APWHM Unit 3 Flashcards
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Qing Dynasty
The last imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Ming Dynasty and succeeded by the People's Republic. Formed the territorial base for the modern Chinese state. Founded in 1644 by the Manchus and ruled China for more than 260 years, until 1912. Expanded China's borders to include Taiwan, Tibet, Chinese Central Asia, and Mongolia.
Manchus
Northeast Asian peoples who defeated the Ming Dynasty and founded the Qing Dynasty in 1644, which was the last of China's imperial dynasties.
Ottoman Empire
Islamic state of Turkic speaking peoples lasting from 1453-1922; conquered the Byzantine Empire in 1453; based at Istanbul (formerly Constantinople); encompassed lands in the Middle East, North Africa, the Caucasus, and eastern Europe. Doesn't fall until 1918 during WWI
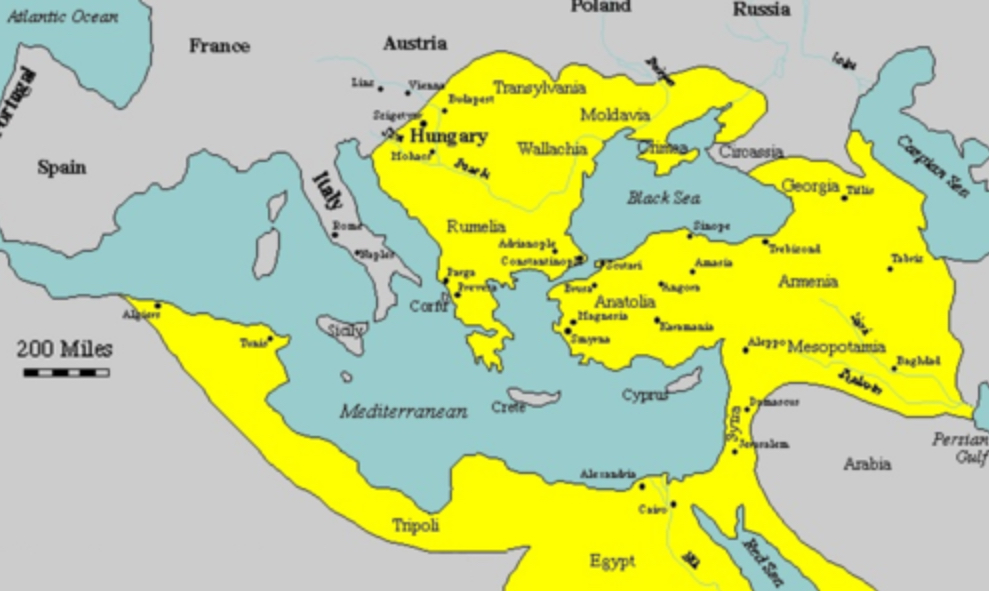
Mughal Empire
Muslim state (1526-1857) exercising dominion over most of India in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.
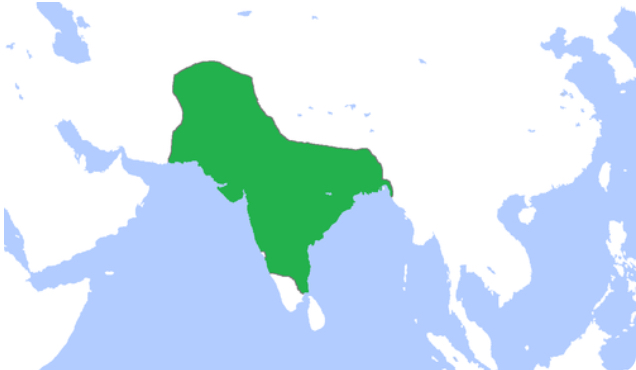
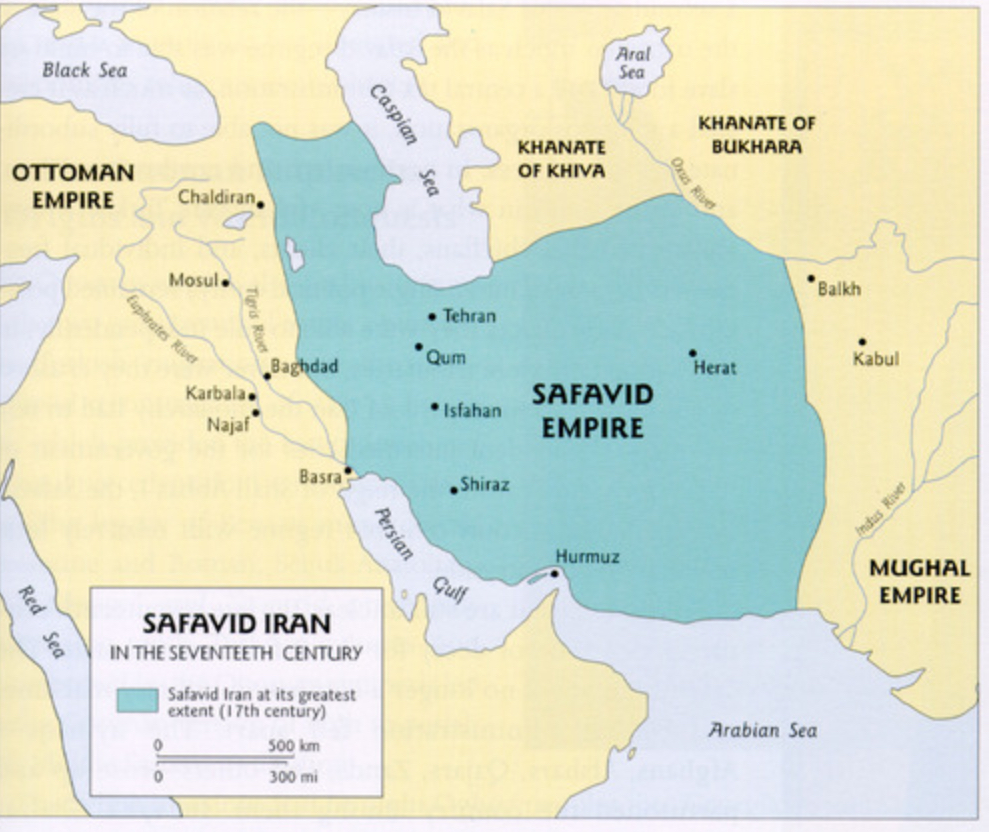
Safavids
A Shi'ite Muslim dynasty that ruled in Persia (Iran and parts of Iraq) from the 16th-18th centuries that had a mixed culture of the Persians, Ottomans, and Arabs. Powerful land-based military that used gunpowder.
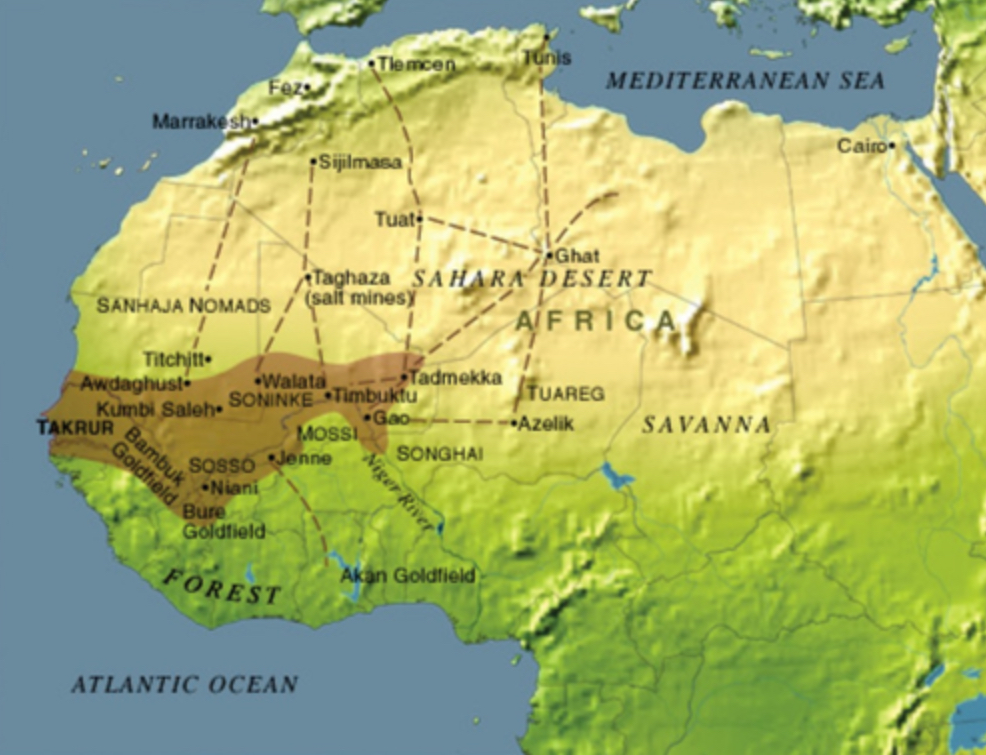
Songhai
An Islamic West African empire that conquered Mali and controlled trade from the into the 16th century; eventually defeated by the Moroccans who were broke after fighting with Portugal
Devshirme
‘Selection’ in Turkish. The system by which boys from Christian communities were taken by the Ottoman state to serve as Janisseries (elite military units)
Janissary
Elite Ottoman guard (trained as foot soldiers or administrators) recruited from the Christian population through the devshirme system, that often converted to Islam; utilized gunpowder weapons
Samurai
Class do salaried warriors in feudal Japan who pledged loyalty to a noble (daimyo) in return for land or rice products
Divine Right
The idea that monarchs are God’s representatives on earth and are therefore answerable only to God.
Absolute Monarchy
A system of government in which the head of state is a hereditary position and the king or queen has almost complete power
Versailles
Palace constructed by Louis XIVoutside of Paris to glorify his rule and subdue the nobility; late 17th-early 18th century (became his primary residence around 1670)
Zamindars
Archaic tax system of the Mughal empire where decentralized lords collected tribute/taxes for the emperor
Taj Mahal
Beautiful mausoleum (tomb) at Agra (India) built by the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan (completed in 1649) in memory of his wife; illustrates syncretic blend between Indian and Arabic architectural styles
Tax Farming
To generate money for territorial expansion Ottoman rulers used this tax-collection system. Under this system. Under this system the government hires private individuals to go out and collect taxes for them.
Protestant Reformation
Religious reform movement begun by Catholic monk Martin Luther who began to question the practices of the Latin Christian Church beginning in 1519. It split the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the ‘protesters’ forming several new Christian denominations, including the Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican Churches, among many others
95 Theses
Arguments written by Martin Luther against the Catholic Church. They were posted on October 31, 1517; ultimately led to Martin Luther’s excommunication
Martin Luther
A German Monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Church. In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices. Began the Protestant Reformation
Counter/Catholic Reformation
The reaction of the Roman Catholic Church to the Protestant Reformation reaffirming the veneration of saints and the same authority of the Pope (to which Protestants objected), ended sale of indulgences and simony, created Jesuits, but also began the Inquisition
Jesuits
Also known as Society of Jesus; founded by Ignatius Loyola (1491-1556) as a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism (a result of the Counter Reformation); were often sent to China, Japan, and around the world to gain Catholic converts
Indulgence
A pardon given by the Roman Catholic Church in return or repentance for sins
Simony
The buying and selling of church offices
Inquisition
A Roman Catholic tribunal for investigating and prosecuting charges of heresy, a reaction to the Protestant Reformation
Thirty Years War
A war that resulted from the Protestant reformation (1618-1648 CE); occurred in the Holy Roman Empire between German Protestants and their allies (Sweden, Denmark, France) and the emperor and his ally, Spain who supported Roman Catholicism; ended in 1648uCTiON with Treaty of Westphalia
John Calvin
1509-1564. French theologian. Developed the Christian theology known as Calvpredestinationinism. Attracted Protestant followers with his teachings; believed in
Sikhism
The doctrines of a monotheistic religion founded in northern India in the 16th century by Guru Nanak and Combining elements of Hinduism and Islam; a result of the presence of the Mughal Empire
Shogunate
The Japanese system of government under a shogun (military warlord), who exercised actual power while the emperor was reduced to a figurehead
Daimyo
A Japanese feudal lord who commanded a private army of samurai; owed allegiance to the shogun
Jizya
Tax paid by Christians and Jews and sometime others faiths who lived in Muslim communities to allow them to continue to practice their own religion; often utilized by Islamic states to manage diverse populations within their empires
Gunpowder Empires
Muslim empires of the Ottomans, Safavids, and the Mughals and Russia that employed cannonry and gunpowders to advance military causes
Gutenburg Printing Press
Used to spread ideas of the Reformation and the Renaissance; First document printed was the Bible; Led to the growth of literacy
Tsar
The Russian term for ruler or king; taken from the Roman word Caesar
Ivan IV
the Terrible, beat the Mongols, Tartars, and the Poles, forced nobles into service and move to Moscow, first ruler to take the title tsar
Stroganovs
Major Russian landowners
Cossacks
Peoples of the Russian Empire who lived outside the farming, villages, often as herders, mercenaries, or outlaws. Cossacks led the conquest of Siberia in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries
Volga River
The longest river in Europe and Russia’s most important commercial river. Moscow could trade with Persian and Ottoman Empire
MIng Dynasty
Succeeded Mongolian Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted huge trade expeditions to Southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China
Kangxi
Chinese Qing Emperor (r. 1661-1722) who promoted Confucian ideas and policies and expanded the Qing Empire (Captured Taiwan, Mongolian, and arts of Central Asia-Tibet)
Qianlong
Chinese Qing emperor (r. 1736-1795), grandson of Kangxi who continued his grandfather’s conquests by consolidating hold on Xinjiang province (westernmost). He made Vietnam, Burma, and Nepal vassal states of China, and Eunuchs, arming the decline of the Qing Dynasty
White Lotus Rebellion
Peasant rebellion; Members of a Buddhist cult called the White Lotus Society revolted because of increased taxes and growing government inefficiency. They wanted the Ming dynasty back. Qing killed over 100,000 peasants to suppress
Tamerlane
He is very much like Genghis Khan; a military leader who conquered the lands of Persia; his empire was decentralized with tribal leaders. Use of heavy violence to take control. His invasions were a testament to the use of gunpowder
Ghazi Ideal
A model for warrior life that blended the cooperative values of nomadic culture with the willingness to serve as a holy fighter for Islam
Samarkand
During the rule of Timor Lane was the most influential capital city, a wealthy trading center known for its for decorated mosques and tombs in modern day Uzbekistan
Mehmed II
Ottoman Sultan called the “Conquerer”; responsible for conquest of Constantinople (renamed Istanbul) in 1453; destroyed what remained of Byzantine Empire. Used cannons and gunpowder to conquer
Sulieman l
Famous for expanding his empire to their greatest size, creating laws, and centralizing power to rule as a absolute ruler in the Ottoman Empire
Ismail
This man was a ruthless leader of the Safavid Empire who executed all Sunni Muslims in his empire
Shah
Persian word for king
Shah Abbas l
“Abbas the Great” Shah of Iran (r. 1587-1629). The most illustrious ruler of the Safavid Empire, he moved the imperial capital to Isfahan in 1598, where he erected many palaces, mosques, and public buildings
Babur
First sultan of the Mughal Empire; took lots of land in India
Akbar
Most illustrious sultan of the Mughal Empire in India (r. 1556-1605). He expanded the empire and pursued a policy of conciliation of Hindus
Jati
A sub-varna in the caste system that gave people sense of community because they usually consisted of people working in the same occupation
Siege of Vienna
Failed attempt by Ottoman Empire to invade Europe, ever since Europe had to fear/keep peace with Ottoman Empire- farthest westward advance into Central Europe of the Ottoman Empire, and of all of the clashes between the armies of Christianity and Islam might be signaled as the battle that finally stemmed the previously-unstoppable Turkish forces
Zane Dynasty
Replaced the Safavid Dynasty in 1760
Aurangzeb
Mughal emperor in India and great-grandson of Akbar ‘the Great’, under whom the empire reached its greatest extent, only to collapse after his death
Tudors
English royal family, dynasty founded by Henry VII; includes some of England’s most influential monarchs; Elizabeth
Justices of the peace
English local officials in the shires appointed by the crown and given wide authority in local government
English Bill of Rights
King William and Queen Mary accepted this document in 1689. It guaranteed certain rights to English citizens and declared that elections for Parliament would happen frequently. By accepting this document, they supported a limited monarchy, a system in which they shared their power with Parliament and the people.
Louis XIII
King of France who from 1610 to 1643 who relied heavily on the advice of Cardinal Richelieu (1601-1643)
Intendants
French government agents who collected taxes and administered justice
Louis XIV
(1638-1715) Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France. One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the Palace at Versailles
Boyars
Russian nobles
Russian Serfdom
Tied the peasants to the land and controlled
Oprichnina
The secret army/police Ivan IV or Ivan the Terrible created to control the Boyars
Romanov Dynasty
Dynasty elected in 1613 at end of Time of Troubles; ruled Russia until 1917
Peter the Great
(1672-1725) Russian tsar (r. 1689-1725). He enthusiastically introduced Western languages and technologies to the Russian elite, moving the capital from Moscow to the new city of St. Petersburg.
Tokagawa Shogunate
Founded by Ieyasu. Under this there was a burst of culture including kabuki theaters and haiku. They found Christianity troublesome, and used violence to get Christians out of their country. Used the Closed country policy, and only kept the one port, Nagasaki, open to Dutch and Chinese merchants.
Askia
Ruler adopted name for the muslim leader of the Songhai Empire after the death of Sunni Ali. Best was Muhammad the Great. Unified and made Islam official religion in West Africa