BCM. 29 Nitrogen metabolism and beta oxidation
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Lipids feed into citric acid cycle through B-oxidation to acetyl CoA
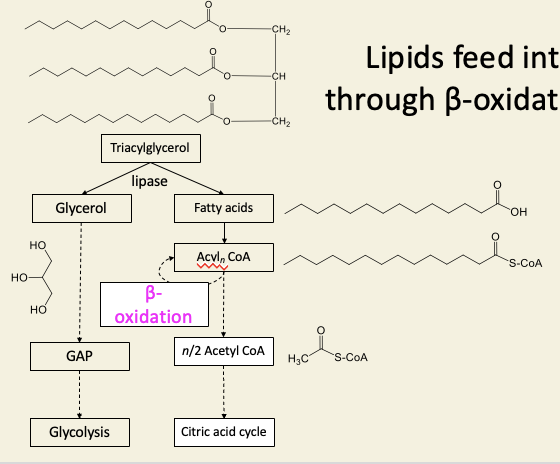
b-oxidation is a cyclic process, cutting fatty acids into acetyl CoA
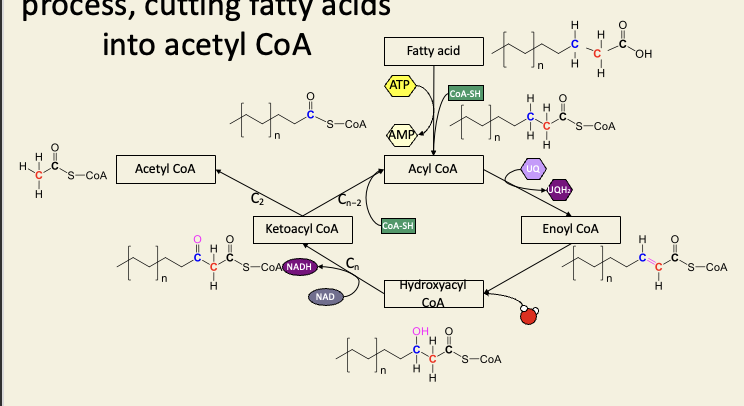
Three steps of b-oxidation are very similar to part of Krebs cycle: homology or homoplasy?
Similarity: alkane→alkene→alcohol→ketone
the cofactors are also identical
the enzyme in beta-oxidation that plays the role of SDH is membrane-bound (like SDH) - in this case is probably homoplasy

The eye has evolved more than once, and so too have some biochemical tricks - homoplasy

Tinbergens question - as applied to biochemistry
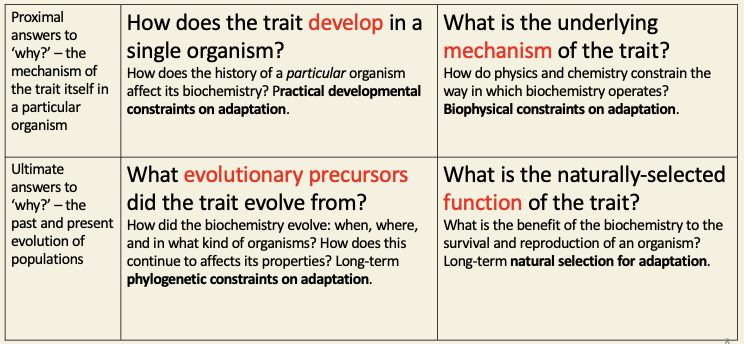
Amino acid and lipid metabolism are intimately linked to glycolysis and citric acid cycle

In autotrophs, ammonia is assimilated via glutamine synthetase
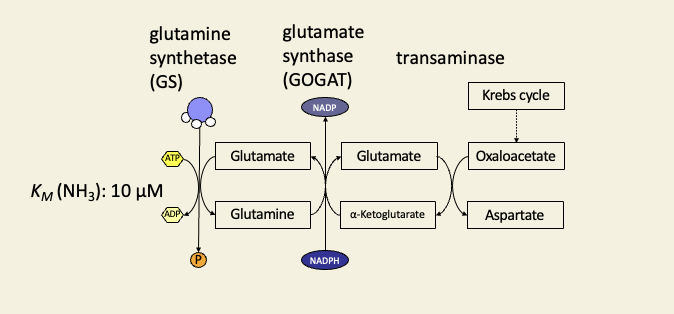
Transaminases (aminotransferases) transfer - NH2 from amino acids to a-keto acids
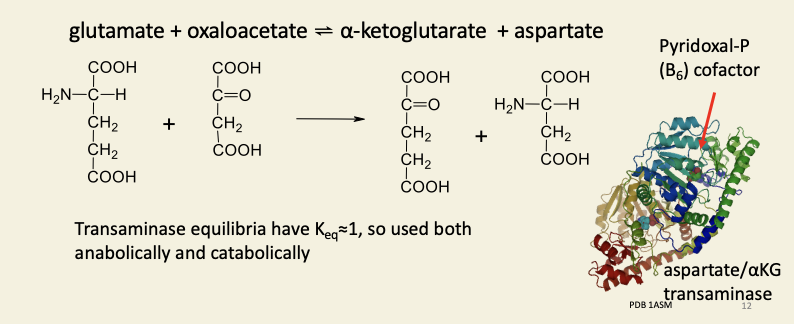
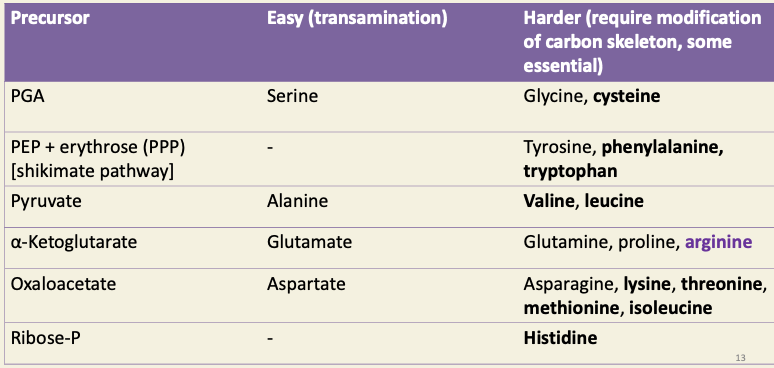
Amino acids and their precursors
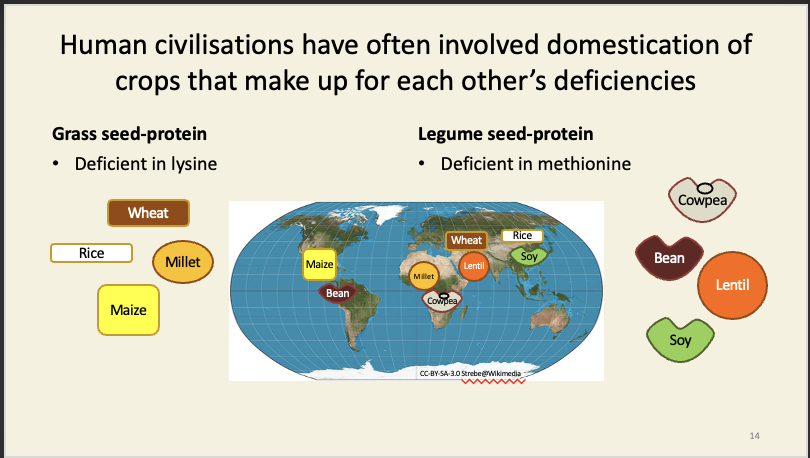
The main areas in which food production are known to have originated somewhat independently (China, Mesopotamia, Egypt, Ethiopia, Indus Valley, Mesoamerica, Andes, West Africa) seem to have had easily domesticated local grasses with large seeds, and easily domesticated local legumes with large seeds.
These made up for one another's amino acid deficiencies.
Soy has a particularly good amino acid profile; maize a particularly bad one.
Obviously, it’s much more complex than that (the Near East had a much larger number of easily domesticated animals than did the Americas), but the history of humankind may have been very different had wheat and rice been New World species rather than Old World ones.
Heterotrophs consume excess nitrogen, which must be excreted
the best waste route depends on current ecology but the available routes depend on evolutionary history

Glutamate dehydrogenase deaminates glutamate, freeing ammonia
reversible, but this route cannot be used to assimilate ammonia by plants
why not? → the enzyme cant work at an appreciable rate unless [NH3] > KM for GDH, that would mean toxic conc. of ammonia for most organisms
![<ul><li><p>reversible, but this route cannot be used to assimilate ammonia by plants </p></li><li><p>why not? → the enzyme cant work at an appreciable rate unless [NH3] > K<sub>M</sub> for GDH, that would mean toxic conc. of ammonia for most organisms</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f94ddc1e-1d96-4850-986a-cbcd3d616c92.png)
Animals with access to water can use ammonotelic excretion
Direct excretion of ammonia:
highly toxic
continuously lost through gills
Teleost fish, most aquatic invertebrates, larval amphibians
But not whales (whales are ureotelic) → due to how they osmoregulate, they produce very conc. urine saltier than sea water surrounding them, so their kidneys are very good at concentrating ions → the same kind of historical constraints that mean that they still breathe air may be responsible for their suboptimal excretory strategy.
Animals with limited access to water can use ureotelic excretion
urea → less toxic: can be conc. and stored
Mammals
but also sharks → urea does double duty for osmoregulation
and adult amphibians
living on land = dont have option to constantly take in water to dilute waste products to non-tosxic levels, therefore need something to concentrate up without it posing a health hazard
Urea cycle
it links to krebs cycle and involves amino acids that are not found in proteins - (other amino acids are available - in this case, citrulline, ornithine and arginosuccinate)
it has two inputs of nitrogen (one from some ammonia generated by the action of GDH on amino acids, and one more directly from an amino acid)
it requires (the equivalent of) 2 ATP per nitrogen
it is how the cell makes arginine
Animals with limited access to water can also use uricotelic excretion
Uric acid
→ insoluble solid
→ made from gln/asp/gly
→ c. 2 ATP per N
birds and many other reptiles - crocs appear to excrete mostly uric acid, but NH3 and urea can also be detected, there seems to be a difference in terms of liquid urine they make and final excrement they pass out
insects
spider - these excrete guanine rather than uric acid, but these compounds are similar both in synthesis and their water-conserving role
some organisms currently using it might be constrained phylogenetically
terrestrial species tend to excrete more uric acid, marine species more urea/ammonia
although we say mammals are ureotelic, they do also excrete some ammonia and uric acid
Pyrimidines can be partly respired, but purines are converted to uric acid
and then to allantoin by uricase in mammals
primates lack uricase
uric acid crystals can accumulate in joints: gout
allantoin - primates cant convert uric acid to this soluble compound
What is the problem with these statements
dinosaurs evolved uricotelic excretion to conserve water during hot and dry Triassic
beetles are so diverse because they have hardened wing cases, which help to prevent water loss