Quiz 2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
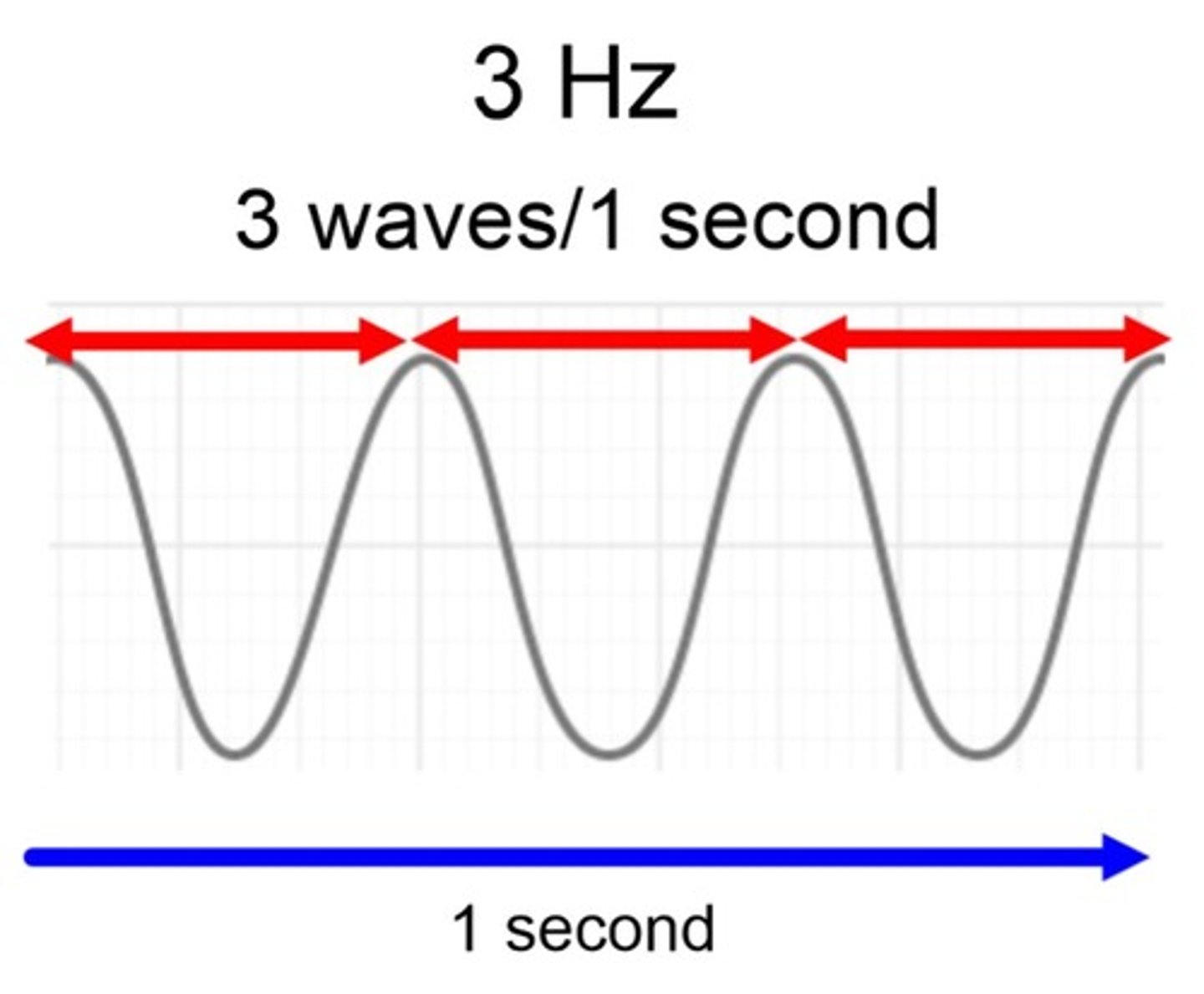
Frequency is
number of waves per second
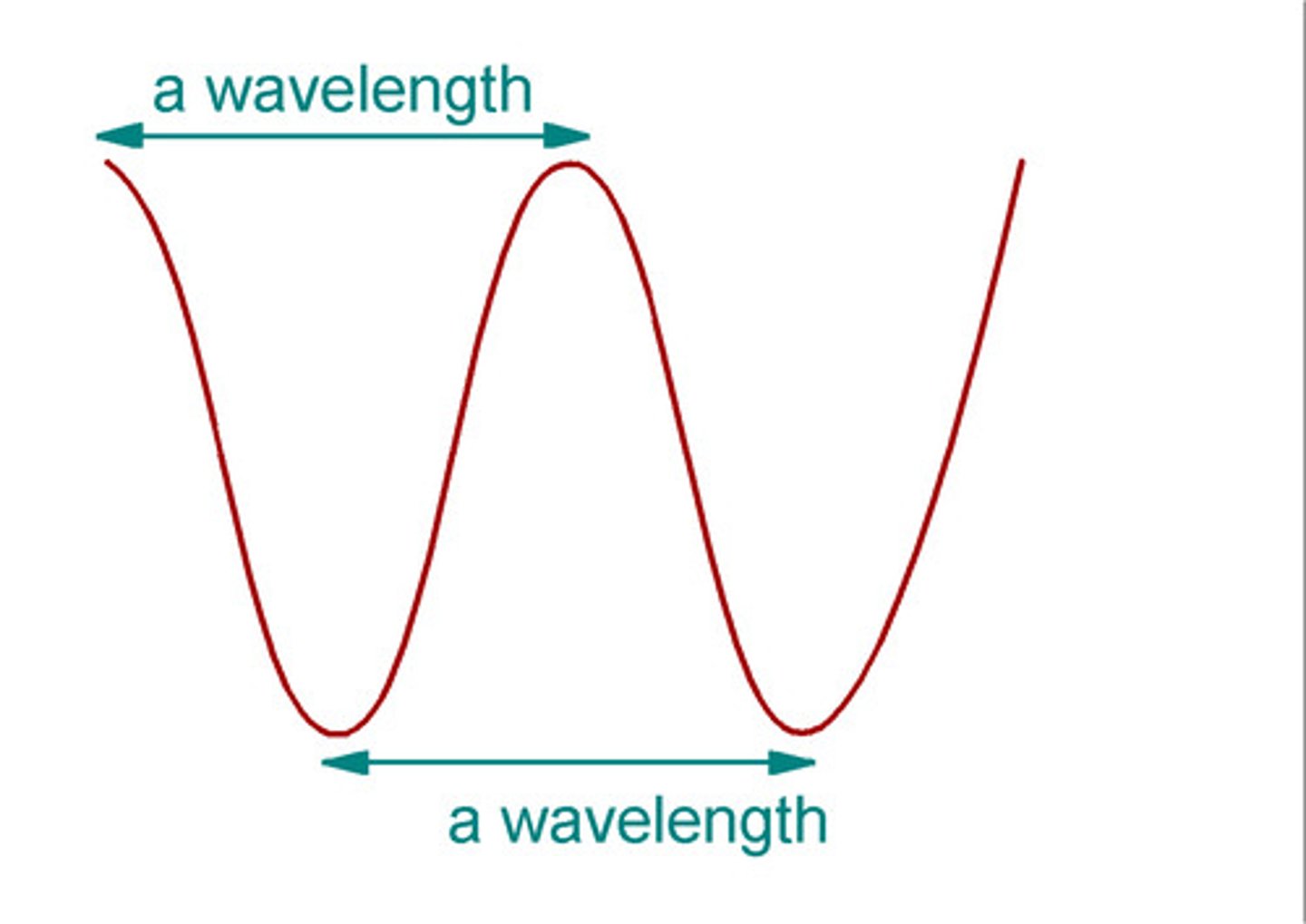
Wavelength is
Horizontal distance between the crests or between the troughs of two adjacent waves
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
The smaller the wavelength the greater the frequency
What is amplitude related to?
Intensity
Resonance Is...
When the frequencies match
Ground state
The lowest energy state of an atom

What happens when electron wave are the same frequency as a light wave?
The energy of the light is absorbed by the electron
When electrons absorb energy how is the electron altered
Its shape and size changes
How does absorption occur?
the oscillating electric field of light tugs the electron wave which causes the wave to oscillating at the same frequency
Photon definition
a quantum assossiated with electromagnetic radiation
Photon energy formula
E=hv
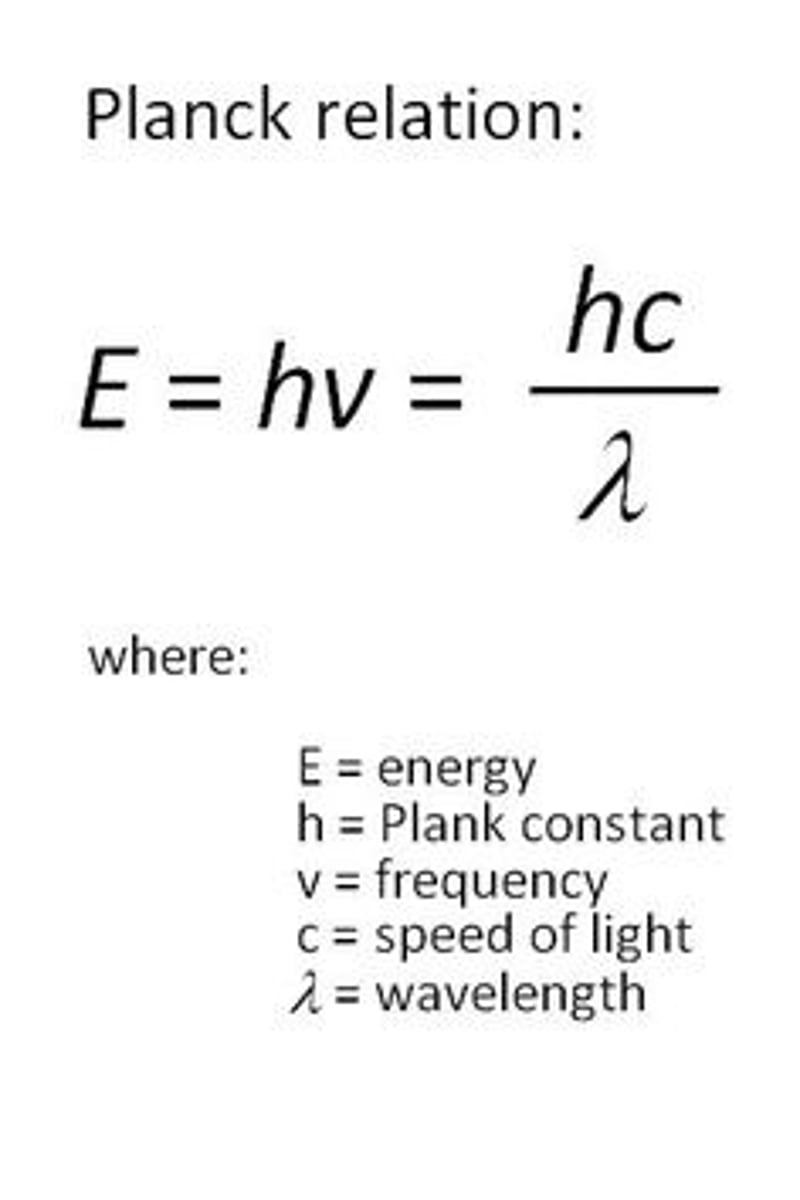
comparing 1 molecule to 3 how much energy can be transferred
for 1, (hv) | for 3, 3(hv)
The higher the energy the ----- stable it is
less
What is the relationship between wavelength and energy?
the smaller the wavelength the higher the energy
is the transformation process for electrons fast
no it takes 100,000 oscillations for an electron to change shape
a standing wave has -------- boundaries
fixed
1 loop equals ---- wavelength
1/2
can standing waves have a half number of loops
no standing waves can only have a whole number of loops
how does standing waves having a fixed boundary affect it?
limited possible shapes and they cant travel
J refers to what type of loops
radial loops
l refers to what types of loops
angular/ nodal loops
What is n
the principal quantum number
how do you get n
you add the # of radial loops and nodal loops together
how does the number of n relate to the number of loops for an electron
the larger the value of n the greater the amount of loops in an electron
what does radial loops let us know?
the energy and the size
what does the nodal and angular loops let us know?
the shape of the electron
if j=3 and l=2 what is the electron shape and size
5d
momentum of a photon formula
h/wavelength of light
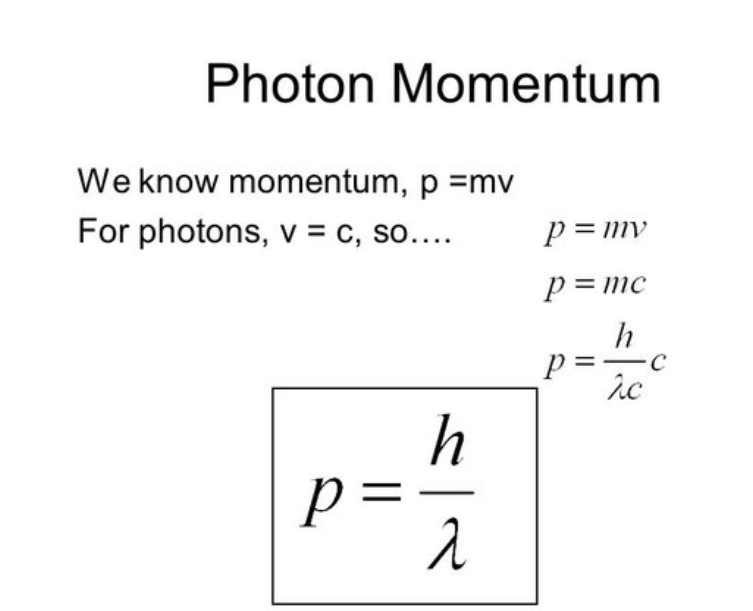
momentum formula
m*v
nodes
places of an electron with no wave density
What does a 3d electron look like
it has one radial loop and one 2 angular loops
Energy of an electron
-13.6 eV (z^2/n^2) or 2.1799 ( z effective)²/ n²
which orbital is less stable 3s or 3p
3p, because of its shape its attraction to the nucleus is less which allows for it to be ionized easier
Energy change formula
En= -2.18aJ(z²/n²)
final- initial
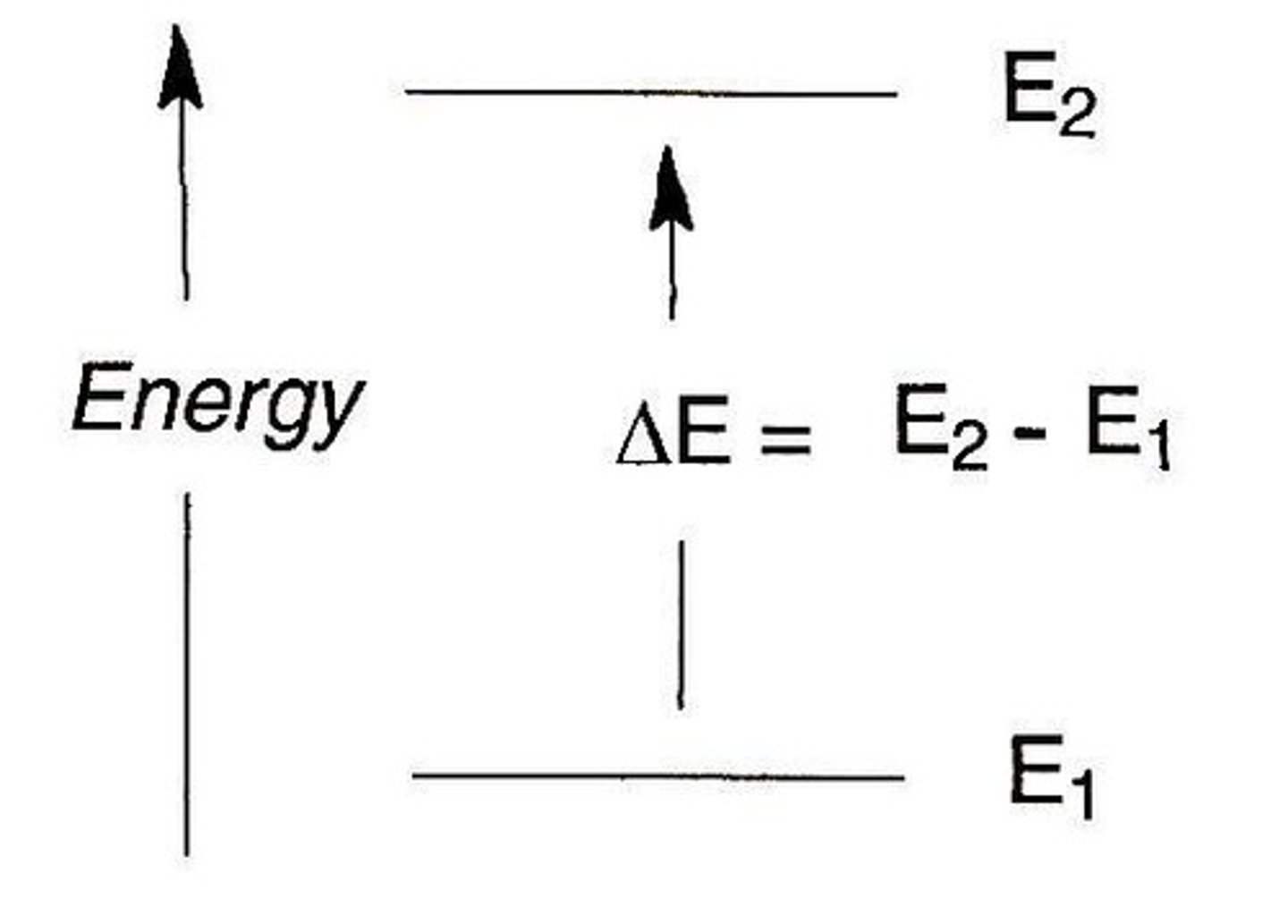
Is energy change equal to the photon energy
yes
when the energy change is negative what does that mean
emission occurred
what is electromagnetic radiation
a kind of radiation including visible light, radio waves, gamma rays, and X-rays, in which electric and magnetic fields vary simultaneously.
what happens when an electron finishes the absorbtion/emission process?
It gains or loses one nodal/ angular plane
what is the magnetic quantum number
indicates the orientation of an orbital around the nucleus
how do you calculate the magnetic quantum number
2L +1
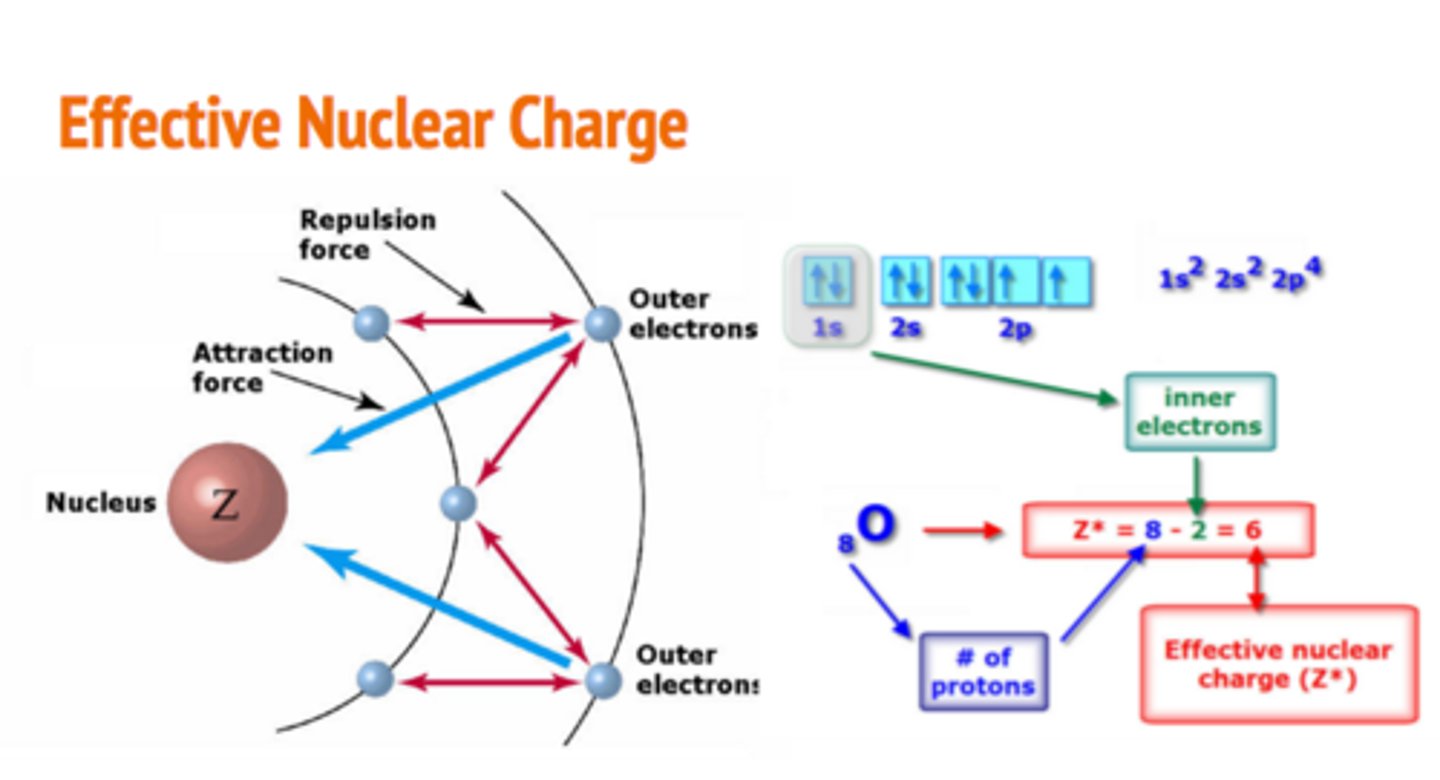
what is effective nuclear charge
The net positive charge experienced by an electron in a multi-electron atom.
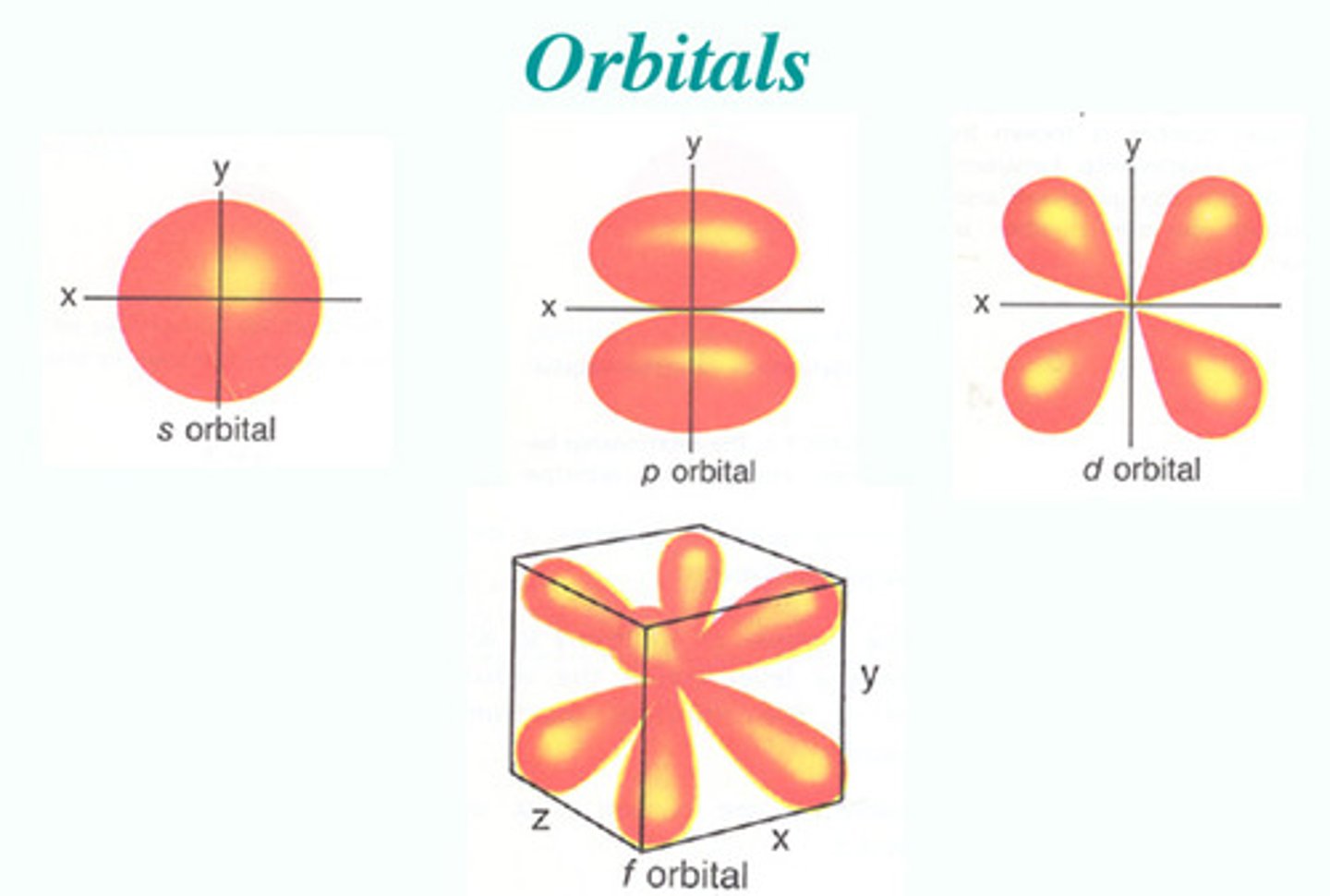
(photo not accurate electrons are waves not particles)
what is ionization energy
the energy required to remove an electron from an atom
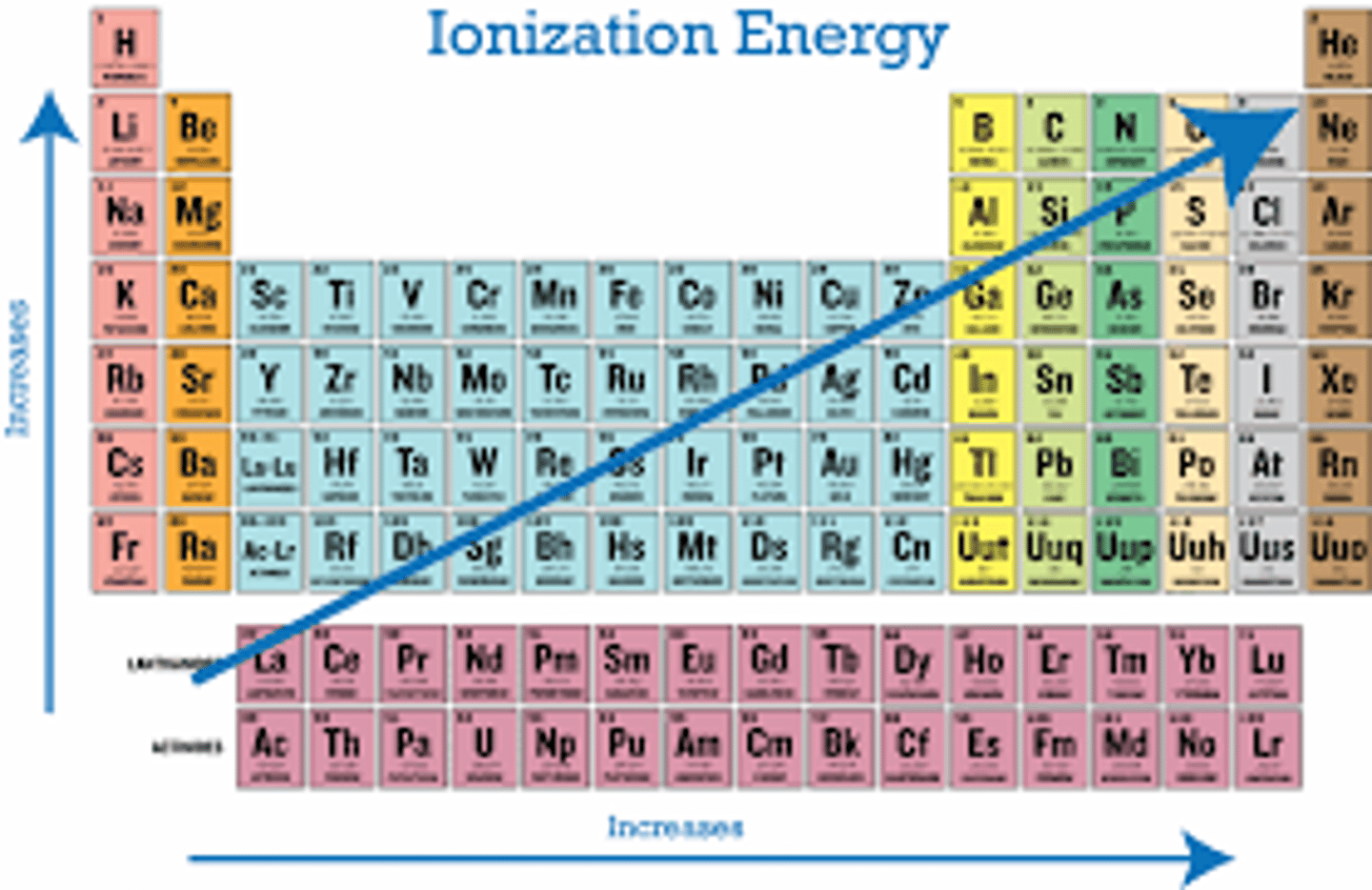
Photo electric effect
The emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
how does adding more photons to a lightsource affect the intensity of light?
it increases the intensity of the light source
does the intensity of a light source affect frequency
no
what is threshold frequency?
The minimum frequency of light required for an electron to be emitted.
if light emitted at an atom is higher than the threshold frequency will electron be ejected
yes, it will use the excess energy to move away faster
the greater the nuclear charge the ----------- the electron wave
smaller due to increased Coulomb's Law attraction, resulting in a smaller atomic radius and thus a smaller "electron wave" or probability cloud.
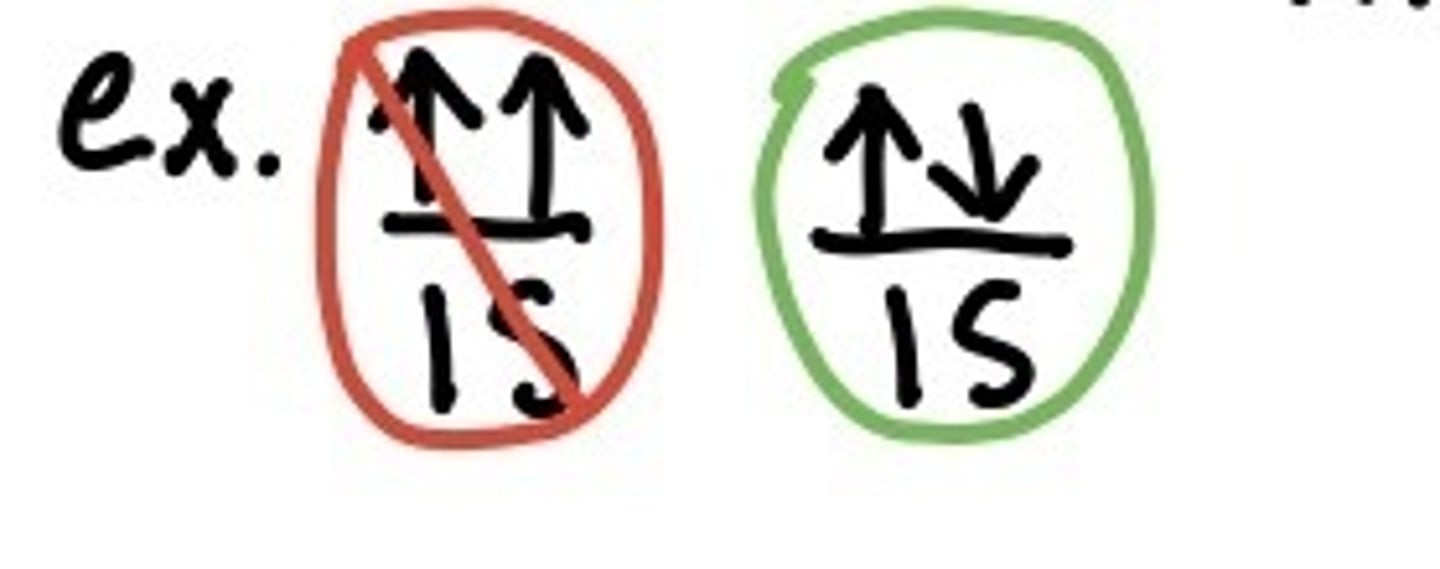
pauli exclusion principal
no two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers
Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it

if there is no magnetic field then all of the energies are---------
degenerate( have the same energy)
when the magnetic quantum number equals 0 what axis is the electron on
z axis
an orbital is
a group of 2 electrons with the same n, l and m sub l value
what does m sub s describe
the magnetic moment of an electron
if the electron in the orbital
Shielding affects ionization energy how?
The greater the shielding effect from inner electrons, the lower the effective nuclear charge felt by the valence electrons. This means the outermost electrons are held less tightly and require less energy to be removed, resulting in a lower ionization energy.
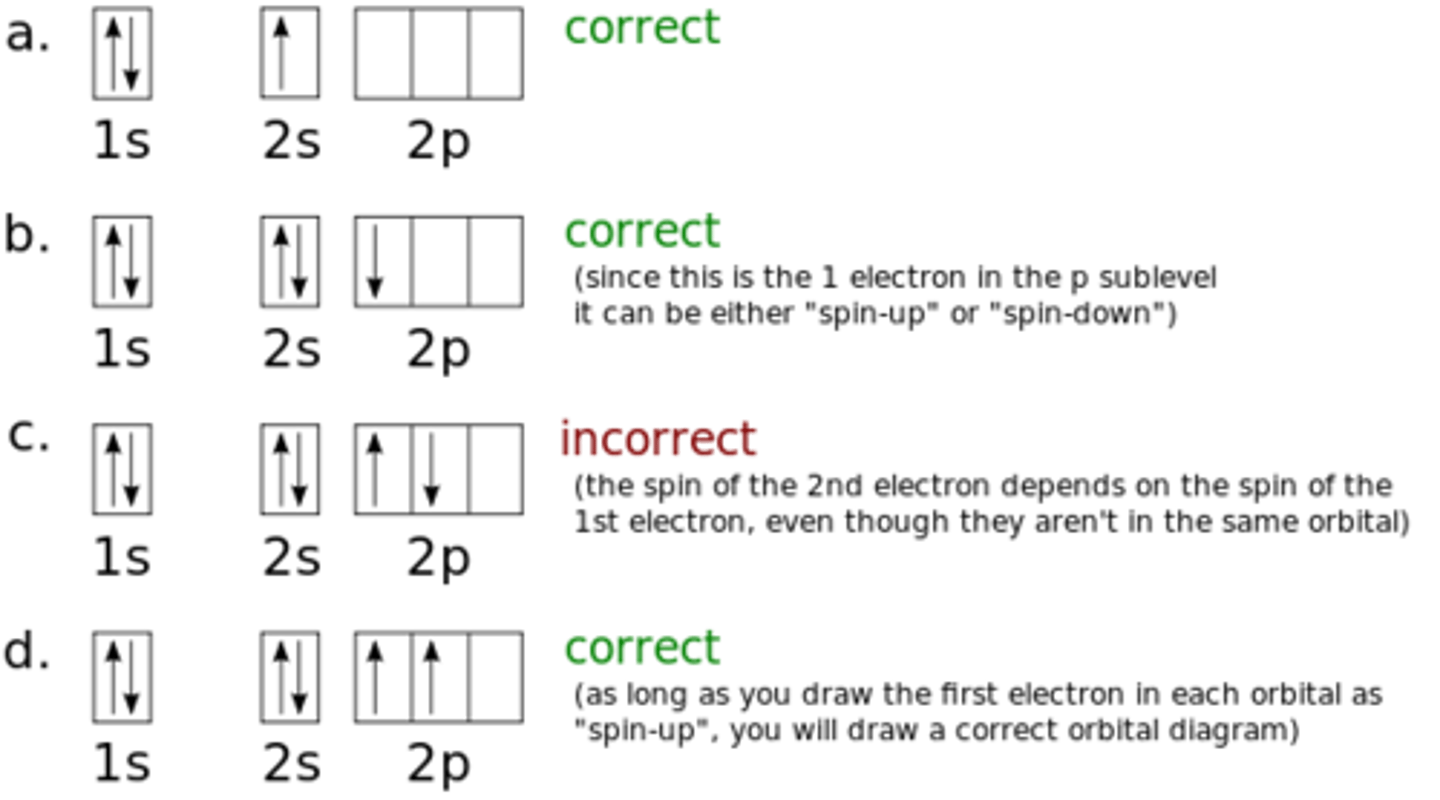
Hunds rule
Hund's rule states that for degenerate atomic orbitals (orbitals of equal energy), electrons will singly occupy each orbital with parallel spins before any orbital is doubly occupied
shielding only happens when there is more than one _________
electron
diamagnetic
all electrons are paired
paramagnetic
unpaired electrons