Psych 257 - Lecture 2
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Psychopathology in Historical Context
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Defining psychological disorders
Many definitions have proposed over history yet none universally accepted - Ongoing debate
It’s more of a spectrum, but medicine likes binary things
Defining psychological abnormality
“The Three Ds”
1. Dysfunction
2. Distress or Impairment
3. Deviance
*** all 3 must be present
Psychological Dysfunction
Breakdown in cognitive, emotional, or behavioural functioning
• How do we know when someone has reached this point?
• normal shyness vs. social anxiety disorder ?
• dieting vs. eating disorder?
(some sports require you to maintain a specific weight - ed?)
• adaptive checking vs. OCD?
out of a person’s control?
Personal Distress or Impairment
At least 1 of these 2 MUST apply
a) Distress
◦ Feeling upset about the problem
◦ BUT does this always apply??
(sometimes present - not always, eg. some ED, abuse of drugs, manic episodes, narcissism)
b) Impairment
◦ Interfering with functioning(life)
occupying a lot of time
interference to day-to-day thing (functional impairment)
Deviant
(Atypical or Not Culturally Expected) - ATLEAST 1 of these 2 MUST apply
a) Atypical / deviates from the average (objective # value, eg. IQ)
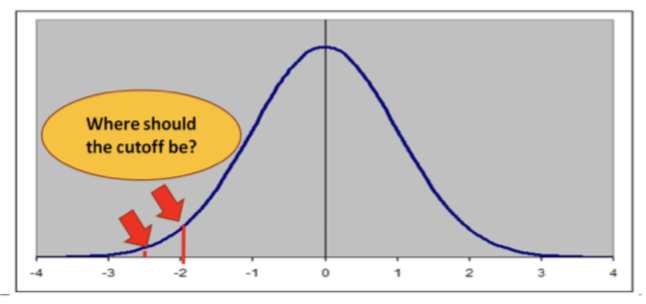
b) Different from socio-cultural norms
deviates from whatever is normal/ societal terms (abnormal)
must understand normative culture (context)
(Innate vs. Taught - lots of things are taught but believed to be innate, boys wearing pink or glitter, not a disorder)
Theories of etiology in history (4) + treatments
Etiology – origins, causes of disorders
• Supernatural (gods, possessions, divine punishment)
treatment: exorcism,
• Biological (Hippocrates - father of modern medicine) (Humoral theory of disorders - related to bodily fluid)
(lobotomies, bleeding or blood letting, shock therapy)
• Psychological
• Social
Over history, theories about etiology inform treatment of mental illness
◦ AND vice versa
Psychoanalytic Theory - treatment and etiology
Based on Sigmund Freud’s theory of the structure of the mind and the role of unconscious processes in dertermining behaviour
Treatment:
◦ Hypnosis, free-association (trying to access unconscious thoughts)
◦ Catharsis (talking things through, releasing tensions)
◦ Dream Analysis
Etiology
◦ Intrapsychic conflicts between different structures of mind
Psychoanalytic Model
1) The structure of the mind
2) The defence mechanisms
3) The stages of early psychosexual developments
Psychoanalytic Theory - Structure of the mind
3 Parts:
Id (pleasure) - unconsious
Seeks pleasure and avoids pain — wants immediate gratification
Ego (reality, balance) - only aware of this
Acts as the rational balance between the id and superego
Superego (moral) - unconscious
Represents morals, values, and guilt — your internalized “right vs. wrong”
Psychoanalytic Theory - Defence Mechanisms (6)
Coping Styles
Unconscious process (protective) where the ego keeps the primitive emotions in check
Adaptive: A healthy or constructive use of defence mechanisms. Reduces anxiety without distorting reality and allows a person to function well.
Maladaptive: A unhealthy or rigid use of defense mechanisms. Temporarily reduces anxiety but distorts reality and can interfere with daily functioning or relationships.
Denial, Projection, Rationalization, Reaction formation, Repression, Sublimation
Psychoanalytic Theory - Psychosexual Stages of Development (5)
The stages—oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital—represent distinctive patterns of gratifying our basic needs and satisfying our drive for physical pleasure.
Freud hypothesized that, if we did not receive appropriate gratification during a specific stage or if a specific stage left a particularly strong impression (which he termed fixation), an individual’s personality would reflect the stage throughout adult life.
Humanistic Theory (20th century) - Etiology & Treatment
Emphasizing the positive, optimistic side of human nature (Carl Rogers)
• Etiology
◦ Unique experiences and perspectives
◦ Thwarted needs (unmet needs)
◦ Conditional regard (believed that ppl with psych issues didn’t receive unconditional positive regard)
• Treatment
Person-centered therapy (Rogers)
• Unconditional positive regard (sees them the best way they can - giving them unconditional love and understanding)
Relationship to therapeutic outcome (have to understand them)
good relationship positively impact outcome regardless of type of solution
Hierarchy of needs (5)
Human needs are arranged in a hierarchy from the most basic (survival) to the most advanced (personal growth). People must satisfy lower-level needs before moving on to higher-level ones.
Physiological Needs - Basic survival needs (Food, water, shelter, sleep, breathing)
Safety Needs - Feeling secure and stable (Physical safety, financial security, health, job stability)
Love and Belongingness Needs - Social connection (Friendship, family, romantic relationships, sense of belonging)
Esteem Needs - Respect and self-worth (Achievement, confidence, recognition, feeling valued)
Self-Actualization Needs - Reaching one’s full potential (Personal growth, creativity, self-fulfillment, realizing talents)
Behavioural Model - Etiology
• Etiology = learning by...
◦ reward/punishment after the behaviour
operant condition – Skinner (1904-1990)
◦ watching others
observational learning
◦ temporal association
classical conditioning – Pavlov (1849-1936)
Treatments
◦Extinguishing / extinction (overtime the bad thing goes away)
◦Systematic desensitization
Systematic desensitization is a behavioral therapy technique used to help people overcome phobias or anxiety by gradually exposing them to the feared object or situation while teaching relaxation at each step.
Cognitive Models - CBT
Etiology
◦ Conscious thoughts
◦ Interpretations of events in ways that are not realistic or accurate
• Treatment
◦ Identify “automatic thoughts” and challenge them with evidence (CBT)
rational-emotive therapy - focuses directly on the irrational beliefs thought to be at the root of maladaptive feelings and behaviour. Worked on modifying what clients say to themselves about the consequences of their behaviour
Thought Record - a key tool used in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to help people identify, challenge, and change (cognitive restructuring) unhelpful or distorted thoughts (called automatic thoughts)
Write the: event, feelings, thoughts, evidence for, evidence against (writing evidence for and against can help change feelings)