MedSurge Exam 1
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
What is Sclerosis?
Hardening of tissue due to fibrous tissue overgrowth
What is Stenosis?
The narrowing or constricting of passage or orifice
What is Atrophy?
Wasting away or a decrease in the size of an organ
What is Calcification?
Calcium and calcium salts are deposited in abnormal locations
ex. Blood vessels
What is the difference between sclerosis and stenosis?
Sclerosis is the hardening and stenosis is the narrowing of vessels
What three things can an RN NOT delegate?
Anything with the nursing process
Client education
Tasks that require nursing judgement (Unstable pt)
Remember TAPE of what a nurse must do
T- initial Teaching
A- Assessment
P- Planning
E- Education
What is the order of conduction in the heart and what is each rate?
SA Node (60-100 bpm) —> AV Node (40-60 bpm) —> Bundle Branches ( <40 bpm)
What is repolarization?
The contraction of the heart
What is Repolarization?
The relaxation of the heart
What does Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) look like?
Normal waves
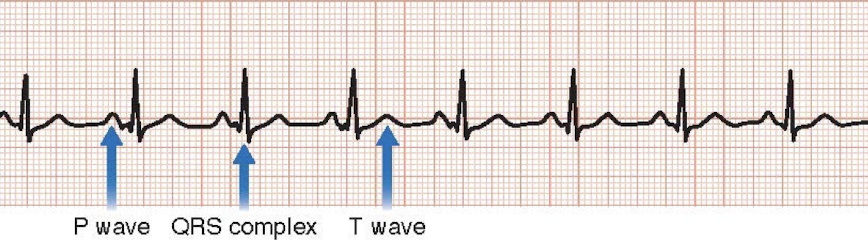
What wave represents atrial depolarization?
The P wave
What wave represents ventricular depolarization?
QRS
What wave represents ventricular repolarization?
The T wave
What causes an arrhythmia or dysrhythmia?
A disruption in cardiac conduction pathways
What is the number 1 risk factor for dysrhythmias?
AGE!
What are some signs and symptoms of dysrhythmias?
Palpitations
Hypotension
Diaphoresis
SOB
Syncope
How many leads are placed for a 12 lead ECG?
Only 10 are placed
Where are the leads placed for an ECG?
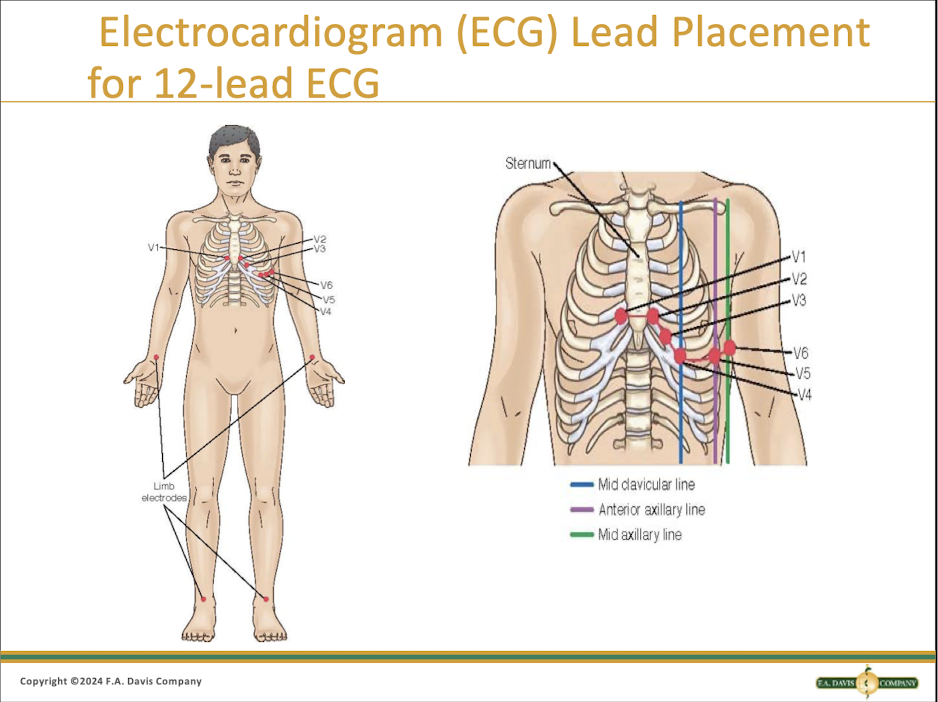
What about just the ones on the chest for an ECG?

Where do the leads go for a 5 lead ECG?
Snow WHITE is over GREEN grass
BLACK smoke over a RED fire
Always keep CHOCOLATE close to your heart
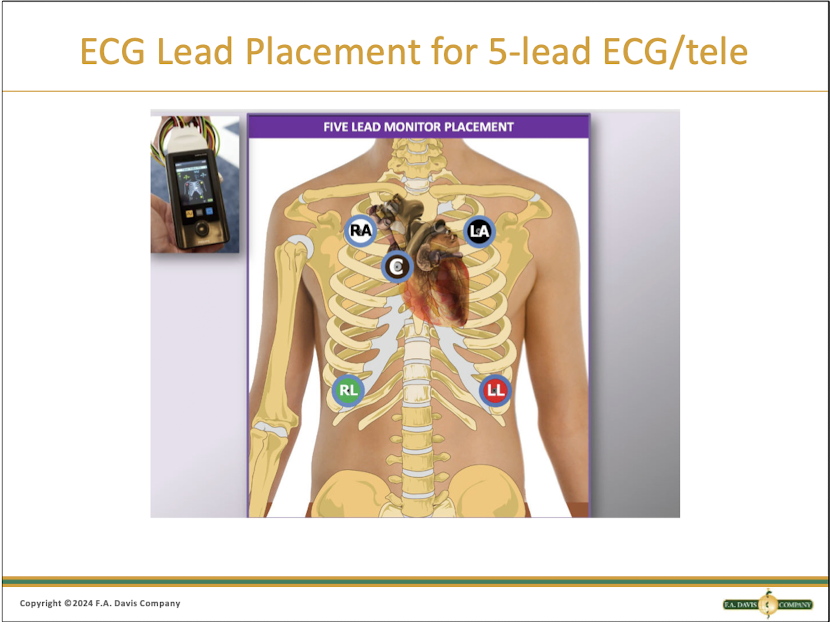
Which lead is the most accurate?
Lead 2
When reading an ECG what does the amplitude reflect?
The strength of the electrical signal generated by the heart
For ECG paper what does everything represent?
Each small box is 1 mm in height and 0.04 seconds
Each big box is 0.20 seconds long and is made up of 5 small boxes
What is sinus bradycardia?
HR <60 caused by hypoxia, hypothermia, medications, sleep, and athletes
What drug is given to treat sinus brady?
Atropine is given because Atropine Accelerates the heart as long as it is symptomatic
What causes sinus tachycardia?
Fever, anemia, hypovolemia, hypotension, pulmonary embolism, and MI
What is a treatment for sinus tachy?
It varies so, if anemic = blood, if hypovolemic = fluids. Medications such as Beta Blockers and CCB
What are premature atrial contractions (PACs)?
This is when the pacemaker cells close to the SA node fires earlier than anticipated? These are non life threatening
What causes a PAC?
Hypoxia
Caffeine
Infection
Digoxin toxicity
Coronary artery disease
What is Atrial Fibrilation?
The most commonly seen dysrhythmia worldwide. It is when the atria of your heart just shake a little
What are some cause of afib?
Genetics
Age
Diet
What are the 4 classifications of afib?
Paroxysmal - spontaneously self limiting
Persistent - Longer than 7 days
Long-standing - Longer than 12 months
Permanent/Persistent - This is resistant to rhythm control therapies
How do you treat afib?
Meds: Digi, BB, CCB, Anticoags, Antiplatelet
What else can be used to treat Afib?
Can also be treated with cardioversion AFTER anticoagulants
What are some risks with Afib?
Loss of cardiac kick (last 20% of blood) and clots
What does Afib look like?
No clear P wave but you do still get the QRS complexes

What is Afib RVR?
It is Afib with Rapid Ventricular Response. It is when the HR is >100
What is an echocardiogram
A noninvasive diagnostic test that uses ultrasound to look at the structure and function of the heart
What is a Trans-Esophageal Echo (TEE)?
This requires sedation and topical anesthesia. A small transducer is put through the mouth and into the esophagus
When is a TEE done?
It is used before cardioversion for afib to ensure there are no blood clots in the atria?
What is aflutter?
It is from a pacemaker cell other than the SA node.
What does aflutter look like?
There are no P waves
Instead, you get Flutter waves (F waves)
Sawtooth pattern
Loss of atrial kick!

What are some causes of AFlutter?
Acute MI
Mitral Valve Disease
Thyrotoxicosis
COPD
Cardiac/Pulmonary Surgery
How do you treat AFlutter?
Rate control drugs: BB, CCB, Digoxin
Antiarrhythmic (Amiodarone)
Cardioversion
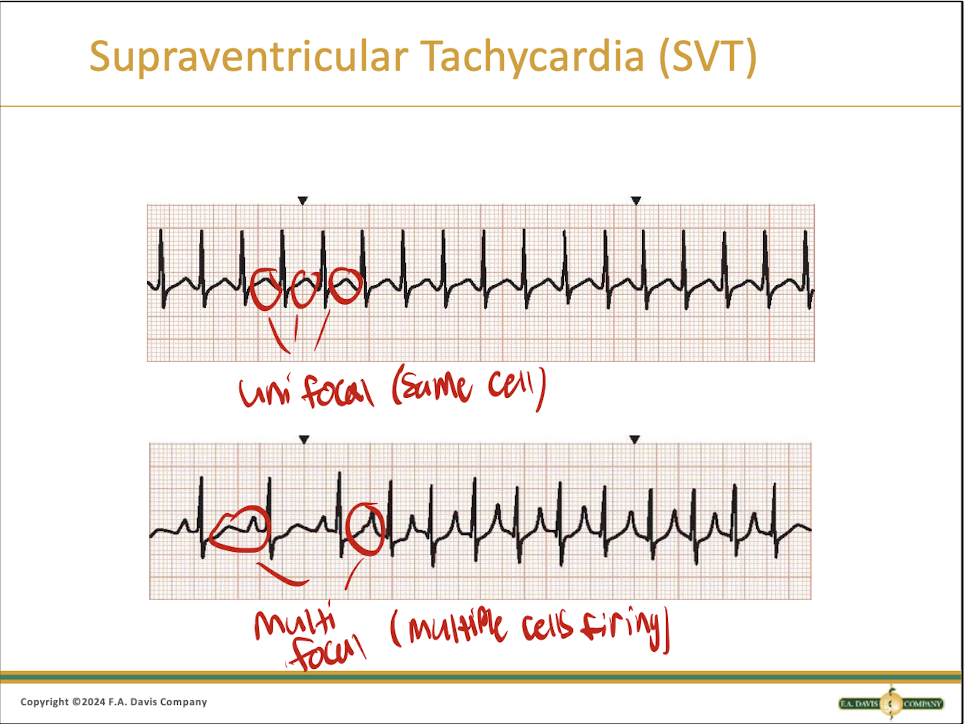
What is SVT?
It is Supraventricular Tachycardia and it has a super narroe QRS complex
What does SVT look like?
Narrow QRS complex with a continuous fast heart rate, often the P wave is absent
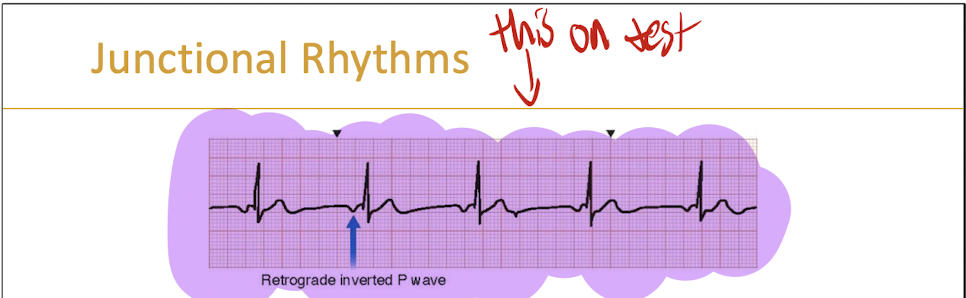
What is a PJC?
It is a premature junctional contraction that typically do not require treatment
What does a PJC look like?
They are often kinda upside down and weird looking
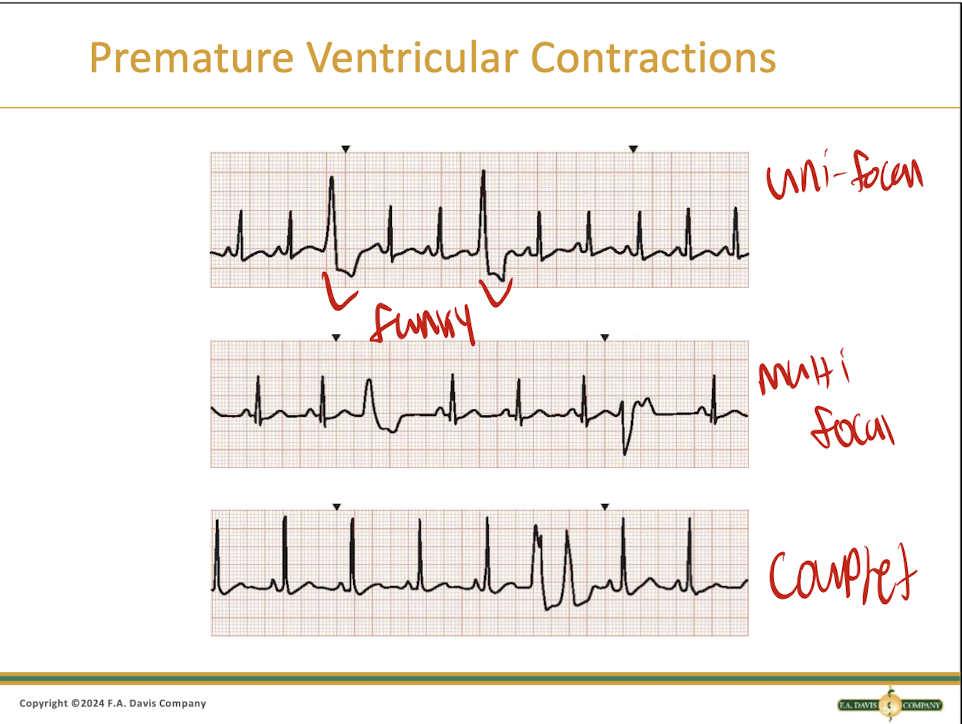
What is a PVC?
It is a premature ventricular contraction that comes from the ventricle firing earlier than expected
What can cause a PVC?
Hypoxia
MI
Cardiomyopathy
Electrolyte imbalance
CAFFEINE
HTN
Recreational drug use
What are two PVCs in a row called?
A couplet
What are three PVCs in a row called?
A triplet, this is the most deadly!
What is a PVC that happens every other beat?
It is called a Bigeminy
What is a PVC that happens every third beat?
A Trigeminy
What do you do to treat a PVC?
You correct the cause as they are typically non life threatening
What does a PVC look like?
They vary based on the type
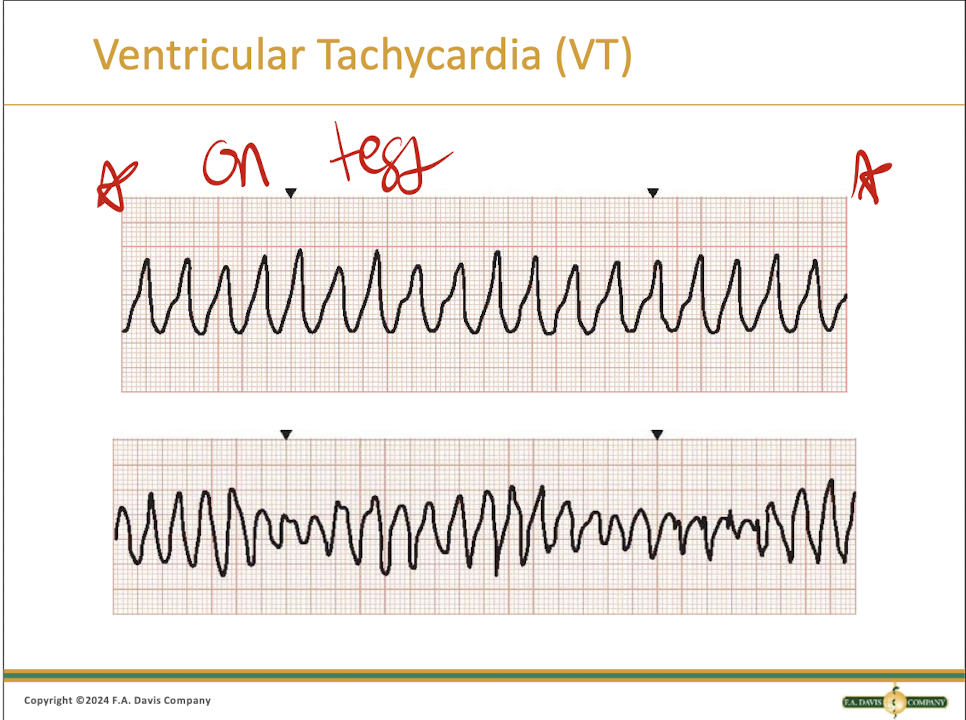
What is Vtach?
It is a wide and fast impulse from the ventricles with a rate greater than 150bpm and it can definitely be life threatening.
What is a Non-Sustained VT?
A NSVT is a run of three or more PVCs that end in 30 seconds and it can act as a warning to ppl with heart problems
What is a sustained VT?
An SVT is an episode of vtach for more than 30 seconds that needs stabilization as it is considered life threatening
How do you treat Vtach if they have a pulse?
Give antiarrhythmic meds (Amiodarone), electrolyte replacement, or cardioversion
How do you treat Vtach that does not have a pulse?
This is cardiac arrest and requires resuscitation and defibrillation as it is lethal
What does Vtach look like?
It looks like a bunch of tombstones bc that is where you are going
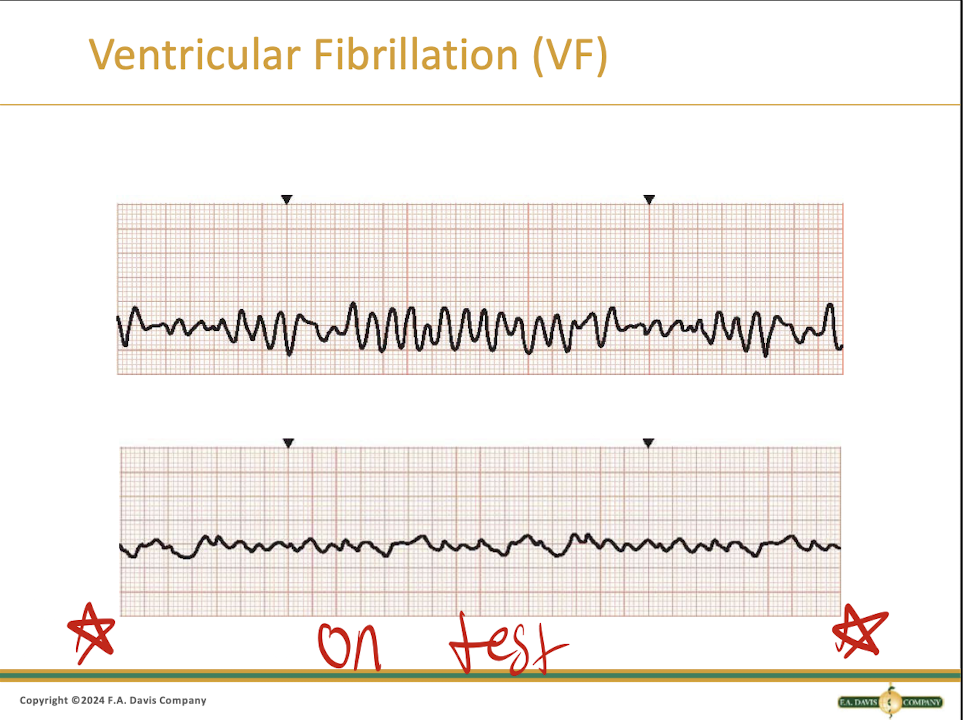
What is Vfib?
It requires IMMEDIATE treatment and happens when the ventricle has multiple impulses rapidly firing
How do you treat Vfib?
Chest compressions and defibrillation
What does Vfib look like?
It just looks like a bunch of squiggles
What is Asystole?
You’re dead, no measurable electrical activity from the heart
How do you treat asystole?
Push epi and start CPR
What is a first degree AV heart block?
It is a prolonged PR interval longer than .20 seconds
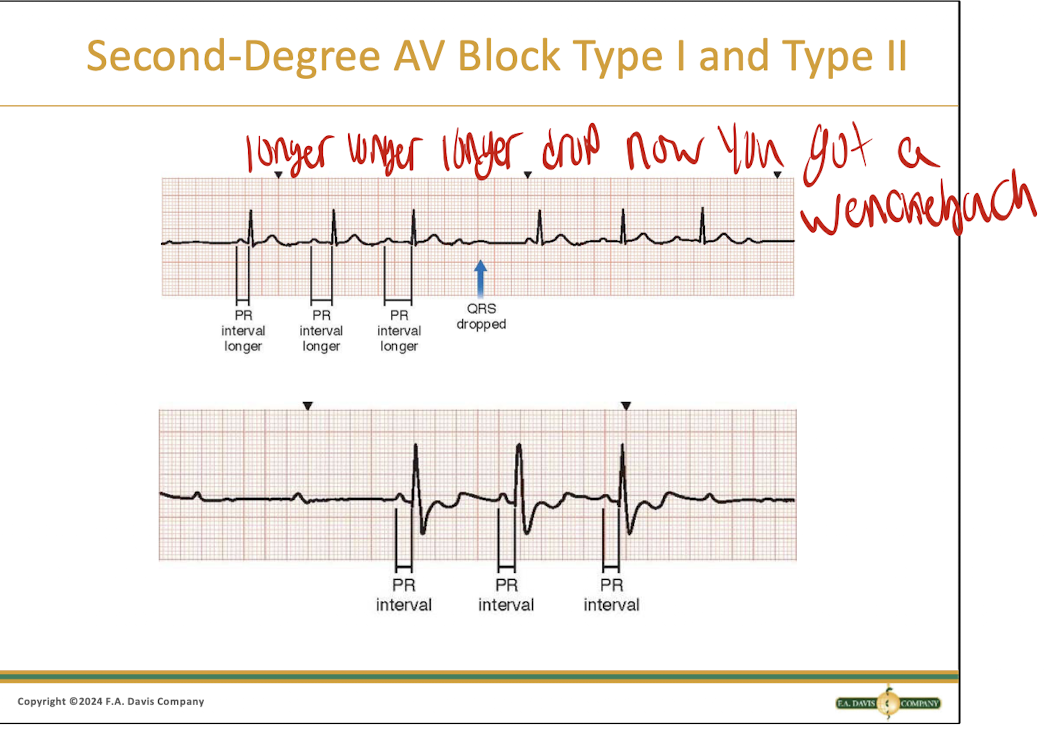
What is a second degree heart block type 1?
It is when the PR interval gets longer and longer until a QRS gets dropped
How do you treat a type 1 heart block?
You give atropine only if they are symptomatic
What is a second degree type 2 heart block
It is a dropped QRS without a prolonged PR interval, not lethal but can quickly change to a type 3 which is lethal
How do you treat a type 2?
If the pt is symptomatic then you treat with a transcutaneous patch which HURTS
What does a Wenckebach look like?
What is a third degree AV heart block?
This is a COMPLETE block of the AV node where the AV is completely independent
What does a third degree complete heart block look like?
Lines with a quick QRS. THE ONE WITH ARROWS!
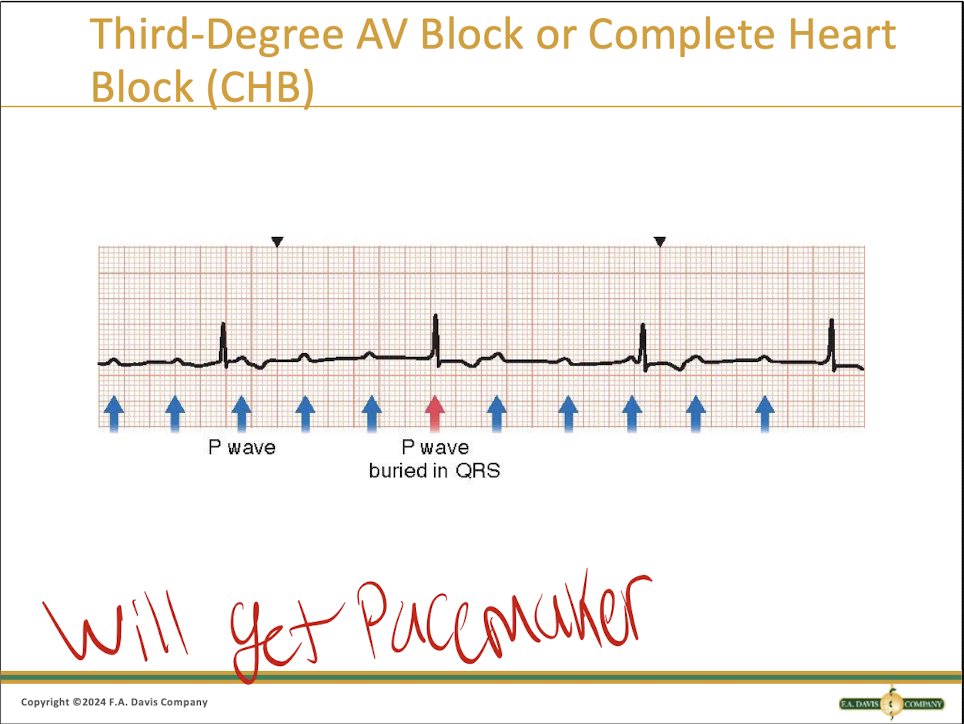
How do you treat a third degree?
You will be getting a pacemaker
What is the poem for a first degree HB?
If the R is far from the P then it must be a FIRST DEGREE
What is the poem for a second degree type 1 HB?
Longer, longer, longer, drop! Then you have a TYPE 1 WENCKEBACH
What is the poem for a second degree type 2 HB?
If PR stays normal and QRS quits, then it must be a TYPE 2 MOBITZ
What is the poem for a third degree complete HB?
If Ps and Qs don’t agree, then you have a THIRD DEGREE
What leads show an Inferior MI STEMI? and what is occluded?
ST elevation in leads 2, 3, aVF, RCA and/or left circumflex
What leads show a Lateral MI STEMI? and what is occluded?
1, aVL, V5, and V6, Left circumflex or diagonal branch of LAD
What leads show an anterior/septal STEMI? and what is occluded?
Leads V1-V4, LAD
What leads show a Posterior STEMI? and what is occluded?
Leads V7, V8, and V9, the descending artery
What is an NSTEMI?
Caused by a partial blockage of a major coronary artery or a blockage in a minor artery that have inverted ST waves
What is a Q wave?
These are signs of a previous MI
What does a pacemaker do?
It gives the heart a “gentle boop” to remind it to keep going that is battery operated
What does a transcutaneous pacemaker do?
It tells the heart to “WAKE THE FUCK UP AND WORK” often used on a 3rd degree HB pt
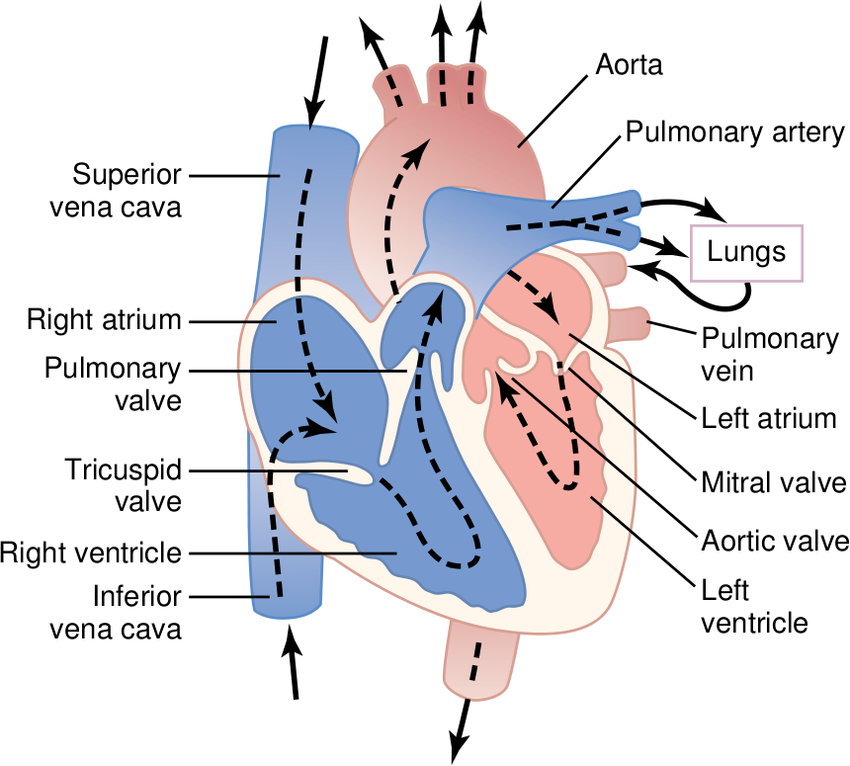
What is the order of blood flow thru the heart?
What does dopamine do for the heart?
It is used to increase HR and contractility in cases of low BP low HR and HF
What does Atropine do for the heart?
It increases HR and improves electrical conduction by blocking the effects of the vagus nerve on the heart
What does Adenosine do for the heart?
It slows the HR and dilates blood vessels
What does Amiodarone do for the heart?
It is an antiarrhythmic med that helps regulate a person’s HR by controlling the signals
What is Senescence?
The process of aging or deterioration that is characterized by a permanent stop in cell division and a decline in cell function