(3.2.2) IC - Group 2, the Alkaline Earth Metals
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
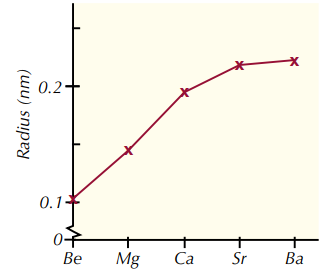
What is the trend in atomic radii down group 2 and why?
1. As you go down group 2, the atomic radii get larger.
2. This is because extra electron shells are added as you go down the group.
3. So the electrons are further away from the nucleus, increasing the radius.
What is the trend with first ionisation energy down group 2 and why?
1. It decreases going down the group.
2. Because each element has an extra electron shell, and more inner shells, compared to the one above.
3. This means there is more shielding, so the outer electrons are further away from the nucleus, reducing the nuclear attraction.
4. This makes it easier to remove outer electrons, resulting in a lower first ionisation energy.
What is the trend in reactivity down group 2 and why?
1. Reactivity increases down the group.
2. As the 1st IE decreases going down the group, it becomes easier to lose electrons, so the elements get more reactive.
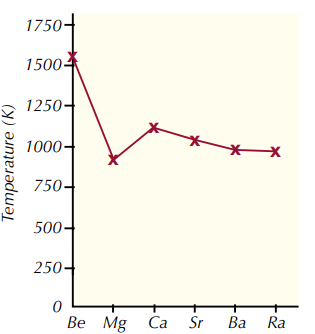
What is the trend in melting point down group 2 and why?
1. Melting points generally decrease down the group.
2. This is because as you go down the group, the metallic bonding gets weaker.
3. This is because the metal ions get bigger, but the number of delocalised electrons remain the same.
4. This means that it takes less energy to break bonds, so the melting points generally increase.
5. Magnesium’s melting point is slightly lower due to its crystal structure.
What happens when group 2 metals react with water? e.g. Mg
1. They react in a redox reaction to produce a metal hydroxide and hydrogen.
2. The metal hydroxide form as an alkaline solution.
e.g. Mg + 2H2O → Mg(OH)2 + H2
3. Magnesium is oxidised from 0 to +2
What happens when magnesium reacts with steam rather than water?
1. They react much faster with steam than water, as it provides the reaction with extra energy.
2. When steam is used, the magnesium burns with a bright white flame to form hydrogen and magnesium oxide, a white powder.
Mg + H2O → MgO + H2
How does solubility of hydroxides vary going down group 2?
1. It increases going down group 2.
2. This means that magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) is the least soluble and barium hydroxide (Ba(OH)2) is the most soluble.
How is magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) used in medicine?
1. Magnesium hydroxide is used in medicine as an antacid as it is alkaline and can neutralise acids.
2. This is due to its solubility.
How does solubility of sulfates vary going down group 2?
1. It decreases going down group 2.
2. This means that magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) is the most soluble and barium sulfate (BaSO4) is the least soluble.
How is barium sulfate used in medicine?
1. As it is insoluble, is can be used as barium meals.
2. These are a form of medical tracer that allow internal tissues and organs to be imaged.
3. Barium sulfate is toxic if it enters the bloodstream, however as it is insoluble, it cannot be absorbed into the blood, so it is safe to use.
How do you test for sulfate ions?
1. React the substance with barium chloride.
2. If it contains sulfate ions they will react and form a white precipitate.
Ba2+ + SO4 2- → BaSO4(s)
How is magnesium involved in metal extraction?
It is used to extract titanium from titanium chloride via a displacement reaction.
TiCl4 + 2Mg → 2MgCl2 + Ti
How is sulfur dioxide removed from flue gases?
1. Calcium oxide reacts with sulfur dioxide to remove it from factory pollutants and prevent it from being released into the atmosphere.
2. This forms calcium sulfite and water.
CaO + 2H2O + SO2 → CaSO3 + 2H2O