Geology Final
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
1
New cards
relative age
cronological order of geological events/processes which is determined within field operations
2
New cards
absolute age
time before the present (yrs vs. billions of yrs) assumption is involved
3
New cards
uniformitarianism
processes occuring now that have happened in the past
4
New cards
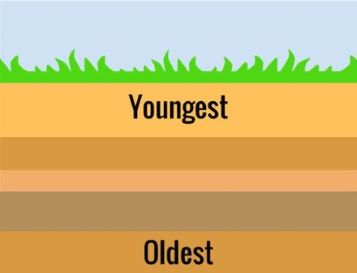
principle of superposition
younger rocks on top of older rocks (used for dating geological events)
5
New cards
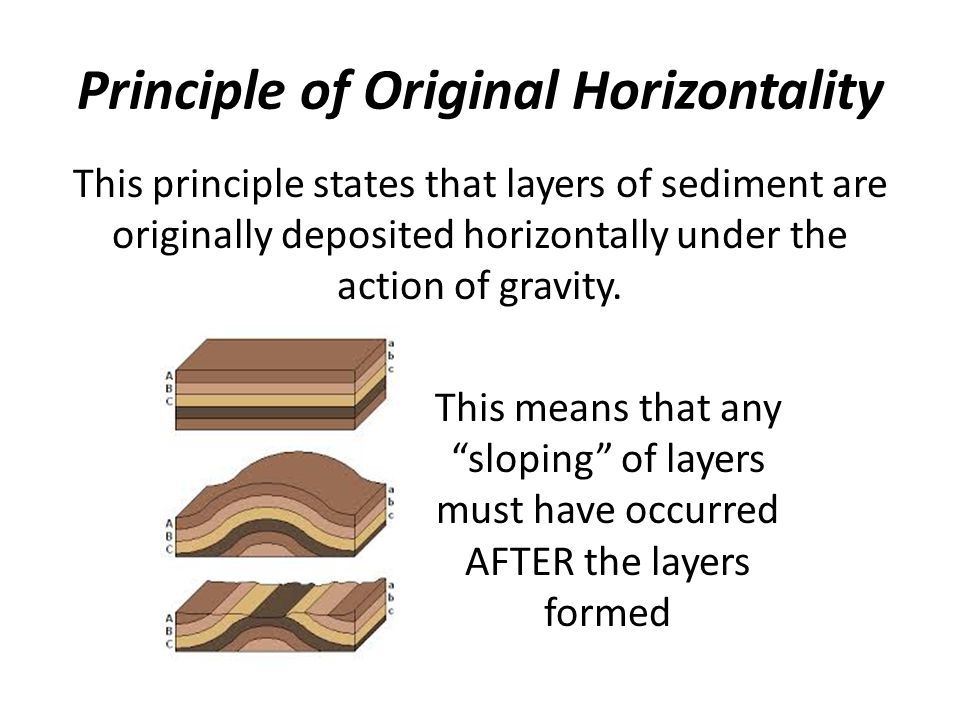
principle of original horizontality
sediments are deposited in flat horizontal layers (meaning tilting/folding must indicate later deformation)
6
New cards
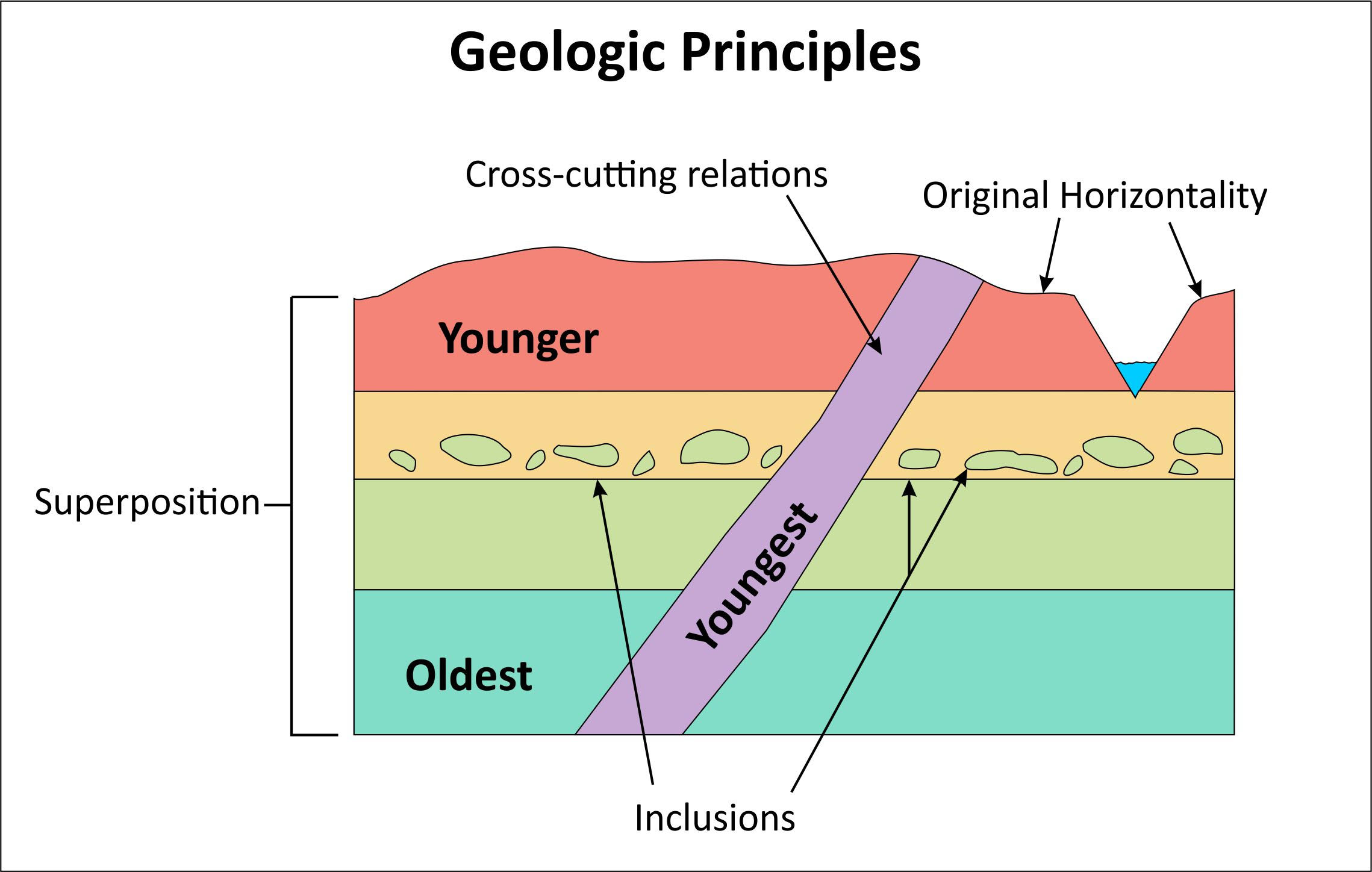
principle of cross cutting relations
features such as dikes, faults, and ignenous rock intrusions are the youngest formation
7
New cards
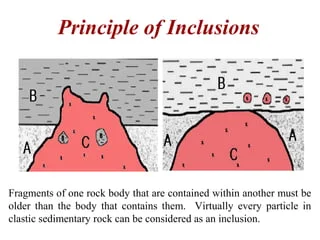
Principle of Inclusions
included rock is older such as Xenoliths, pebbles and cobbles that are imbedded with in the rock
8
New cards
Principle of faunal sucession
evolutionary fossils can dictate how old a rock is
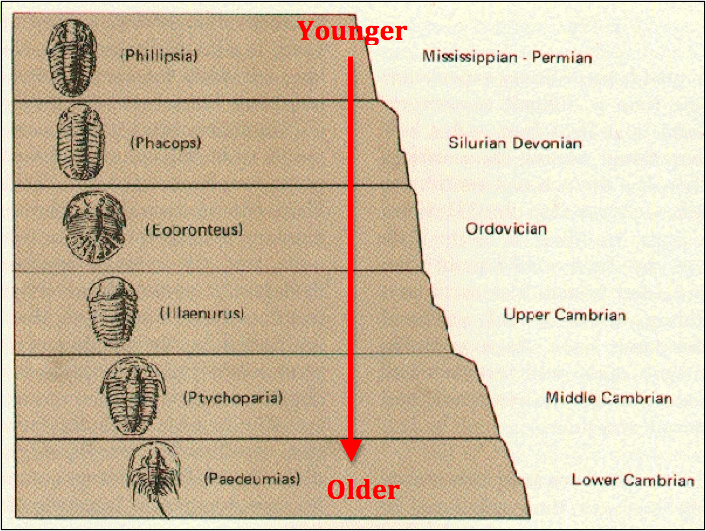
9
New cards
unconformity
time gap in the sedimentary record; different types such as angular unconformity, nonconformity, and disconformity
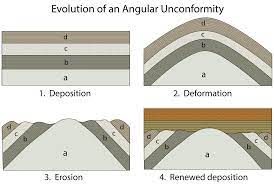
10
New cards
angular unconformity
deformation at an angle that results in a gap in sedimentary record
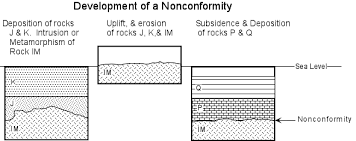
11
New cards
Nonconformity
deformation where younger sedimentary rock overlies eroded “basement” ingenous/metamorphic rocks
12
New cards
Disconformity
a sort of “hidden” unconformity where the layers above and below an eroded boundary have the same orientation

13
New cards
Hadean Eon (a part of the Pre-Cambrian)
* first time period of our planet
* Earth differentiated during this time (core, mantle, primitive crust)
* Moon formed during this period due to a large impact with a Mars-sized planet called Theia. Some of the mantle from Theia combined with some of Earth’s created the moon
* time of major impacts
* Earth differentiated during this time (core, mantle, primitive crust)
* Moon formed during this period due to a large impact with a Mars-sized planet called Theia. Some of the mantle from Theia combined with some of Earth’s created the moon
* time of major impacts
14
New cards
Archean Eon (Pre-Cambrian)
* “late heavy bombardment”
* records Earth’s earliest life: biomarkers
* Stromalites - bacterial mounds
* Late Archean: photosynthetic organisms
* Beginning of free oxygen (O2) in atmosphere
* banded iron formations
* photosynthetic organisms, which were making oxygen, reacted to iron that was dissolved within seawater to form iron oxide minerals on the ocean floor - creating banded iron formations
* records Earth’s earliest life: biomarkers
* Stromalites - bacterial mounds
* Late Archean: photosynthetic organisms
* Beginning of free oxygen (O2) in atmosphere
* banded iron formations
* photosynthetic organisms, which were making oxygen, reacted to iron that was dissolved within seawater to form iron oxide minerals on the ocean floor - creating banded iron formations
15
New cards
Proterozoic Eon (Pre-Cambrian)
* Eukaryotes evolve to have a cell nucleus
* multi-cellular organisms
* carbon films - small, dark compressions most resembling circles, ribbons, or leaves
* “Snowball earth” - amount of greenhouse gas was very little during this time, as global climate becomes colder larger areas of ice begin to form. Ice and snow reflect solar radiation back out into space and the earth becomes colder (positive feedback loop)
* multi-cellular organisms
* carbon films - small, dark compressions most resembling circles, ribbons, or leaves
* “Snowball earth” - amount of greenhouse gas was very little during this time, as global climate becomes colder larger areas of ice begin to form. Ice and snow reflect solar radiation back out into space and the earth becomes colder (positive feedback loop)
16
New cards
Phanerozoic Eon
* rich fossil records
* hard-shelled animals
* plants
* insects, dinosaurs, mammels
* life as we know it
* hard-shelled animals
* plants
* insects, dinosaurs, mammels
* life as we know it
17
New cards
Palaeozoic Era
* hard shelled organisms, vertebrates
* beginnings of life on land - predinosaur
* beginnings of life on land - predinosaur
18
New cards
Cambrian Period
* marks first preservation of animal shells
* invertebrates - trilobite
* faunal diversity
* rapid diversification followed by rapid disappearance
* possibilities for this
* natural selection
* preservation
* global warming
* supercontinent breakup - Gonwana
* produced shallow seas
* expanding environmental niches
* invertebrates - trilobite
* faunal diversity
* rapid diversification followed by rapid disappearance
* possibilities for this
* natural selection
* preservation
* global warming
* supercontinent breakup - Gonwana
* produced shallow seas
* expanding environmental niches
19
New cards
Ordovician Period
* first marine vertebrate animals
* jawless fish - ostracoderm
* mass extinction of organisms near the end of the Ordovician
* major glaciation centered in Africa → severe drop in sea level
* 85% of species were lost
* jawless fish - ostracoderm
* mass extinction of organisms near the end of the Ordovician
* major glaciation centered in Africa → severe drop in sea level
* 85% of species were lost
20
New cards
Devonian and Silurian
* vascular plants arose
* mosses, ferns
* has internal structure to move water and photosynthesis
* spiders, scorpions, insects, crustaceans
* jawed fish
* sharks
* Silurian → first clear evidence of life on land
* Devonian → armored fish such as Dunkelosteus
* transition from aquatic to land based organisms
* mosses, ferns
* has internal structure to move water and photosynthesis
* spiders, scorpions, insects, crustaceans
* jawed fish
* sharks
* Silurian → first clear evidence of life on land
* Devonian → armored fish such as Dunkelosteus
* transition from aquatic to land based organisms
21
New cards
Carboniferous Period
* Made up of Mississippian and Pennsylvanian Epochs
* reptiles
* laid eggs
* giant insects
* large swamps
* development of limestone and higher concentrations of oxygen in the atmosphere
* Antrhropleura, Meganeura, and Pulmonoscorpian
* reptiles
* laid eggs
* giant insects
* large swamps
* development of limestone and higher concentrations of oxygen in the atmosphere
* Antrhropleura, Meganeura, and Pulmonoscorpian
22
New cards
Permian Period
* supercontinent of Pangea
* age of reptiles
* lystrosaurus - formed herds
* dimetrodon - predatory with sail on back
* postosuchus - ambush predator → thought to be bipedal
* mass extinction at end
* 90% went extinct
* reasons:
* volcanic activity on a massive scale in the Siberian Traps
* produced carbon dioxide on massive scale
* global warming followed which may have increased ocean water temperatures which would have been toxic for marine life
* age of reptiles
* lystrosaurus - formed herds
* dimetrodon - predatory with sail on back
* postosuchus - ambush predator → thought to be bipedal
* mass extinction at end
* 90% went extinct
* reasons:
* volcanic activity on a massive scale in the Siberian Traps
* produced carbon dioxide on massive scale
* global warming followed which may have increased ocean water temperatures which would have been toxic for marine life
23
New cards
Mesozoic Era
“age of the dinosaurs”
24
New cards
Triassic Period
* land vertebrates
* first true dinosaurs
* Coelophysis
* plateosaurus
* first mammels
* Ezostrodon
* first true dinosaurs
* Coelophysis
* plateosaurus
* first mammels
* Ezostrodon
25
New cards
Jurassic Period
* dinsaur renaissance
* air, land and sea dinos
* flying reptiles NO BIRDS
* Pteranodon
* Sauropods
* evolved from Plateosaurus
* designed depending upon the type of vegetation that they ate
* apatosaurus - swallowed large chucks of plants without chewing → consistent with jaw structure
* Brachiosaurus -swallowed chunks whole as well → consistent with jaw structure
* air, land and sea dinos
* flying reptiles NO BIRDS
* Pteranodon
* Sauropods
* evolved from Plateosaurus
* designed depending upon the type of vegetation that they ate
* apatosaurus - swallowed large chucks of plants without chewing → consistent with jaw structure
* Brachiosaurus -swallowed chunks whole as well → consistent with jaw structure
26
New cards
Cretaceous Period
* pangea begins to break apart
* extensive swamps
* flowering plants
* T-rex, Spinosaurus, Argentinosaurus, Deadnoughtus
* ended with mass extinction
* all dinosaurs
* possible causes
* climate change
* plate tectonics - continental configuration
* disease
* competition with mammels
* volcanic eruptions
* meteorite impact
* can cause Tsunami, dust in stratosphere resulting in global cooling
* Deccan Traps, India → started the climate shift and metorite finished the dinosaurs off
* extensive swamps
* flowering plants
* T-rex, Spinosaurus, Argentinosaurus, Deadnoughtus
* ended with mass extinction
* all dinosaurs
* possible causes
* climate change
* plate tectonics - continental configuration
* disease
* competition with mammels
* volcanic eruptions
* meteorite impact
* can cause Tsunami, dust in stratosphere resulting in global cooling
* Deccan Traps, India → started the climate shift and metorite finished the dinosaurs off
27
New cards
Cenozoic Era
* “age of mammals”
* Paleogene and Neogene
* see early forms of modern mammels in Eocene and Oligocene
* Moerotherium and Deinotherium → Elephants
* Ambulocetus and Basilosaurus → Whales
* Ambulocetus means “walking whale”
* ate fish and other animals that strayed into water
* powerful jaw and bite
* Indricothere
* rhinocerous is the closest living relative
* Paleogene and Neogene
* see early forms of modern mammels in Eocene and Oligocene
* Moerotherium and Deinotherium → Elephants
* Ambulocetus and Basilosaurus → Whales
* Ambulocetus means “walking whale”
* ate fish and other animals that strayed into water
* powerful jaw and bite
* Indricothere
* rhinocerous is the closest living relative
28
New cards
Quanternary Era
* where we are now in the time period
* glacial cycles
* saber-tooth cats did not exist
* human evolution
* australopithecus → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens
* Holocene Epoch wraps up the Quaternary
* proliferation of humans
* glacial cycles
* saber-tooth cats did not exist
* human evolution
* australopithecus → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens
* Holocene Epoch wraps up the Quaternary
* proliferation of humans
29
New cards
Drainage
consists of all forms of water reaching Earth’s surface
30
New cards
water shed
collects water from a broader region resulting in catching or drainage basins
31
New cards
permanent
running water all year round
32
New cards
ephemeral
only contains water after rain/melt events. Dried out bed is called a dry-wash
33
New cards
Longitudinal profile
* heavily affected by geology
* steep near headwaters
* affected by resistant rock units
* waterfalls
* steep near headwaters
* affected by resistant rock units
* waterfalls
34
New cards
meandering
* water flows in a curvy, bendy path like a snake
* gets more exaggerated as time goes on
* process of deposition and erosion
* point bars
* a low, curved ridge of sand and gravel along the inner bank of a meandering stream
* cut banks
* located on the outside of stream bend. shaped like a small cliff and formed by the erosion of soil as the stream collides with the river bank
* oxbow lakes
* starts out as a curve or meander in a river, however, over time the lake finds a shorter course to follow thus cutting off the meander and it becomes a oxbow lake
* gets more exaggerated as time goes on
* process of deposition and erosion
* point bars
* a low, curved ridge of sand and gravel along the inner bank of a meandering stream
* cut banks
* located on the outside of stream bend. shaped like a small cliff and formed by the erosion of soil as the stream collides with the river bank
* oxbow lakes
* starts out as a curve or meander in a river, however, over time the lake finds a shorter course to follow thus cutting off the meander and it becomes a oxbow lake
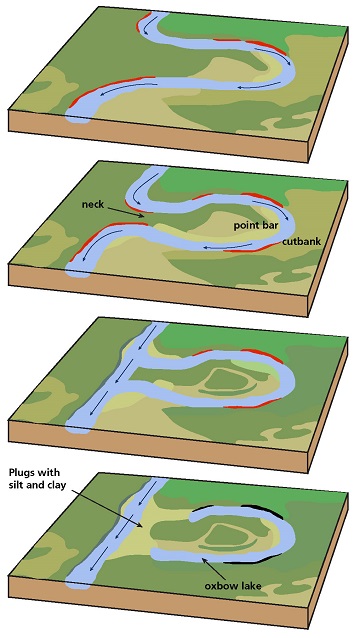
35
New cards
Floodplains
streams will overtop its banks where the velocity will then suddenly decrease
36
New cards
levees
barriers that formed coarser sediments fall out of suspension
37
New cards
causes of flooding + flood events
excess rainfall, rapid snowmelt, ground saturation, urbanization - prevents movement of water through soils, dam failure
100 yr flood events - reccurence interval of floods - every year has a 1% chance of flooding in any given year
2 yr flood events - 50% chance of flooding in any given year (frequent)
100 yr flood events - reccurence interval of floods - every year has a 1% chance of flooding in any given year
2 yr flood events - 50% chance of flooding in any given year (frequent)
38
New cards
porosity
volume of pore space in rocks or sediment
39
New cards
Permeability
the connectivity of pores in rocks or sediments
40
New cards
water table
boundary between saturated and unsaturated zones
41
New cards
aquifers
* rock or sediment units that store water underground
* confined
* layers of impermeable material are both above and below the aquifer are called a aquitard
* water is under pressure
* when water is penetrated by a well the water will rise above the acquifer
* Unconfined
* top of the water table
* able to rise and fall according to atmospheric pressure
* usually closer to Earth’s surface than confined aquifers
* confined
* layers of impermeable material are both above and below the aquifer are called a aquitard
* water is under pressure
* when water is penetrated by a well the water will rise above the acquifer
* Unconfined
* top of the water table
* able to rise and fall according to atmospheric pressure
* usually closer to Earth’s surface than confined aquifers
42
New cards
Karst Aquifers, Limestone, and Calcite
* karts aquifers consist of interconnected cracks and caves and forms in the dissolution of limestone
* calcite:
* carbonic acid passes through joints and cracks in limestone → calcite is dissolved from limestone → water now holds dissolved rock and when exposed to air in the cave it releases carbon dioxide gas → when carbon dioxide gas is release calcite is precipitated on cave ceilings (stalacite) and cave floors (stalagmite) and over time they will grow to meet and make a limestone column
* calcite:
* carbonic acid passes through joints and cracks in limestone → calcite is dissolved from limestone → water now holds dissolved rock and when exposed to air in the cave it releases carbon dioxide gas → when carbon dioxide gas is release calcite is precipitated on cave ceilings (stalacite) and cave floors (stalagmite) and over time they will grow to meet and make a limestone column
43
New cards
cone of depression
* pumping water from a well in a water table aquifer lowers the water table near the well
* land area above the cone of depression is called the area of influence
* can change the natural direction of groundwater flow within the area of influence around the well
* wells can run dry and contamination could occur
* acid mine waste, landfills, sewage, etc. can all lead to contamination of groundwater
* remediation work is required to preserve health
* land area above the cone of depression is called the area of influence
* can change the natural direction of groundwater flow within the area of influence around the well
* wells can run dry and contamination could occur
* acid mine waste, landfills, sewage, etc. can all lead to contamination of groundwater
* remediation work is required to preserve health
44
New cards
Deserts
* an area of land that recieves no more than 25 cm of precipitation a year
* temperature is not part of the definition
* type and cause of desert aridity varies globally
* temperature is not part of the definition
* type and cause of desert aridity varies globally
45
New cards
subtropical deserts
* global atmospheric circulation
* hadley cells: air rises at the equator → moisture comes from clouds and rains → air cools → air decends about fifteen to thirty degrees north or south of the equator
* descending dry air prevents cloud formation
* example: Sahara
* hadley cells: air rises at the equator → moisture comes from clouds and rains → air cools → air decends about fifteen to thirty degrees north or south of the equator
* descending dry air prevents cloud formation
* example: Sahara
46
New cards
Rain-Shadow deserts
* clouds form as air rises over mountains
* air is rained out by the time the air mass crests the mountain range
* mountains prevent cold air from travelling inward and by the time the air mass crests the mountain range the air is dry
* example: eastern california
* air is rained out by the time the air mass crests the mountain range
* mountains prevent cold air from travelling inward and by the time the air mass crests the mountain range the air is dry
* example: eastern california
47
New cards
coastal deserts
* related to cold ocean currents
* colder air masses with little to no moisture in them is dominant in these areas
* example: Atacama Desert, Chile/Peru
* colder air masses with little to no moisture in them is dominant in these areas
* example: Atacama Desert, Chile/Peru
48
New cards
Continental interior deserts
* far from ocean or source of moisture
* moisture has already been used up by the time the air mass reaches the desert
* Example: Gobi Desert, Central Asia
* moisture has already been used up by the time the air mass reaches the desert
* Example: Gobi Desert, Central Asia
49
New cards
Polar Deserts
* cold, dry air
* example: Antarctica
* example: Antarctica
50
New cards
Dunes
* form when there is a high enough sediment supply and winds that can transport it
* called Eolian Features and is found on other planets such as Mars
* called Eolian Features and is found on other planets such as Mars
51
New cards
Transverse Dunes
* characterized by slipfaces in one direction - representing unidirectional wind regime

52
New cards
Barchan Dunes
* crescent shape
* only one wind direction
* only one wind direction

53
New cards
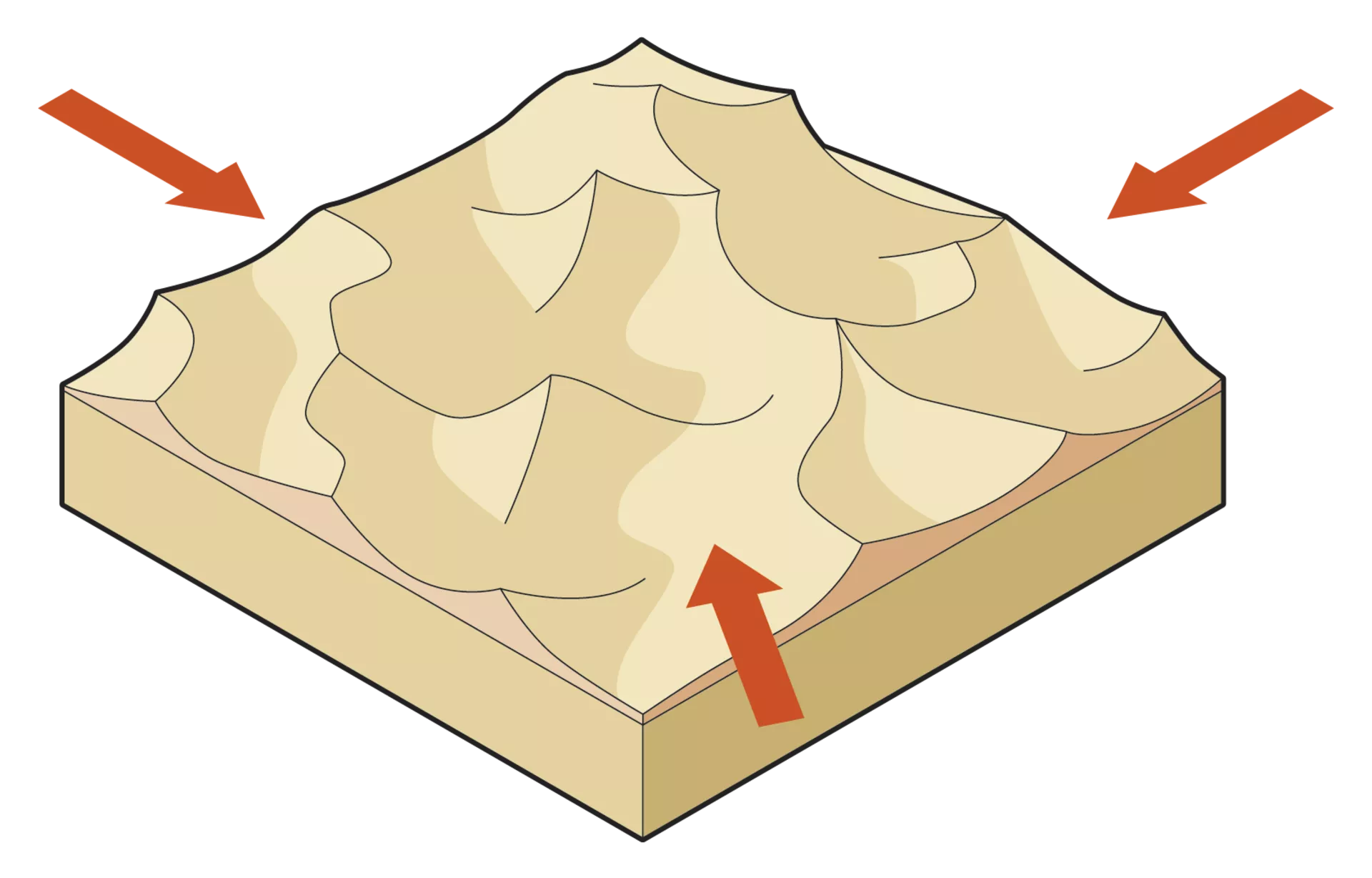
Star Dunes
* multiple wind directions
* wind blows from varied directions throughout the year
* wind blows from varied directions throughout the year
54
New cards
Glaciers
* slowly moving mass or river of ice formed by the accumulation and compaction of snow on mountains or near the poles
* stream or sheet of recrystalized ice
* mostly frozen all year round
* flows under the influence of gravity
* snow at surface transforms into solid ice
* snow → firn → ice
* firn: granular snow not yet pressed into ice
* stream or sheet of recrystalized ice
* mostly frozen all year round
* flows under the influence of gravity
* snow at surface transforms into solid ice
* snow → firn → ice
* firn: granular snow not yet pressed into ice
55
New cards
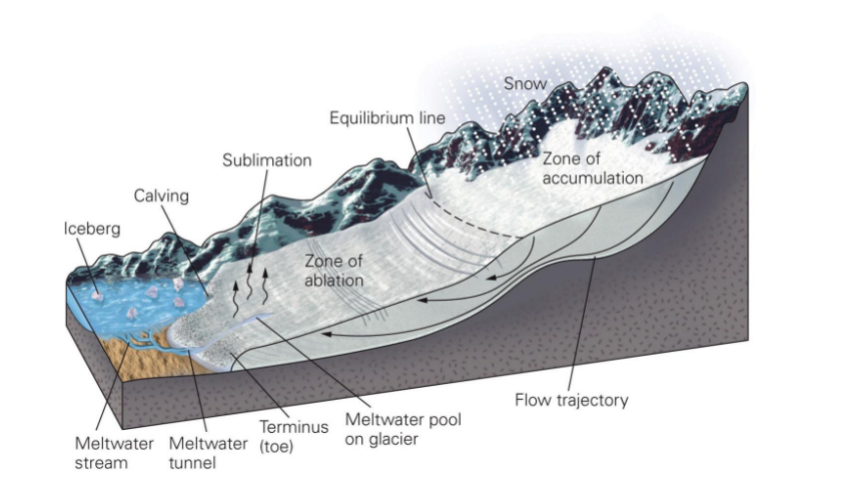
mountain glaciers
* balance on accumulation and loss
* growth/accumulation at high elevation: snowfall
* loss/ablation at low elevation: melting/calving/sublimation
* flow: from high to low
* retreat/advance of glaciers happens at the toe of the glacier NOT at the origin
* growth/accumulation at high elevation: snowfall
* loss/ablation at low elevation: melting/calving/sublimation
* flow: from high to low
* retreat/advance of glaciers happens at the toe of the glacier NOT at the origin
56
New cards
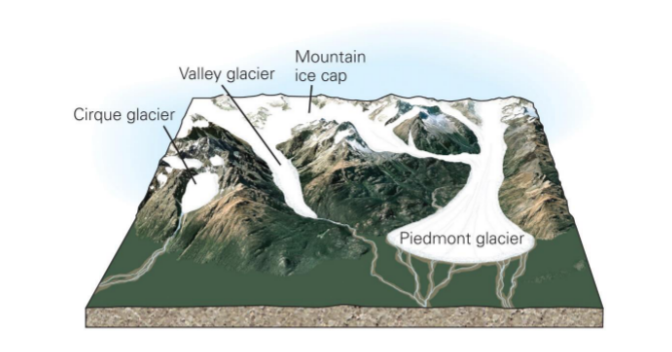
glacier types
* based on typography
* cirque glacier
* bowl-shaped, ampitheater like depressions that glaciers carve into mountains at high elevations
* valley glacier
* glacier that is flowing downward between walls of a valley
* piedmont glacier
* a valley glacier that spills out of mountains onto the flat foreland - spreading out to form a lobe
* cirque glacier
* bowl-shaped, ampitheater like depressions that glaciers carve into mountains at high elevations
* valley glacier
* glacier that is flowing downward between walls of a valley
* piedmont glacier
* a valley glacier that spills out of mountains onto the flat foreland - spreading out to form a lobe
57
New cards
continental glaciers
* currently only in Greenland and Antarctica
* used to be on other continents
* used to be on other continents
58
New cards
Glacial distinctive landforms
* glacial erosion
* movement of glacial ice over bed
* scrapes away rock
* cirques
* bowl like structures in mountains (usually left behind by cirque glaciers)
* aretes
* narrow ridge of rock that seperates two valleys
* glaciers eroding towards each other
* horns
* pointed peaks that are bounded on at least 3 sides by glaciers
* caused by erosion
* hanging valleys
* glaciers forming a U-shaped valley through erosion
* movement of glacial ice over bed
* scrapes away rock
* cirques
* bowl like structures in mountains (usually left behind by cirque glaciers)
* aretes
* narrow ridge of rock that seperates two valleys
* glaciers eroding towards each other
* horns
* pointed peaks that are bounded on at least 3 sides by glaciers
* caused by erosion
* hanging valleys
* glaciers forming a U-shaped valley through erosion
59
New cards
glacial deposits
* glaciers move sediment
* fine glacial “flour” to boulders
* results in glacial till - sediment deposited by a glacier
* supraglacial (on top of ice)
* englacial (within the ice)
* subglacial (below the ice)
* morraines - materials left behind by a glacier
* deposits can be used to determine past glaciers
* fine glacial “flour” to boulders
* results in glacial till - sediment deposited by a glacier
* supraglacial (on top of ice)
* englacial (within the ice)
* subglacial (below the ice)
* morraines - materials left behind by a glacier
* deposits can be used to determine past glaciers
60
New cards
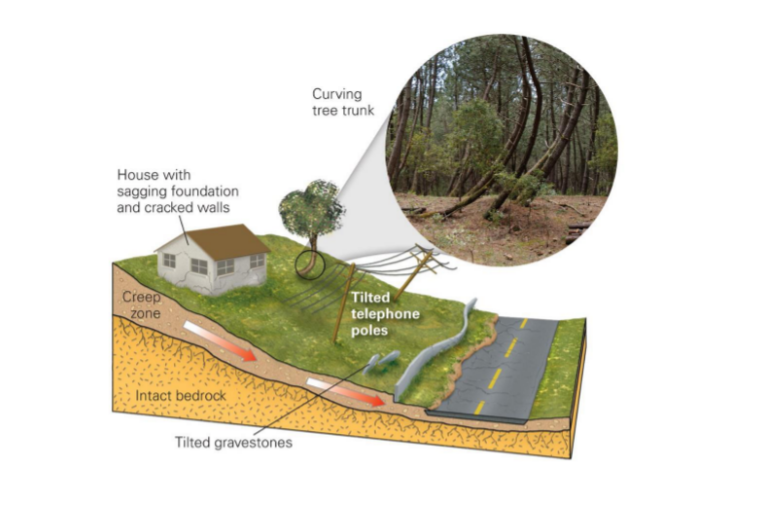
Creep
* takes place in soil zone
* movement caused by shear stress sufficient to produce permanent deformation
* can be seen in areas that experiene constant alternation of wetting and drying periods
* 3 types
* seasonal - affected by seasonal changes in soil moisture/temperature
* continuous - shear stress continuously exceeds strength of material
* progressive - slopes are reaching the point of failure as other types of mass movements
* movement caused by shear stress sufficient to produce permanent deformation
* can be seen in areas that experiene constant alternation of wetting and drying periods
* 3 types
* seasonal - affected by seasonal changes in soil moisture/temperature
* continuous - shear stress continuously exceeds strength of material
* progressive - slopes are reaching the point of failure as other types of mass movements
61
New cards
slumping
* failure along a surface
* takes place in think unconsolidated deposits
* referred to as a rotational slide
* portion or block of the slope ‘slides’ down as it ‘rotates’ around an axis parallel to the slope
* takes place in think unconsolidated deposits
* referred to as a rotational slide
* portion or block of the slope ‘slides’ down as it ‘rotates’ around an axis parallel to the slope
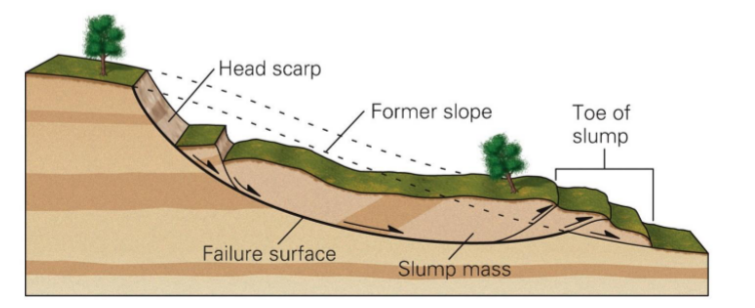
62
New cards
landslides
* forces acting down-slope exceed the strength of the earth materials that compose the slopes
* 5 different modes
* falls
* loose material - talus
* breaking off rocks from steep bedrock slopes
* topples
* loose blocks that lean forward before collapsing
* slides debris/rock
* debris (unconsolidated) and rock (consolidated)
* rotational or translational (PICTURE)
* spreads
* extension of soil or rock
* extrusion of underlying material
* often lateral
* flows
* loose material
* flow mixed with water downslope
* occurs during rapid snowmelts or heavy rains
* if the material involved is primarily sand-sized or smaller: mudflow
* if the material involved is primarily gravel-sized or larger - debris flow
* 5 different modes
* falls
* loose material - talus
* breaking off rocks from steep bedrock slopes
* topples
* loose blocks that lean forward before collapsing
* slides debris/rock
* debris (unconsolidated) and rock (consolidated)
* rotational or translational (PICTURE)
* spreads
* extension of soil or rock
* extrusion of underlying material
* often lateral
* flows
* loose material
* flow mixed with water downslope
* occurs during rapid snowmelts or heavy rains
* if the material involved is primarily sand-sized or smaller: mudflow
* if the material involved is primarily gravel-sized or larger - debris flow
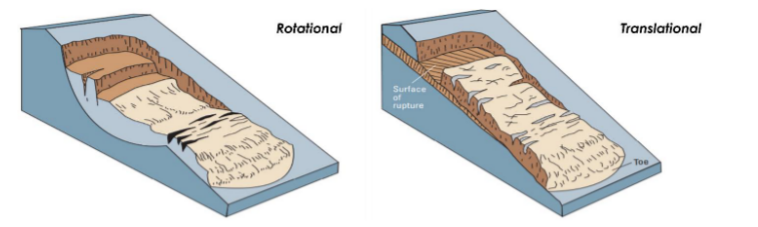
63
New cards
avalanches
* mass movement of snow
* can be caused by
* heavy snowfall
* deforestation - makes the slope less stable
* vibrations - from EQ or noise
* layering of snow - fresh snow can slide down ice
* wind direction
* can be caused by
* heavy snowfall
* deforestation - makes the slope less stable
* vibrations - from EQ or noise
* layering of snow - fresh snow can slide down ice
* wind direction
64
New cards
slope failure
* angle of repose - slope stability
* depends on types of material
* many factors can trigger slope failure
* EQ or vibrations
* undercutting - an erosion of material at the foot of a cliff or steep bank
* change in slope strength - weakening of slope surface
* depends on types of material
* many factors can trigger slope failure
* EQ or vibrations
* undercutting - an erosion of material at the foot of a cliff or steep bank
* change in slope strength - weakening of slope surface
65
New cards
terracing
\
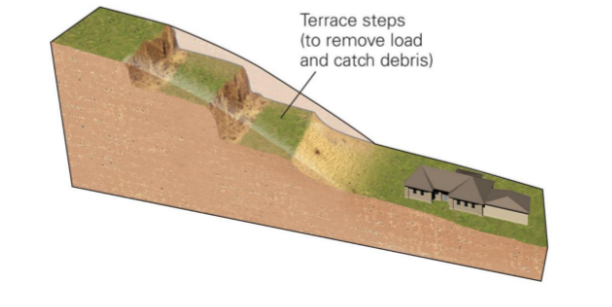
66
New cards
rip-rap
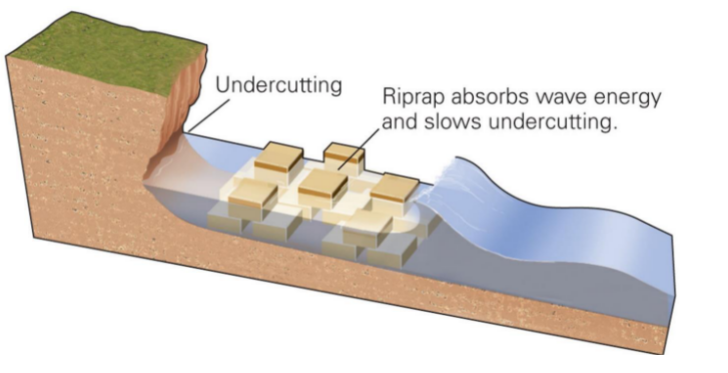
67
New cards
forestation
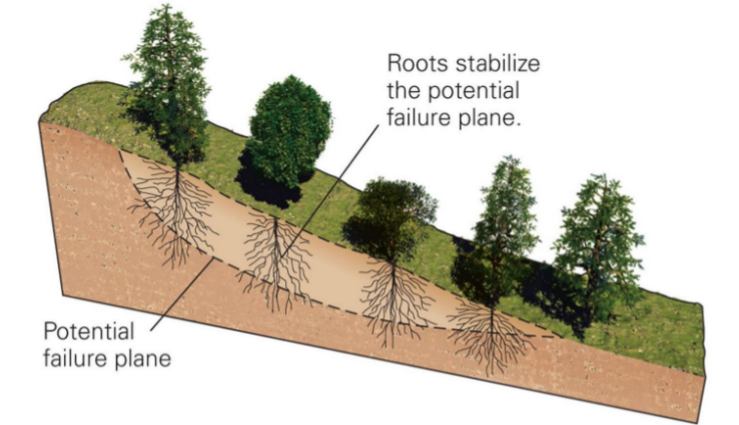
68
New cards
geological resources
* energy resources
* hydrocarbon
* oil, gas, coal
* nuclear fuel
* uranium
* mineral resources
* nonmetallic
* rock, sand salts
* ores
* primarily in industrialized countries
* massive amounts per person
* hydrocarbon
* oil, gas, coal
* nuclear fuel
* uranium
* mineral resources
* nonmetallic
* rock, sand salts
* ores
* primarily in industrialized countries
* massive amounts per person
69
New cards
ore requirements
* rock must contain ore minerals
* must be abundant enough to be economically extractable
* depends on
* concentration of ore minerals
* ability to extract/extraction process
* cost of metal
* form through magmatic processes
* concentration determined by crystalization
* heavy ore minerals crystallize together
* chromite
* PGE (platinum group element) sulfides
* ores form via hot water interacting with rock
* water infiltrates ground → interacts w/ magma → creates future ores
* magmatic intrustions are heat source
* heat causes water circulation
* extraction/reprecipitation of metals
* mineralization (metal sulfides) - formed by hydrothermal processes
* must be abundant enough to be economically extractable
* depends on
* concentration of ore minerals
* ability to extract/extraction process
* cost of metal
* form through magmatic processes
* concentration determined by crystalization
* heavy ore minerals crystallize together
* chromite
* PGE (platinum group element) sulfides
* ores form via hot water interacting with rock
* water infiltrates ground → interacts w/ magma → creates future ores
* magmatic intrustions are heat source
* heat causes water circulation
* extraction/reprecipitation of metals
* mineralization (metal sulfides) - formed by hydrothermal processes
70
New cards
ores in sediments
* direct precipitation from waters
* banded iron formations
* ores are then concentrated by erosion
* stream transport
* ore vein on cliff side → ore falls and breaks up as it tumbles down → picked up and taken down stream via river current → grains are sorted within the mineral
* called placer deposits - california gold rush
* banded iron formations
* ores are then concentrated by erosion
* stream transport
* ore vein on cliff side → ore falls and breaks up as it tumbles down → picked up and taken down stream via river current → grains are sorted within the mineral
* called placer deposits - california gold rush
71
New cards
Energy
* nuclear
* geothermal
* hydrocarbon
* fossil fuels
* geothermal
* hydrocarbon
* fossil fuels
72
New cards
oil and gas
* oil forms in sedimentary basin
* burial → heating → migration
* source: oil formation rock
* migration: movement upwards
* reservoir: contains oil deposit
* trap: seals rock and prevents loss
* burial → heating → migration
* source: oil formation rock
* migration: movement upwards
* reservoir: contains oil deposit
* trap: seals rock and prevents loss
73
New cards
oil reserves
* found in different parts around the world
* accurately measured by drilling
* recoverable economically at current prices with current technology
* must be extracted \*
* different than resources
* resources are geologically proven but not extractable
* accurately measured by drilling
* recoverable economically at current prices with current technology
* must be extracted \*
* different than resources
* resources are geologically proven but not extractable
74
New cards
conventional gas
* trapped with oil
* more bouyant less viscous
* more bouyant less viscous
75
New cards
unconventional gas
* harder to extract
* found lower in rock where it is harder to extract
* shale gas - unconventional reservoir
* horizontal drilling - fracking
* found lower in rock where it is harder to extract
* shale gas - unconventional reservoir
* horizontal drilling - fracking
76
New cards
environmental impacts
* emissions
* disruption of wild areas
* oil spills
* Co2 buildup -climate change
* acid rain
* pyrite in coal releases CO2 when burned, forms sulfuric acid in rainwater and is augmented to form nitric acid
* Acid mine drainage
* contamination of wells and waterways
* issue in Marcellus Shale region
* fracking fluid contaminates groundwater
* induced earthquakes
* from hydraulic fracture process
* disruption of wild areas
* oil spills
* Co2 buildup -climate change
* acid rain
* pyrite in coal releases CO2 when burned, forms sulfuric acid in rainwater and is augmented to form nitric acid
* Acid mine drainage
* contamination of wells and waterways
* issue in Marcellus Shale region
* fracking fluid contaminates groundwater
* induced earthquakes
* from hydraulic fracture process
77
New cards
Venus
* atmosphere 92 times thicker than Earth’s
* dominated by carbon dioxide
* traps more solar radiation as a result
* dominated by carbon dioxide
* traps more solar radiation as a result
78
New cards
Mars
* 168 times thinner than Earth’s
* dominated by carbon dioxide
* ancient riverbed flows on Mars
* used to have running water
* flowing water = thicker atmosphere and higher temperatures
* ice caps - alternating sediments and ice = seasons
* dominated by carbon dioxide
* ancient riverbed flows on Mars
* used to have running water
* flowing water = thicker atmosphere and higher temperatures
* ice caps - alternating sediments and ice = seasons
79
New cards
Earth
* atmosphere is different from venus because of plate tectonics and the recycling of materials
* venus and mars do not have plate tectonics
* warm periods/ice ages
* variable resolution record
* poor resolution in distant past
* better resolution closer to the present
* venus and mars do not have plate tectonics
* warm periods/ice ages
* variable resolution record
* poor resolution in distant past
* better resolution closer to the present
80
New cards
past climate determination
* certain fossils can record climate conditions
* fossil pollen
* often in lake sediments
* grass pollen = warmer
* tree pollen = colder
* sea level provides information
* relative extent (volume) of world’s oceans are preserved in sedimentary record
* functions of temperature and glacial extent
* fossil pollen
* often in lake sediments
* grass pollen = warmer
* tree pollen = colder
* sea level provides information
* relative extent (volume) of world’s oceans are preserved in sedimentary record
* functions of temperature and glacial extent
81
New cards
oxygen isotopes
* reveals past climate through glaciation
* ratio of oxygen 16 to 18
* oxygen 18 is heavier and harder to evaporate
* non-glacial period
* ratio of oxygen 16 to 18 is more similar because of water runoff
* glacial period
* more oxygen 18
* ocean water is more isotopically heavy
* ratio of oxygen 16 to 18
* oxygen 18 is heavier and harder to evaporate
* non-glacial period
* ratio of oxygen 16 to 18 is more similar because of water runoff
* glacial period
* more oxygen 18
* ocean water is more isotopically heavy
82
New cards
Variation in Earth’s climate
* Short term
* tree rings
* grow wider in warm, wet years and they are thinner in years when it is cold and dry
* lake cores (varves)
* seasonal sediment alternations which appear to represent annual cycles
* Long term
* extensive warm periods
* ice ages
* tree rings
* grow wider in warm, wet years and they are thinner in years when it is cold and dry
* lake cores (varves)
* seasonal sediment alternations which appear to represent annual cycles
* Long term
* extensive warm periods
* ice ages
83
New cards
climate forcing
* plate tectonics - ocean currents, sea levels
* greenhouse gases
* volcanoes
* weathering
* biota
* the CO2 connection
* greenhouse gases
* volcanoes
* weathering
* biota
* the CO2 connection
84
New cards
CO2
* greenhouse gas
* traps heat radiating from the Earth’s surface
* CO2 correlates with temperature in the geological record
* depends on the global carbon cycle
* traps heat radiating from the Earth’s surface
* CO2 correlates with temperature in the geological record
* depends on the global carbon cycle
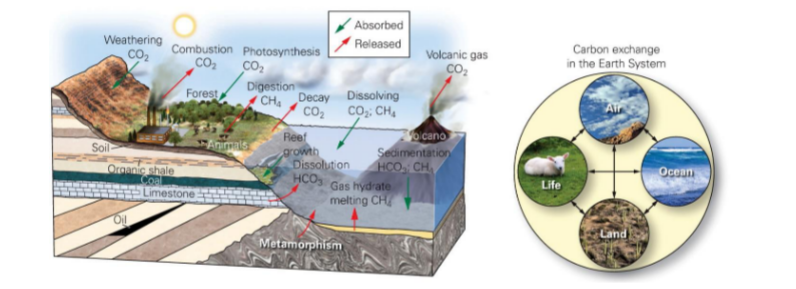
85
New cards
solar luminosity
* “faint young sun paradox”
* early sun was smaller and created less energy
* early sun was smaller and created less energy
86
New cards
Milankovitch Cycles
* explain glacial-interglacial variations
* recent rapid swings in climate
* three types of Earth’s orbital movements
* affect how much solar radiation reaches the top of the Earth’s atmosphere
* recent rapid swings in climate
* three types of Earth’s orbital movements
* affect how much solar radiation reaches the top of the Earth’s atmosphere
87
New cards
Eccentricity
* change in the shape of the Earth’s orbit
* 100,000 year periodicity
* affects season length
* 100,000 year periodicity
* affects season length
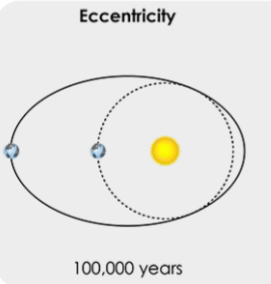
88
New cards
axial tilt
* change in the Earth’s rotational axis tilt
* 41,000 year periodicity
* less tilt = glacial periods
* more tilt = inter-glaciations
* 41,000 year periodicity
* less tilt = glacial periods
* more tilt = inter-glaciations
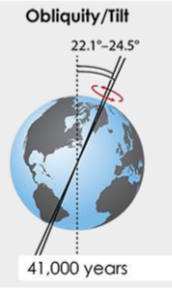
89
New cards
axial precession
* “wobble” of the Earth’s axis
* 23,000 year periodicity
* makes seasonal contrasts more extreme in one hemisphere than the other
* 23,000 year periodicity
* makes seasonal contrasts more extreme in one hemisphere than the other
90
New cards
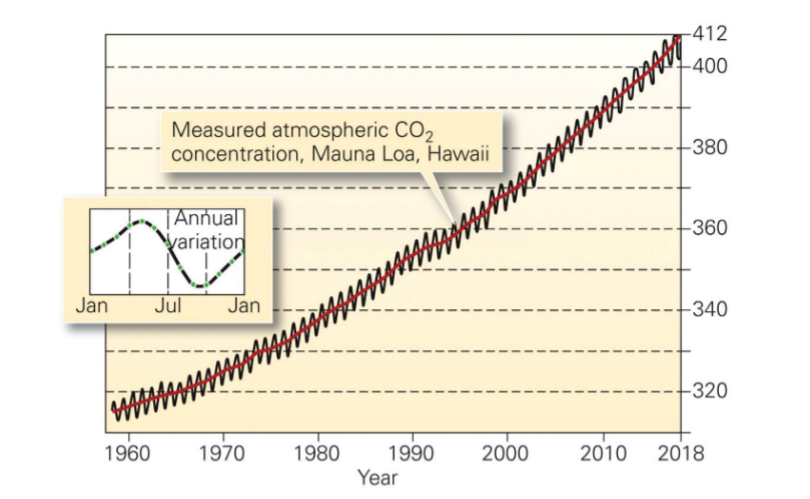
zig-zag in graph
* caused by seasons
* winter months pull less CO2
* shows influence of plants in the atmosphere
* CO2 has never been higher in the past millions of years
* winter months pull less CO2
* shows influence of plants in the atmosphere
* CO2 has never been higher in the past millions of years
91
New cards
what can we expect in the future for climate change?
* fossil fuels short circuit the carbon cycle
* exacerbated by deforestation
* higher average global temperatures
* continued loss of ice - sea levels rising
* increased number of extreme storm events
* exacerbated by deforestation
* higher average global temperatures
* continued loss of ice - sea levels rising
* increased number of extreme storm events