Tooth anatomy MIDTERM
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Parts of the tooth (hardest to softest)
Enamel, dentin, cementum, pulp
Anatomic Crown
Part of tooth that enamel covers & ends at cervical line
Clinical Crown
Part of tooth visible in oral cavity
Anatomical root
part of tooth that has cementum surface
clinical root
part of a tooth which is under the gingiva & is not exposed to the oral cavity
How many lobes in central & lateral incisors
4 lobes (3 facial & 1 lingual cingulum)
How many lobes in canine
4 lobes (3 facial & 1 cingulum)
How many lobes in premolars
3 facial lobe & 1 lobe for each lingual cusp
how many lobes in molars
#of cusps = # of lobes
1st molar= 5 lobes
2nd molar= 4 lobes
3rd molar= 3 or more
Fossa
an irregular depression or concavity
developmental groove
a shallow groove on line between primary parts of a tooth
supplemental groove
less distinct & does not mark junction of primary parts
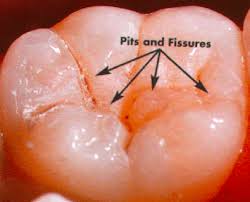
pits
small pin point depression located at junction of developmental groove
ridge
linear elevation on surface of tooth & is named based on location
triangular ridge
ridges that descend from tip of cusp toward central part of occlusal surface
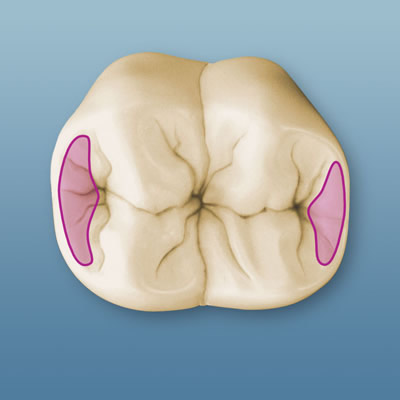
marginal ridge
rounded borders of enamel which form mesial & distal margins of lingual surface for anterior teeth and margins of occlusal surface for posterior teeth
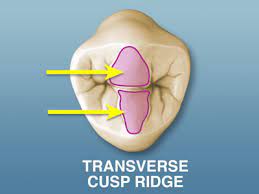
transverse ridge
when a buccal & lingual ridge join
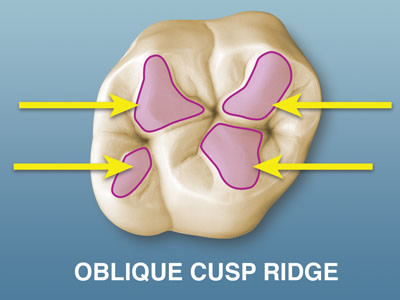
oblique ridge
ridge crossing obliquely the occlusal surfaces of maxillary molars. Only found on maxillary molar
tubercle
small cusp-like elevation on crown produced by extra formation of enamel
fissure
narrow, deep cleft on surface of a tooth due to imperfect fusion of enamel lobes
point angle
junction of 3 teeth surface at a point
line angle
junction where 2 tooth surfaces meet
cusp
a round pyramidal elevation w/a peak
furcation
place on multirooted teeth where root trunk divides in separate roots
Cementoenamel junction (CEJ)
part of the tooth where two vital substances that protect the tooth meet on the tooth's surface
Permanent (secondary) dentition
numbers, 32 teeth
Primary (deciduous) dentition
Letters (A-T), no premolars, 20 teeth
Human dentition classification
brachyodont, heterodont, diphyodont
What permanent teeth are the succedaneous teeth for primary molars
Permanent premolars
are permanent molars succadaneous
Permanent molars are not succedaneous teeth because they do not replace any primary teeth
embrasure space
area below contact, caused by gum tissues not completely filling space between teeth
crest of curvature
The shape & extent of the greatest bulge on facial & lingual crown surfaces help determine the direction that food particles are deflected as they get crushed when we chew
mamelons
3 small bulges on incisal edges of newly erupted incisors, gets worn off after tooth comes into functional contact
primary function of teeth
mastication, assisting in development & protection of supporting tissue
secondary function of teeth
aid in production of speech, give form & symmetry to face
incisors function
designed to cut
canine function
designed to grasp & hold food
premolar function
designed to grind & crush food
molar function
designed to grind food
which arch is wider
maxillary arch
where would you find pits
Found deep in the grooves of premolars & molars
How many roots do incisors have
1
How many roots do canines have
1, w/exception for mand canine which can have 2 occasionally
How many roots do premolars have
Max 1st premolar- 2 roots, all other premolars have1 root
How many roots do molars have
Maxillary molars - 3 roots
mandibular molar- 2 roots
bifurcation
2 rooted
trifurcation
3 rooted
what tooth is widest & smallest mesiodistally
central incisors
cusp of carabelli
the 5th cusp found only on maxillary 1st molars
which tooth has the longest root
canines
What does the deciduous maxillary 1st molar resemble?
Permanent maxillary 1st premolar
What does the deciduous maxillary 2nd molar resemble?
Permanent maxillary 1st molar
What does the deciduous mandibular 2nd molar resemble?
Permanent mandibular 1st molar
What does the deciduous mandibular 1st molar resemble?
does not resemble anything in the permanent dentition (fish shaped)
On the deciduous molars, what feature would you find to help determine if it’s a left or right side?
Cervical bulge on MB side of the tooth
Deciduous teeth root charcteristics
Shorter root trunk, more flared out to make room for the “bigger” succedaneous teeth
When do the first permanent teeth erupt into the oral cavity? Which tooth would that be?
Mandibular and maxillary first molars erupt at 6-7 years old
When does mixed dentition occur?
Age 6-12 is usually when teeth are still coming in
Key features between max & mand canine
maxillary canine have prominent features, a cingulum bulge, looks bulky, has a distal hump
Mandibular canine appears more slender, no cingulum bulge, mesial marginal ridge appears straighter
deciduous crown characteristics
enamel & dentin is thinner
crown smaller
appears whiter
max vs mand 1st premolar
Max 1st premolar- 2 roots, Deeper M root depression (unique)
Mand 1st premolar- 1 root, resembles a canine due to non-functioning L cusp
Max vs Mand 2nd premolar
Max 2nd Premolar- B & L cusp similar height, deeper d root depression
Mand 2nd premolar- 1-2 L cusp, ML cusp tallest, L crown tilt
Max Vs Mand Molars
Max molar- 5th cusp is cusp of carabelli, 3 roots, oblique ridge
mand molar- 5th cusp is distal, 2 roots, L crown tilt
Pit
oblique ridge
transverse ridge
marginal ridge