GIT Examination
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
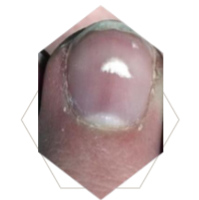
What’s this called & what’s it a sign of
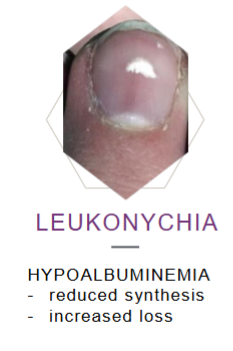
What’s this called & what’s it a sign of
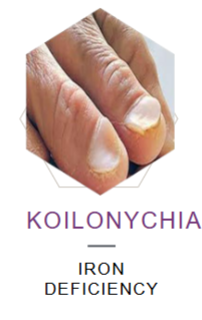
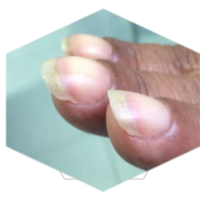
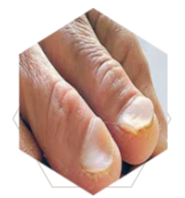
What’s this called & what’s it a sign of
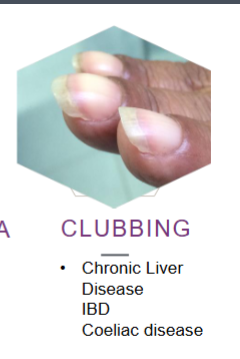
What’s this called & what’s it a sign of
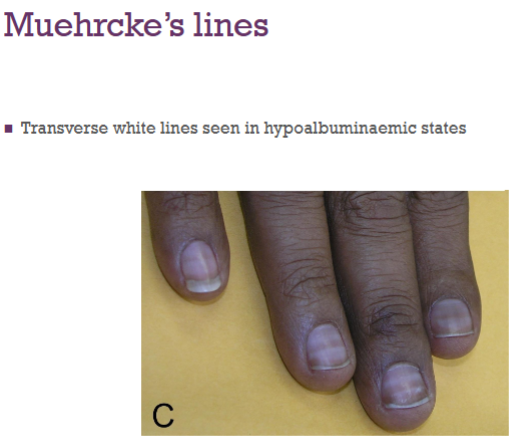
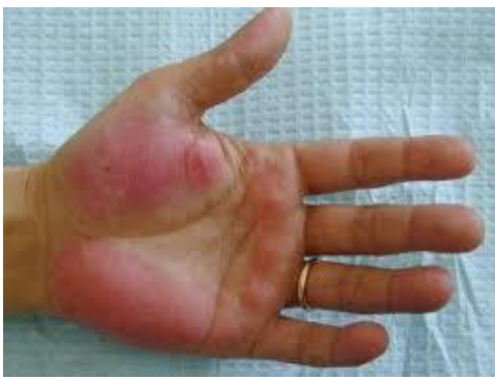
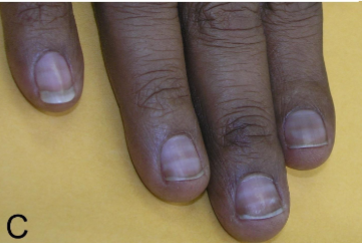
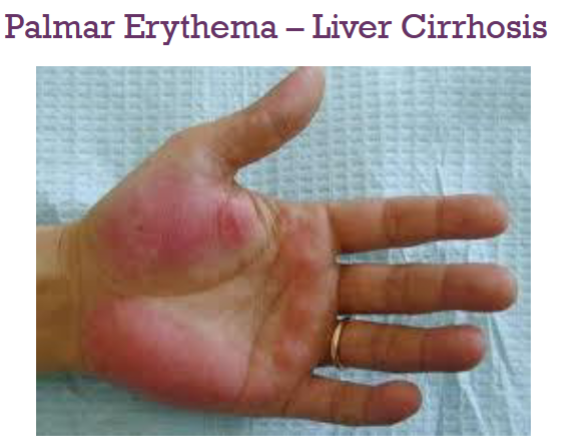
What’s this called & what’s it a sign of
What’s this called & what’s it a sign of
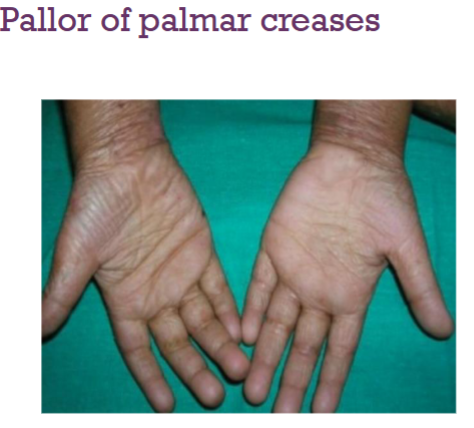
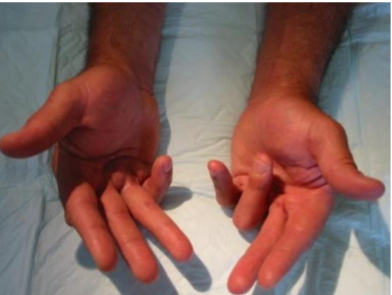
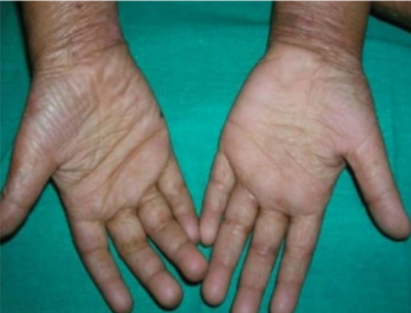
What’s this called & what’s it a sign of
What is Asterixis & what’s it a sign of
Asterixis, or "flapping tremor," is an involuntary, rhythmic, jerking movement commonly in the hands, wrists, and feet
Associated with Encephalopathy
What’s Ecchymosis
Bruising
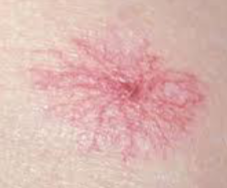
What’s that
Spider naevus/naevi
(to tell that its a spider naevus & not anything else you press it down to blanch it & if it fills out red again starting with the centre it is spider naevus)
What could cause Spider naevi?
cirrhosis / pregnancy
What are Petechiae & what are they a sign of
Tiny dots of bruises associated with portal HTN... Hypersplenism... low platelets
What’s muscle wasting associated with
malnutrition / chronic liver disease
What could Scratch marks be a sign of
obstructive jaundice / bile salt retention
Where would you spot Lymphadenopathy
cervical and supraclavicular region
Where is Virchow’s node & what is it a sign of
Left supraclavicular node associated with gastric cancer
What is jaundice
Elevated Bilirubin
What level of bilirubin in umol/L = jaundice
> 35 umol/L
3 types of jaundice
Pre-hepatic
Hepatic
Posthepatic
Where is jaundice often first detected
sclera & soft palate - due to high elastin content
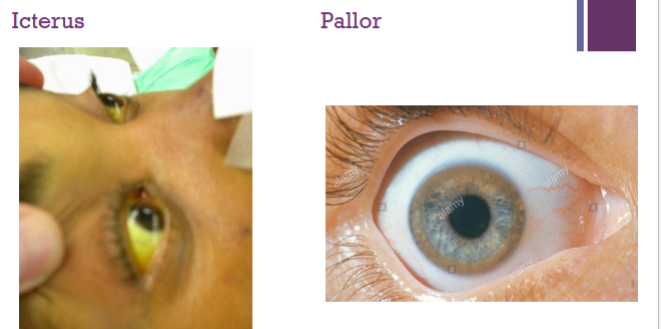
What 2 things do you look out for in someone’s eyes & where in the eyes do you see it
Icterus seen when pull up top lip & look at white of eye
Pallor seen when pull down bottom lid & look at inner lid
When examining the mouth, what is Peri-oral pigmentation a sign of?
Peutz Jeghers Syndrome
When examining the mouth, what is Angular Stomatitis a sign of?
IDA - iron-deficiency anemia
When examining the mouth, what is Ulceration of oral mucosa a sign of?
Crohn’s disease
When examining the tongue, what is Glossitis a sign of?
Iron-def/B12 def
Other than Glossitis what do you look for in examination of the tongue
Leukoplakia
Lesions in the gums are associated with what
Crohn’s
Bleeding of the gums are associated with what
scurvy
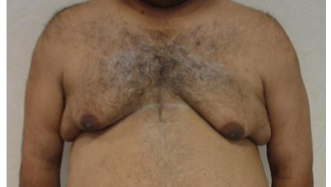
What would you call this
Gynaecomastia
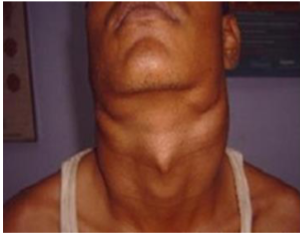
What’s up with this person
JVP - associated with right heart failure
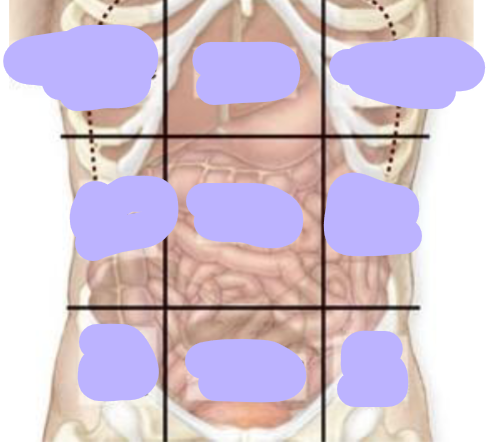
On inspection of the abdomen what do you look out for
Epigastrium: pulsation
Visible peristalsis
Skin lesions:
- Vesicles of Herpes Zoster
- Sister Joseph nodule
- Cullen’s sign
- Grey Turner’s sign
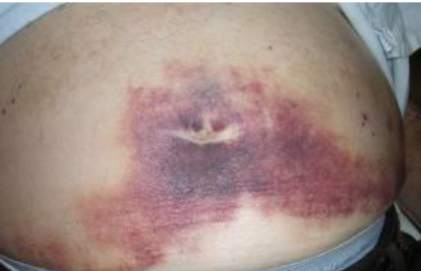
What’s this called & what’s it associated with
Cullen’s sign
- haemoperitoneum
- acute pancreatitis
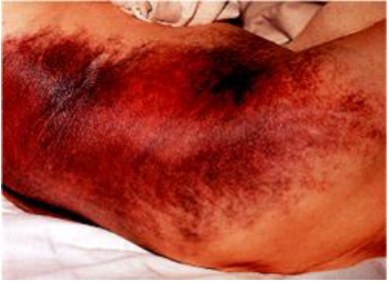
What’s this called & what’s it associated with
Grey Turner’s sign
- severe acute pancreatitis
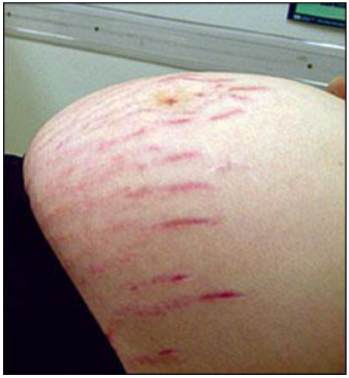
What’s this called
Striae
What’s guarding
resistance to palpation (contraction of abdominal muscles)
What is rigidity
constant involuntary contraction of the abdominal muscles, always associated with tenderness & peritoneal irritation
What is rebound tenderness
compress abdomen slowly, release suddenly + sudden stab of pain = suggests peritonitis
How do you examine the liver with just your hands
Start in RIF
Move towards RUQ
Remember liver descends with respiration
Percuss out the liver span
How do you examine the spleen with just your hands
Start in RIF
Move towards LUQ
Remember spleen descends with respiration
How do you examine the kidneys with just your hands
Balloting the kidneys
Dominant hand under patient and flex at MCPJ
Non dominant hand apply continous pressure in Flank while dominant hand does all the work
If kidney is enlarged it should hit off non-dominant hand
Are the spleen/kidney dull/resonant on percussion
Spleen - Dull to percussion
Kidney - Kidney is resonant to percussion due to overlying bowel gas
How to test for Murphy’s sign
Place had just below the costal margin
Ask patient to take a deep breath in
If the gallbladder is inflamed i.e. cholecystitis, the patient may catch their breath when the gallbladder hits off your hand
The sign is only positive if negative on left side
Why must we percuss
Defines size & nature of organs & masses e.g. percussing for the upper border of the liver in the mid-clavicular line
To detect free fluid
What would suprapubic dullness on percussion suggest
distended bladder
What would percussion of free fluid suggest
Ascites
Borgorygmi
audible bowel sounds
What do we suspect if there are no bowel sounds on auscultation for 3 mins
paralytic ileus
Where could you auscultate Renal artery stenosis
either side of the mid-line just above the umbilicus
On auscultation what could Hepatic bruit be a sign of
hepatocellular CA or an AV malformation
On auscultation what could Epigastric bruit be a sign of
mesenteric artery stenosis
After all the examination you’ve already done, what else do you check
Hernias (direct and indirect inguinal, femoral)
Digital rectal exam
Testicular exam (masses, hydrocoeles, torsion)
Urinalysis
What are some signs of chronic liver disease you’d spot in each place:
Hands
Face
Chest
Abdomen
Legs
Overall
Hands: leuconychia, clubbing palmar eythema, bruising, asterixis
Face: jaundice, scratch marks, fetor hepaticus
Chest: gynaecomastia, spider naevi, loss of body hair, bruising
Abdomen: hepatomegaly, ascites, testicular atrophy, spleomegaly (portal HTN)
Legs: oedema, muscle wasting
Fever (infected ascites)
A 65-year-old male presents with painless jaundice
History of presenting complaint: loss of appetite, weight loss of 1 stone over 3 months, low energy
On examination: (General and hands) jaundice, palmar erythema, clubbing, leukonychia
Abdomen: tenderness in RUQ, palpable liver with nodular liver edge (enlarged)
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis:
A. Choledochelithiases
B. Fatty liver disease
C Haemolytic anaemia
D. Gallstones
E. Liver metastases
E. Liver metastases