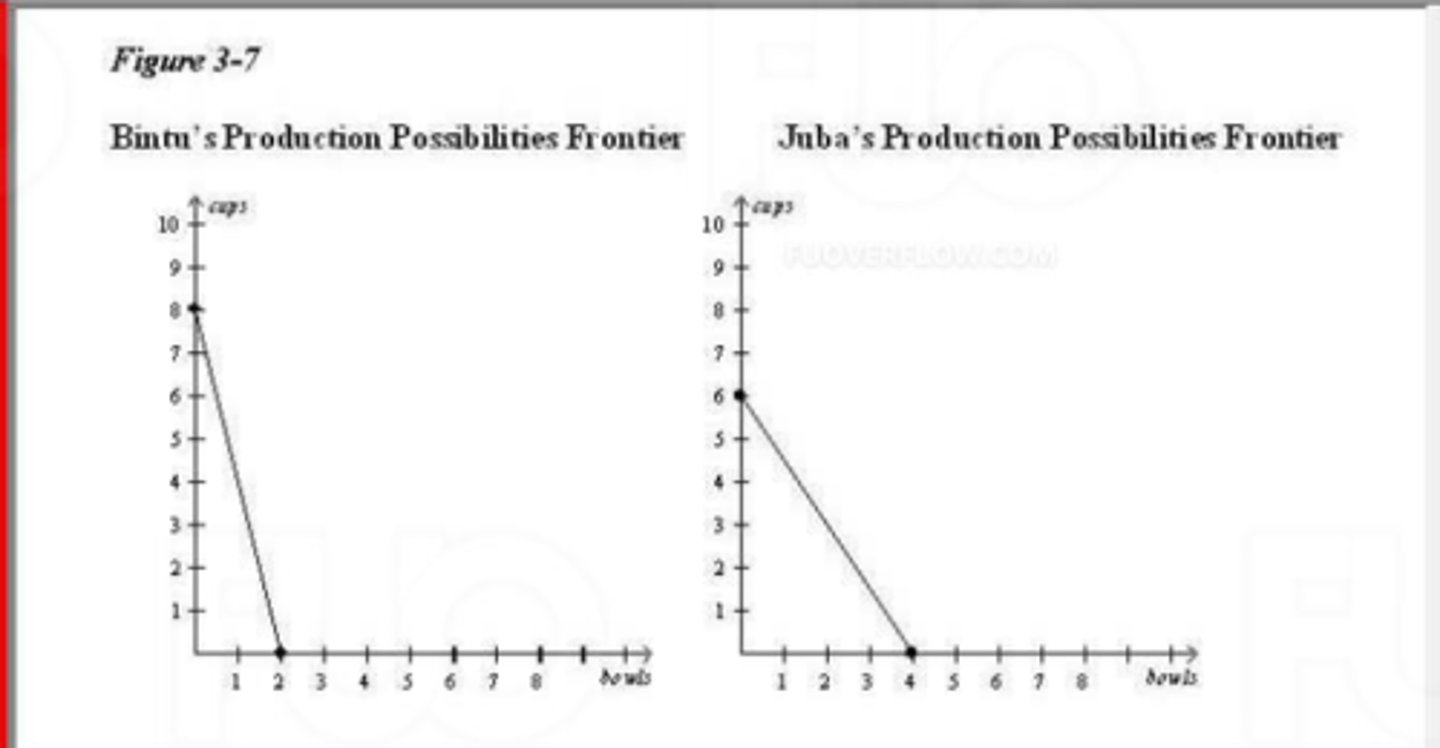
(17761) Refer to Figure 3-7. The opportunity cost of 1 bowl for Juba is
A. 1/4 cup.
B. 3/2 cups.
C. 4 cups
D. 2/3 cup.
B. 3/2 cups.
(17948)
The claim that increases in the growth rate of the money supply increase nominal interest rates but not real interest rates is known as the
A. (i) Friedman Effect.
B. (ii) Hume Effect.
C. (iii) Fisher Effect.
D.None of (i), (ii), and (iii) is correct.
C. iii) Fisher Effect.
Suppose that efficiency wages become more common in the economy. Economists would predict that this would
A. increase the quantity demanded and decrease the quantity supplied of labor, thereby decreasing the natural rate of unemployment.
B. decrease the quantity demanded and increase the quantity supplied of labor, thereby increasing the natural rate of unemployment.
C. increase the quantity demanded and decrease the quantity supplied of labor, thereby increasing the natural rate of unemployment.
D. decrease the quantity demanded and increase the quantity supplied of labor, thereby decreasing the natural rate of unemployment.
B. decrease the quantity demanded and increase the quantity supplied of labor, thereby increasing the natural rate of unemployment.
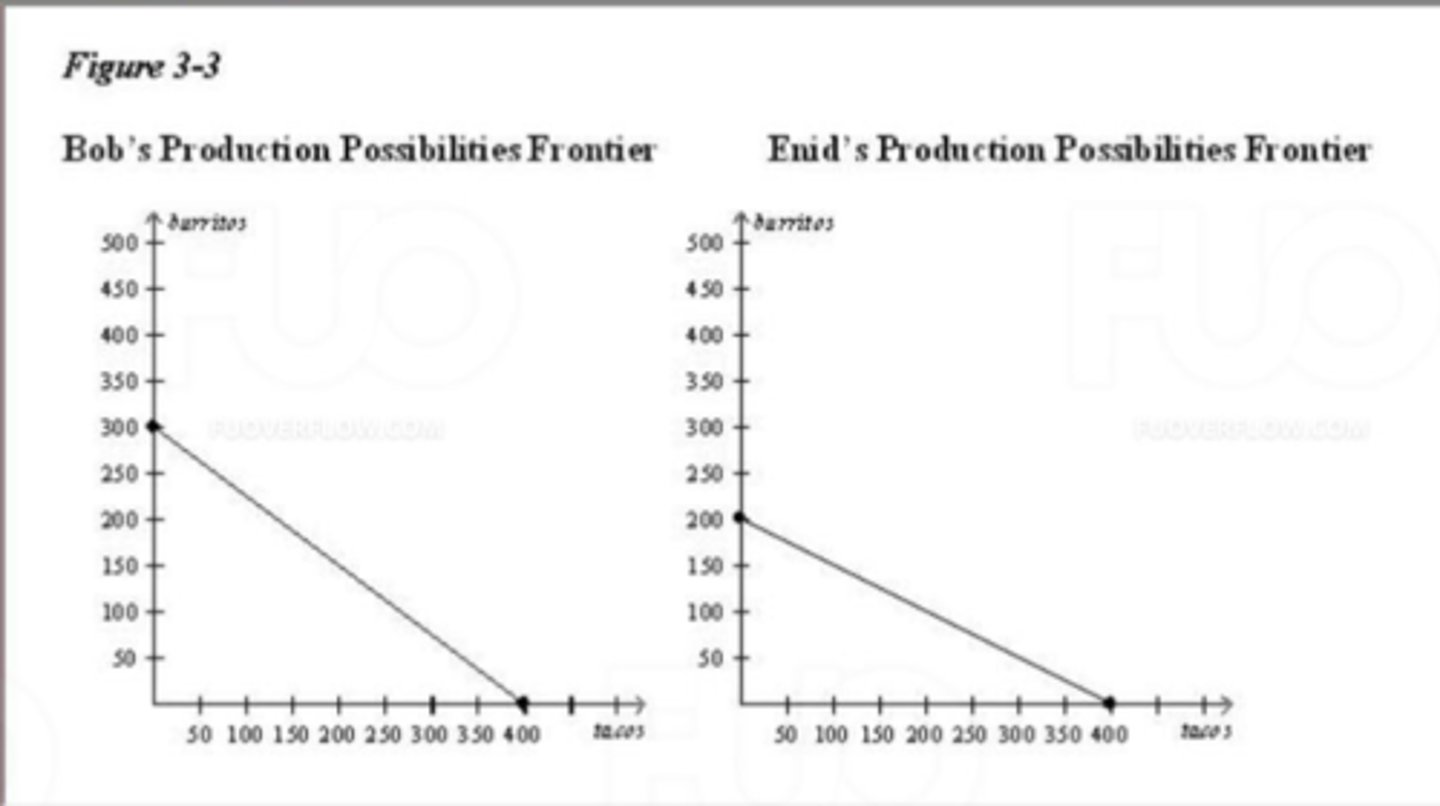
(17758) Referto Figure 3-3. Enid has an absolute
advantage in the production of
A. burritos and a comparative advantage in the production of burritos.
B. neither good and a comparative advantage in the production of burritos.
C. neither good and a comparative advantage in the production of tacos
D. burritos and a comparative advantage in the production of tacos.
C. neither good and a comparative advantage in the production of tacos
(Choose 1 answer)
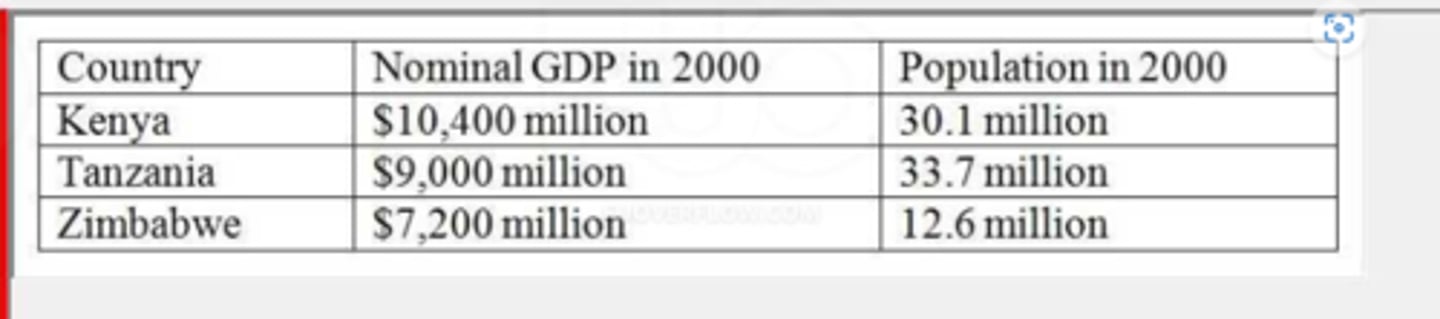
(17781) The information below was reported by the World Bank. On the basis of this information, which list below contains the correct ordering of GDP per person from highest to lowest?
A. Zimbabwe, Kenya. Tanzania
B. Kenya, Tanzania, Zimbabwe
C. Zimbabwe, Tanzania, Kenya
D. Tanzania, Kenya, Zimbabw
A. Zimbabwe, Kenya. Tanzania
(17793)
In the CP|, goods and services are weighted according to
A. how long a market has existed for each good or service.
B. the extent to which each good or service is regarded by the government as a necessity.
C. how much consumers buy of each good or service.
D. the number of firms that produce and sell each good or service.
C. how much consumers buy of each good or service.
(17959)
One year a country has negative net exports. The next year it still has negative net exports and imports have risen more than exports.
A. its trade surplus fell.
B. its trade surplus rose.
C.its trade deficit fell.
D. its trade deficit rose
D. its trade deficit rose
(17919)
Which list ranks assets from most to least liquid?
A. currency, fine art, stocks
B. currency, stocks, fine art
C. fine art, currency, stocks
D. fine art, stocks, currency
B. currency, stocks, fine art
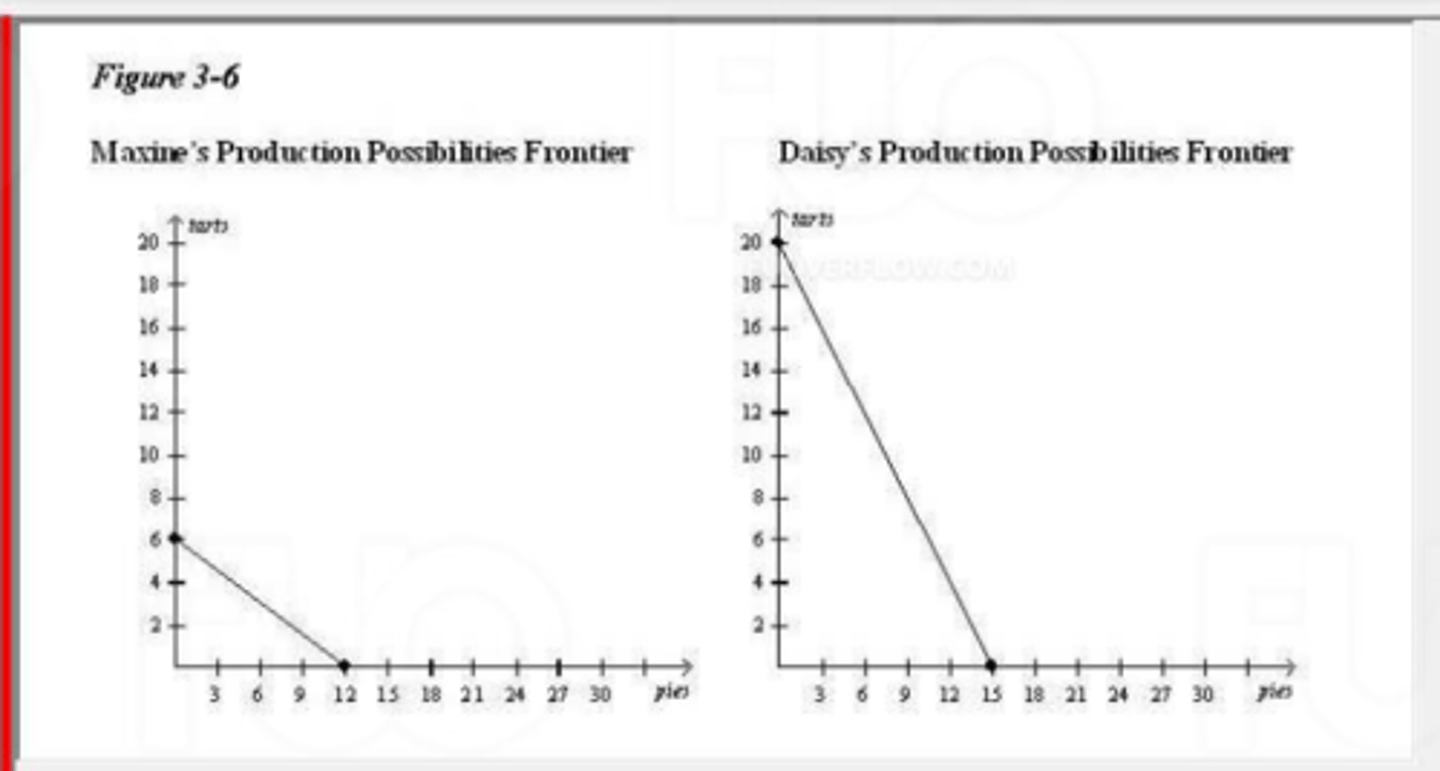
(Choose 1 answer)
(17760) Refer to Figure 3-6. Daisy has an absolute
advantage in the production of
A. neither good and a comparative advantage in the production of pies.
B. both goods and a comparative advantage in the production of tarts.
C. both goods and a comparative advantage in the production of pies.
D. neither good and a comparative advantage in the production of tarts.
B. both goods and a comparative advantage in the production of tarts.