Atom Structure, Balancing Equations, Acids
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry Revision Pre-IB T1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Atom
Smallest part of a chemical element
groups
column (vertical)
periods
rows (horizontal)
metaloid
properties of metals and non-metals
isotope
more neurons than protons
diatomic elements
H2, N2, F2, O2, I2, Cl2, Br2 (Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer)
(most are halogens except astatine).
compound
2+ different elements chemically bonded
molecule
2 or more same element
atom
smallest particle/unit of a chemical element
molecule properties
discrete (isolated) in connectedness:
e.g. crystalline organised arrangement
relative mass
add both elements together
stoichiometric ratio
ratio of coefficients
balancing equations layout
reactant/s yields product/s
Law of Conservation of Mass
mass is neither created nor destroyed
state symbols
solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g), and aqueous (aq)
Ionic Compounds
electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
stable octet / noble gas configuration
a stable electron configuration consisting of 8 valence electrons
cations
+ charged ions
anions
- charged ions
ion
a molecule with a net electrical charge
ionic compound properties
-High Melting / Boiling points
-When solid it can't conduct electricity
-Dissolve easily in water
-hard, brittle, lattice structure, crystalline solids
naming ionic compounds
metal+non-metal(ide)
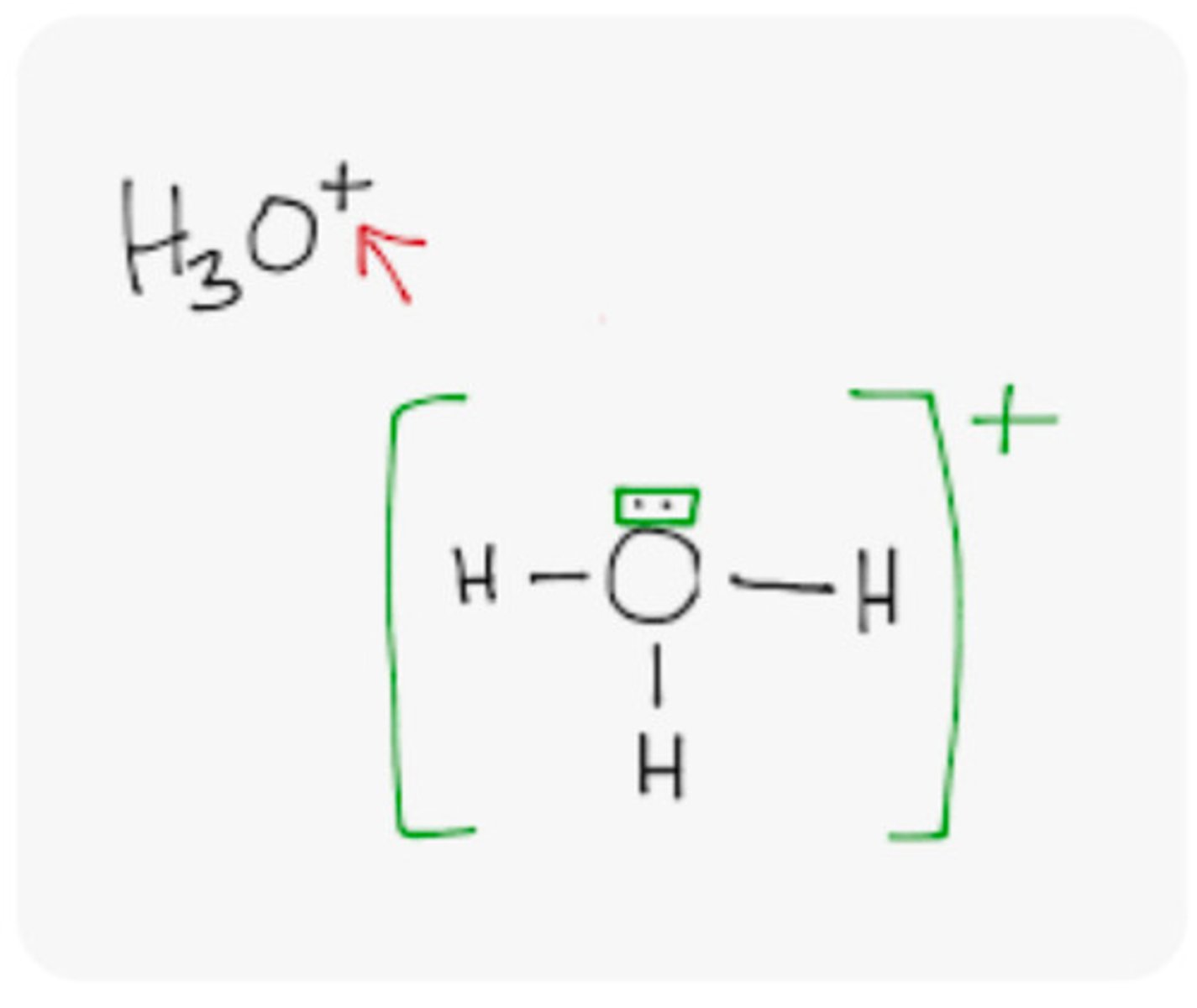
Polyatomic Ion
A charged group of covalently bonded atoms
Isoelectronic species
Atoms or ions with the same electron configuration.
How to draw a polyatomic ion
if not lewis structure, remove the silly bonding lines)
Solubility
if soluble in water, will form an aqueous solution
if not, stays the same state
net ionic vs ionic equation
net ionic equation - without spectator ions
ionic equation - every individual w/ charge
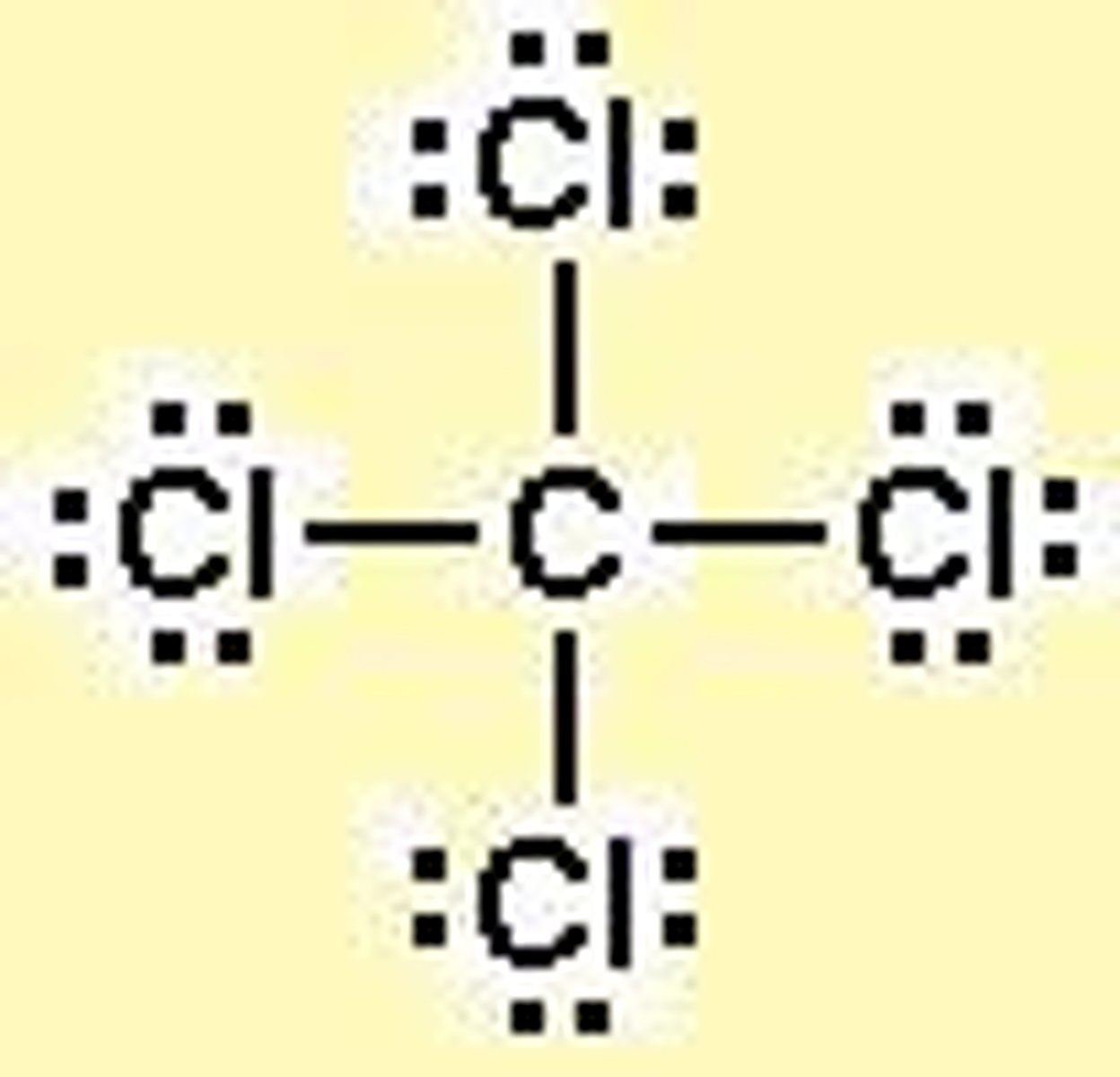
covalent bonding
sharing electrons between 2 non metals
ionic bonding
linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a chemical compound
non-bonding pairs/lone pairs
not involved in forming the bond in the valence shell
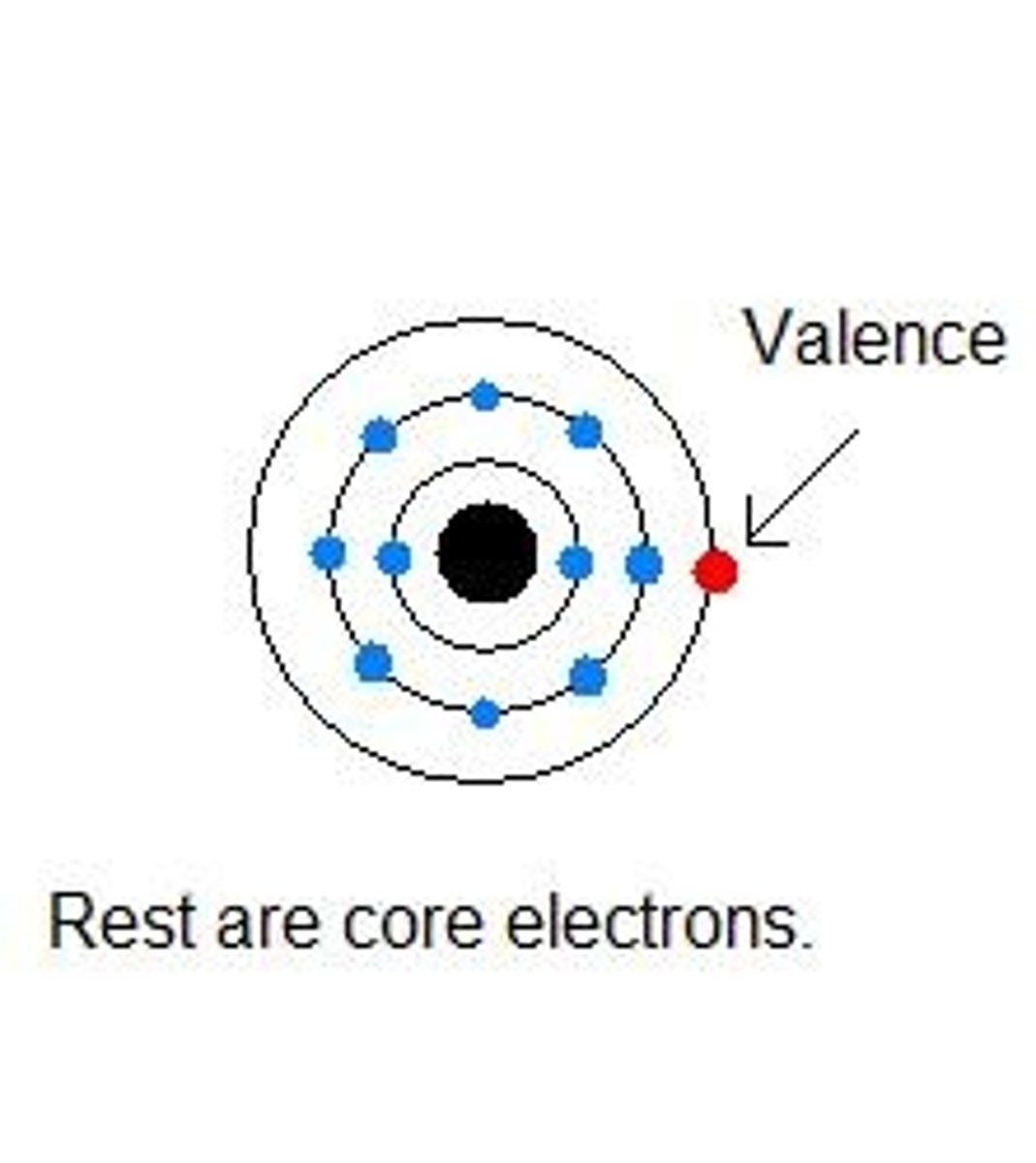
core electrons
The electrons that are not in the outermost shell of an atom.
covalent bond properties
-low melting/boiling points
-bad electricity conductivity
-single double or triple bonds
-weaker bonding
naming covalent compounds
mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta, octa, nona, deca
lewis dot diagram
only represents valence shell bonding electrons
-usually covalent compounds
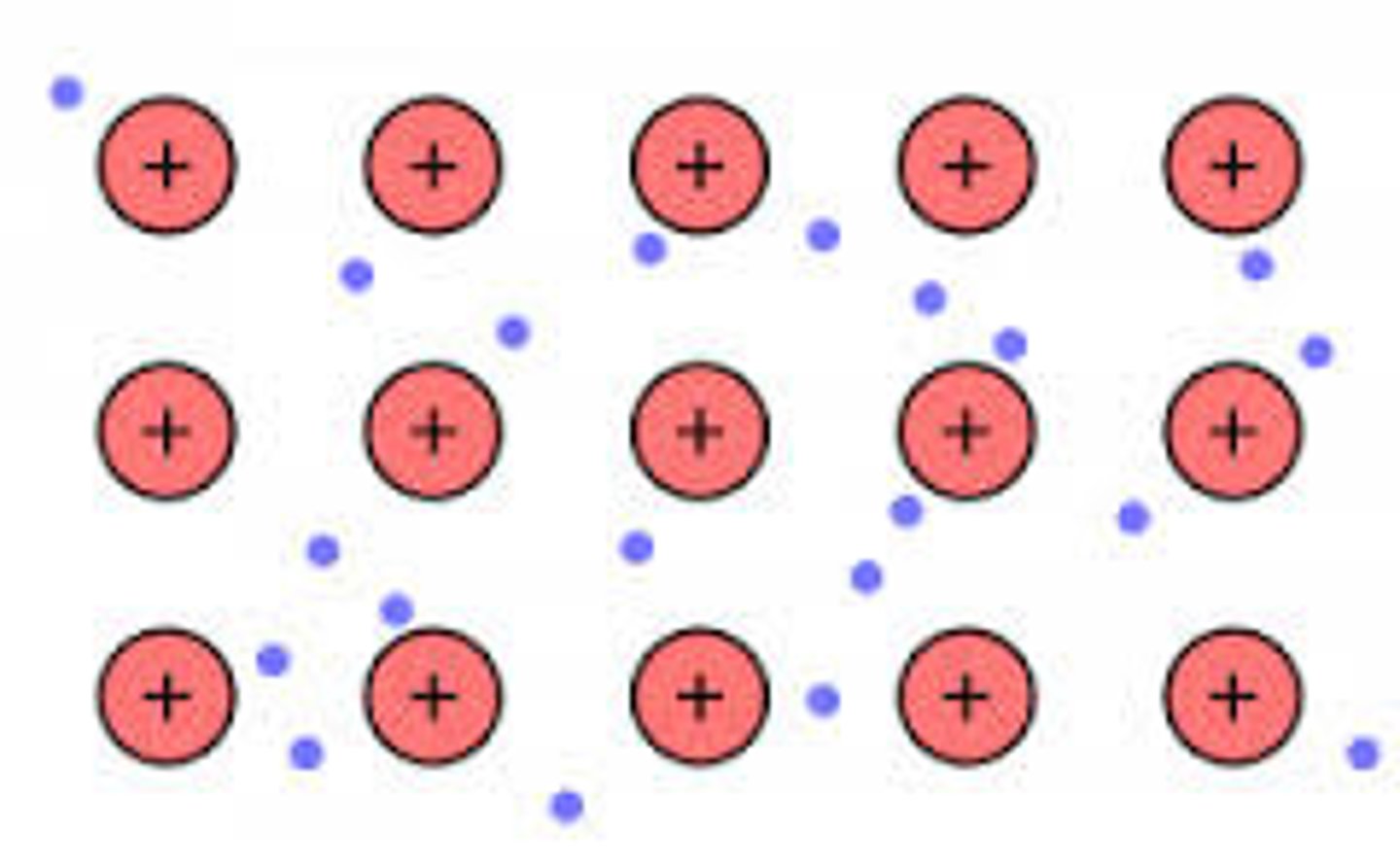
metallic bonding
The electrostatic attraction between metal cations and delocalised electrons.
metallic bonding properties
1) lattice structure
2) Delocalised electrons
3) Strong forces of ELECTROSTATIC ATTRACTION between positive metal ions and negative electrons
4) Solid at room temperature
5) High melting and boiling points
6) bright lustre
7) hardness
8) resonant sounds
9) excellent conductors
metals
electropositive elements with relatively low ionisation energy (not much energy to remove an electron)
lattice
regular repeating structure
alloy
A mixture of two or more metals
Quantitative
numerical data and allows for math analysis
-trends, patterns, relationships, limitations and uncertainty
Qualitative
descriptive data
-colour, chaage, state, temp, length/time of reaction
-descriptions on before, during and after
-can be recorded
Acid
a compound in which one or more H+ ions are bonded to a negative ion
ide - hydro___ic acid
ate - ____ic acid
ite - ____ous acid