A&P 1 - Chapter 4: Tissue: The Living Fabric
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
The types of tissues
Epithelial, connective, muscle, and nerve
Two types of epithelial tissue
Covering and lining, and Glandular
Glandular Epithelium
Composed of cells that are specialized to produce and secrete substances.
The two types of Glandular Epithelia
Endocrine and exocrine
Endocrine glands
Ductless glands, they secrete hormones that travel through lymph or blood to target organs.
Exocrine glands
They have ducts, examples include mucous, sweat, oil, and salivary glands.
Connective tissue
most abundant and widely distributed tissue in the body
The four classes of connective tissue
connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, blood
The Functions of connective tissue
Tissue that supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body. Connective tissue also stores fat, helps move nutrients and other substances between tissues and organs, and helps repair damaged tissue
The three types of fibers
collagen, elastic, reticular
Collagen
The strongest and most abundant type, they provide high tensile strength.
Elastic
Networks of long, thin, elastin fibers that allow for stretch
Reticular
short, fine, highly branched collagenous fibers
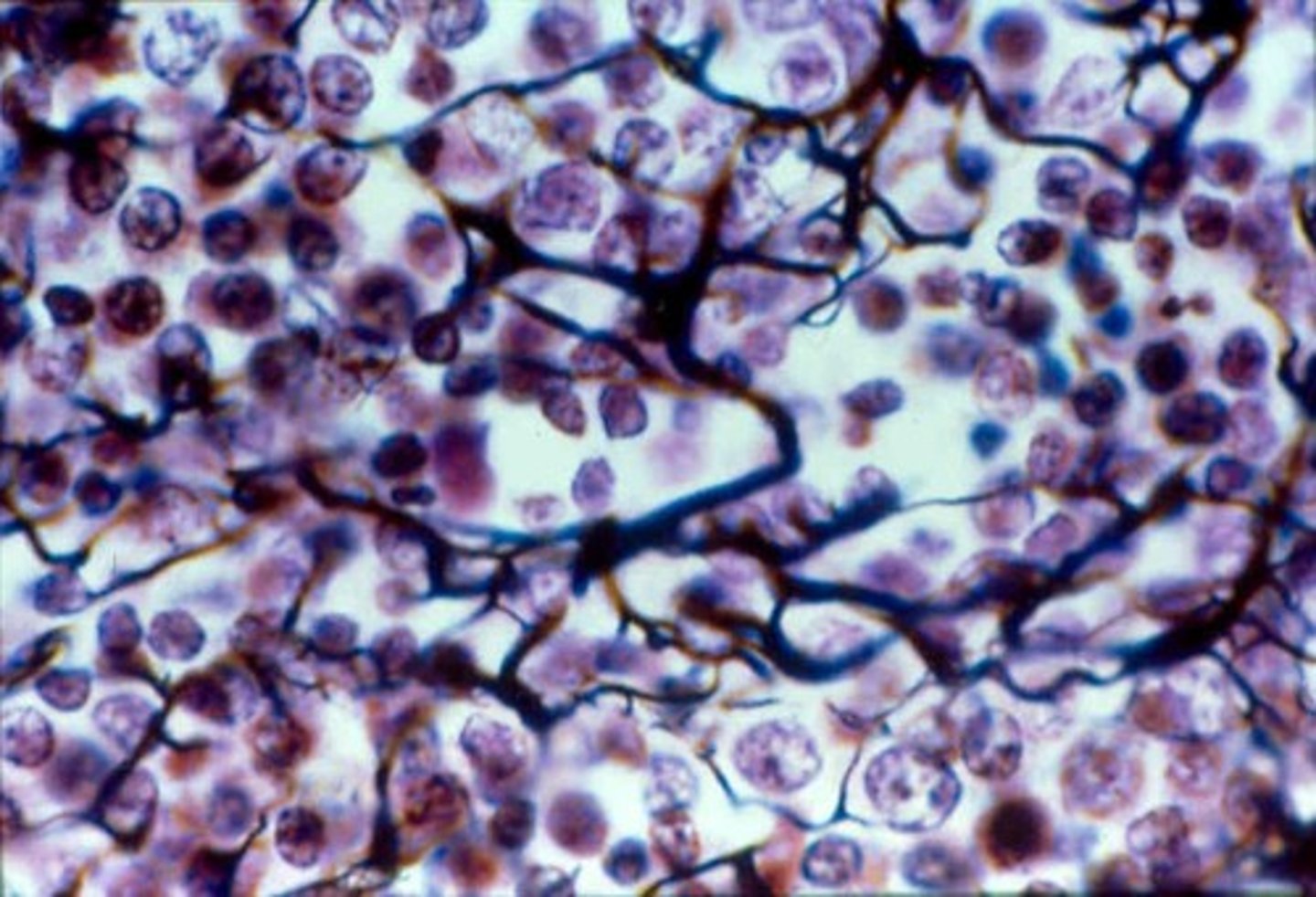
Areloar
A loose connective tissue
It wraps and cushions the organs, it plays an important role in inflammation.
It is located in the lamina propria, this is were the Basal side connects to.
Areolar Tissue
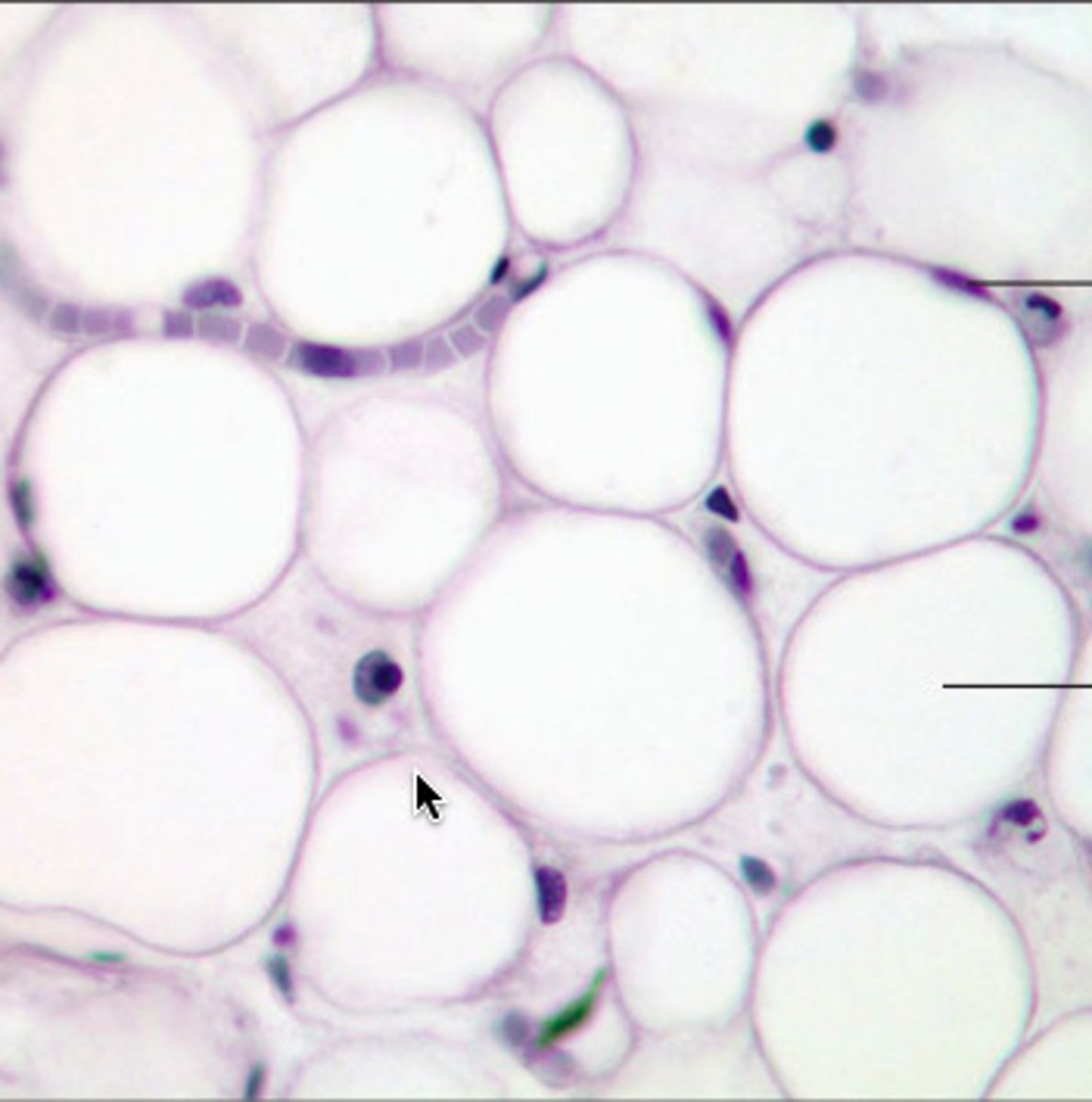
Adipose
A loose connective tissue
Provides reserve food fuel, it also insulates heat, and supports and protect the organs.
It is located under the skin in the hypodermics, around the organs, and around the body (it is fat)
Adipose Tissue
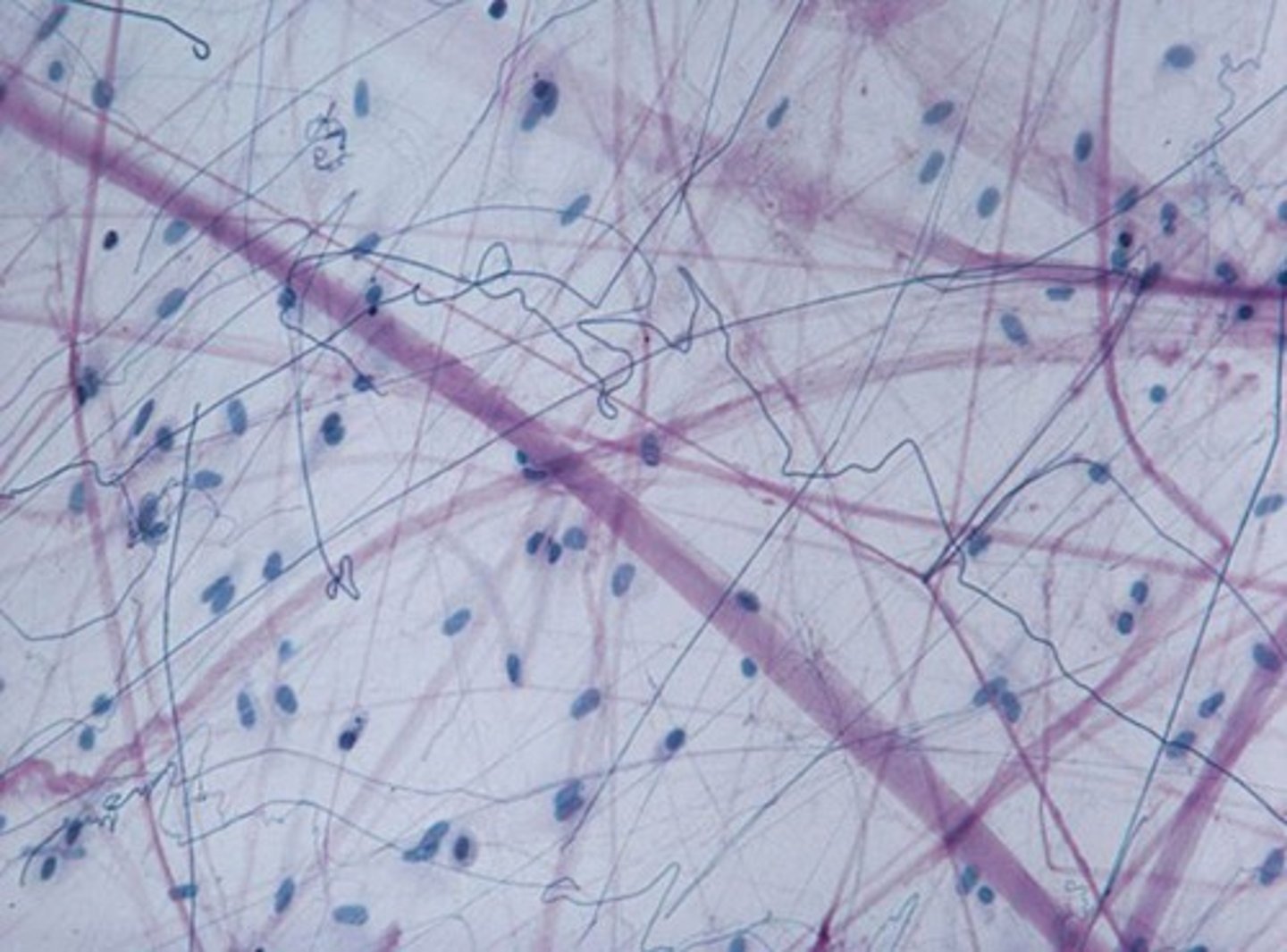
Reticular tissue
A loose connective tissue
The fibers form a soft internal skeleton that supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages.
It is located in the Lymphoid organ like the spleen.
Reticular Tissue
Dense Regular
A dense connective tissue
It attaches muscles to bones or muscles, and attaches bones to bones.
Located in the tendons and most ligaments
Dense regular tissue
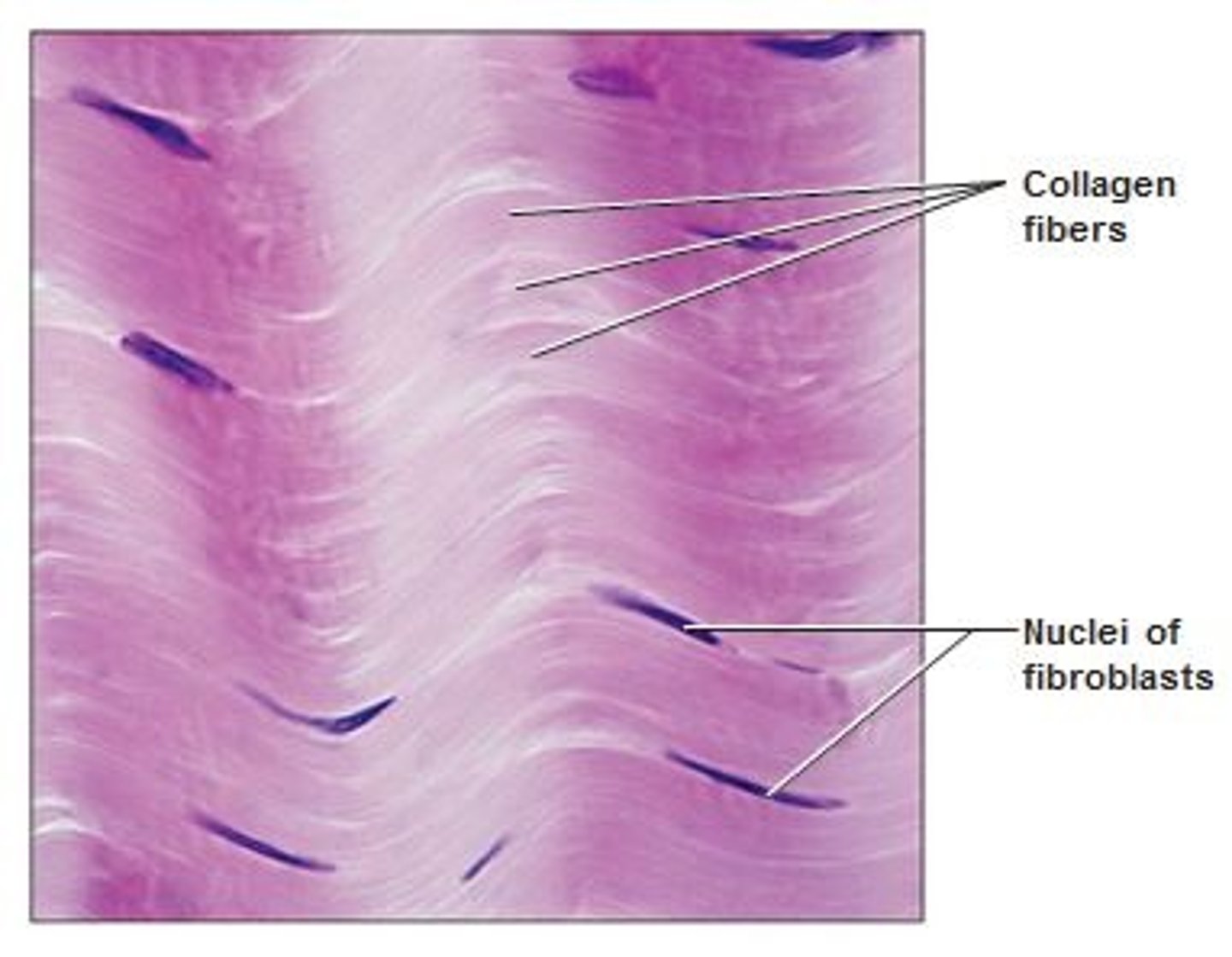
Tendons
Connect muscle to bone
Ligaments
Connect bone to bone
Dense Irregular
A dense connective Tissue
able to withstand tension exerted in many directions; provides structural strength.
Located in the dermis of the skin, and in the fibrous joint capsule.
Dense irregular tissue
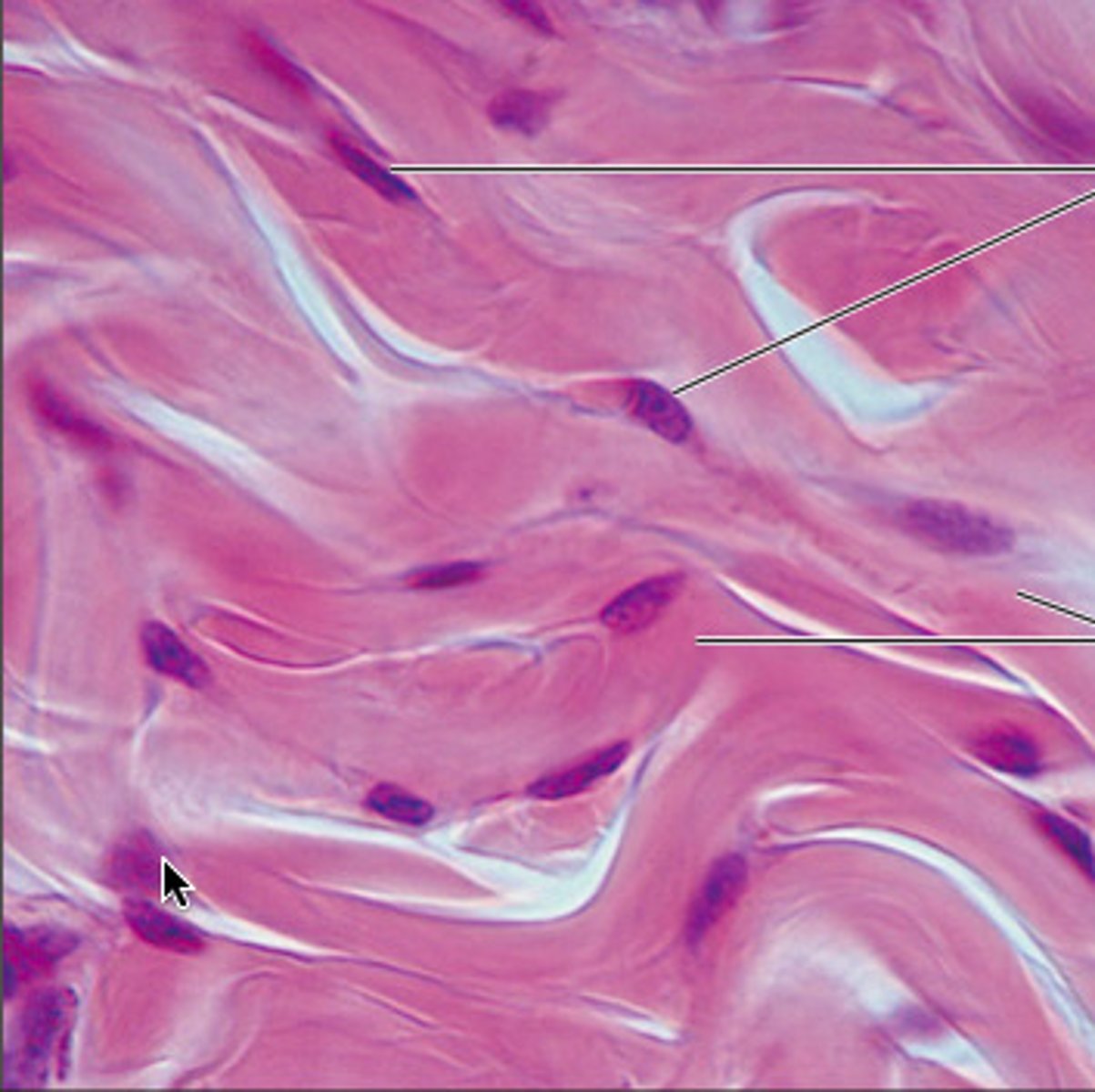
Elastic
A dense connective tissue
Allows recoil of tissue following stretching
Located in the wall of large arteries; within ligaments associated with the vertebral column; within the wall of the bronchial tubes.
Elastic tissue
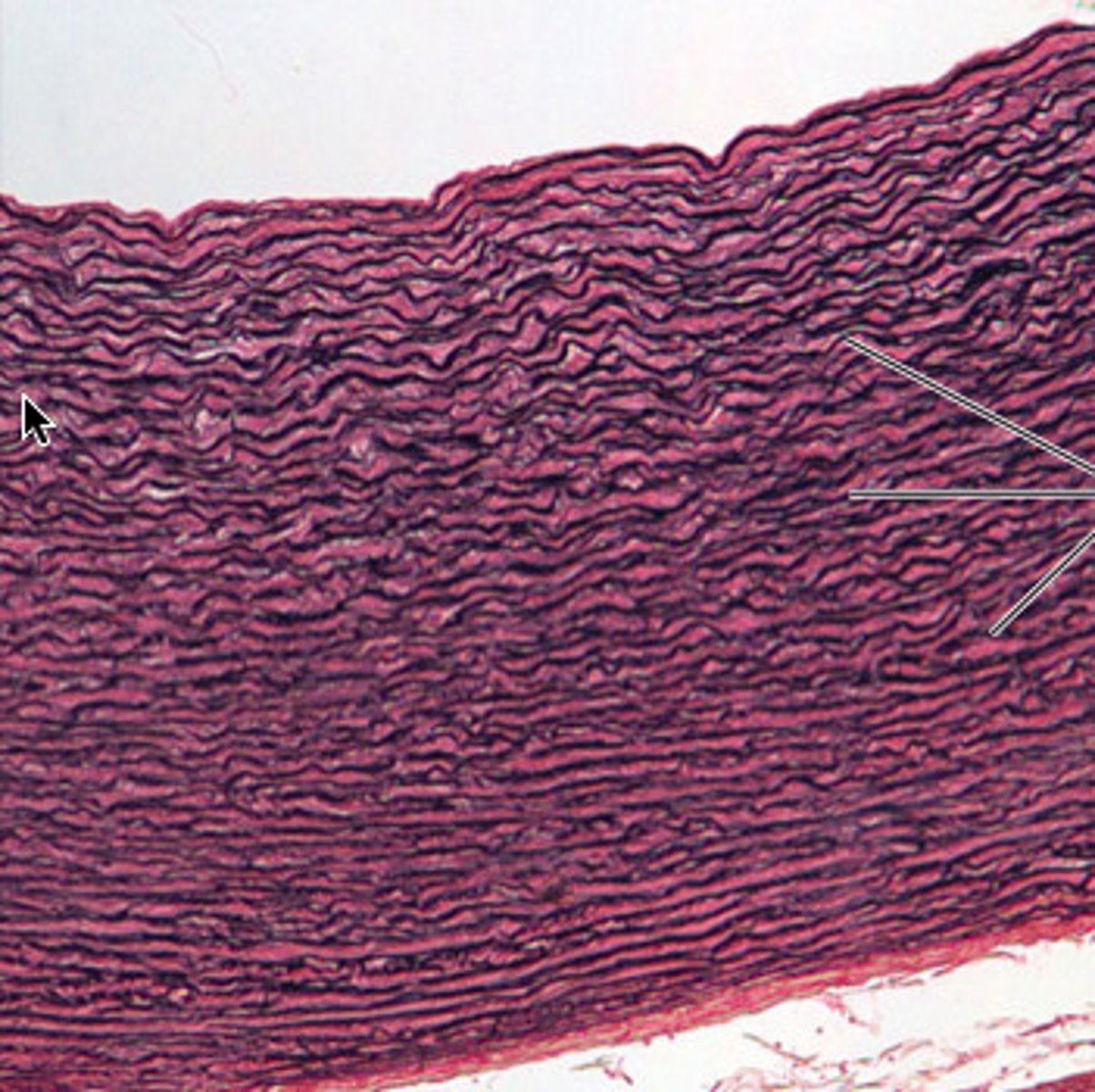
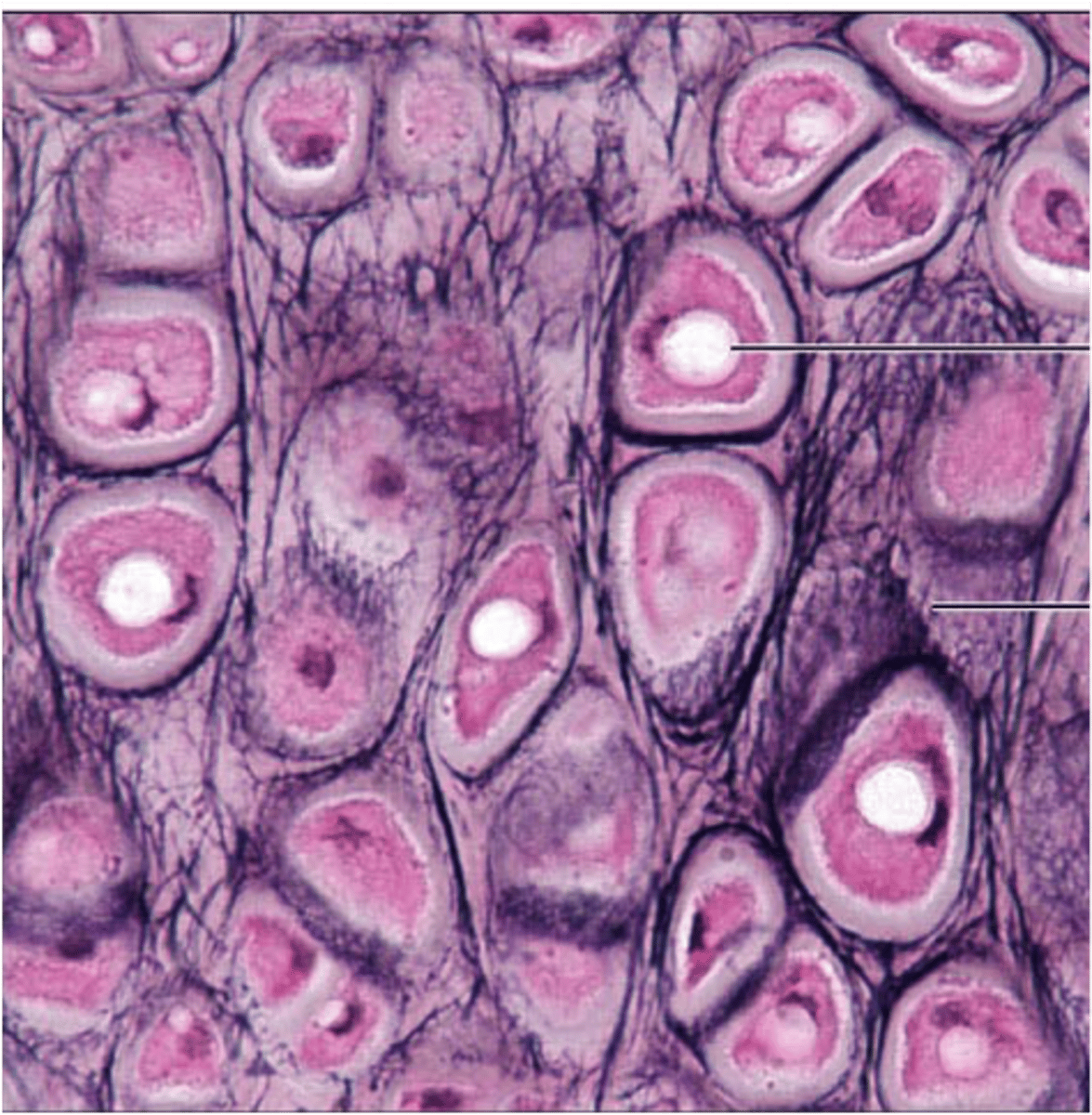
Cartilage: Hyaline
It supports and reinforces; has resilient cushioning properties; resists compressive stress.
Located on the ends of long bones in joint cavities, the costal cartilages of the ribs; the nose, trachea, and larynx.
Cartilage: Hyaline
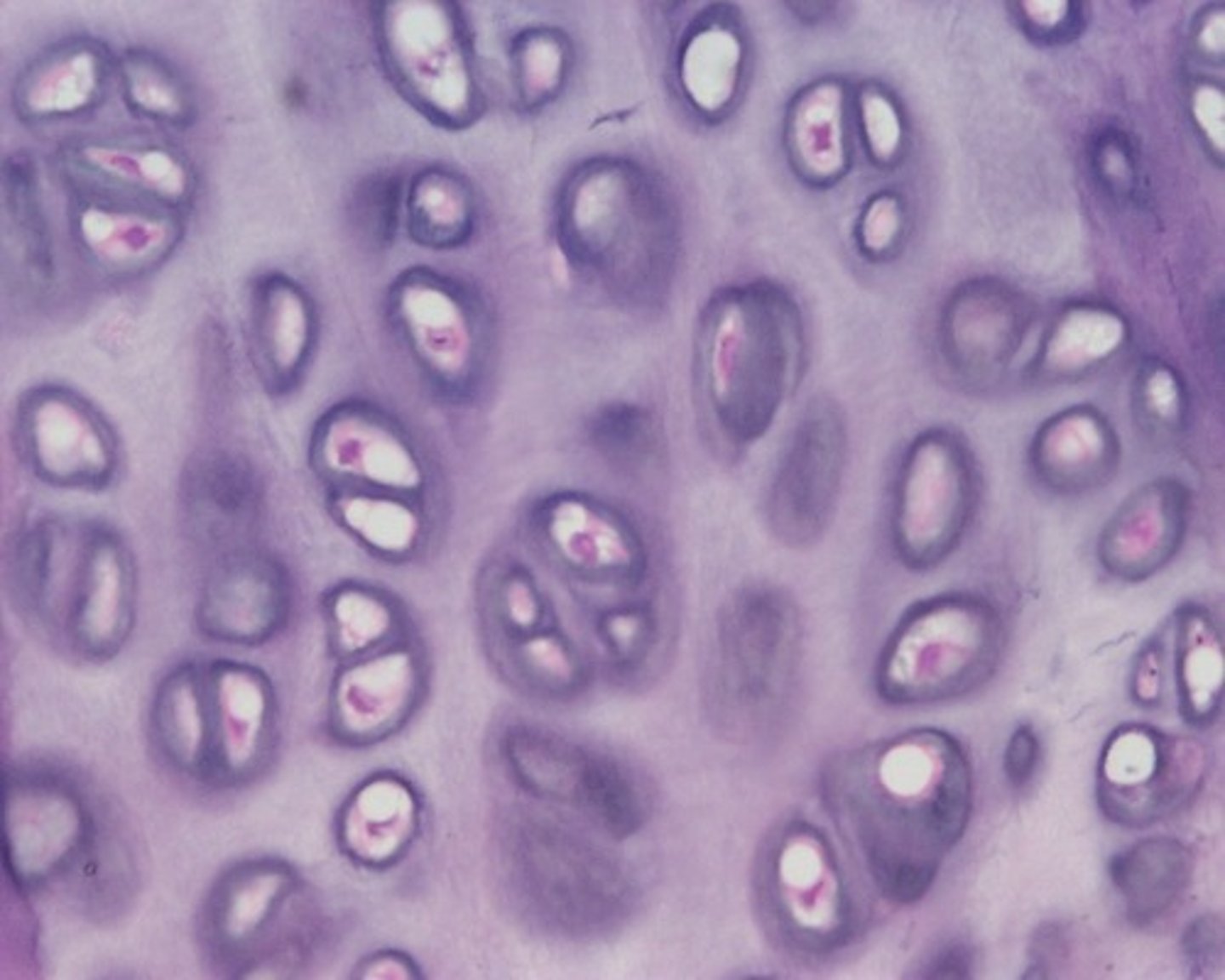
Cartilage: Elastic
More elastic that the hyaline cartilage, has more elastic fibers,
It maintains the shape of the structure whiles allowing for flexibility.
The ear is an example
Cartilage: Elastic