chemical component of cells, dna replication and translation, rna stuff (BMS EXAM 1)
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
mostly in laymans terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the smallest particle of an element that retains its distinctive chemical properties
An atom, which consists of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons
what 4 elements make up about 96% of a cells mass
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
the number of ??? in an atoms nucleus determines its atomic number
protons
how is the mass of an atom calculated
number of protons + neutrons in the nucleus of the atom
why is a complete atom electrically neutral
because the number of protons and electrons are equal
an atom is most stable when its outermost ??? is completely filled
electron shell
what is a covalent bond
bond formed when 2 outer shell electrons are shared between two atoms that are locked in (next to each other)
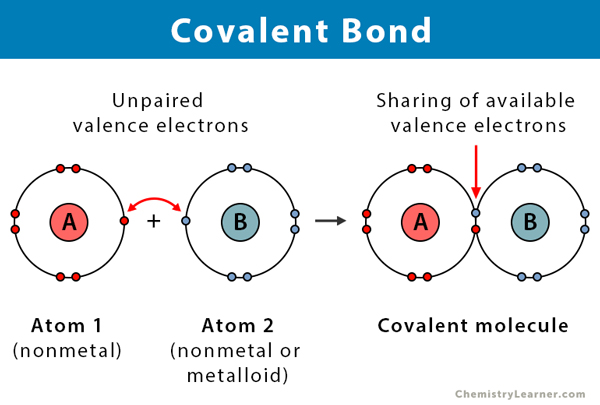
2+ atoms held together by covalent bonds is a ???
molecule
how does polar covalent bond differ from nonpolar covalent bond
polar covalent bond is a covalent bond where the sharing is unequal
causes one atom to pull their shared electron more to its side, becoming more negative >:(
and in turn the losing atom to become more positive <:D
result is a magnet with a positive end and a negative end.
Non polar covalent is when the sharing is equal so both atoms remain unelectrified(neutral) :I
non polar = no problems bcuz they share
polar = problems, unequal
the nucleus of the atom is
dense and positively charged because its packed with protons
explain causes an atom to be “stronger”, pull electrons closer?
elements with a bigger atomic number have more protons.
The more protons you have, the stronger the attraction between the positive nucleus of the atom and the negative electron cloud of the shell, making this atom exert more force
explain electronegativity rq
its the atoms tendency to attract electrons, aka how strong an atom is an element can be
fun fact, oxygen and nitrogen are stronger and hydrogen and carbon are weaker
therefore O and N develop partial negative charges while H and C get partial positive charges because they’re losers
what typa bond forms when an electron jumps ship from one atom to another
ionic bond
explain ionic bonds rq
all atoms want a full shell. atoms interact bc they want to be stable, have a full outer shell
when 2 atoms with a big difference in strength(electronegativity) meet, they transfer electrons instead of sharing them
stronger atom takes as many electrons from the weaker as it needs to be stable
stronger atom now has extra electrons, making it negatively charged, and the weaker one now has less electrons than protons making it positively charged
stronger atom is now an anion (aniiiii- no- negative)
weaker atom is now a cation
their opposing charges make them form ionic bond
whats the chemistry word for an overpowered atom
a highly electronegative atom
what happens if a very electronegative atom leave behind a few electrons on the lesser electronegative one after their relations?
the less electronegative one is now gonna find another partner to get rid of these electrons or share them with someone who had more because it simply must be stable
which bond is stronger in humans and why, covalent or ionic
covalent because cellular environment is juicy (its mostly water)
explain hydrogen bond
the actual atoms of oxygen and hydrogen have a power imbalance, so they have a polar covalent bond (unequal sharing)
this causes O to be slightly negative and 2H to be slightly positive
the resulting molecule H2O binds to other H2O molecules because of the magnetic attraction- O to H and H to O >:)
since the bond is only based on the attraction (electrostatic btw) and not on sharing electrons or anything, its VERY WEAK
why hydrogen bond so weak compared to ionic bond and what’s the kicker
bcz hydrogen bonds are based on PARTIAL CHARGES, ionic bonds are based on FULLY CHARGED IONS
The kicker: since the cells are juicy the hydrogen bond is weaker in the body. ionic bonds are only stronger in a vacuum
hydrogen bonds can include hydrogen, oxygen and ???
nitrogen, because nitrogen is the only other abundant element in the cells that is so very electronegative like oxygen
hydrophilic substances requirements?
can form hydrogen bonds
must have polar bonds
mixes well with water
hydrophobic is what
uncharged substance
makes little to no hydrogen bonds
no mix with water
explain hydrophobic force
pushing of nonpolar surfaces out of the hydrogen bonded water network which helps them get together. phospholipid bilayer basically
acid
a molecule what releases a proton when it dissolves in water, which lowers the pH
base
molecule that accepts a proton when dissolved in water, raising the pH
what are the monomers and their polymers
nucleotide - nucleic acid
amino acid - protein
sugars - carbohydrate/polysaccharide
fatty acid - lipid
explain condensation reaction
builds polymers by forming a sharing bond(covalent) bond, releasing a water molecule in the process
hydrolysis
separates polymers by breaking the covalent bond with the addition of a water molecule
primary role of sugars in cells
main source of chemical energy for the cell (glucose)
when glucose is broken down cell gets energy
can form carbs (polysaccharides) for energy storage or structural support
polysaccharide is a chain of sugars so when the cell needs energy it breaks some off
2 distinct regions of a fatty acid molecule
the head (carboxyl group) charged and hydrophilic
the tail (hydrocarbon chain) not charged and hydrophobic
molecules that have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions are called
amphipathic
whats the main function of fatty acids/lipids
forming lipid bilayers for structure in the cell
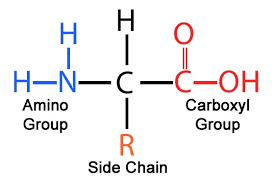
whats the basic amino acid structure
central carbon attached to amino group, carboxyl group, and side chain (r group)
bond formed between two amino acids
peptide bond
3 parts of a nucelotide
a 5 carbon sugar, nitrogenous base, and phosphate group
pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil- the small ones
purines
adenine and guanine, the big ones
ATP primary function
energy
central dogma
DNA → RNA → protein. transcription then translation
gene expression
when the information in a dna sequence turns into something useful, like protein or RNA
2 main differences between DNA & RNA
RNA uses ribose(H) while DNA uses deoxyribose(OH)
RNA uses uracil instead of thymine
mRNA
RNA that has instructions for making proteins
ribosomal RNA function