(9) Angular Kinematics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Angular kinematics
units
degree
radian
Quantities
angular position and displacement
angular velocity
angular acceleration
linear motion vs angular motion
circular motion
Units
Degree
1 revolution= 360°
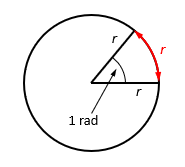
Radian
the angle with which the length of the arc becomes the same to the radius
1 rad=57.30°
r=1rad
2r=2rad
3r=3rad
2pi r= 2pi rad
1 rev= 2pi rad= 360 degree
pi rad= 180 deg
pi/2 rad= 90 deg
pi/3 rad= 60 deg
pi/4 rad= 45 deg
pi/6 rad= 30 deg
pi=3.141592654
180/pi=57.29577951
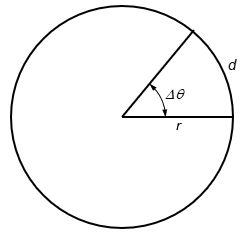
why radian?
simple relationship between the angle and length of the arc
d=r𐤃Θ
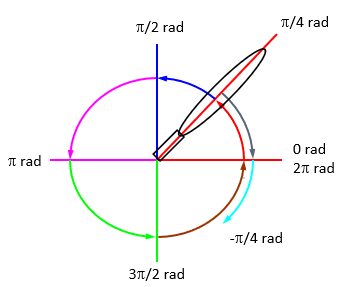
angular location at a given instant
unit: rad
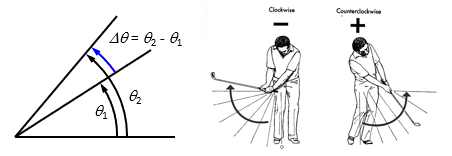
direction
counterclockwise= +
clockwise= -
angular displacement
change in angular position
net effect of angular motion
unit: rad
direction
counterclockwise: +
clockwise:-
zero angular displacement
no net rotation 𐤃Θ= Θ2-Θ1=0
no rotation dΘ= Θ2-Θ1=0
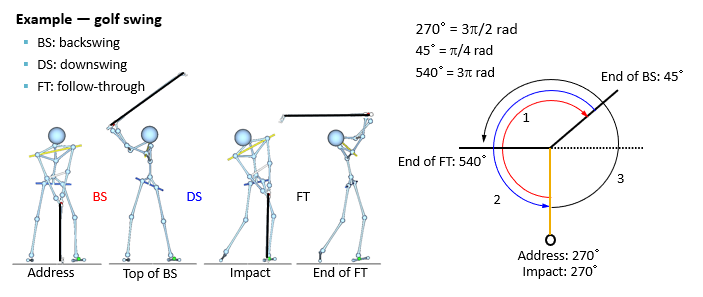
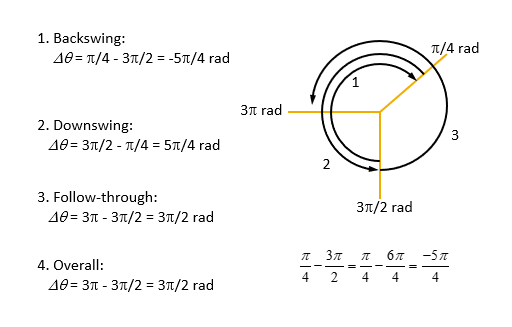
example of angular displacement
Angular velocity
rate of change in angular position
angular displacement/time
direction
positive: counterclockwise rotation
negative: clockwise rotation
vector
unit: rad/s
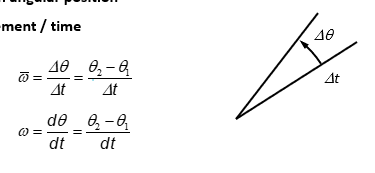
zero angular velocity
zero average angular velocity: no displacement=no net motion
zero instantaneous angular velocity: no motion=constant angular position
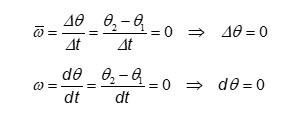
angular acceleration
rate of change in angular velocity
a(bar)= 𐤃ω/𐤃t= ω2-ω1/𐤃t a= dω/dt= ω2-ω1/dt
positive angular acceleration
speed-up of counterclockwise ω
slow-down of clockwise ω
negative acceleration
Slow-down of counterclockwise ω
speed up of clockwise ω
vector
unit: rad/s2
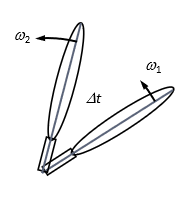
zero angular acceleration
a(bar)= 𐤃ω/𐤃t= ω2-ω1/𐤃t =0 a= dω/dt= ω2-ω1/dt= 0
zero average a: no net change in ω
zero instantaneous a: constant ω
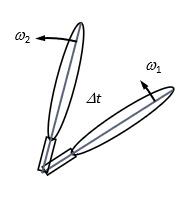
example angular acceleration
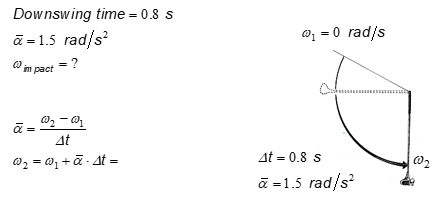
linear vs angular quantity differences
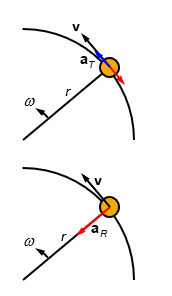
circular motion
directions
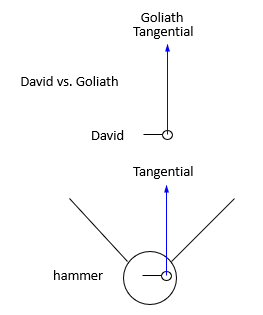
tangential (T): along the tangent
radial (R): Along the radius, perpendicular to the tangent
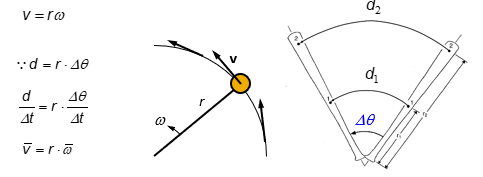
Velocity relationship
direction of the linear velocity: tangential
magnitude of the linear velocity
velocity relationship cont.
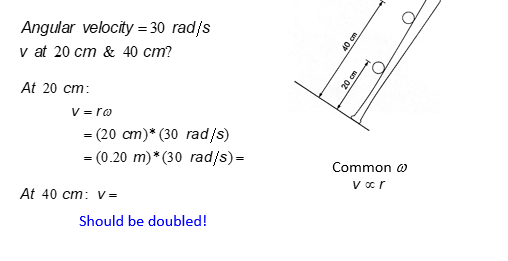
for a given ω: v is proportional to r
v=rω
v∝r
for a given r: v is proportional to ω
v=rω v∝ω
to hit the ball farther, one has to swing the bat faster
velocity relationship cont. pt 2
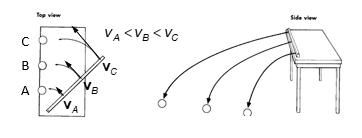
for a give v: r and ω are inversely proportional to each other
v=rω ω∝1/r
v remains constant
r decreases —→ ω increases
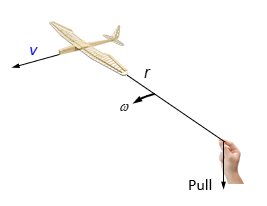
example: Slinging and hammer throw
example: batting
two different kinds of acceleration
acceleration relationship
tangential acceleration
due to the change in speed (magnitude of v)(speed up or slow)
aT= ra= v2-v1/𐤃t
radial acceleration
due to the change in the direction of v
aR=rω2= v2/r
towards the center of rotation: centripetal acceleration