The Muscular System
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
smooth muscle
Fiber appearance: no striations, spindle-shaped, 1 nucleus
Involuntary
Location: walls of visceral organs and blood vessels
Anatomy of a muscle
large mucscle--> small muscle--> fascicle--> myofiber (cell)--> myofibril--> myofilaments
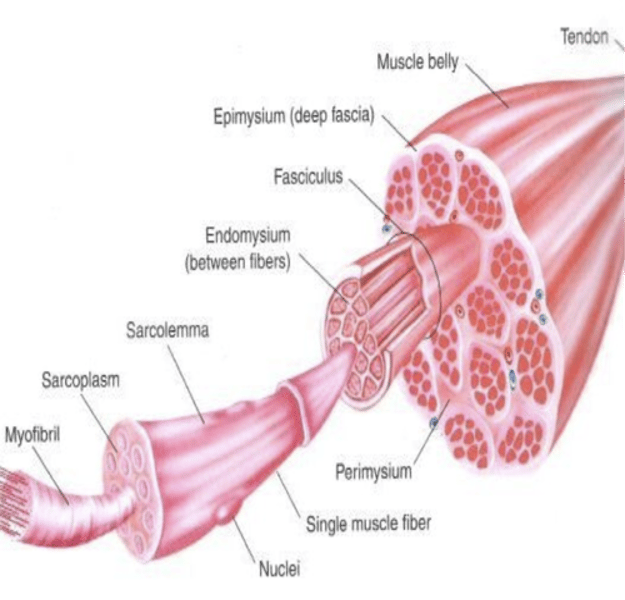
What are skeletal muscle cells specifically called?
muscle fibers (myofibers)
Layers of fascia
-epimysium
-perimysium
-endomysium
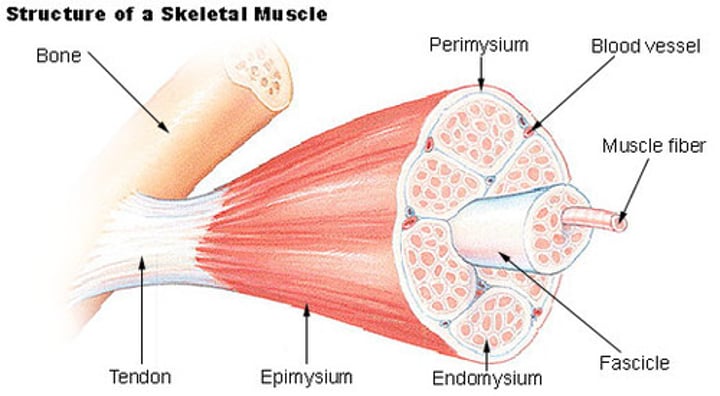
perimysium
covers each fascicle
ATP
energy storage compound
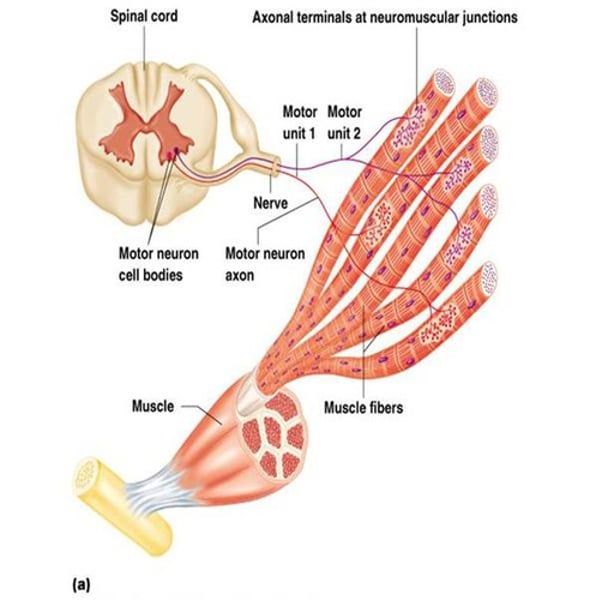
neuromuscular junction
where motor neuron meets muscle fiber
calcium
ion stored in sacs
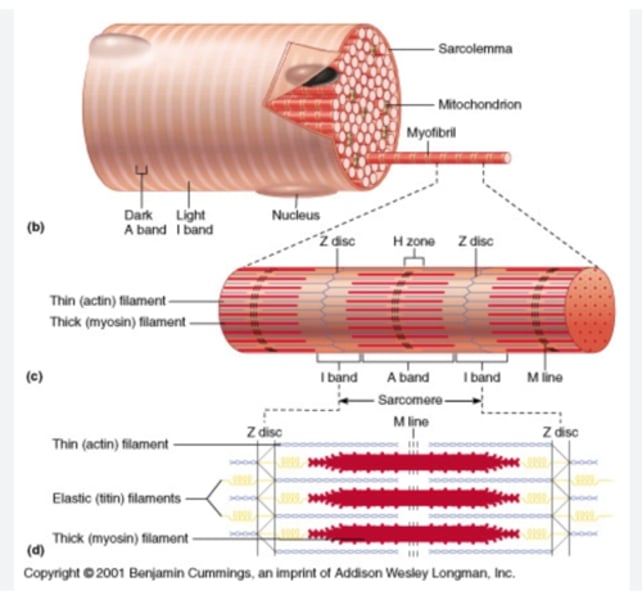
Structure of the sarcomere. What causes the striations?
Arrangement of protein filaments in myofibrils causes striations
Border: Z line to Z line
Myosin overlapped with part of actin: dark band
Actin not overlapped with myosin: white band
Difference between neuromuscular junction and motor unit
Motor unit: one motor neuron stimulating many muscle fibers
Neuromuscular junction: one motor neuron, one fiber
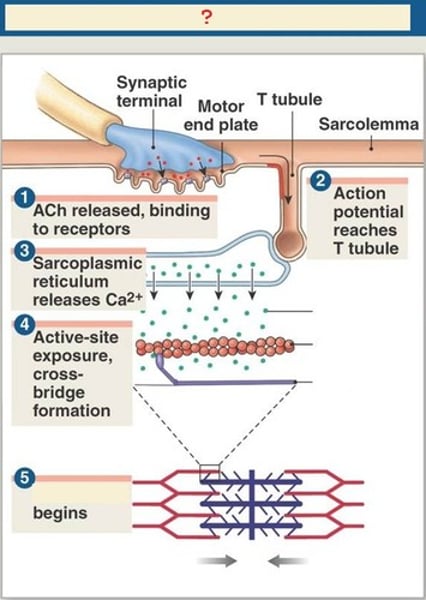
Steps that occur when a nerve impulse reaches a muscle and how muscle contraction occurs
1. impulse travels down motor neuron--> NM junction
2. neuron releases acetylcholine (ACh)
3. ACh travels across synaptic cleft--> plate of fiber--> sarcolemma T system--> SR
4. Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) releases Ca^+2
5. Ca^+2 stimulates myofibrils
6. Crossbridges form/ATP activated: filaments slide, causing sarcomere to shorten: contraction
How is ATP supplied to muscles (3 ways)? What is oxygen debt?
1. cellular respiration
2. creatine phosphate breakdown
3. fermentation: occurs when oxygen is in short supply (oxygen debt); lactic acid builds up
What is meant by "all or none response"?
muscle fibers contract completely or not at all
summation
second stimulus before 1st cycle is complete (no rest)
tetany
sustained contraction
What causes muscle "tone"?
small number fibers stay contracted
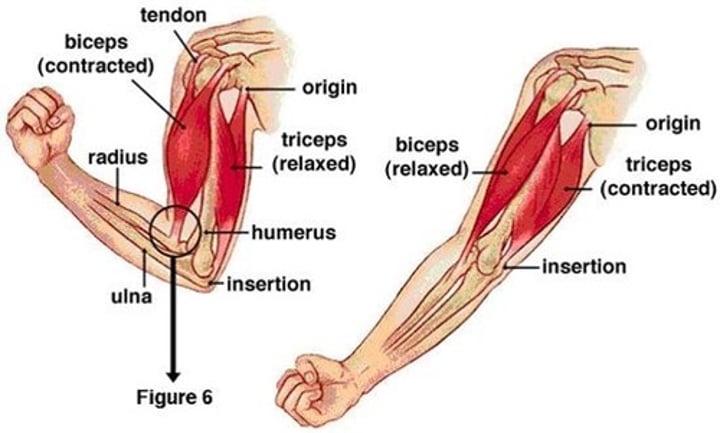
origin
the fixed, immovable end of muscle attachment
example of muscle named for size
gluteus maximus
example of muscle named for action
flexor digitorium
electromyography
recording of electrical events in contraction
myotonia
muscle doesn't relax after contraction
What is meant by "cardiac markers"?
protein elevations that follow a heart attack
clinical term for a heart attack
myocardial infarction
3 types of muscle tissue
-skeletal
-cardiac
-smooth
skeletal muscle
Fiber appearance: striated, cylindrical, multinucleated
Voluntary
Location: attached to skeleton or skin
cardiac muscle
Fiber appearance: striated, cylindrical, 1 nucleus, fibers interlock at intercalated disks
Involuntary
Location: heart walls
Four functions of skeletal muscle
1. Movement of body parts
2. Support
3. Heat production
4. Tendons of muscles stabilize joints
fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
Why are muscle cells referred to as "fibers"?
They are elongated
endomysium
covers each individual myofiber
epimysium
covers the entire skeletal muscle
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
T system
tubule composing transverse system
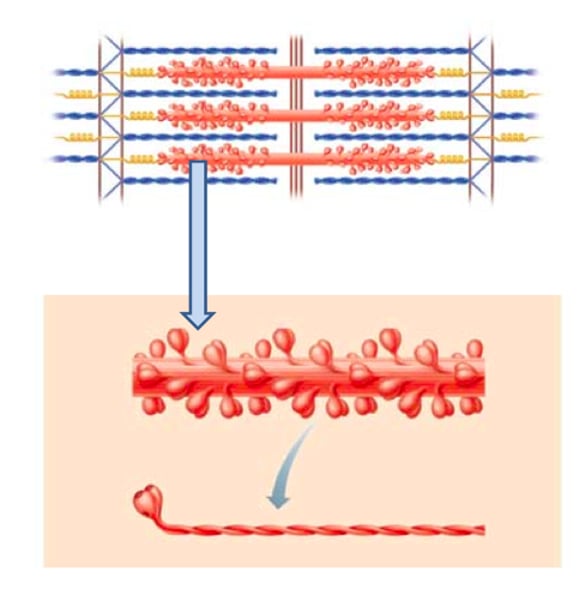
myosin
thick myofilament
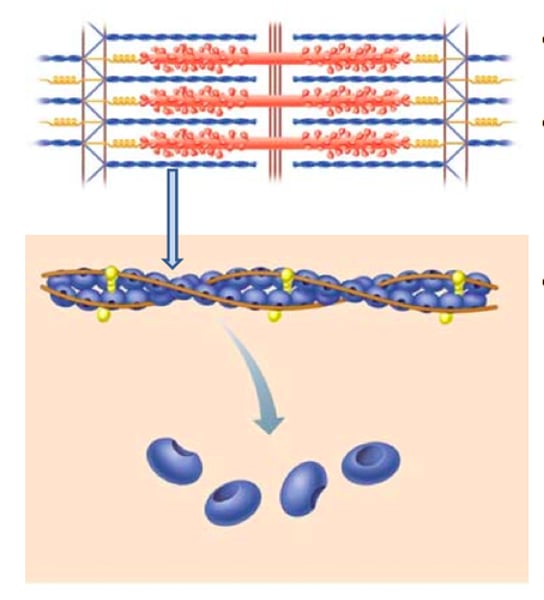
actin
thin myofilament
myofibril
cylindrical cords composed of protein filaments
-a series of sarcomeres are its units
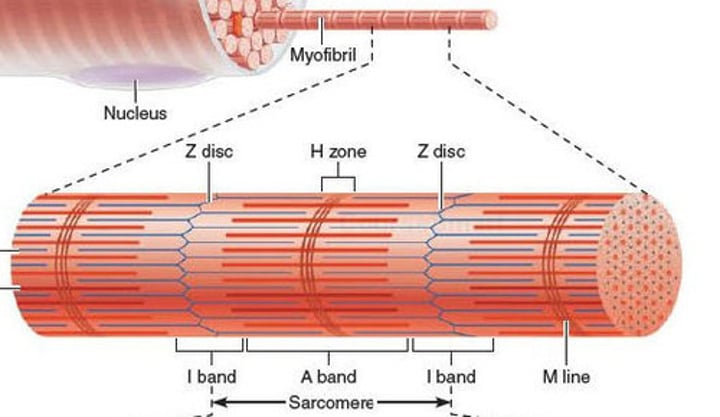
sarcomere
the working unit of skeletal muscle fiber
Sliding filament theory
Crossbridges form between actin and myosin--> myosin "pulls" actin filaments together--> sarcomere shortens in length: contraction

Three requirements for muscle contraction
1. Innervation
2. Ca^+2
3. ATP
Innervation
nerve stimulus
What may happen after depletion of ATP?
fatigue
twitch
single stimulus-contraction-relaxation sequence in a muscle fiber
hypertrophy
increase in muscle size
Ex: benefit of exercise
atrophy
decrease in muscle size due to nerve damage, broken bones, etc
Ex: bedridden patients; muscle not used
insertion
the movable end of muscle attachment
group action
prime movers and synergists working together
prime mover
major contracting muscle in a body action
synergist
muscle that assists the major contracting muscle in a body action
antagonist
a skeletal muscle that can produce the opposite motion of the prime mover and that relaxes when the prime mover contracts
-does not contract during a specific body action
example of muscle named for shape
deltoid (triangle)
example of muscle named for direction of fibers
rectus femoris (straight)
example of muscle named for location
tibialis anterior
example of muscle named for number of attachments
triceps brachii
charleyhorse
muscle cramp, especially calf; often occurs at night
muscular dystrophy
genetic, degenerative disease of muscle
myalgia
muscle aches/pain
myasthenia gravis
decreased ACh--> impairs nerve impulses at NM junction--> weakness, muscle fatigue
myoglobin
protein in muscle tissue that carries oxygen
-elevated in blood/urine following muscle trauma
myoma
a benign tumor of muscle tissue
myositis
inflammation of muscle tissue
What 2 cardiac markers are most often used to help diagnose heart attacks?
CK-MB and troponin