ch 1-5 terms + concepts
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
phosphorus, carbon, nitrogen cycles not included but still important !
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1
New cards
ecological footprint
the total area of biologically productiveland and water needed to produce the resources and absorb the wates of a given person or population
2
New cards
humanity is using renewable resources ____ faster than they are being replenished
50%
3
New cards
natural capital
the earth’s store of resources and the ecosystem services of the planet; think of it like a bank account
4
New cards
current u.s. eco footprint
china’s eco footprint
india’s eco footprint
china’s eco footprint
india’s eco footprint
7\.2ha/person
2\.1ha/person
0\.9ha/person
2\.1ha/person
0\.9ha/person
5
New cards
triple bottom line
people, planet, profit
6
New cards
sustainable development
satisfies our current needs without compromising the future availibility of natural resources or future quality of life
7
New cards
__% of the planet’s land surface is used for agricultural purposes
50
8
New cards
how to promote sustainability
audits, recycling, waste reduction, green buildins, water conservation, energy efficiency, renewable energy, transportation alternatives, sustainable foot alts, etc.
9
New cards
millennium ecosystem assessment (2005)
evidence shows how value is maximized by conserving natural resources rather than exploiting them for short term profit
10
New cards
consumer power
vote govt officials with environmental awareness, vote with your wallet, reconsider economic growth as ultamite goal
11
New cards
acidic water pH
12
New cards
basic water pH
>7
13
New cards
water is ___. hydrogen bonds give the proporties of _______.__
polar, cohesion, high ability to dissolve substances, high specific heat
14
New cards
organic compounds
always composed of hydrogen and carbon atoms, and somtimes the elements N, O, S, and P, are essential to all living things
15
New cards
selective pressures
environmental conditions determine what pressures natural selection will exert, and these selective pressures affect which members of a population will survive and reproduce
16
New cards
speciation
process by which new species are generated
17
New cards
allopatric speciation
main mode of speciation, occurs when a population is geographically seperated and do not interbreed. isolated populations will adapt to surrounding environment differently and acquire traits specfic to that area. confirmed when the seperated populations come back together and *cannot* mate or reproduce viable offspring
18
New cards
sympatric speciation
occurs when a small part of a populayion becomes a new species because of reproductive isolation within the *same* geographic area
19
New cards
popultions vulnurable to extinction
endemic or small populations (not enough genetic variation or adaptability)
20
New cards
there have been ____ mass extinctions
5, thought to have wiped out 50-95% of species each time
21
New cards
sixth mass extinction
caused by human impact, population growth, industrialization, and resource extraction + use
22
New cards
K-strategists
species having few offspring that are larger in size, require longer parental care, and reach maturity at a later age
(big K = big Kids !)
(big K = big Kids !)
23
New cards
r-strategists
species devoting energy and resources to producing many offsprinf in a relatively short time, with little to no parental care, that are small in size and reach maturity early
(little r = little runts !)
(little r = little runts !)
24
New cards
specialists
species that can survive in a very narrow range of habitats that contain specific resources
25
New cards
generalists
species with broad tolerances, able to use a wide array of resources, and suceeed by being able to live in many different places with variable conditions
26
New cards
ecology
the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environments
27
New cards
ecological hirarchy
organisms
populations
communities
ecosystems
biosphere
populations
communities
ecosystems
biosphere
28
New cards
niche
an organism’s use of resources and its functional role ina community, its “profession”
29
New cards
population ecology
examines the dynamics of popuation change
30
New cards
community ecology
focuses on patterns of species diversity and interactions among species
31
New cards
ecosystem ecology
reveals parterns like energy flow and nutrient cycling
32
New cards
population growth potential attributes
population size
density
distribution (spatial arrangement)
sex ratio
age structure
birth/death rates
density
distribution (spatial arrangement)
sex ratio
age structure
birth/death rates
33
New cards
population growth rate
(births + immigration) - (deaths + emmigration) / pop size = growth rate
34
New cards
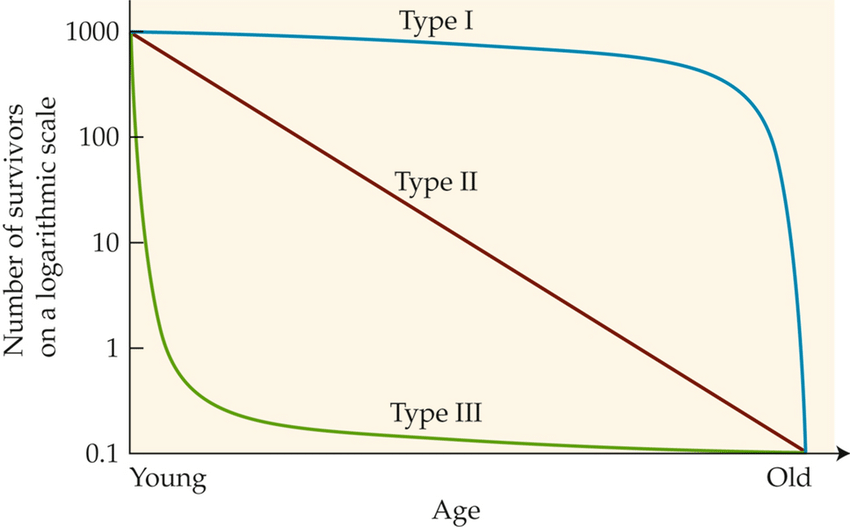
survivorship curves
type 1: humans. low death rates early in life, increases with age
type 2: birds. constant death rate over whole life
type 3: frogs. high death rates early in life, decreases for the small surviving poplation as they age
type 2: birds. constant death rate over whole life
type 3: frogs. high death rates early in life, decreases for the small surviving poplation as they age
35
New cards
expotential growth
population increases by a fixed percent each year, J-CURVE, growth under ideal conditions
36
New cards
limiting factors
physical, chemicalm and biological attributes of the environment that restrain population growth
37
New cards
carrying capacity
maximum population size that a given environment can sustain. humans exceeded our planet’s carrying capacity for us in 2012, at 7b
38
New cards
logistic growth
pattern of growth in which a population initially growths rapidly, then slowly, then stabilizes at carrying capacity due to limiting factors, S-CURVE
39
New cards
density dependent factors
diseases, predation, competition
40
New cards
density idependent factors
temperature extremes, floods, fires
41
New cards
introduced species
bad! 0/10 would not recommend
42
New cards
intraspecific competition
occurs beteween two members of the same species
43
New cards
interspecific competition
occurs between two or more different species
44
New cards
resource partitioning
species adapt to competition by using slightly different resources and/or using them in slightly different ways
45
New cards
parasitism
one species derives benefit by harming without killing another
46
New cards
mutualism
both species benefit
47
New cards
trophic levels contain ___ the energy of the one below it
10%
48
New cards
tropic levels top-bottom
tertiary consumers, top carnivores
secondary consumers, carnivores
primary consumers, herbivores
producers, plants n’ shit
secondary consumers, carnivores
primary consumers, herbivores
producers, plants n’ shit
49
New cards
ecological succession
transition in species composition of an area over ecological time
50
New cards
temperate deciduous forest
fertile soils, deciduous trees (oaks and maple), precipitation spread evenly throughout the year
51
New cards
deserts
very sparse rainfall, extreme temperatures, plants and animals good at water conservation
52
New cards
temperate grassland (prairie)
marked by too little rainfall to support trees, fertile soil, occasional fires, large grazing mammals
53
New cards
tropical rainforest
biodiversity, warm temps and high rainfall, poor soil
54
New cards
tundra
permafrost, cold temps, little rainfall, low vegetation, no trees
55
New cards
boreal/coniferous forest (taiga)
cone-bearing plants, poor soil, cold winters, moderate precipitation
56
New cards
savanna
tropical grassland, high temps, rainy seasons, grazing animals
57
New cards
negative feedback loop
system’s output acts as an input that moves the system in the opposing direction, towards stabilization. these are good! common in nature, contribute to overall balance on Earth
58
New cards
positive feedback loops
increased ouput leads to increased input and destabilization of system (exponential pop growth and glacial melting)
59
New cards
hypoxia
low dissolved oxygen, excessive nitrogen and phosphorus in fertilizer
60
New cards
eutrophication
increaed nutrients like n and p causes algal blooms, which results in low dissolved oxygen, suffocating aquatic life
61
New cards
gross primary productivity
energy into biomass by autotrophs during photosynthesis
62
New cards
net primary productivity
energy/biomass that remains after respiration and is available for consumption by heterotrophs/consumers
63
New cards
ocean acidification
excess CO2 being absorbed by the ocean ! if you don’t remember this, i’d be concerned 🥳
64
New cards