BMSC 200 - Midterm (quizzes)
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
The study of life at a molecular level
What is Biochemistry
Chemical, Energy, Genetic, Evolutionary
What are the 4 different perspectives or foundations of the living state?
All
-are carbon-based
-generate biomolecules as polymers of smaller building blocks
-are stereo specific in utilization of building blocks to generate bio molecules
-utilize common building blocks to generate biomolecules
All known forms of life:
That there is a natural tendency towards increasing disorder
The second Law of Thermodynamics states:
?
The bioavailability of which chemical element is most limiting to human population growth?
Lipids
Which category of biomolecules involves aggregates rather than polymers?
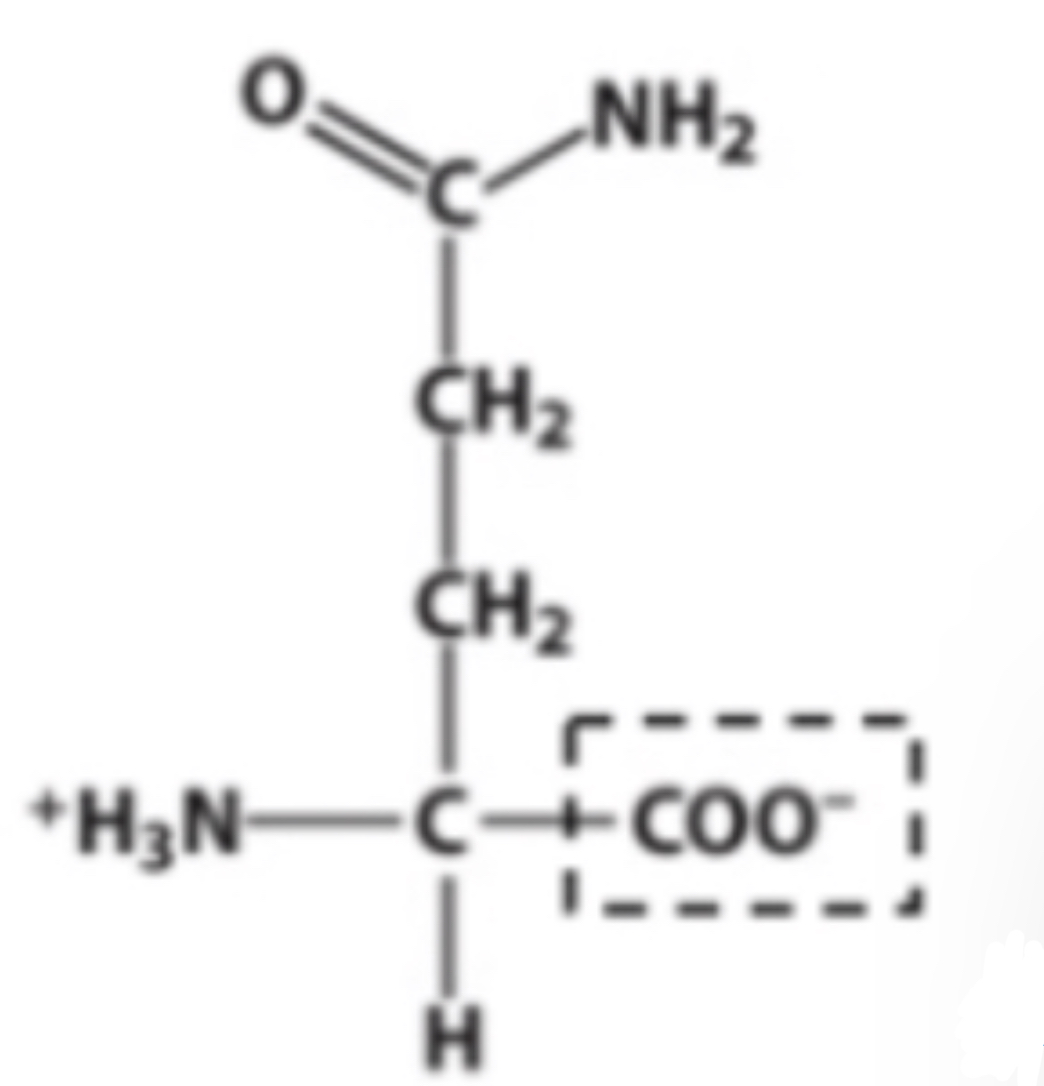
Amido
Identify the functional group within the box
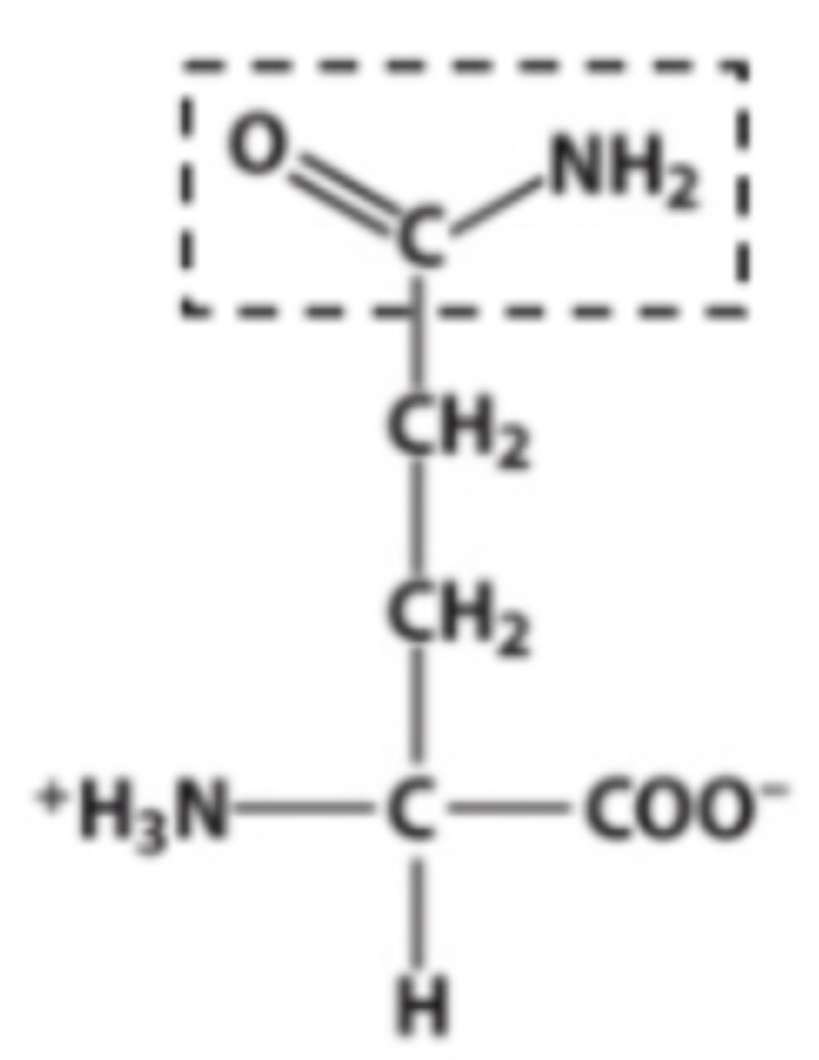
C?
Which of these molecules contains an amino group?
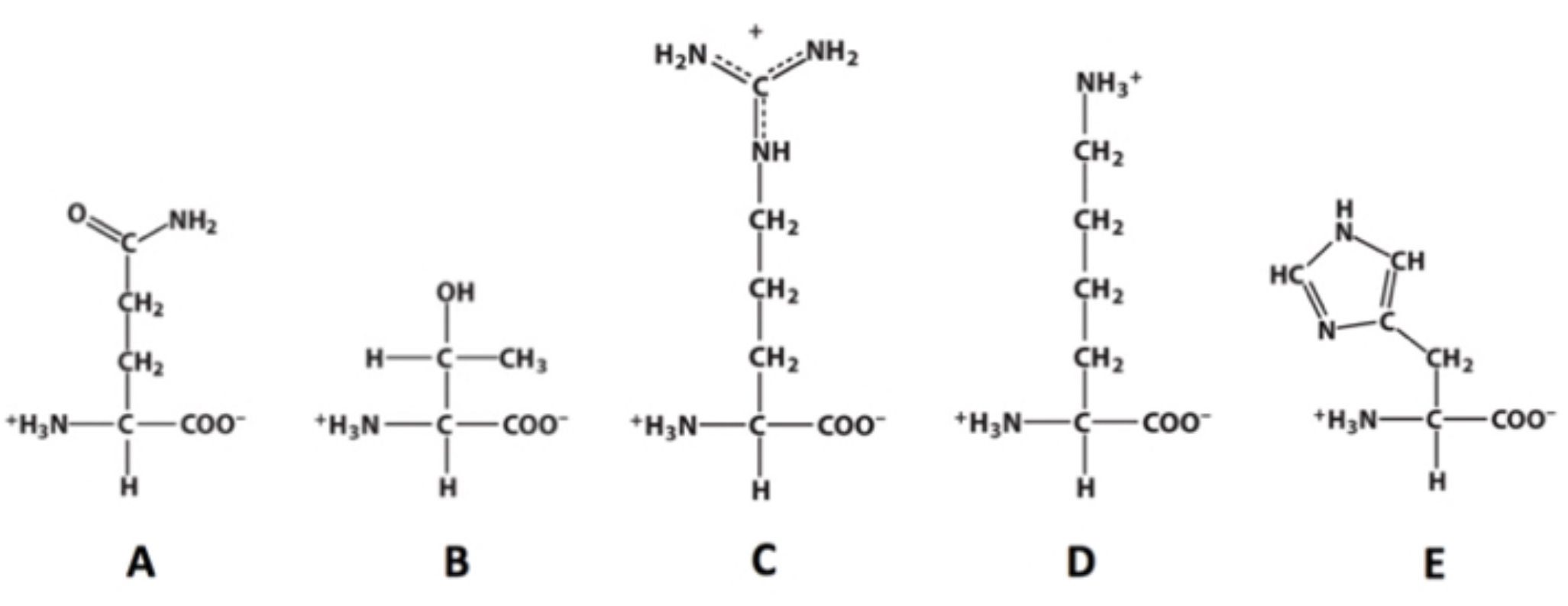
DNA from a DNA template
Replication is the process of making:
B
Which of these molecules contains a hydroxyl group?
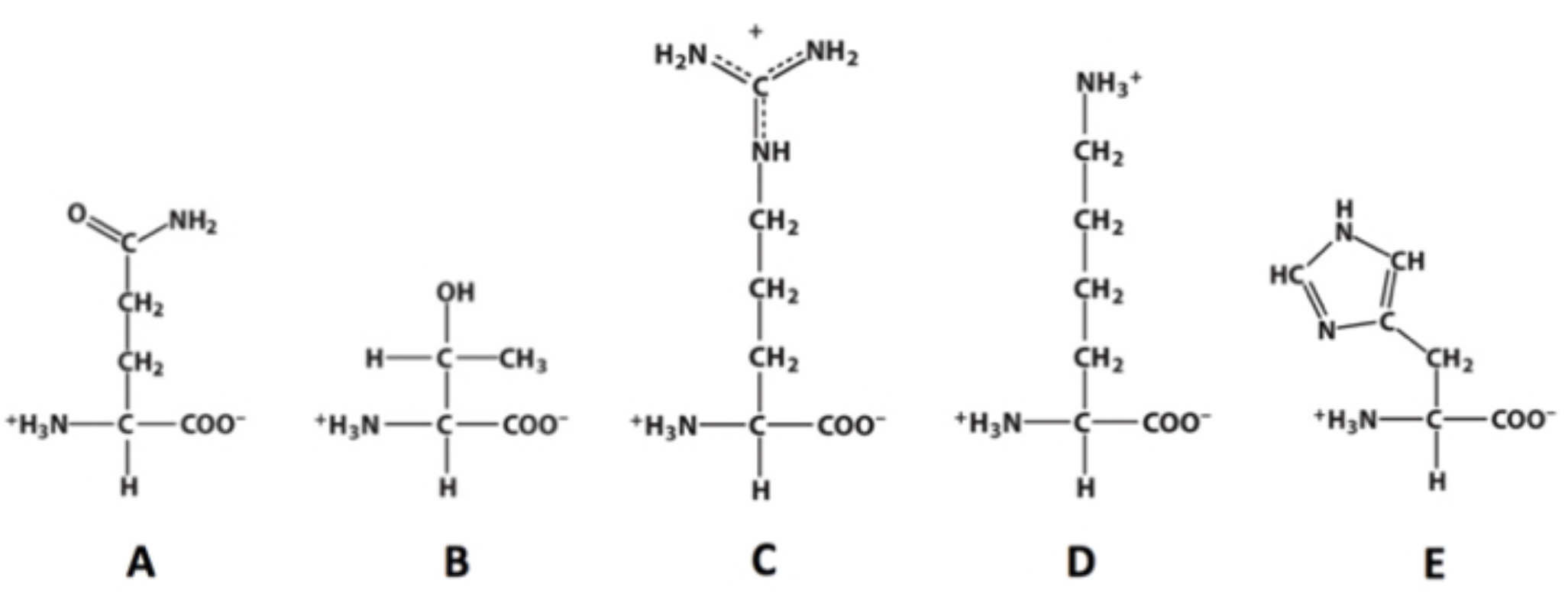
All:
-the strength of carbon bonds enables the creation of stable biomolecules
-carbon can form a diverse number of bonds and structures
-the metabolism of carbon-based molecules produces by-product that remain active in the biosphere
-considerable energy is released. during the metabolism of carbon-based molecules
which of the following is an advantage of being a carbon-based form of life?
C?
Which of these molecules contains a guanidino group?
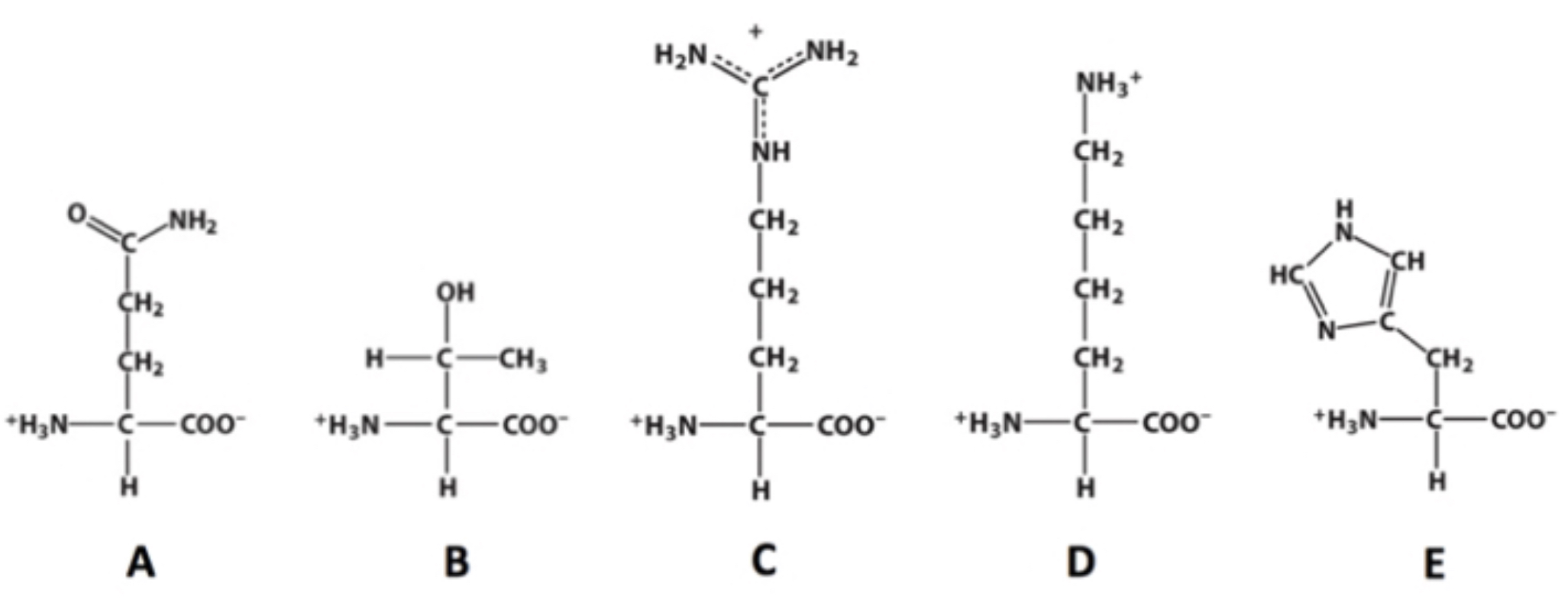
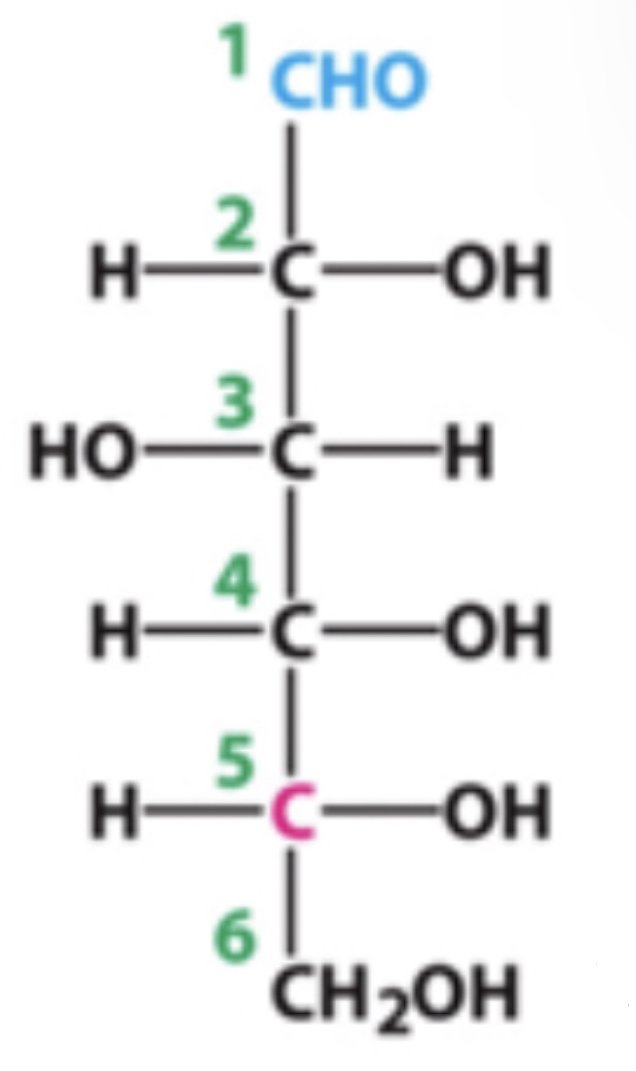
4?
how many chiral carbons are present within this molecule?
Carbohydrates
Which category of biomolecules includes both linear and branched polymers?
RNA from a DNA template
Transcription is the process of making:
Changing a double bond from cis to trans and changing an amino acid from D to L forms are both changes in configuration
Which of the following represents a change in configuration?
In vivo
A new drug is being tested in a mouse model of disease. This is called an ___ experiment.
Proteins
Which of these biomolecules is composed from amino acid building blocks?
That the amount of energy in the universe remains constant, although the forms of the energy may change
The first law of thermodynamics states:
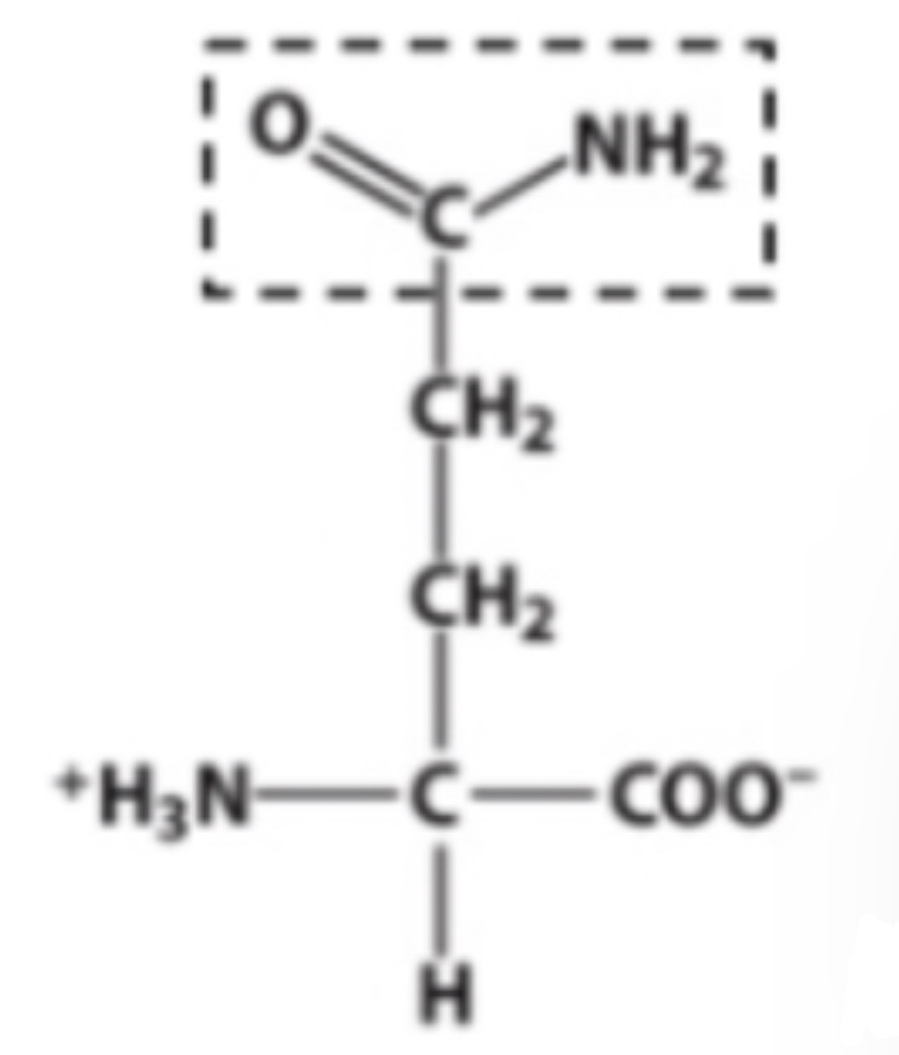
Carboxyl
Identify the functional group within the box.
Carbonyl
Identify the functional group within the box.
DNA, RNA, protein
What is the functional order of utilization of biomolecules according to the Central Dogma of Biochemistry
The unity of biochemistry
That all living organisms utilize a common repertoire of biomolecular building blocks and employ a common core of biochemical processes is:
COOH- CH2- +NH3/ COO^- -CH2- +NH3
pKa = 2.34
Which of these weak acids is the strongest acid?
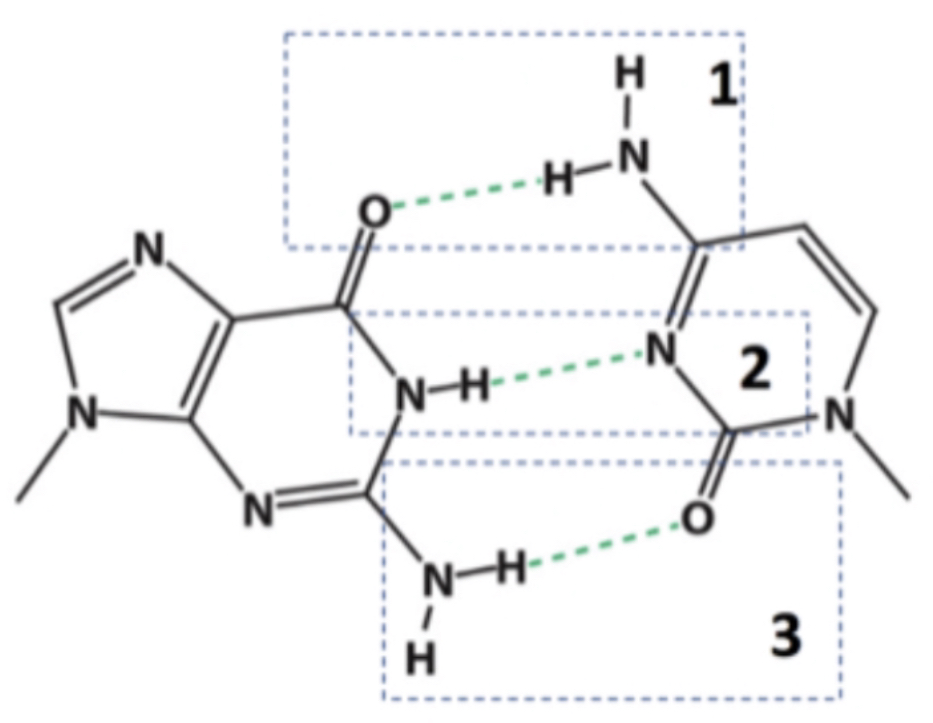
1, 2, and 3
In which of the indicated hydrogen bonds does nitrogen serve as the hydrogen bond donor?
4.2 to 6.2
What is the buffering range of a weak acid with a pKa of 5.2?
2
In which of the indicated hydrogen bonds does nitrogen serve as the hydrogen bond acceptor?
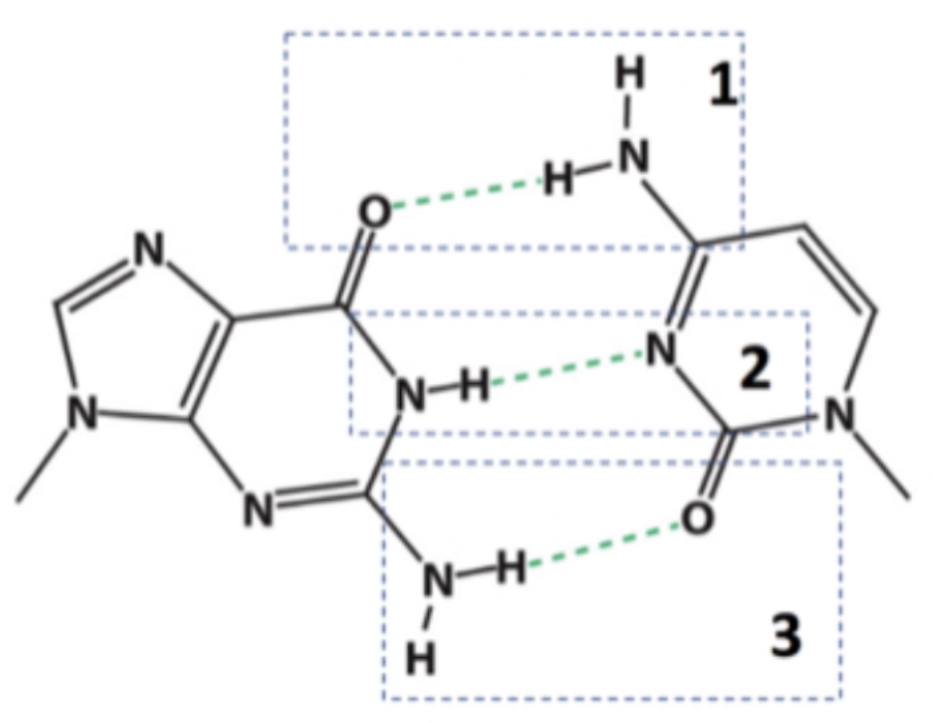
The interaction between H and A is electrostatic
Within a hydrogen bond where D represents the hydrogen bond donor, A represents the hydrogen bond acceptor, and H represents the hydrogen atom:
? not 4.2; not 6.2
A weak acid solution of pH 6.2 has 1000-fold excess of the acid form (HA) relative to the conjugate base (A-) form of a weak acid. What is the pKa of that weak acid?
All:
-carry a permanent dipole
-are the most abundant molecules in living organisms
-are effective at accepting and donating hydrogen bonds
-are effective solvents for polar molecules
Water molecules:
?not when the desired pH matches the pKa of the weak acid
not at the pKa point
A monoprotic weak acid has the greatest buffering capacity:
1 unit below the pKa of the weak acid
When there is a 10-fold excess of the protonated (HA) versus the conjugate base (A-)forms a weak acid the pH is:
?not van der waals
which non-covalent force is the primary driver for biomolecules to adopt their biologically-active conformations?
pH= pKa + log [A-]/ [HA]
which of the following is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
Decrease; Increase
The folding of a polypeptide into its biologically active conformation serves to ___ the entropy of the polypeptide and ___ the entropy of the associated water.
When the pH is 2 units above the pKa.
In what situation is there be a 100-fold excess of the conjugate base (A-) form versus the protonated (HA) form the of a weak acid?
Amphipathic
Molecules with both polar and non-polar groups are called:
All:
-Hydrogen bonds
-Electrostatic interactions
-Hydrophobic interactions
-Van der Waals interactions
Which non-covalent forces contribute to the structure and stability of a biomolecule?
In aqueous solutions, [H+] is always equal to 10-7M
Which statement(s) about pH is FALSE?
Shielding of charged groups by water molecules
The strength of electrostatic interactions within biomolecules is often reduced by:
All:
-whether the solution is a buffer
-the number of buffering regions
-the pKas of buffering groups
What information can be determined from a titration experiment?
Oxygen is not the donor in any of these hydrogen bonds.
In which of the indicated hydrogen bonds does oxygen represent the hydrogen bond donor?
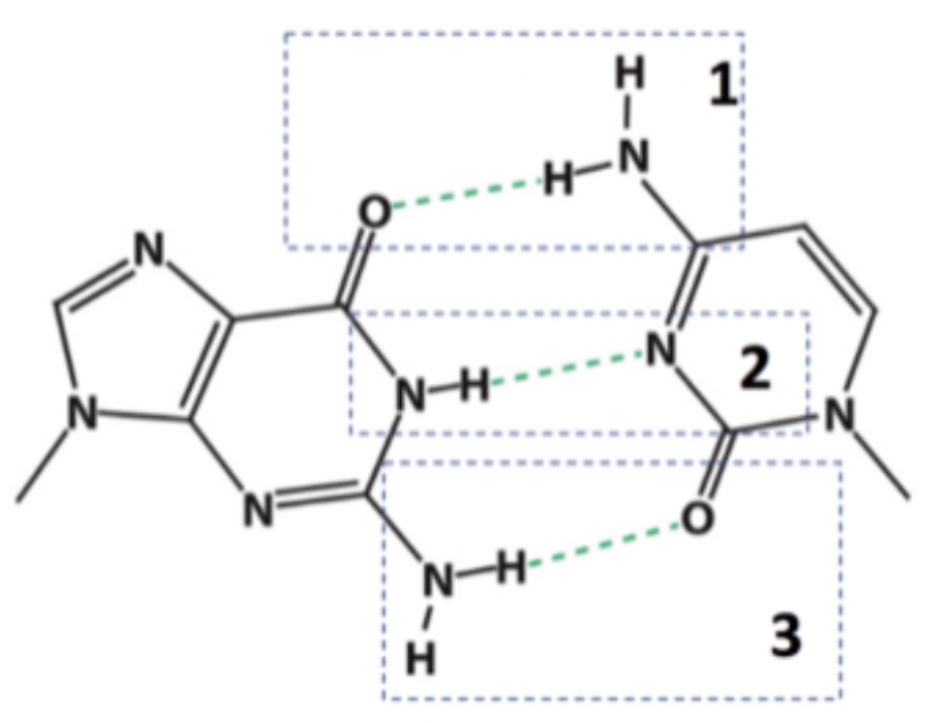
All:
-H.B within biomolecules often involve either and/ or nitrogen atoms.
-The length of a hydrogen bond is approx. double that of a covalent bond.
-The strengthof a h.b depends on the geometry of the donor and acceptor atoms.
-within a h.b, the H atom is covalently linked to the donor atom and electrostatically linked to the acceptor atom.
Which statement about hydrogen bonding is TRUE?
S,T,Y
In which set do all the amino acids have the potential to be modified through phosphorylation?
?not Asp
Which amino acid often serves as a proton donor or acceptor in biochemical reactions?
D,E
Which amino acids carry a net charge of -1 physiological pH?
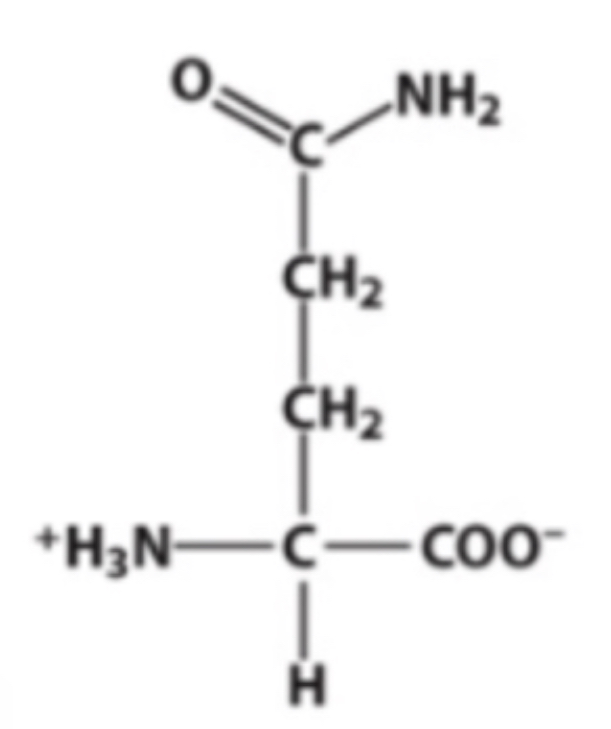
Gln
Identify this amino acid.
Isoleucine?
Identify this amino acid.
G, D, E, W ?
Which set correctly lists the amino acids from smallest to largest molecular weight?
A,L,I
Which set of amino acids is most likely to be buries in the core of a folded protein?
F, Y, Q, N
List the amino acids F, Y, E, and D from lowest to greatest molecular weight
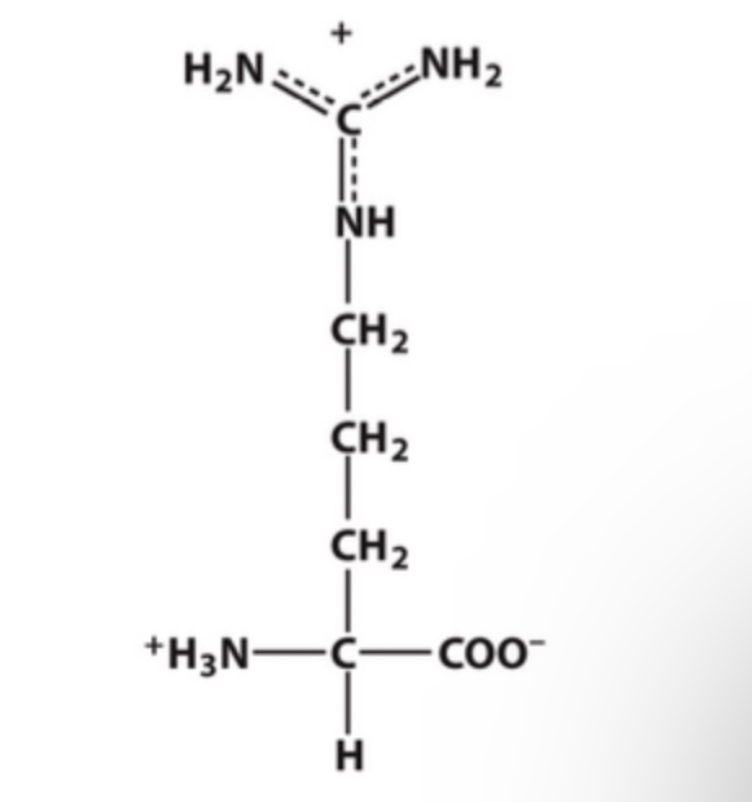
Arginine
Identify this amino acid.
3.0
Given the following pKas calculate the isoelectric point for aspartate; alpha carbon carboxyl (pKa 2.0), side chain carboxyl (pKa 4.0), and amino (pKa 10.0).
2
How many letters in the word “BIOCHEMISTRY” are not one letter codes for amino acids?
All amino acids have at least one carbonyl group
Which statement about amino acids is TRUE?
?not L has a side chain carboxyl group
Which pairing of amino acid one letter codes and side chain functional group is correct?
F,A,I ?
In which set of amino acids are the side chains composed exclusively from carbon and hydrogen?
?not below pH 2
For valine, the pKas are carboxyl (pKa 2.0) and amino (pKa 10.0). At what pH range is valine in the zwitterionic form?
?not -1
Given the following pKas for glutamate; alpha carbon carboxyl (pKa 2.0), side chain (pKa 3.0), and amino (pKa 10.0), what is the charge on glutamate when the pH is equal to the pKa of the side chain carboxyl group?
Arginine
For which of these amino acids is the one letter code NOT the first letter of the full name?
Between pH 2 and 10
For leucine, the pKas are carboxyl (pKa 2.0) and amino (pKa 10.0). At what pH range is valine in the zwitterionic form?
0?
How many letters in the word “SASKATCHEWAN” are no one letter codes for amino acids?
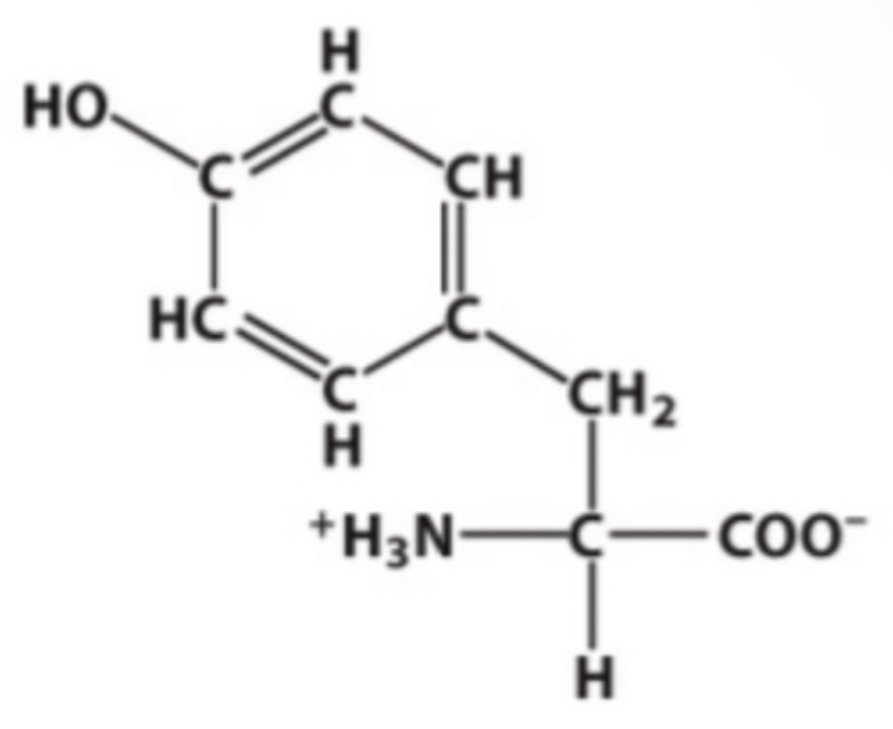
Y
Identify this amino acid.
?not -1
Given the following pkas for aspartate; alpha carbon carboxyl (pKa 2.0), side chain carboxyl (pKa 3.0), and amino (pKa 10.0), what is the charge on aspartate when the pH is equal to the pKa of the alpha carbon amino group?
6.0? ((2.0+10.0)/ 2)
Given the following pKas calculate the isoelectric point for aspartate; alpha carbon carboxyl (pKa 2.0), side chain carboxyl (pKa 4.0), and amino (pKa 10.0).
N,Q,F,Y
List the amino acids F, Y, Q, and N from lowest to greatest molecular weight.
?not between pH 2 and 6
Given the following pKas for histidine; carboxyl (pKa 2.0), imidazole (pKa 6.0), and amino group (pK 10.0), at what pH would histidine carry a net charge of +2?
G, N, Q, W
Which set correctly lists the amino acids from smallest to largest molecular weight?
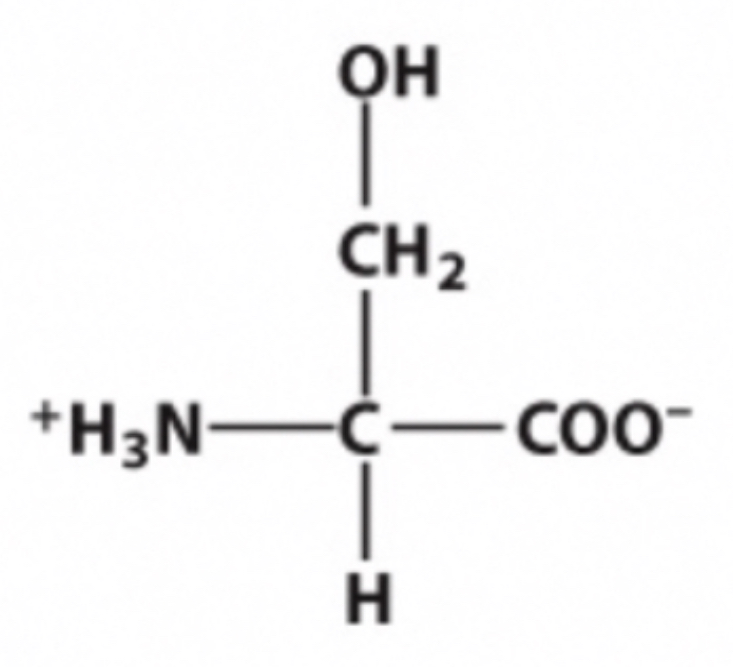
Serine
Identify this amino acid.
?not 4.0
Given the following pKas, calculate the isoelectric point of histidine; carboxyl (pKa 2.0), imidazole (pKa 6.0), and amino (pKa 10.0).
0
Which letters in the word “SASKATOON” are not one letter codes for amino acids?
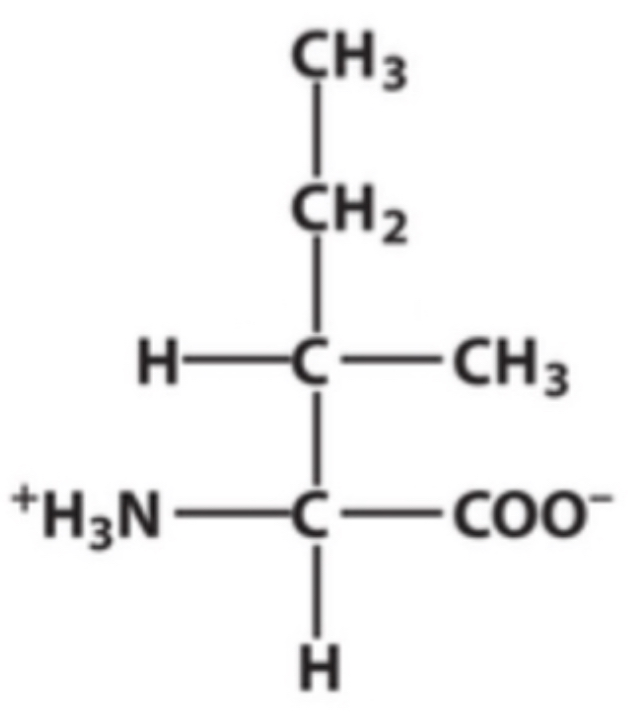
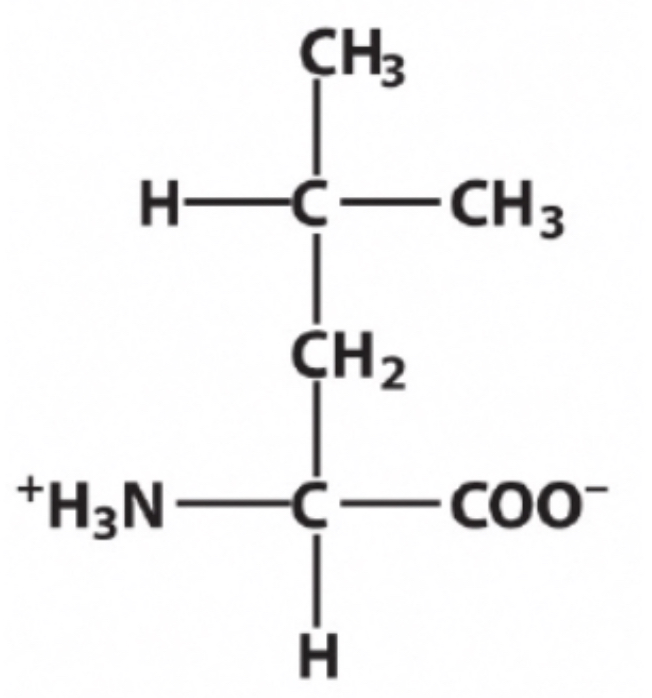
Leucine ?
Identify this amino acid.
R
Which of these amino acids can carry a net charge of +1 at physiological pH?
peptide bonds
The amino acid residues of a polypeptide chain are linked together though:
Fully extended polypeptide chains
The strength of silk arises as a consequence of:
All:
-rotations between the alpha carbon to the amide nitrogen and carbonyl carbon are described by the phi and psi respectively
-there is a repeating pattern of NCCNCC
-conformational flexibility is limited to rotation at the alpha carbons
-sequential residues are linked by covalent bonds
Within the main chain of a polypeptide:
?not c terminal arginine
?not C terminal proline
For the peptide PADNCA:
Carbonyl and amino
Which functional groups are involved in the formation of a peptide bond?
?not the folding pattern of polypeptide chain that bestows biological activity
The secondary structure of a protein reflects:
Exactly three carboxyl groups
The peptide ILDHYVE has:
Hydrophobic interactions
Which non-covalent force is the primary driving factor for the formation and stabilization of the biologically active form of proteins?
?not most proteins are marginally stable
?not that protein folding….optimize non-covalent interactions
That many proteins spontaneously adopt their native conformations without the need for chaperones indicates:
tertiary structure
The final folding pattern of a single polypeptide chain represents:
?not all are true
Which statement about tertiary structure is TRUE?
?not is required for the biological function of protein
?not is driven in an effort…. most stable conformation
Folding of a protein into its native conformation:
?not N terminal is glutamate
For the peptide YADNCG:
Vitamin C
Which vitamin is required for post-translational modifications of collagen?
?not all are true
Keratin is similar to collagen in that they both:
?not leu
Which of these residues is most likely to be found at the N-terminus of an alpha helix?
All:
-have conserved structural features independent of the specific protein in which they are contained
-have phi and psi angles within the allowed regions of a Ramachandran plot
-include alpha helicies and beta sheets
-optimize main-chain hydrogen bonding potential
Elements of a secondary structure:
Collagen
Vitamin C is required for post-translational modification of:
Arg
Which of these residues is most likely to be found at the C-terminus of an alpha helix?
All:
-are usually trans with respect to their carbonyl and amide groups
-are covalent linkages between residues of proteins
-can donate and accept hydrogen bonds
-are rigid and planar with a partial double bond characteristic
Peptide bonds:
?not hydrogen bonds between amino acid side chains
Which type of bonding is responsible for secondary structure of proteins?
?that protein folding is a cooperative process
That many proteins will spontaneously fold into their biologically active conformations indicates:
The linear arrangement of covalently linked amino acids
The primary structure of a protein reflects:
?not the number and geometry of hydrogen bonds between strands
Parallel and anti-parallel beta sheets differ in:
All:
-there is a repeating pattern of NCCNCC
-sequential residues are linked by covalent bonds
-rotations between the alpha carbon to the amide nitrogen and carbonyl carbon are described by phi and psi respectively
-conformational flexibility is limited to rotation at the alpha carbons
Within the main chain of a polypeptide:
None are correct
Hemoglobin and Myoglobin:
a single amino acid change in hemoglobin
The molecular basis of sickle cell anemia is: