IB business management unit 4
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
marketing goods and service
Promotion- to build brand recognition, awareness and trust
use physical environment
make it easy to visualise service quality
branding, logos, celebrity endorsement, slogans
Product strategy - a tangible good or intangible services that satisfies the needs and wants of a customer (attracts more customers)
Price strategy- The amount paid for a particular good or service that should entice customer yet allow the firm to be profitable
source of value to customer- used to price product
Place strategy- Distribution channels that enable customers to conveniently buy the product
online
customers would not go to inconvenient and remote location

marketing goods vs service
Goods: Use of the 4Ps (place, price, product, promotion)
- Services: Use of the 7Ps (place, price, product, promotion, process, people, physical evidence)
Market research
Market research is essential in helping businesses to identify products/services they can develop in response to the needs and wants that their customers have
Market research is the process of systematically gathering data from consumers which can be used to influence the business decisions
Market orientation
An approach to marketing that focuses on the needs of a customer and uses this information to design products that meet customer needs
Market orientation aims to develop products to meet consumer needs identified during the market research process
The result of market orientation is that the firm will benefit from increased demand, increased profits, and a valued brand image as its products become more desirable
However market research (needed for the process) is expensive and does not guarantee success

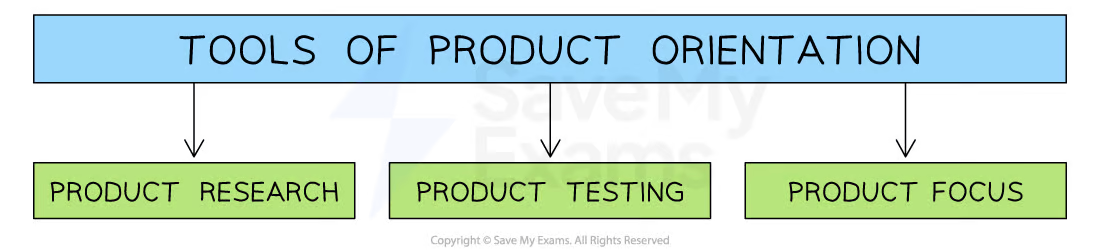
Product orientation
An approach to marketing that focuses on the characteristics of the product rather than the needs of the consumer
marketing plan
The process of formulating the marketing strategies and tactics that will help a business to achieve its marketing objectives
Three tools of marketing planning include
Market segmentation
Market mapping
Market positioning
marketing audit- review of current position of an organisation’s marketing- once completed marketing plan is prepared
Marketing objectives
These are specific SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time bound)
Research
Marketing research identifies the factors expected to impact upon the marketing plan such as
Market size and growth
Market segments
Competitor positioning- SWOT
Customer tastes, preferences and views
The nature of distribution channels
The marketing mix
This involves planning the medium- and short-term marketing activities the business intends to undertake
Pricing strategies and tactics
Promotional activity
Distribution and logistical plans
Product specifications, features and packaging
Physical evidence such as branding
How people and process are developed to support delivery of the rest of the marketing mix

advantage and disadvantages of market planning
advantages-
improves chances of success
clearer idea of objectives
disadvantages-
no time
inflexible
Quickly outdated
Marketing objectives
Targets the marketing departments aims to achieve
These are specific SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time bound)
Market strategies
Market development-
selling existing products in new markets
e-commerce- selling over the internet
internationally
Product development-
new products in existing markets
Diversification-
new products in new markets
high risk
stable businesses looking for growth
Product innovation-
original or new product launch
first mover advantage
Unique selling point
A unique selling point (USP) is a distinguishing factor or characteristic of a product, service or brand that sets it apart from its competitors
The USP helps a business to differentiate itself and give customers a reason to choose one product or service over others because it offers something distinct and valuable
There are a range of reasons why businesses develop a USP which can include
Developing a brand identity
Achieving a competitive advantage over rivals
Effective communication with customers
The attraction and retention of customers
Achieving power over pricing
Encouraging innovation and adaption
Differentiation
Product differentiation is an attempt by a business to distinguish its products from those of competitors
reasons for differentiation
Strong product differentiation helps the firm to develop its competitive advantage
The development of product differentiation often helps a firm to create a unique selling point for its product which can be used in marketing
Common methods used by businesses to differentiate products include
Marketing and branding activities
Eye-catching packaging
Attractive functions and features
Product customisation
Excellent customer service
Commercial marketing
marking strategies that focus on meeting the demands of customers in a profitable way
the main purpose is to generate benefits for the owners of the business
Social marketing
marketing activities that aim to influence or change people’s attitudes and behaviour for the good of society as a whole, rather than primarily to make a profit
Market share (%)
(firm's sales)/(total sales in the market) x 100
Importance of market share and leadership
Benefits
- Increased sales ---> higher profits
- Economies of scale
- Branding
Limitations
- Market share calculations must be looked at carefully
Elements of a marketing plan
- Marketing objectives
- Key strategic plans
- Detailed marketing actions
- Marketing budget
Four P's of marketing mix
Marketing mix: Key elements of a marketing strategy that ensure the successful marketing of a product
Product: a tangible good or intangible services that satisfies the needs and wants of a customer
Price: The amount paid for a particular good or service that should entice customer yet allow the firm to be profitable
Promotion: communicating relevant products information to inform and persuade customers to buy the good or service
Place: distribution channels that enable the customers to conveniently buy the product
Bargain products
Goods or services that are perceived by customers to be high quality but sold at a low price
customer profiles
the demographic and psychographic characteristics of consumers in different market segments
cowboy products
goods or services that are perceived by customers to be of low quality
Market segment
A distinct group of customers with similar characteristics, tastes, preference
Targeting
Targeting is the marketing practice of creating and using an appropriate marketing mix and marketing strategies to cater for different marketing segments
Target market
The group of customers that an organisation focuses on selling its product to
Niche market
marketing approach that focuses on supplying highly specialised products to cater to a small and select target market
Mass market
industries that buy and sell mass market products, catering for a broad range of target markets
non-profit organisation (NPO)
a business that does not primarily aim to earn a profit but to serve a purpose beyond the organisation itself, the betterment of society as a whole
people
the employees who deliver the customer service element of the extended marketing mix
physical evidence
the observable and tangible aspects of a service
premium products
goods or services that are perceived by customers to be of high quality and high price
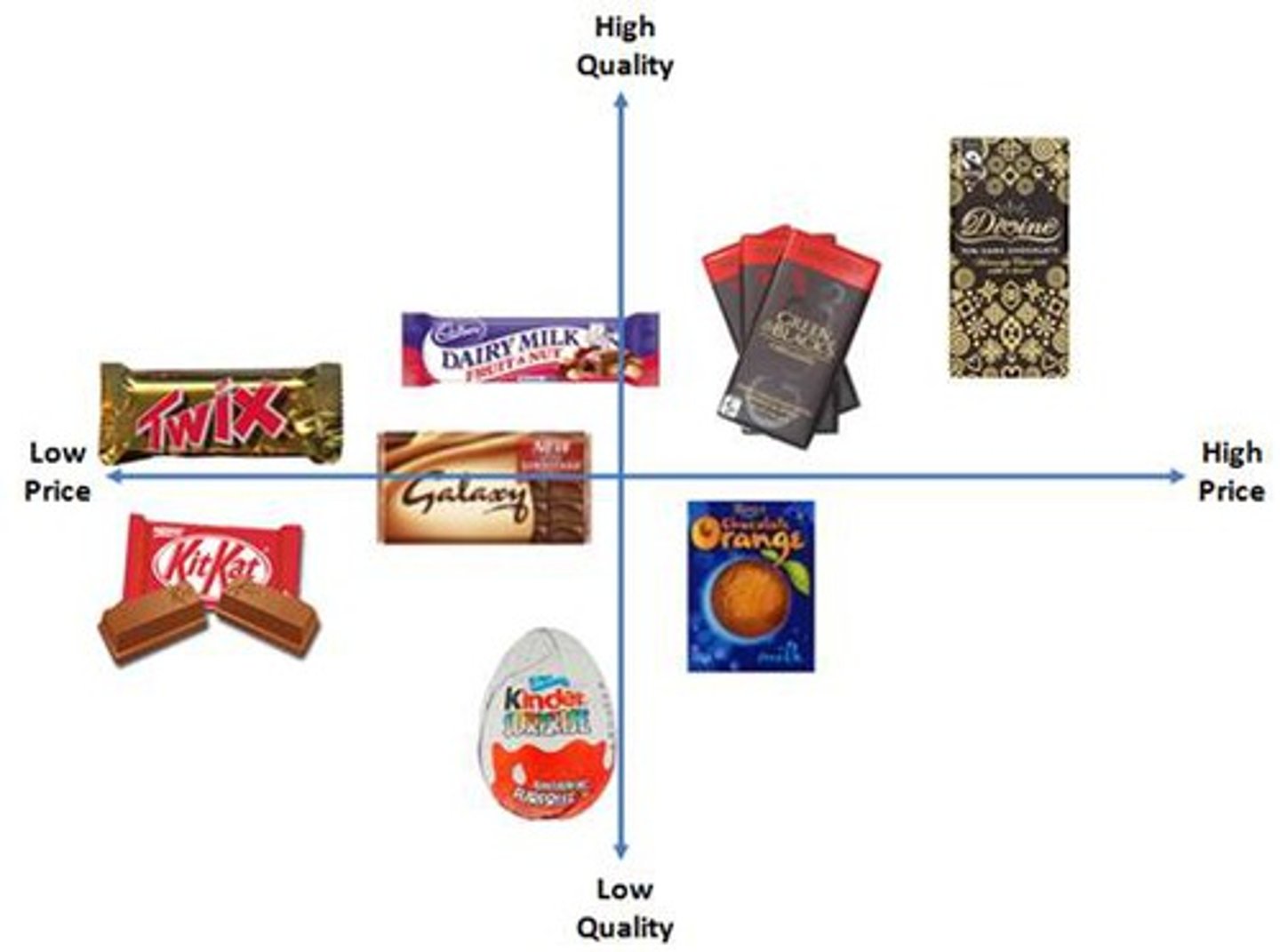
Product position map
A map showing how consumers perceive a business, its products, and/or its brand in comparison to other businesses in the industry
psychographic segmentation
segmentation that involves characterising consumers according to people’s lifestyle choices and personal values
Sales forecasting
A quantitative technique used to predict a firm’s level of sales revenue over a given period of time
Terminology of sales forecasting
- Sales trend: Underlying movement or pattern of the data presented, either in months of years (can be used to determine future sales)
- Seasonal/cyclical variations: When the trends vary in seasons, there are seasonal variations. When trends vary over years, there are cyclical variations
- Random variations: Some times there are one off events which affect data
Methods of primary research
- Surveys
- Interviews
- Focus groups
- Observations
Methods of secondary research
- Market analysis
- Academic journals
- Government publications
- Media articles
Qualitative and quantitative research
Quantitative: A category of market research based on the opinions of participants. it creates detailed and non-numerical information
Qualitative: A category of market research based on gathering facts and numerical information
sampling methods
quota sampling- select a number of candidates from different market segments
random sampling - selects anyone in the population for market research
snowballing- relies on participants referring or recommending further subjects to take part in the market research
stratified sampling - segmented into various strata
Product
- Any good or service that is offered to the market with the aim of satisfying consumer needs or wants
Product life cycle
- Shows the course that a product takes from its developments to its decline in its market
Stages:
1- Development (market research, innovation, prototypes, commercialisation)
2- Introduction (launch of product into market)
3- Growth (revenue increases after repreated sales)
4- Maturity (slow growth)
5- Saturation (saturation of market)
6- Decline (Steady drop in sales)
Each stage has different use/effect on marketing mix, investment, profit and cash flow
Extension strategies
- Plans by firms to stop sales from falling by lengthening product life cycle (repackaging, new markets, reposition of product, promotion)
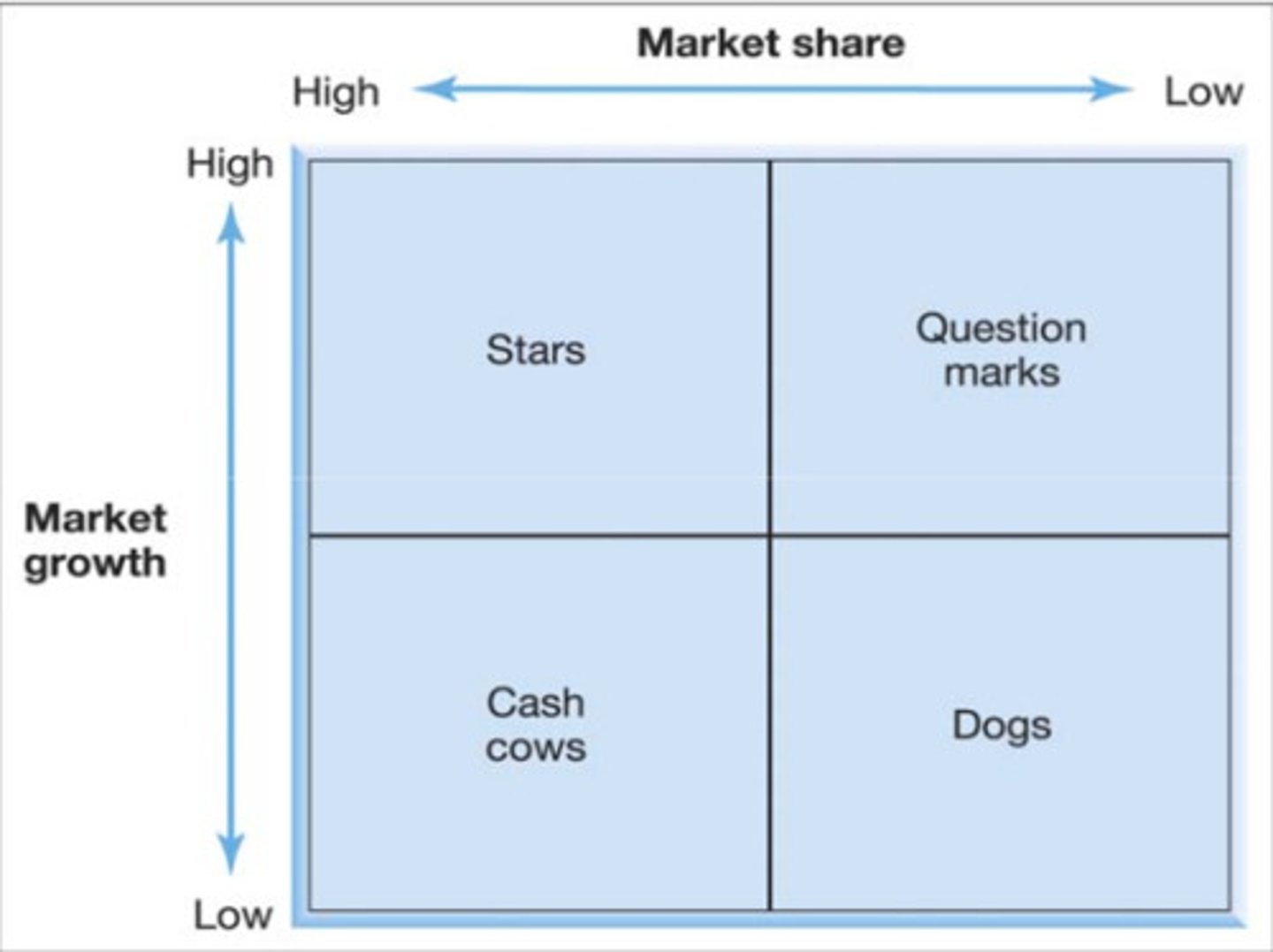
BCG matrix
Visual marketing management tool used to analyse a firm’s product portfolio
Stars: High market growth and high market share
Cash cows: Low market growth and high market share
Question mark: High market growth and low market share
Dogs: Low market share and low market growth
Branding
- The process of distinguishing one firm's product from another
Brand awareness
The ability of consumers to recognise the existence and availability of a firm's good or service
Brand development
part of a firm’s marketing strategy in communicating the value of a brand and what the brand stands for
Brand loyalty
When consumers become devoted to a brand
Brand value
The expected earning potential of a brand
Cost plus pricing
Adding a percentage or predetermined amount (markup) to average cost per unit to set the selling price
Ensures a product will produce contribution
competition based pricing
price leadership
Set by the market leader and other firms simply follow
Predatory pricing
Temporary reduction in price to drive away competition
Going-rate pricing
Simply pricing at about the average price level of most products in the market
market led pricing
Penetration pricing
Price/market skimming
Price discrimination
Loss leadership
psychological pricing
promotional pricing
Penetration pricing
Newcomers set their prices low to entice people to buy
Price changes from low to high
Risk: lower prices = lower reputation
Price skimming
understand what the market is like, set the price high, then as you understand the market better your prices will slowly decrease
Prices changes from high to low
price discrimination
The price of a product varies per country, which depends on the market; however, the products should not be easily traded
Results to the government applying taxes/tariffs
loss leadership
Products are sold at a loss, but regain their losses through their other products
Psychological pricing
Some numbers are more appealing
promotional pricing
Offer discounts, rebates, promotions, etc.
types of promotion
Above the line (ATL)
Use of mass media for promotions
Very wide reach, but also very expensive
e.g. TV, radio, newspaper, magazine, outdoor, cinema, etc.
Below the line (BTL)
Use of non-mass media promotional activities focused at target market
e.g. price deals, money-off coupons, direct Marketing/direct selling, sponsorship
Promotional mix
Promotional mix is the combination of promotional techniques that communicate benefits from a product
Elements
Advertising – information and persuasion
Public relations – image building and goodwill
Sales promotions – stimulate sales and activities
Personal selling – sales forces and agents
Guerilla marketing
Use of unconventional, and memorable interactions in order to promote a product
Generally used by smaller businesses
Uses smaller teams of promoters in a specific area, rather than through mass media campaigns
Benefits
Relatively low in cost and risk
Helps engage in networking with not only customers, but even other potential business partners as well
Limitations
Success depends highly on market research
Distribution channels
The different ways the product reaches the customers
Zero level distribution- manufacturer sells directly to consumers
Two channel distribution- involves the use of two intermediaries usually wholesalers and retailers
Three channel distribution channel- three intermediaries-wholesalers sell to retailers on behalf of the producers
wholesalers
buy products from a manufacturer and sells these in smaller quantities to retailers
direct agents
independent businesses w/ exclusive right to trade a product in a territory
agents may act on behalf of buyer or seller
retailers
outlets that sell directly to customers
International marketing
Sale and marketing of a firm’s products in a foreign country
Methods of entry into intl. markets
internet
Exporting
Direct investment
Joint venture
International franchising
Opportunities and intl. markets
Expand marketing operations into growing and emerging markets
Spreading overall risk between more markets, each at different stages within the economic cycle
Threats
High-barriers of entry
Strong competition from the well-established local industry
Differing consumer demands
Globalisation
Globalisation
Adopting a differentiated marketing mix that meets national and regional tastes and cultures
advantages
Caters to local tastes
More products (diversification)
Spreads risks
Cater to wider market
Disadvantages
More costly
E-commerce
- The buying and selling of goods and services through the internet
types of e-commerce
B2B – Business to business
Caters to needs of business, transactions and distribution
B2C – Business to consumer
Sells directly to customers and provides other necessary services
C2C – Consumer to consumer
Customers trade with each other for either good and/or services
E-commerce and the marketing mix
Product: Higher customisation and broader product range to suit wide variety of individual
Price: direct selling approach
Promotion: Quicker and cheaper communication
Place: 24/7 accessibility and global reach
Costs of e-commerce
- Internet security
- Vulnerable to competition
- Starting website may be expensive
Benefits of e-commerce to consumers
Convenient and accessible
Relatively inexpensive when considering the total size of the potential market reach
cost benefit