Bio 269 Lab Exam 1
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
what does GSR measure?
skin conductance
What are the units of GSR?
microsiemens (uS)
How is the GSR related to the ANS activity?
during a GSR, sweat glands are innervated by the sympathetic branch of the ANS and fill with fluid and skin resistance decreases
How is the GSR affected by stressful stimuli?
when sympathetic activity increases, an increase in sweat production occurs, thereby increasing skin conductance
What happens to the GSR recording
and its underlying physiological processes when the stressful stimulus is removed?
when the stress is removed, GSR decreases because the sweat glands are no longer being innervated
What physiological process is skin temperature an indicator of?
blushing, metabolism
How is skin temperature related to the autonomic nervous system?
circulation in the microvasculature is under autonomic control
How is skin temperature affected by stressful stimuli?
stress responses that activate the sympathetic nervous system usually result in reduced peripheral circulation- cases decrease in skin temperature; strong signal from the parasympathetic nervous system can cause a localized increase in peripheral circulation (blushing)
Describe the changes that occur to pulse rate and depth when the ANS is up regulated
When the ANS is up regulated, norephrine is released by sympathetic upregulation, causing pulse rate to increase
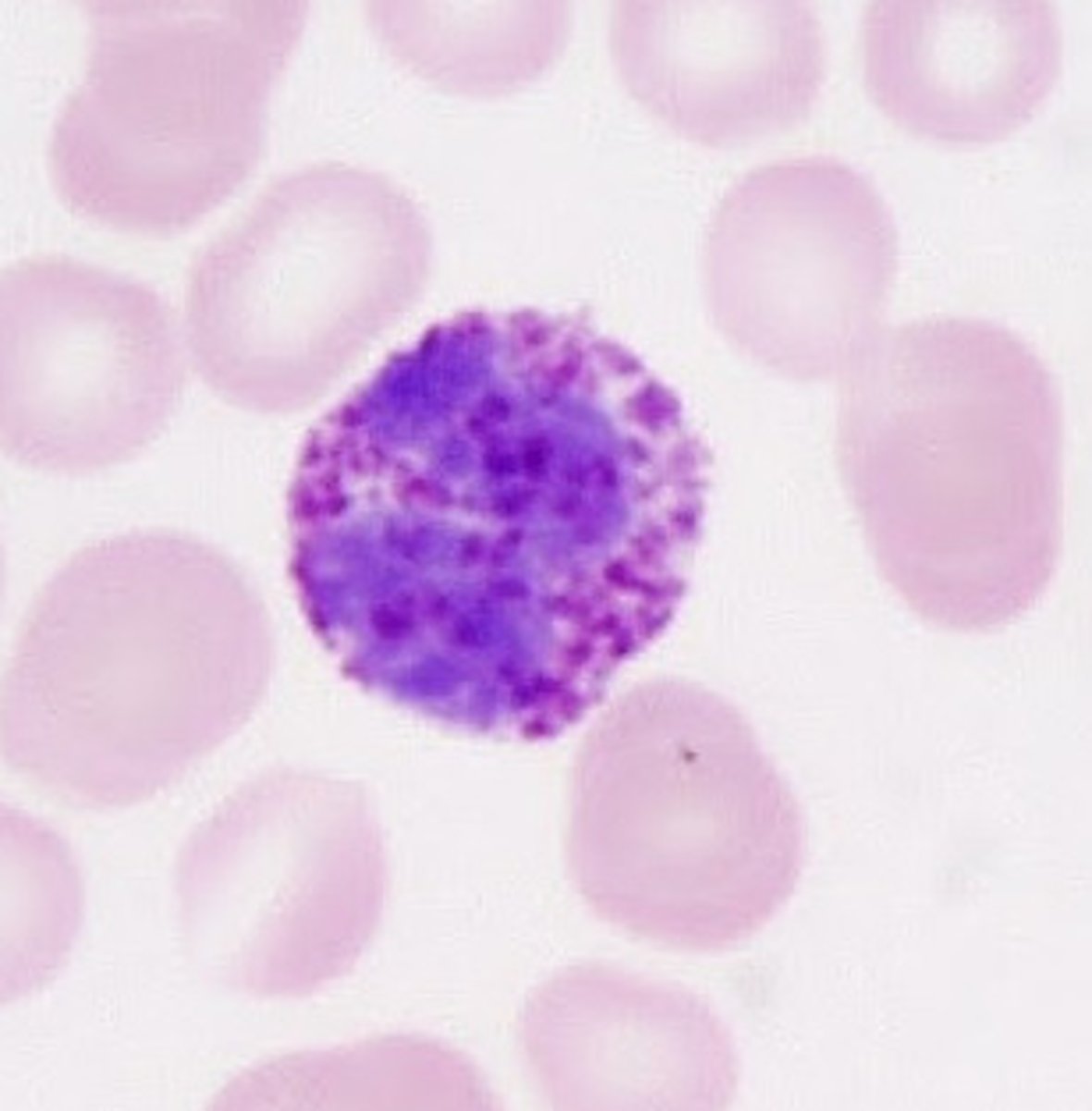
Basophil
has granulocytes
lighter purple overall color and big black nucleus
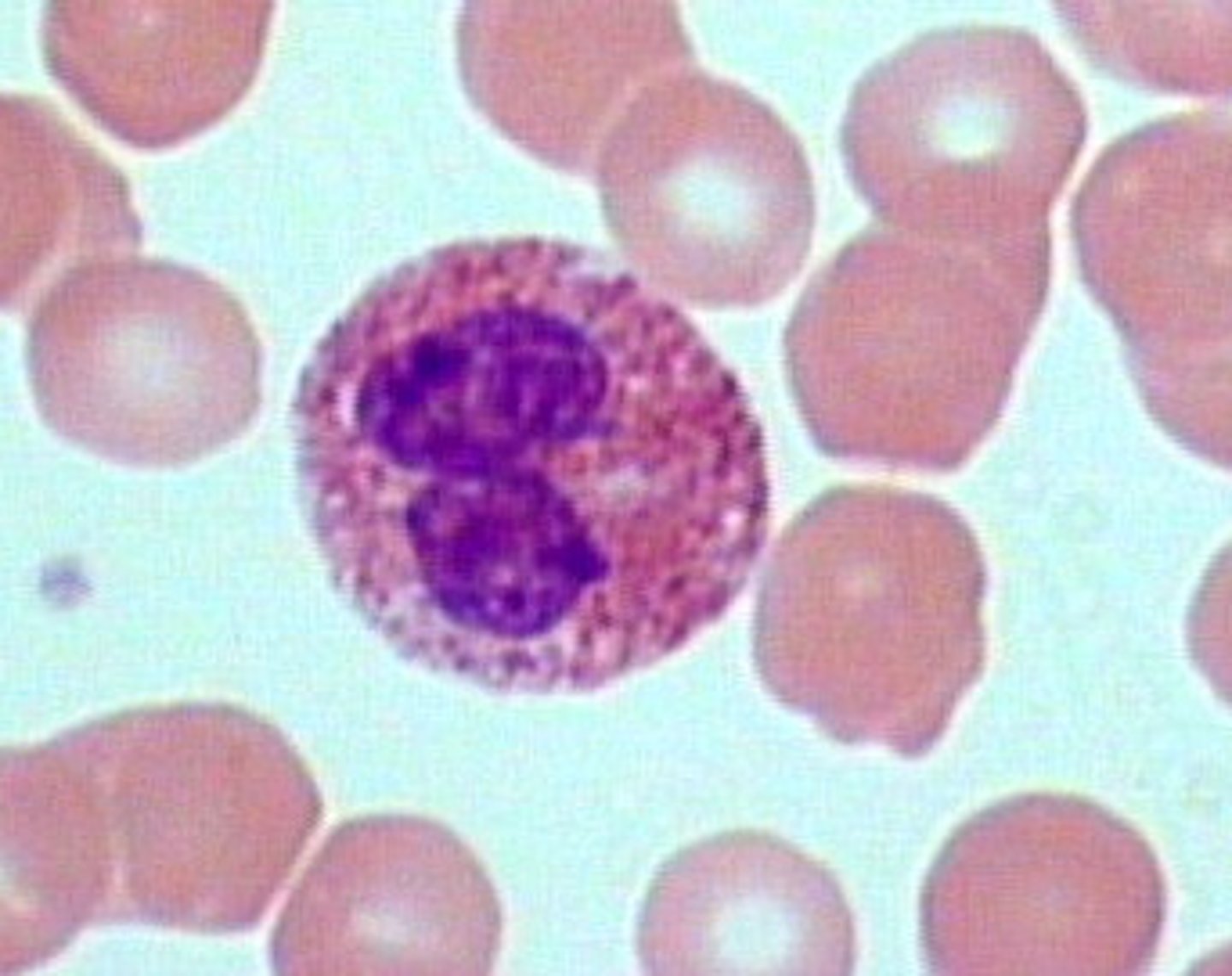
Eosinophil
has granulocytes
nucleus is bi lobed
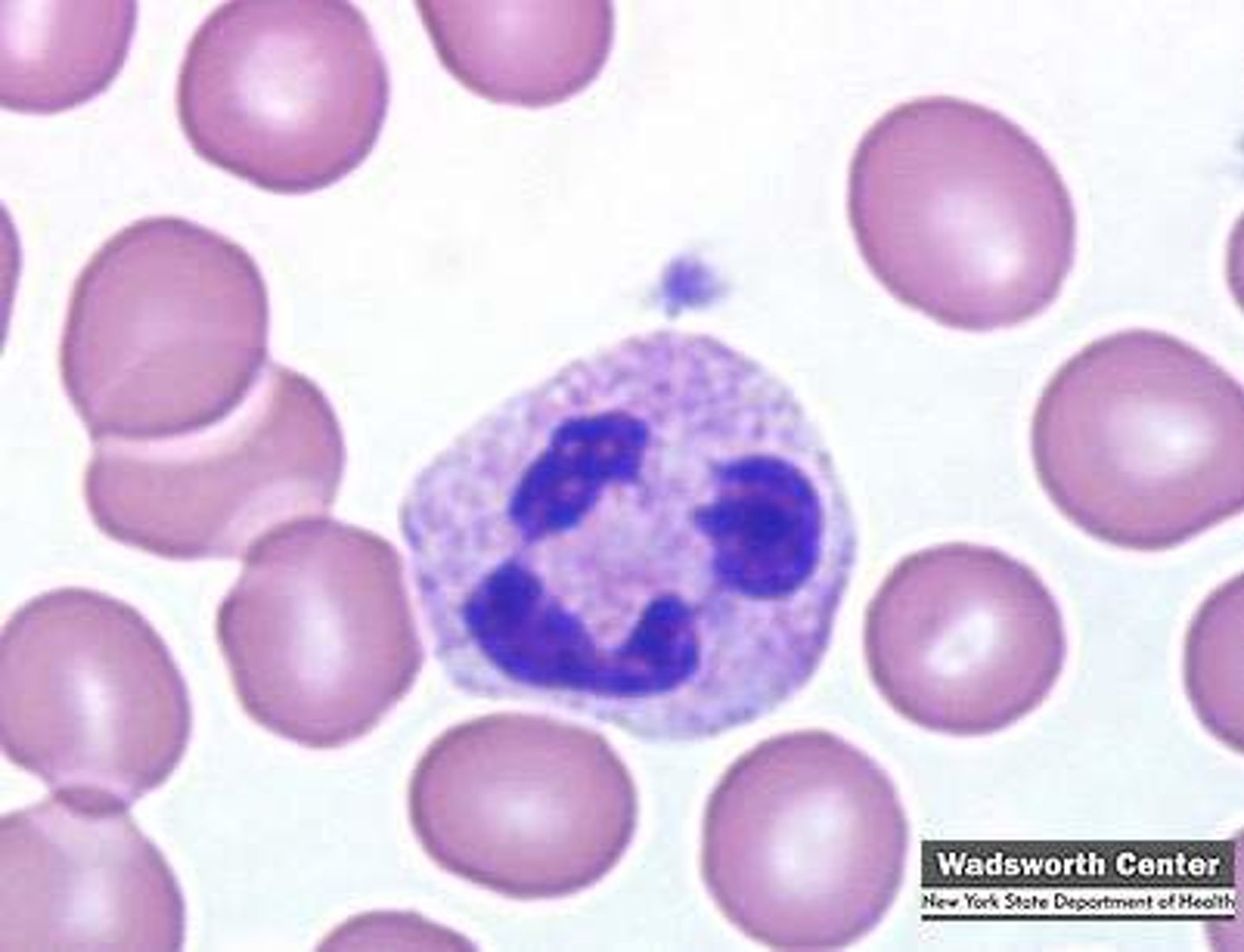
neutrophil
has granulocytes
nucleus has numerous lobes
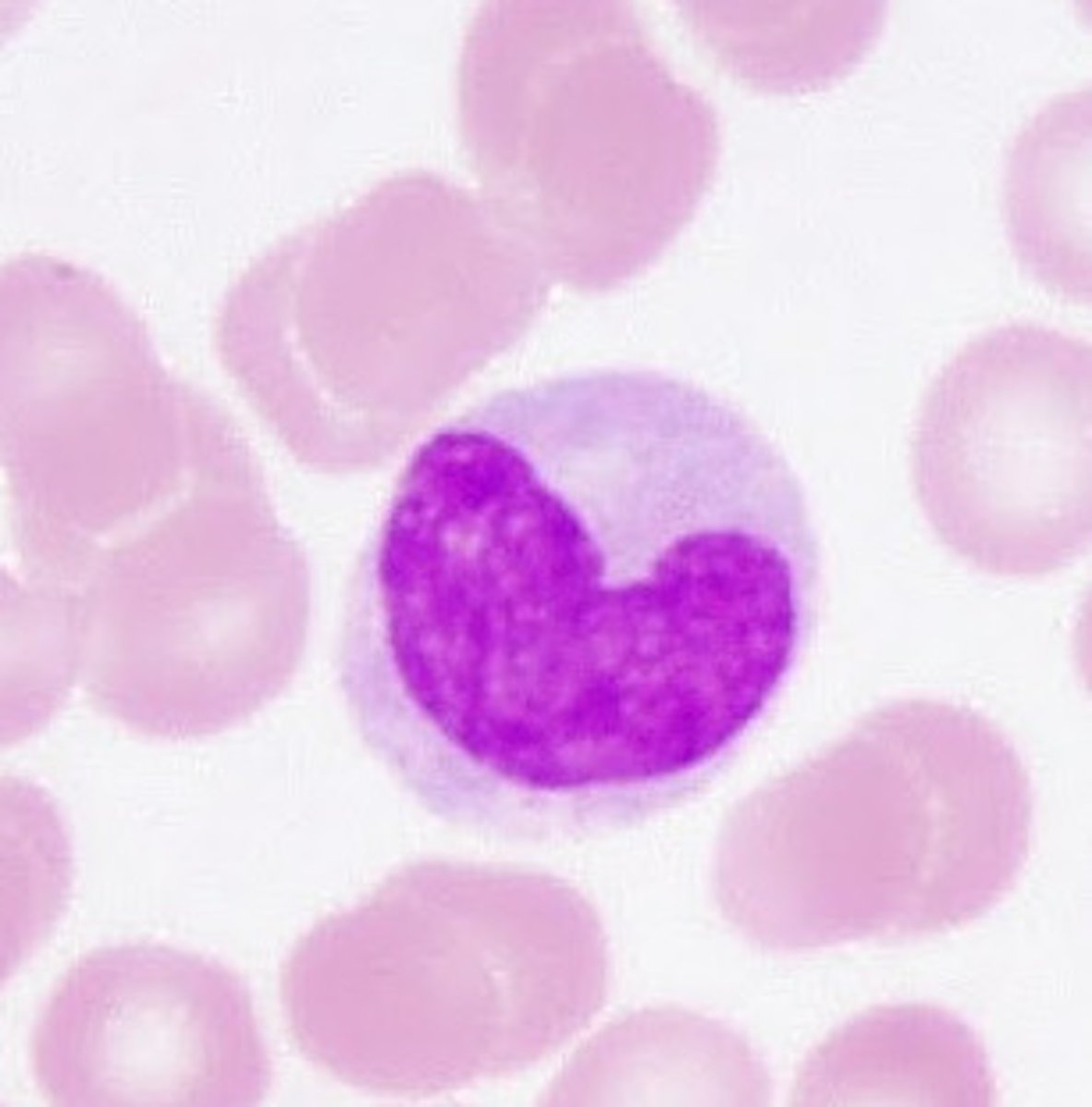
monocyte
nucleus looks like a kidney and has no granulocytes
lymphocyte
large nucleus
"lunar" darker purple color
no granulocytes
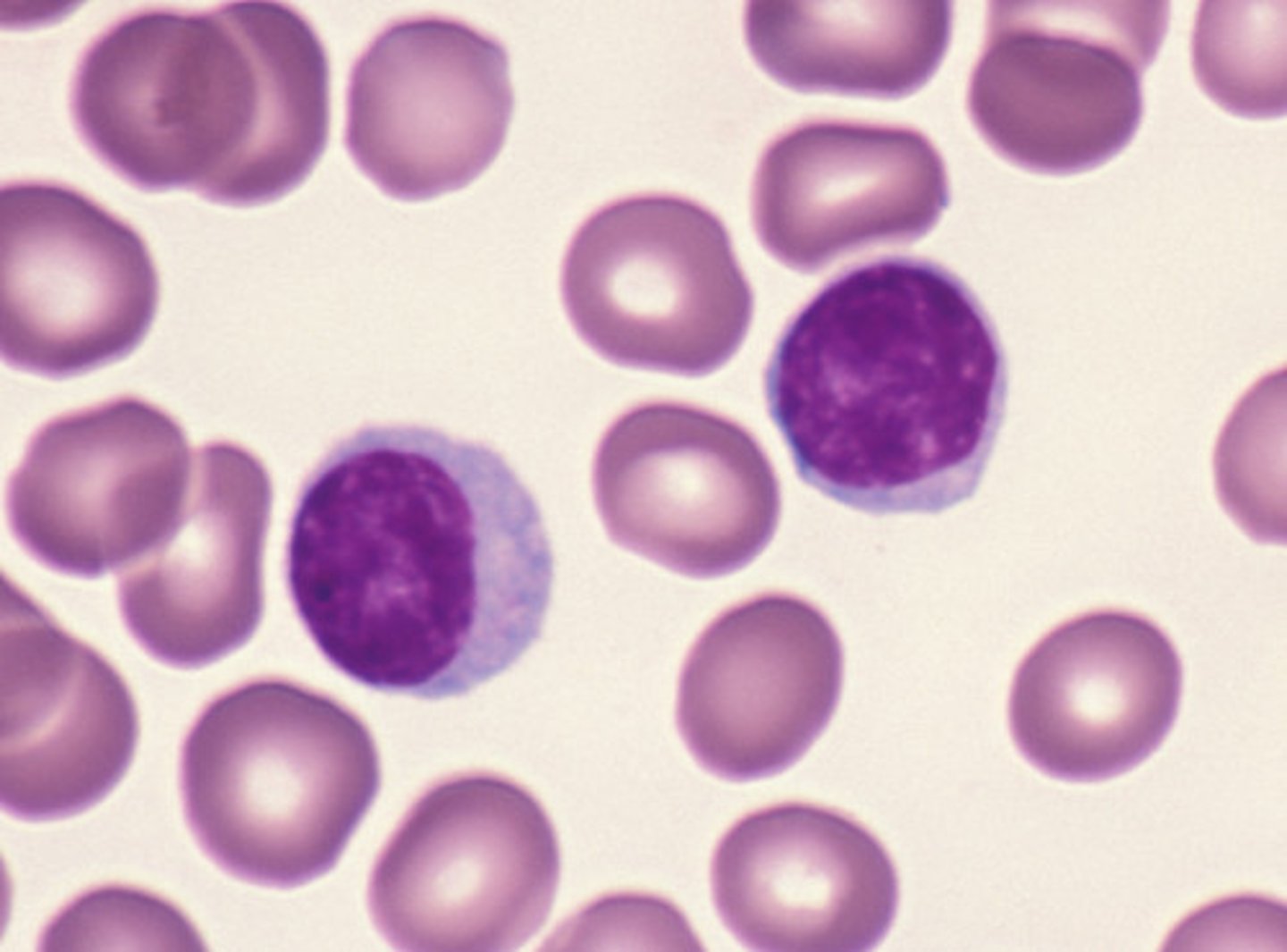
What is the least abundant WBC?
basophils
What is the most abundant WBC?
Neutrophils (60-70%)
Hematocrit
The percent of the volume of whole blood that is composed of red blood cells
how is a hematocrit used?
How is hematocrit determined?
Determined by using a centrifuge
calculation for RBC count
count number of rbc's in 5 squares then multiply by 10,000
calculation for WBC count
count number of wbc's in 4 squares then multiply by 10,000
calculation for MHCH
Hb (g/dL Blood)
_______________ x 100
hematocrit (%)
normal value for humans is 32-36%
calculation for MCV
hematocrit x 10 / RBC count
Agglutination
clumping of red blood cells
what is the significance of agglutination?
if agglutination occurs after adding antibodies to blood, it means that an antigen is present
how do you determine blood type for ABO?
based on antigens on rbcs and antibodies in plasma
how do you determine blood type for Rh?
+ or - for Rh factor
what is happening during the first heart sound?
early phase of ventricular contraction; Av valves are closing
what is happening during the second heart sound
onset of diastole; semilunar valves closing
Heart Anatomy
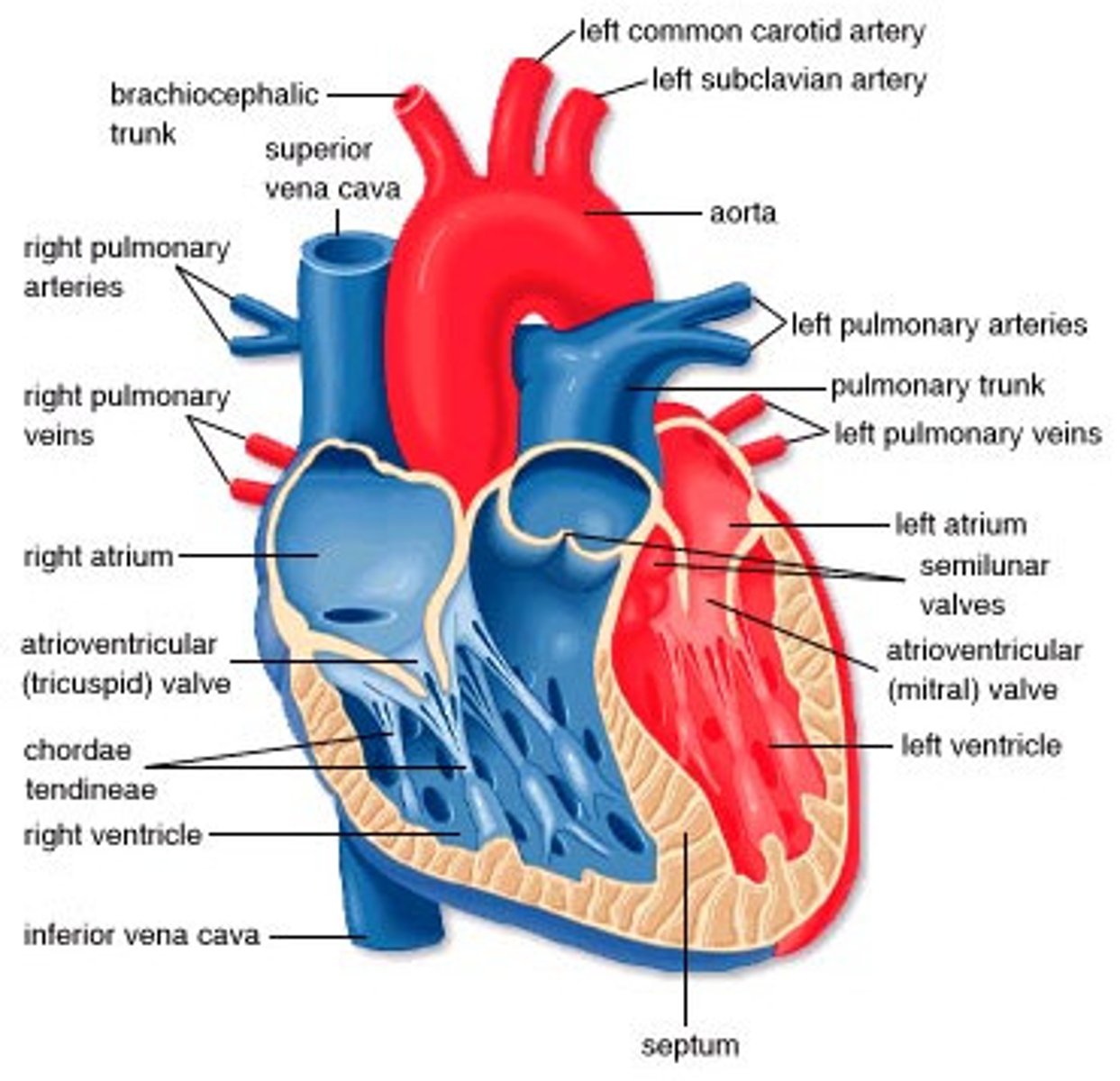
what does the P wave of an ECG represent?
depolarization (contraction) of the atria
What does the QRS complex represent?
ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
What does the T wave represent?
repolarization/relaxation of ventricles
What does the PR interval indicate?
Combined atrial and AV conduction delay.
What does the QT interval indicate?
the total timing of the refractory period of ventricular systole
what does the ST interval tell you
when ventricular myocites are in their plateau phases, the entire ventricular myocardium is depolarized
What does the RR interval tell you?
one heart beat
how do you measure heart rate from an ECG trace?
60 seconds/R-R interval = beats per minute
how do you measure the time periods of systole and diastole from an ECG trace?
The peak of the R in the QRS complex is where systole starts, ends just after T wave
Diastole everywhere else
What do heart sounds represent?
-S1: Closing of AV valves
-S2: closing of aortic and pulmonary valves
and blood reverberating back on them
how do you measure systole and diastole from the trace of heart sounds?
-S1: onset of ventricular systole
-S2: onset of early diastole
what is the relationship of electrical signals of an ECG to heart sounds?
S1: occurs between R and S
S2: occurs right after T wave
how do you measure blood pressure?
sphygmomanometer
what do the numbers mean when measuring blood pressure?
systolic: the pressure in your arteries when your heart is pumping
diastolic: pressure inside arteries when heart is resting between beats
what is the mechanism responsible for the changes in blood pressure when you change position from lying down to standing up?
When you are lying down, the effect of gravity on your body is reduced, allowing more blood to flow back to your heart through your veins (low bp). Because more blood returns to the heart, the body is able to pump more blood per beat, which means that less beats per minute are required to satisfy your body's demand for blood, oxygen and nutrients. If you move from a lying or sitting position to a standing position, you may experience a sudden increase in heart rate (increase in BP).
what factors are important for increasing or decreasing BP?
When there is a greater volume of fluid, more fluid presses against the walls of the arteries resulting
in a greater pressure.
When there is less volume there is less pressure.
if you increase blood volume, what happens to BP?
bp will increase
MCHC- mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
Why is it useful?
useful in evaluating the clinical response of an anemic patient to therapy
the normal value for humans of MCHC is
32-36%
why does bp increase from sitting to standing?
increased force of contraction and fighting agaisnt gravity
why might a very fit person have a lower heart rate
their heart is stronger and more conditioned (its a muscle) which allows them to move more blood per beat so there isnt a need for as many beats (more efficient at pumping/circulating blood= doesnt have to work as hard)
what % of blood is Rbcs?
45%
what % of blood is wbcs
1%
what are normal hemoglobin levels for males and females
males: 16g/100ml
females: 13g/100ml
what does an elevated MCHC mean?
spherocytosis- production of spherical RBCs that are destroyed by the spleen
what does a low MCHC mean
iron deficiency
what is MCV
mean corpuscular volume- measure of the average blood cell volume
if MCV is elevated...
RBCs are larger than normal - vitamin b12 deficiency anemia
if MCV is depressed...
RBCs are smaller than normal- iron deficiency anemia
Agglutinogens
antigens on the surface of the RBC that is the basis for blood typing
what does less than 45% rbc in blood mean
anemia- oxygen delivery problem
what does greater than 45% rbc in blood mean
polycythemia- circulation issue
average blood volume for males and females
Males: 5-6 L
Females: 4-5 L
plasma
liquid portion of blood; makes up 54%
platelets
make up 1%
blood type A
has A antigens present on RBC membranes; has anti-b antibodies present in plasma
blood type b
antigen B, antibody A
blood type AB
A and B antigens and no antibodies (universal recipient)
blood type O
neither A or B antigens (universal donor);
has both anti A and anti B antibodies (can only receive from O)
MCV (mean corpuscular volume) formula
hematocrit (% rbcs) x10/rbc count (millions/mm^3)
factors causing anemia
rbc frailty, maturation deficiency, hemorrhage
What does MCHC stand for?
mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration