Intro to perception
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the 5 basic senses according to Aristole
Seeing (vision)
Taste (gustation)
Hearing (audition)
Touch (somatosensation)
Smell (olfaction)
What are the additional senses used to perceive the world beyond the five basic senses?
Balance (vestibular)
Body position (proprioception) - awareness of body perception in space
Pain (nociception)
Body motion (kinesthesia) - awareness of movement in space
What is the function of sensory modalities in the brain?
Sensory modalities convert energy from the outside world into neuronal communication within the brain.
What types of neural receptors are involved in sensory modalities?
Mechano – Detects air pressure waves, mechanical force, or motive force.
Chemo – Detects chemical (molecule) contact.
Noci – Detects damage to the body via mechanical or chemical contact.
Photo – Converts electromagnetic radiation into useful signals, processing vision.
All have different number of neurons
Why is vision considered one of the most prominent senses in humans?
Vision has the most neurons dedicated to it, making it a dominant sense compared to others like taste.
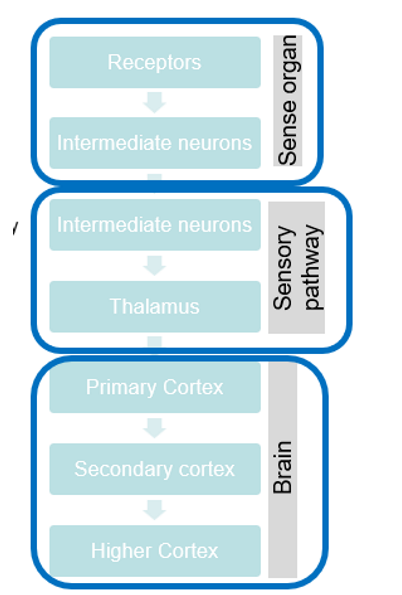
Where does sensory processing begin in the brain?
Sensory information is first processed in the sense organs (e.g. receptors) then by the sensory pathway (e.g. thalamus) and then by the brain (primary, secondary and higher cortexes).
What is the role of the homunculus in the brain?
The homunculus reflects cortical representation, showing how much of the brain is dedicated to processing different sensory information.
How does density of neurons relate to brain function?
The density of neurons is related to how much we use a particular part of the brain.
What are the three steps in understanding perception?
External stimuli arrive at the sense organ (e.g., light).
Sensory receptors produce a neural response. (what our brains do in response)
The brain generates a perceptual response based on the stimulus. (how we perceive the stimulus)
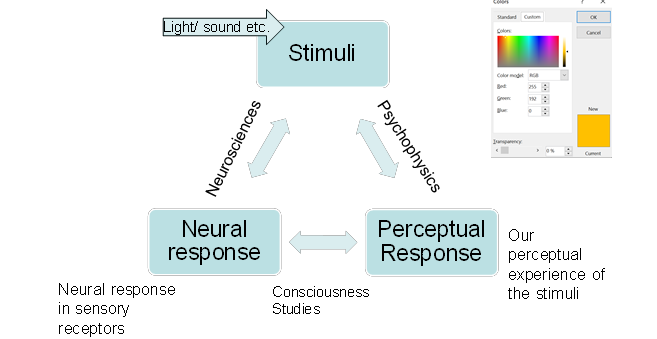
What is psychophysics?
Psychophysics is the study of how we perceive stimuli in our environment.
What does neuroscience focus on in relation to perception?
Neuroscience studies how the brain processes stimuli, often using imaging techniques.
What is the concept of Just Noticeable Difference (JND)?
JND is the minimum change required between two stimuli for it to be perceived as different.
e.g. start with orange and then ask is it more of less orange in 6 increments, when change is noted that is JND
What is Weber's Law?
Weber's Law states that JND is a constant fraction of the original stimulus, rather than an absolute number.
How does Fechner's Law relate to perception?
Fechner's Law suggests that sensory increments are equally spaced, not the stimuli themselves.
How does sensory adaptation affect perception?
Sensory adaptation helps prevent sensory overload, allowing the brain to adjust and focus on relevant stimuli over time (e.g., adjusting to a dark room)
What is visual prosopagnosia? (found in behavioural observations of neural responses)
Visual prosopagnosia is a condition where a person can see faces but cannot recognize them, due to processing issues in the brain.
what would be an invasive technique used to observe neural responses
Put electrode in cell In brain and present with images to see at what point the neurone decides to process the information
what is sound?
sound is a stimuli - mechanical wave of air pressure by vibrating air molecules
simple sounds (longitudinal waves)
complex sounds (average of several simple sounds)
what is amplitude, pitch and Hrtz
Hrtz - how many cycles per second
Higher amplitude (height of wave) = louder
More cycles = increase pitch (increase Hrtz)
What is the function of the outer and middle ear?
1) Vibrating sound wave
2) tympanic membrane (ear drum) vibrates
3) This moves the malleus incus and stapes (hammer anvil and stirrup) bones
4) vibrates oval window (this forms one end of the cochlea)
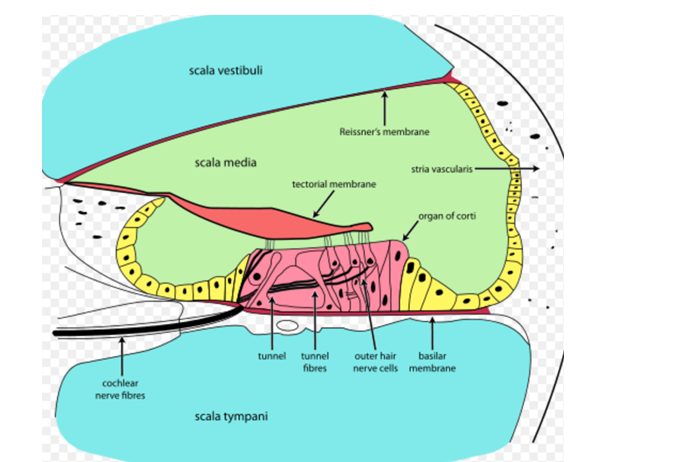
What is the function of the cochlea in the inner ear?
The cochlea processes sound vibrations and converts them into neural signals sent to the brain.
What are the different sections of the cochlea
Scala Vestibuli
Scala Media
Scala tympani
How does the cochlea process sound frequencies?
The vibration on the oval window causes the Basilar Membrane (BM) to vibrate. Different parts of the cochlea are tuned to different sound frequencies, with specific areas responding to certain pitches/vibrations, they vibrations move sensory hairs.
What are the two pathways used by the brain to process sound?
What’ pathway – Processes attributes like duration, loudness, and frequency.
‘Where’ pathway – Localizes sound and helps determine its source.
How does the brain localize the position of sound?
The brain uses the interaural time difference (ITD) to determine the sound's location, where the left and right cochlear action potentials converge in the Medial Superior Olive (MSO).