Aggression
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Aggression
Any behavior indebted to inflict psychological or physical harm on another organism or object
Impulsive Aggression
Aggressive behavior that pic yes with only a small amount of forethought or intent and that is determined primarily by impulsive emotions
Hostile Aggression
Aggressive behavior stemming from angry or hostile impulses with a primary goal to inflict pain on someone
Instrumental Aggression
Aggressive behavior stemming from a desire to achieve a goal separate from inflicting pain on someone
Physical Aggression
Aggressive behavior intended to cause physical harm
Non Physical Aggression
Verbal Aggression (name calling) & Relational Aggression
Relational Aggression
Also an example of indirect aggression, aggressive behavior indented to cause harm to a person’s relationships
Gender Differences in Aggression
91% of murders committed by males
93% or robberies committed by males
89% of aggravated committed by males
Biological Basis for Aggression
Ultimate Answers: Defending territory, Establishing dominance hierarchies, competing for resources or mates
Evolutionary Perspective
natural selection shaped the human mind to include adaptations that helped ancestors survive and reproduce
Technology and distortion bc of aggression
Hunsns and other animals respond to cues to indicate submission (i.e. dogs display their throats)
But this doesn’t work if the aggressive act occurs so quickly that the aggressor can’t react to these cues
Violence Inhibition Mechanism
Physiological process that stops aggressive behavior when the victim displays distress signals
Violence inhibition mechanism: An experiment
Psychopaths and non-psychopathic criminals where shown 3 kinds of pics: Neutral, threatening & Distress Cues
Electrodermal Response (Skin conductance) was recorded (indicator of physiological arousal)
Violence inhibition mechanism: An experiment Results
Psychopaths showed reduced electrodermal responses to distress cues compared to controls → support for deficit in the violence inhibition mechanism
Alcohol produced behavior like
Reduced self-consciousness→ deindividuation
Reduced atrito consequences of actions
Reduced self control
Relationship between alcohol & aggression
65% of homicides and 55% of domestic violence, assailant and/84 victim had been drinking
In lab studies comparing with placebo: People give stronger shocks & report more anger when thinking about conflict with romantic partner
Alcohol & Aggression (Kreutzer, Schneider & Myatt 1984)
Participants who were told that they drank a large amount of alcohol (high expectancy) show more hostility
Social Learning Theory
Behavior is acquired through observational learning and to a lesser extent operant conditioning
Social Learning Theory: Operant Conditioning
Rewards obtained by aggression today will increase ins use tomorrow
Microaggression
When seemingly “small” think individuals say or do in the workplace or other environments can leave a long-lasting impression in people’s’ minds
Microinvalidations
Characterized by communications or environmental cues that exclude, negate, or nullify the psychological thoughts, feelings, or experiential reality of certain groups
Bobo Doll Experiment
Demonstrated that children can learn aggressive behaviors through observation and imitation
Bobo Doll Experiment Results
Children in the aggressive condition showed significantly more aggressive behavior than those in the non-aggressive behaviors
Vicarious Reinforcement
Form of observational learning where an individual learns a behavior by observing another person’s actions and the consequences they experience
Inhibition Reinforcement (Vicarious Reinforcement)
When a child stops performing a behavior because they observe that someone else gets punished for it
Disinhibition Reinforcement (Vicarious Reinforcement)
When a child starts performing a behavior because they se someone else getting rewarded for it
Does Punishment Work?
When the punishment itself is aggressive that aggression can be modeled- leading to more aggression
Punishment leads to extrinsic motivation to comply not intrinsic
Aggressive Scripts
An internalized representation of how events progress that include aggressive behavior
Cause people to behave more aggressively, and to perceive more aggression in the actions of others
Aggressive Scripts (Steps)
Acquisition and Encoding Phase: Script is 1st learned
Maintenance Phase: Script is reinforced when person thinks about it, or when they see other examples of it
Retrieval and Emission Phase: Script is enacted
Culture of Honor
An evolved culture in the southern U.S. in which violence is relatively widely accepted and practiced
“A man has the right to kill in order to defend his family and house”
Media Effects: The Effects of Violent lyrics (Method)
Participants listened to violent vs. non-violent songs that were either humorous or not
Media Effects: The Effects of Violent lyrics (Results)
Violent lyrics lead to an increase in aggressive irrespective of whether they are humorous or not
Media Influence Experiment
Participants play the play station game Mortal Kombat on various levels of bloodiness. Aggressive thoughts are measured before and after the game
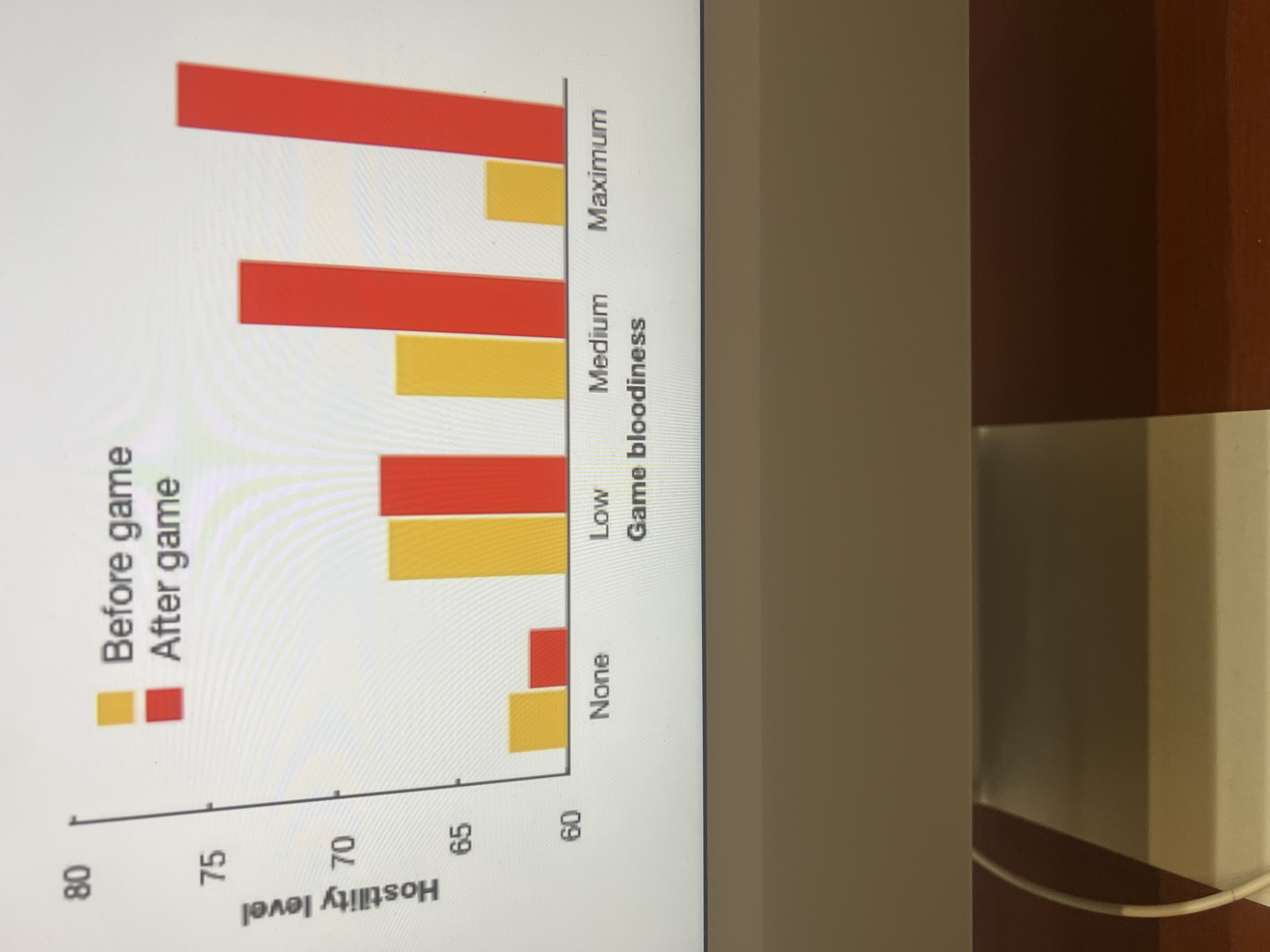
How media leads to violence
Through habituation become desensitized to violence. Depictions of violence can change values and attitudes through cultivation
Frustration-Aggression Theory
When humans are prevented from achieving an important goal they become frustrated and aggressive
Amygdala
Influences and controls our aggression is part of the brain. Mostly responsible for how we react to and perceive aggression and fear
Social Reinforcement
When a person is rewarded, or reinforced by their society for performing a certain action of displaying a specific behavior
Gender Socialization
Process in which children learn these gender roles begins at birth
Laboratory Aggression Paradigms (Eagly & Steffen, 1986; Bettencourt & Miller, 1996)
Meta analyses of gender differences
Laboratory Aggression Paradigms (Eagly & Steffen, 1986; Bettencourt & Miller, 1996) Results
Concluded that women are less aggressive than men because social roles encourage aggression in men but not women
Situational Factors
Any important features of the situation, such as the presence of provocation or aggressive cue. Influence aggression is temperature
Excitation Transfer Theory
The phenomenon that occurs when people who are already experiencing arousal from one event tend to also experience unrelated emotions
Social Reinforcement
When a person is rewarded, or reinforced, by their society for performing a certain action or displaying a specific behavior
Reciprocal Determinism
The ideas that there is an interplay between our personality and the way we interpret events and how they influence us
The Social-Ecological Model: A Framework for Prevention
To better understand violence and the effect of potential prevention strategies
Individual
First level, identifies biological ands personal history factors that increase the likelihood of becoming a victim or perpetrator of violence
Relationship
Second level, examines close relationships that may increase the risk of experiencing violence as a victim or perpetrator
Community
Third level, explores the settings, such as schools, workplaces and neighborhoods, in which social relationships and seeks to identify characteristics of these settings that associated with becoming victims or perpetrators of violence
Societal
Fourth level, looks at the broad societal factors that help create in which violence is encouraged or inhibited
Genetic Determinants of Aggression
Finding from large selection of the twin and adoption studies that have investigated the genetic and environmental architecture of aggressive behavior
Aggression & Sports
Types Aggression: Instrumental & hostile aggression
In this aspect aggression is a characters can have many negative was well s posture d effects in performance