03 - atoms & bonding
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Atomic ionization
Number of electrons can change
ions form by addition or subtraction
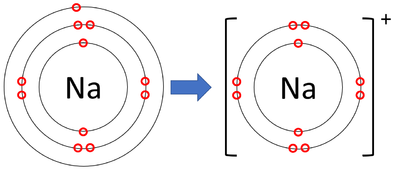
ex: sodium can give electron atom away
Where are the elctrons?
Wave mechanical:
electron found somewhere in a volume of space
a lot of energy (moving around everywhere)
What are the laws for electrons to find homes?
low energy (close to energy)
repel each other (they are spaced)
occupy distinct bands (must fill all of each energy level (7 total))
Not much room close to nucleus (2,8,8,8,8…)
orbitals
SUBDIVISION
within energy levels
volumes where electrons hag out
higher energy levels == more orbitals
4 kinds of orbitals
What are the 4 types of orbitals?
S-orbital
P-orbital
D-orbital
F-orbital
How many orbitals in S sublevel?
1
How many orbitals in P sublevel?
3
How many orbitals in D sublevel?
5
How many orbitals in F sublevel?
7
Ground State:
Electrons are gonna fill the lowest energy state
Electrons in lowest energy configuration
Valence electrons
Outermost shell of electrons
# of s,p,d,f
S=2
P=6
D=10
F=14
Electronegativity
The relative electron attracting power of an atom
Electronegativity in periodic table
Increases going upwards and right
families (left to right)
alkali metals
alkali earth metals
halogens
noble gases
Bonding types
Ionic
Covalent
Metallic
ionic bond
metal / nonmetals
electrons transferred
covalent bonds
non metal/ non metal
electrons shared
metallic bonds
metal / metal
electrons shared
Mixed Character Ionic/Covalent Bonds
Calculate the % of Covalent & Ionic
Mainly Ionic or Covalent, will have HIGHER TM
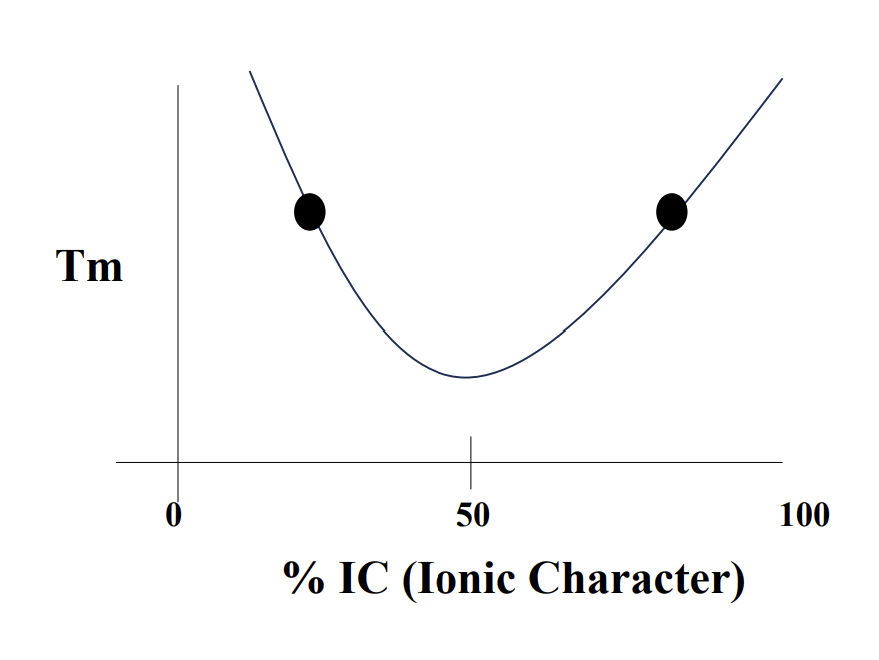
strength of bonding types
ionic
covalent
metallic
van der waals
What are the 3 types of Secondary Bonding (Van der Waals)
Fluctuating Induced Dipole Bonds (random)
dipole-dipole
Polar Molecule-Induced Dipole Bonds (induced-dipole)
Fluctuating Induced Dipole Bonds (random)
Random Electrons distribution fluctuation
Short-lived induced dipole
Weak, short-lived bond
ex: n2 + n2
Polar Molecule-Induced Dipole Bonds (Induced-dipole)
Unbalanced electronegativities
Molecule is polar (dipole)
Induces dipole in neighbor
Bond
ex: h2o + o2
dipole-dipole
two polar molecules
ex: h2o & h2o
hydrogen bonding
hydrogen with N, F, O
% Ionic character problem:
What electronegativity will give you 50% IC?
X = 1.67