1.3 Introduction to Macromolecules
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
Monomers
the repeating units that make up polymers
might say sub unit
Polymers
chain like macromolecules of similar or identical repeating units that are covalently bonded together
Four macromolecules
Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids
Carbohydrates,proteins, and nucleic acids are polymers but lipids are not because they don’t include true polymers and are hydrophobic molecules
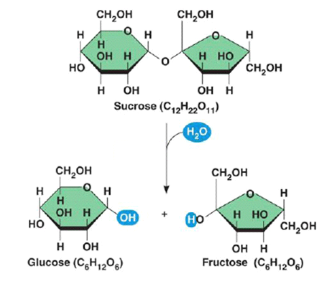
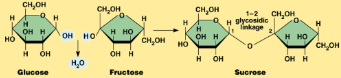
Dehydration reaction
covalently bonds two monomers with the loss of H2O
The OH of one monomer bonds to the H of another monomer forming H2O, which is then released
A hydrogen ion is removed from one monomer and a hydroxyl group is removed from the other
This causes the loss of the equivalent of a water molecule from the reactants and the connection of the two remaining monomers.
The connection of many monomers is known as polymerization.
A+b—> AB + H2O
Hydrolysis
breaks the covalent bonds in a polymer by adding H2O
One H of the H2O bonds to one monomer and the remaining OH of the H2O attaches to the other monomer
This type of reaction breaks down molecules into smaller molecules
When water is added to the bond between monomers in a polymer, the bond is broken
The hydrogen ion from a water molecule is added to one monomer and the hydroxyl group of the water molecule is added to the other monomer, completing the reaction
AB+H2O—> A + B