A+P: LAB UNIT 3
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Fibrous Joint
Two bones held together by collagen fibers
Cartilaginous joint
Joint held together by hyaline cartilage/fibrocartilage
Rating of mobility in fibrous joints
Limited mobility
Rating of mobility in cartilaginous joints
Moderate mobility
Synovial join (diarthrosis)
Fluid filled joint cavity within a fibrous capsule
Rate of mobility in synovial joints
High mobility
What is the most superficial part of a synovial joint
The ligament
What is a ligament
Band of dense regular connective tissue that binds two bones together
What tissue is the band in a ligament made of
Dense regular connective tissue
What is deep to the ligament
Articular capsule (joint capsule)
Articular capsule (joint capsule)
Outer tough fibrous layer, inner delicate synovial membrane
Synovial membrane
Secretes lubricating synovial fluid
Function of synovial fluid
Fills joint cavity, helps articular cartilages to freely glide past each other
What kind of joint holds teeth into a jaw
Fibrous joint
Flexion
Decrease in joint angle
Extension
Increase in joint angle
Hyperextension
Extend joint beyond anatomical position
Abduction
Lifting appendage away from midline while in the frontal plane
Adduction
Moving appendage toward midline of body while in frontal plane
Medial rotation
End of appendage is rotated toward midline of body
Lateral rotation
End of appendage is rotated away from midline of body
Circumduction
Appendage is moved along a conical path
Supinate
Rotate the hand laterally, palm faces anteriorly
Pronate
Rotate the hand medially, palm faces posteriorly
Protract
Move joint anteriorly with no change in elevation
Retract
Move joint posteriorly with no change in elevation
Elevate
Move joint superiorly with no change in anterior/posterior orientation
Depress
Move joint inferiorly with no change in anterior/posterior orientation
Dorsiflex
Move feet, toes point superiorly
Plantarflex
Move feet, toes point toward ground
Inversion
Soles of feet face medially
Eversion
Soles of feet face laterally
Shoulder AKA
Glenohumeral joint
Shoulder (glenohumeral joint)
Ball-and-socket joint
Where is the shoulder (glenohumeral joint) formed by
Head of humerus, scapula, clavicle
Coracohumeral ligament connects:
Coracoid process and humerus
Coracoacromial ligament connects:
Coracoid process and acromion
Glenohumeral ligaments connect:
Glenoid cavity and humerus
Glenoid labrum
Wrapped around glenoid cavity
Function of glenoid labrum
Adds stability; Makes socket of ball-and-socket joint deeper
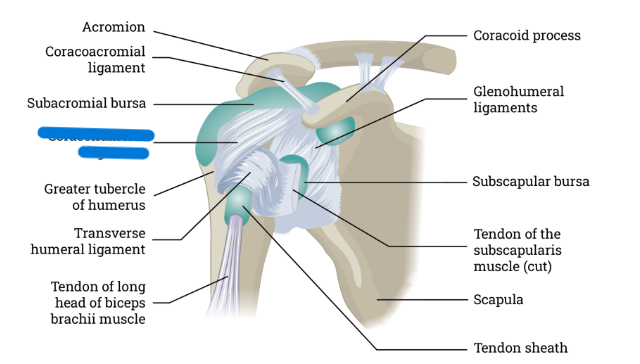
What is this
Coracohumeral ligament
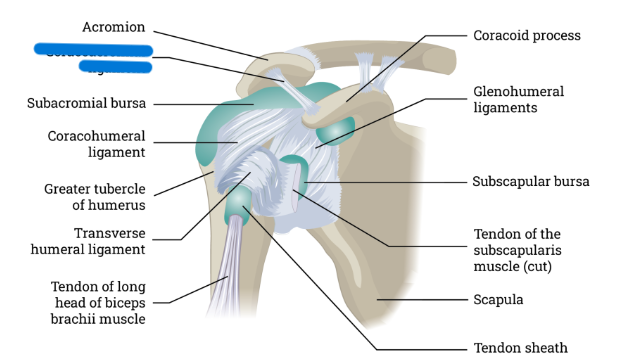
What is this
Coracoacromial ligament
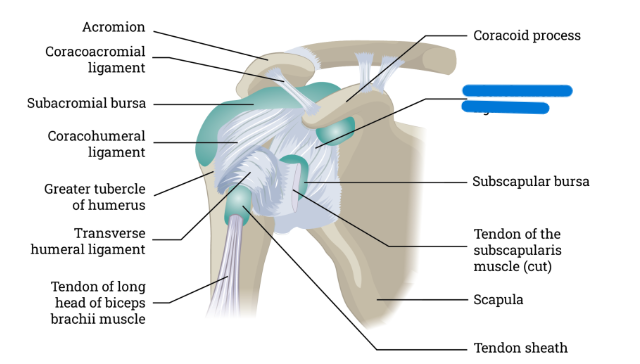
What is this
Glenohumeral ligaments
How many joints are in the elbow
Two
What joint in the upper limb has more degrees of freedom and more ligaments
The shoulder
Hip is AKA
Acetabular femoral joint
What is the hip formed by
Head of the femur and acetabulum of the coxal bone
iliofemoral ligament connects
Ilium to the femur
Ischiofemoral ligament connects:
Ischium to the femur
Pubofemoral ligament connects:
Pubis to the femur
Acetabular labrum
Band of cartilage wrapped around the acetabulum
Function of acetabular labrum
Adds stability by making socket of ball-and-socket joint deeper
Ligamentum teres is AKA
Round ligament
Ligamentum teres
Adds more stability; Anchors fovea capitis of the head of the femur to deepest part of acetabulum
What joint is the most complicated and has the most problems
The knee!
Where is the posterior cruciate ligament
Distal end; Posterior of tibia
Where is the anterior cruciate ligament
Distal end; Anterior of tibia
Medial collateral ligament is AKA
Tibial collateral ligament
Medial collateral ligament connects:
Femur to tibia (ON MENTAL SIDE OF KNEE)
Lateral collateral ligament is AKA
Fibular collateral ligament
Lateral collateral ligament
Connects femur to fibula on lateral side of knee
Patellar ligament connects:
Patella with tibial tuberosity
Menisci function
Cushions knee
Lateral meniscus
Between lateral condyles of femur and tibia
Medial meniscus
Between medial condyles of femur and tibia
Which ligament directly anchors the head of the radius to the distal end of the humerus in the elbow
Latera collateral ligament
What ligaments of the knee are perpendicular to each other
Posterior cruciate ligament and the anterior cruciate ligament
Which ligament directly anchors the humerus to the margins of the glenoid cavity
Glenohumeral ligaments
Which ligament directly anchors the head of the femur deep into the acetabulum
Ligamentum teres
If someone is cupping their hands together to hold multiple small rocks, how have they moved their hands
Supination
If someone is standing on their tippy toes, how are their moving their foot
Plantar flexion
If someone is standing up and squeezes their legs together, what movement are they doing with their legs
Adduction
If someone shrugs their shoulder, what movement did they do with their scapula
Elevate
If someone is using their hands to push as a car as hard as they can, what position will their hands most likely be in
Hyperextension
If someone brings their finger to the tip of their nose, what movement did they do at their elbow
Flexion
Sarcolemma
Muscle cell membrane
Myofibrils
Elongated structures in striated muscle cells
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Network of tubes surrounding a myofibril
Terminal cisterna of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Tubule that runs completely around each diameter of the sarcomere
T-Tubule
Third tube that runs around the perimeter of each myofibril
Where is the t-tubule located
Between two terminal cisterns
Triad
The segment where the terminal cisterns and t-tubule meet
Sarcomere
Short segment of a myofibril; Smallest contractile unit of skeletal muscle
What is the smallest contractile unit of skeletal muscle
Sarcomere
Z-disc
Forms the connection between sarcomeres
M-line
Middle of sarcomere
Myofilaments
Protein filaments of myofibrils; Produce light and dark bands of tissue
Dark bands represent:
Where thick and thin filaments overlap
Light bands represent:
Where thick and thin filaments do not overlap
Mitochondria
Produces ATP
Where is the muscle fiber nucleus found
Between the sarcolemma and underlying structures
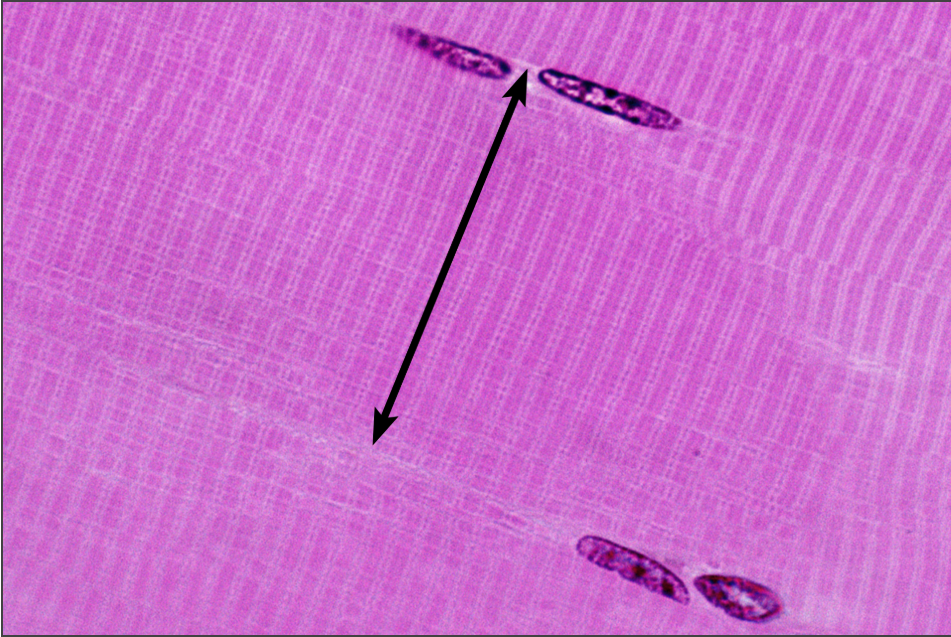
What is this highlighting
Muscle fiber/myocyte
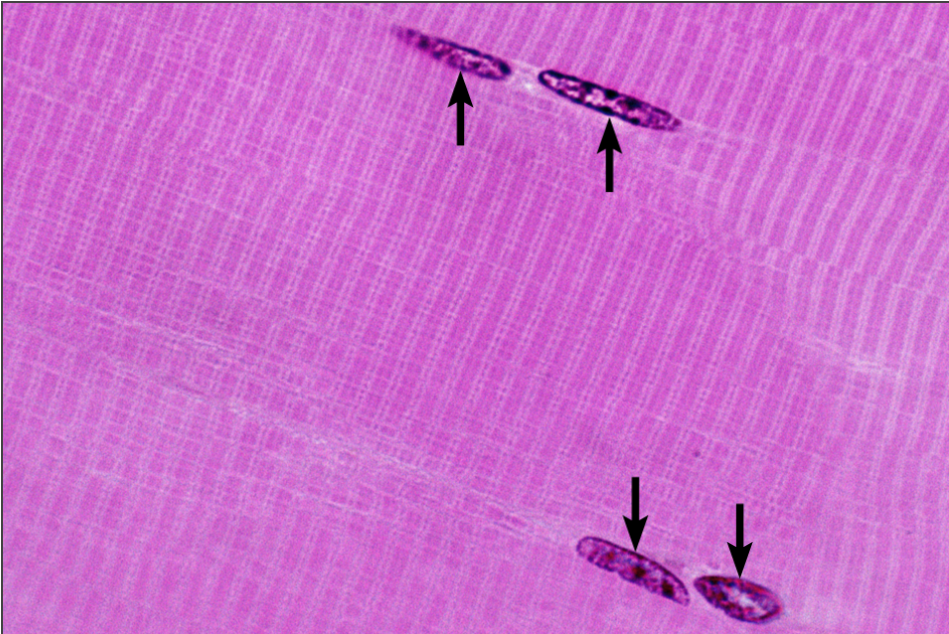
What is this highlighting
Nuclei
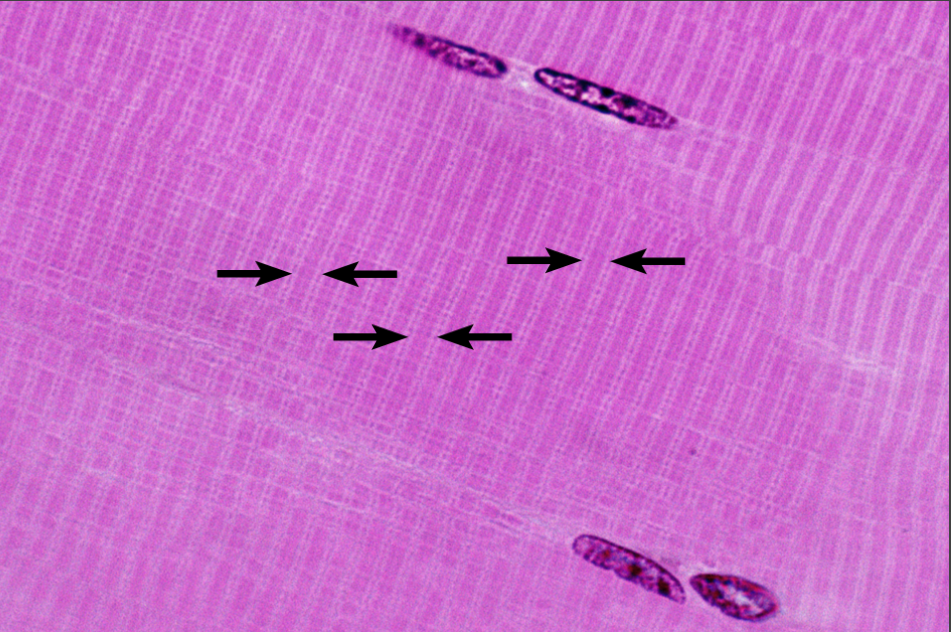
What is this highlighting
Sarcomere
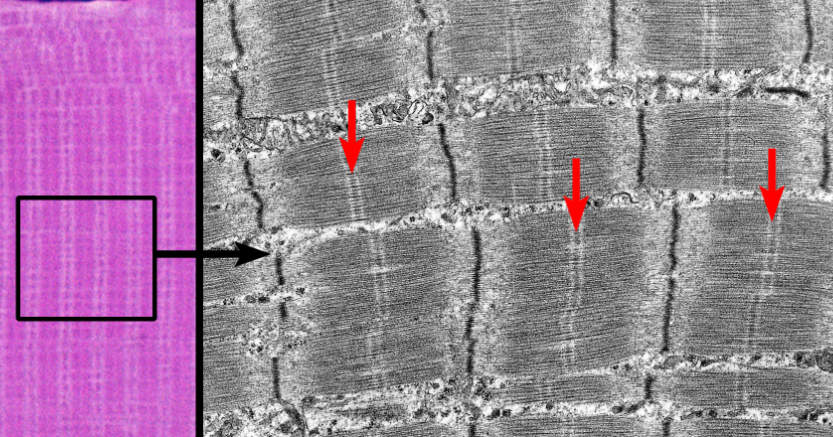

What is this highlighting
M-line
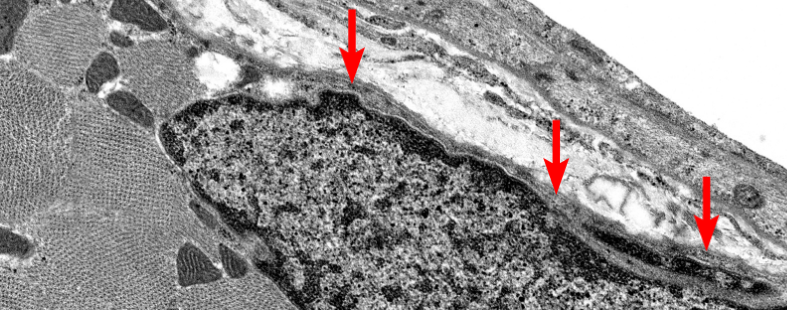
What is this highlighting
Sarcolemma
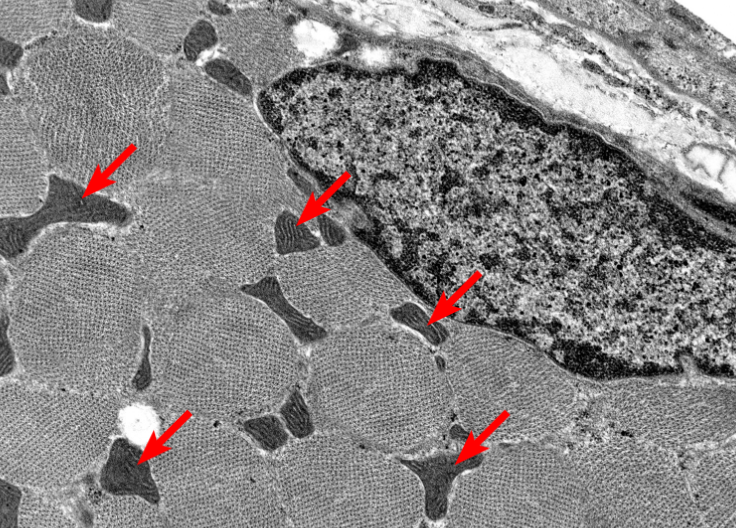
What is this highlighting
Mitochondria
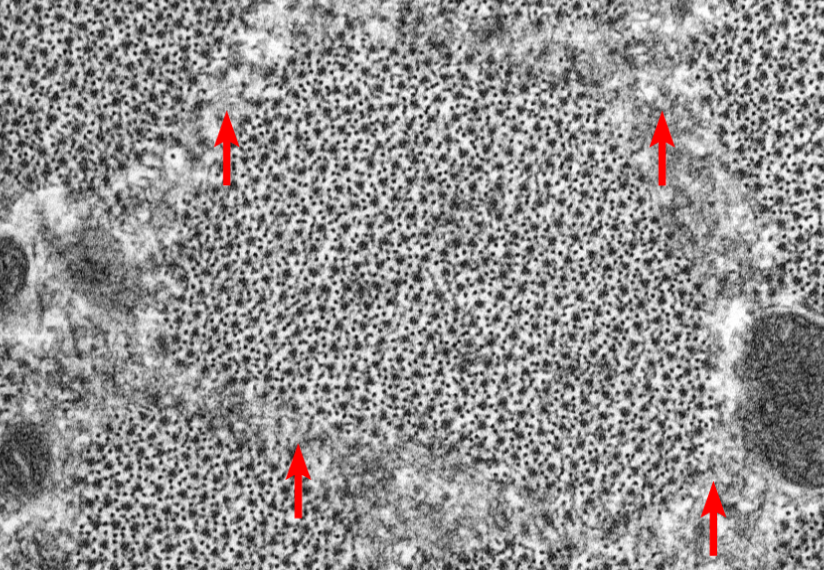
What is this highlighting
Sarcoplasmic reticulum

What is this highlighting
Triad

What is this highlighting
T-tuble