IB Biology HL - Unit A2.3: Viruses
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
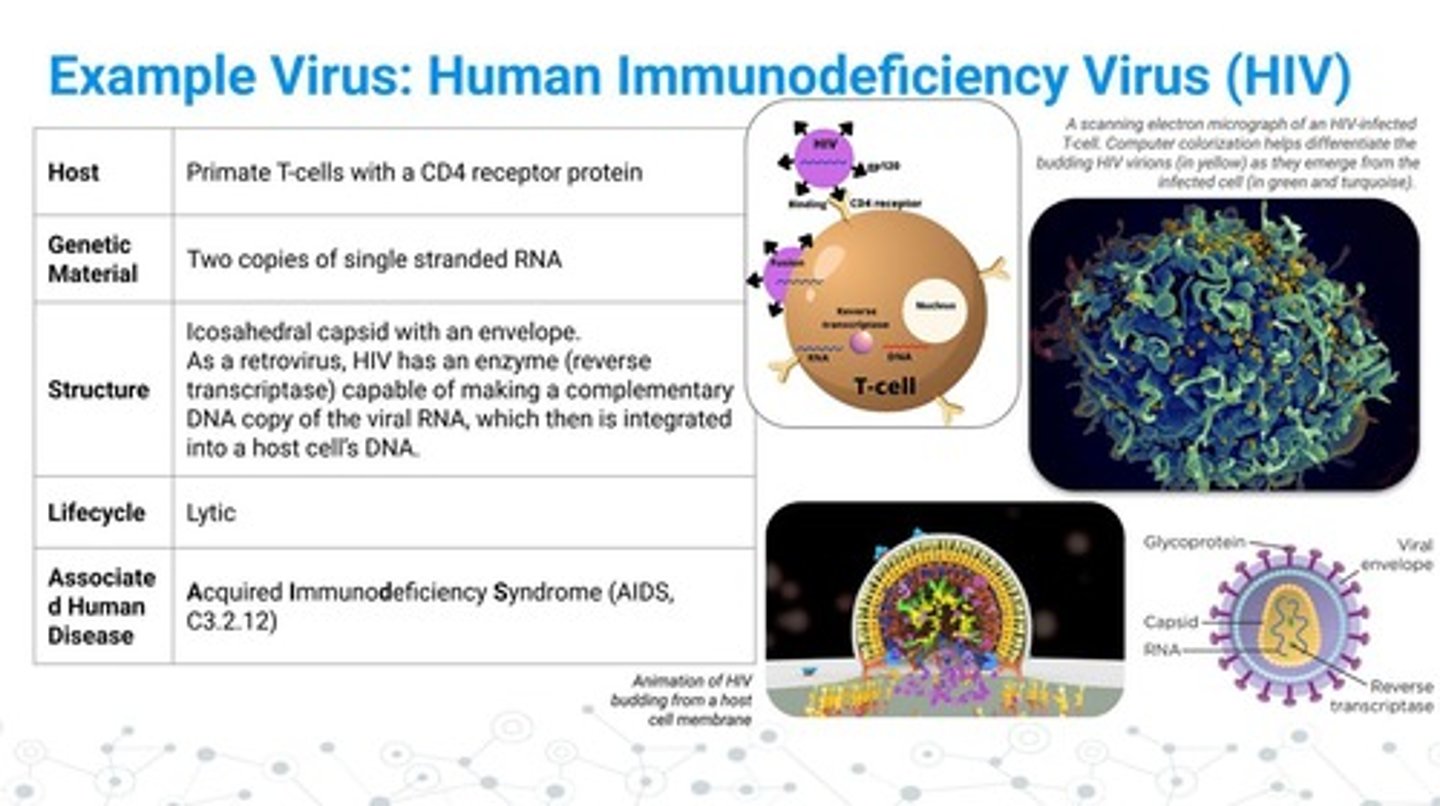
Obligate intracellular parasites
AKA Viruses, must infect cells to reproduce.
Non-living Characteristic of Viruses
To lack cellular structure and metabolism.

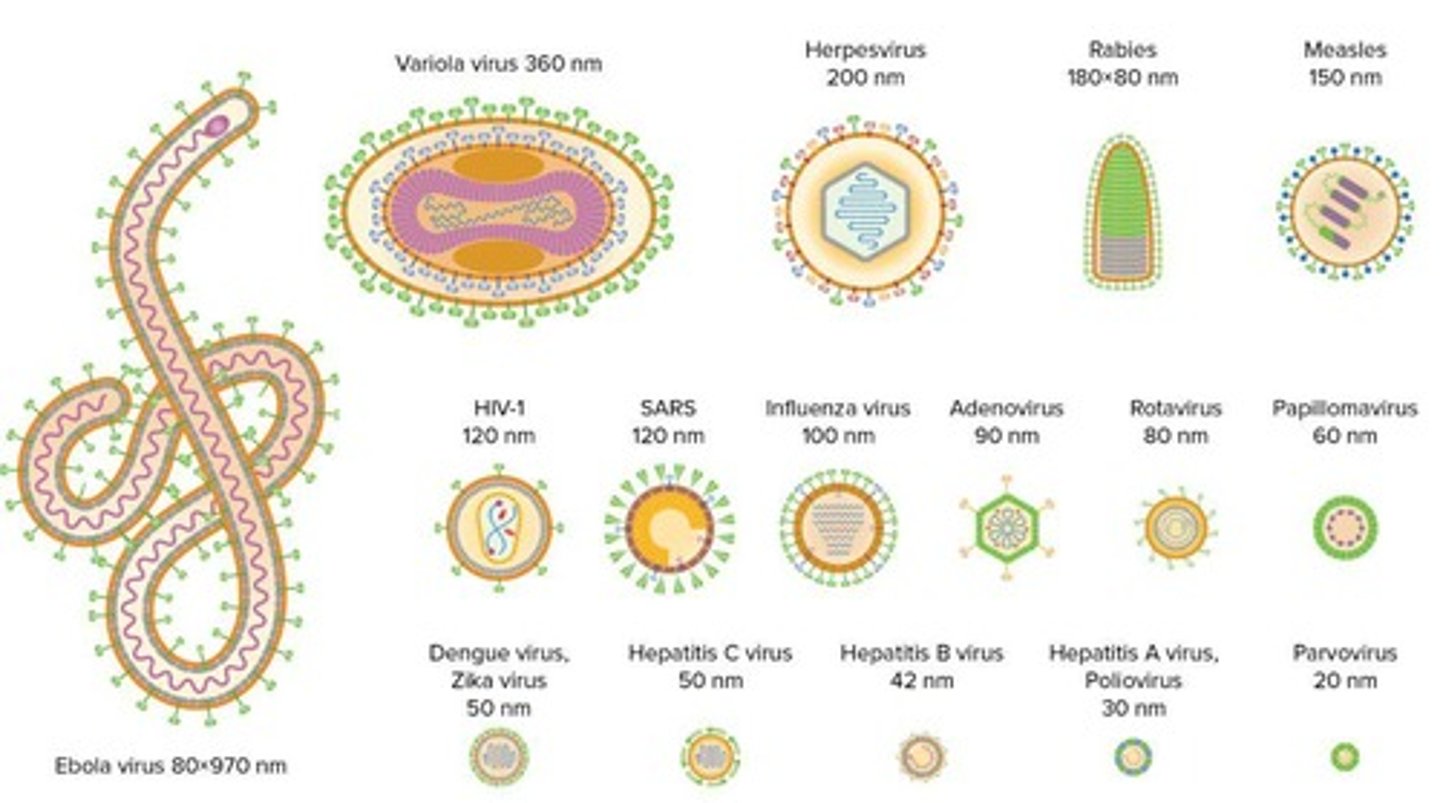
Fixed size of Viruses
Viruses typically range from 20-300 nm.
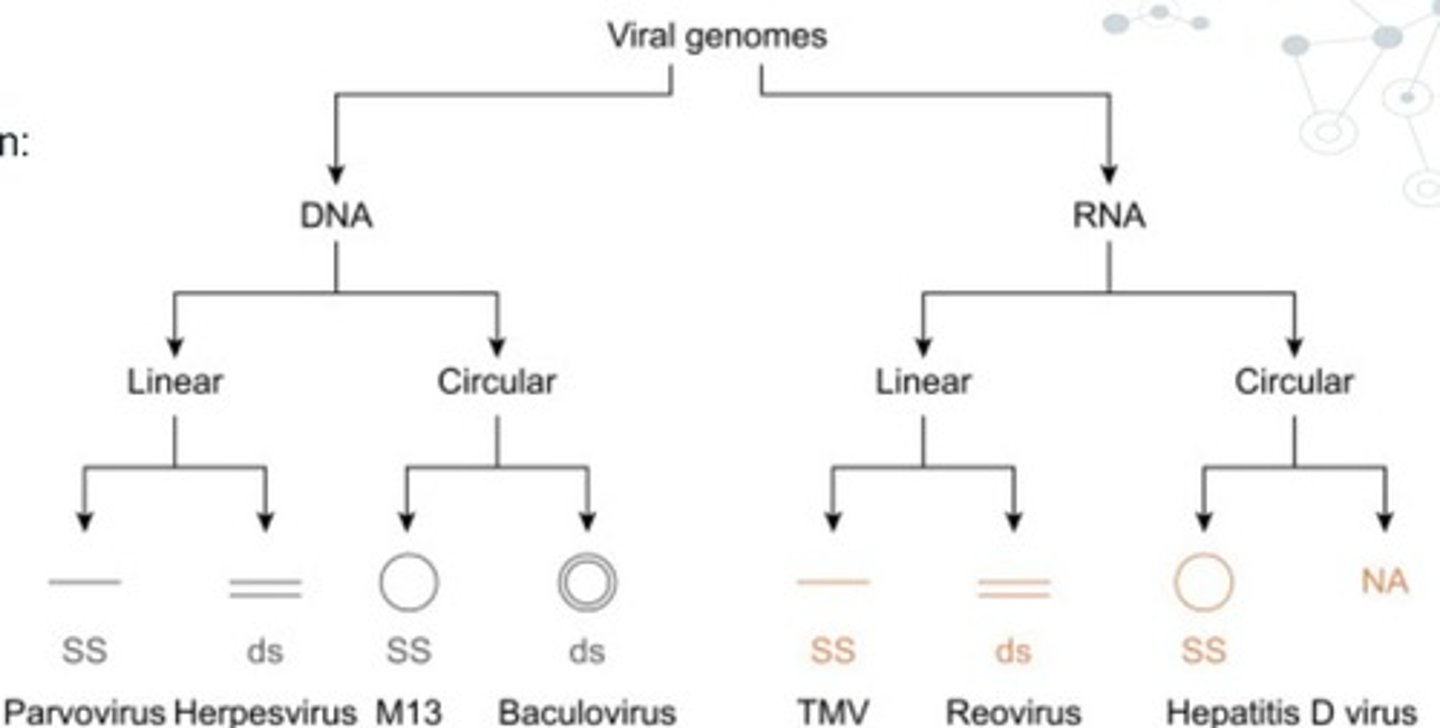
Nucleic acid Composition of Viruses
Viruses contain either DNA or RNA.
Protein capsid
Protective outer shell made of protein subunits.
Viruses contain no cytoplasm
Viruses lack cellular organelles and cytoplasm.
Viruses with enzymes
Some viruses carry specific enzymes like reverse transcriptase.
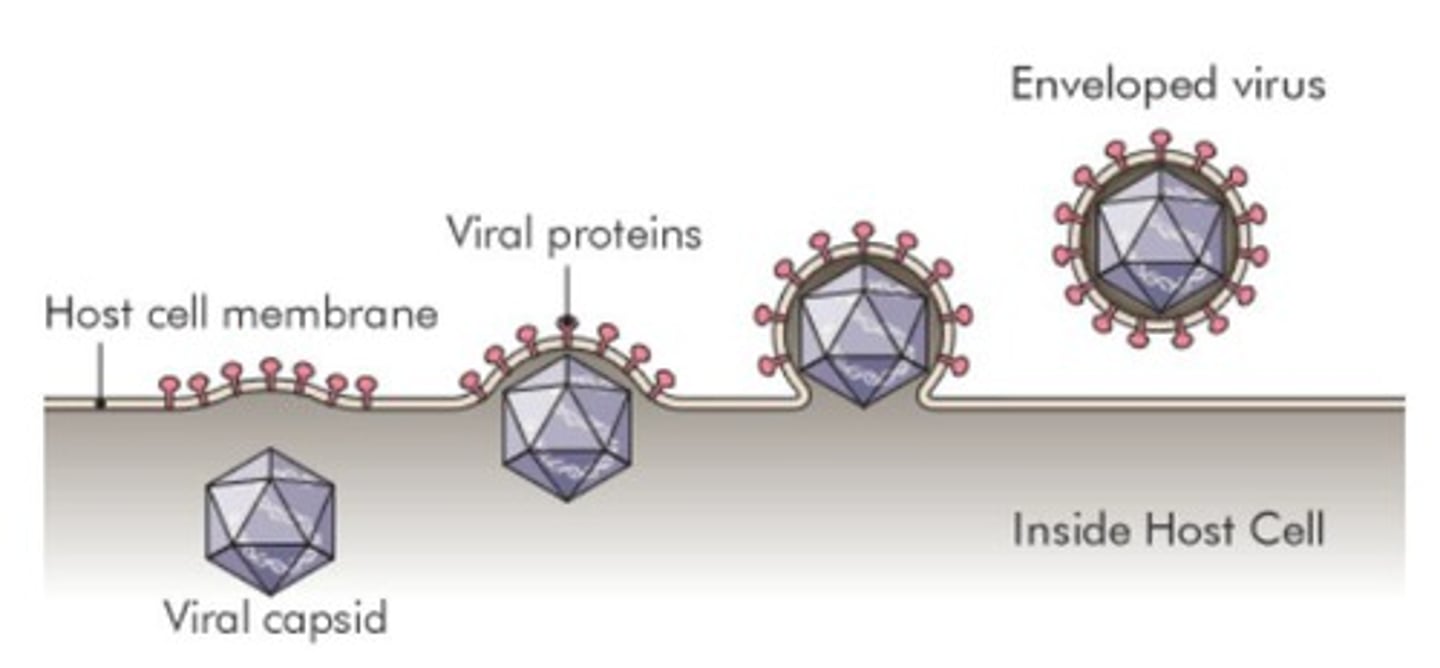
Enveloped viruses
Viruses with a lipid membrane from host cells.
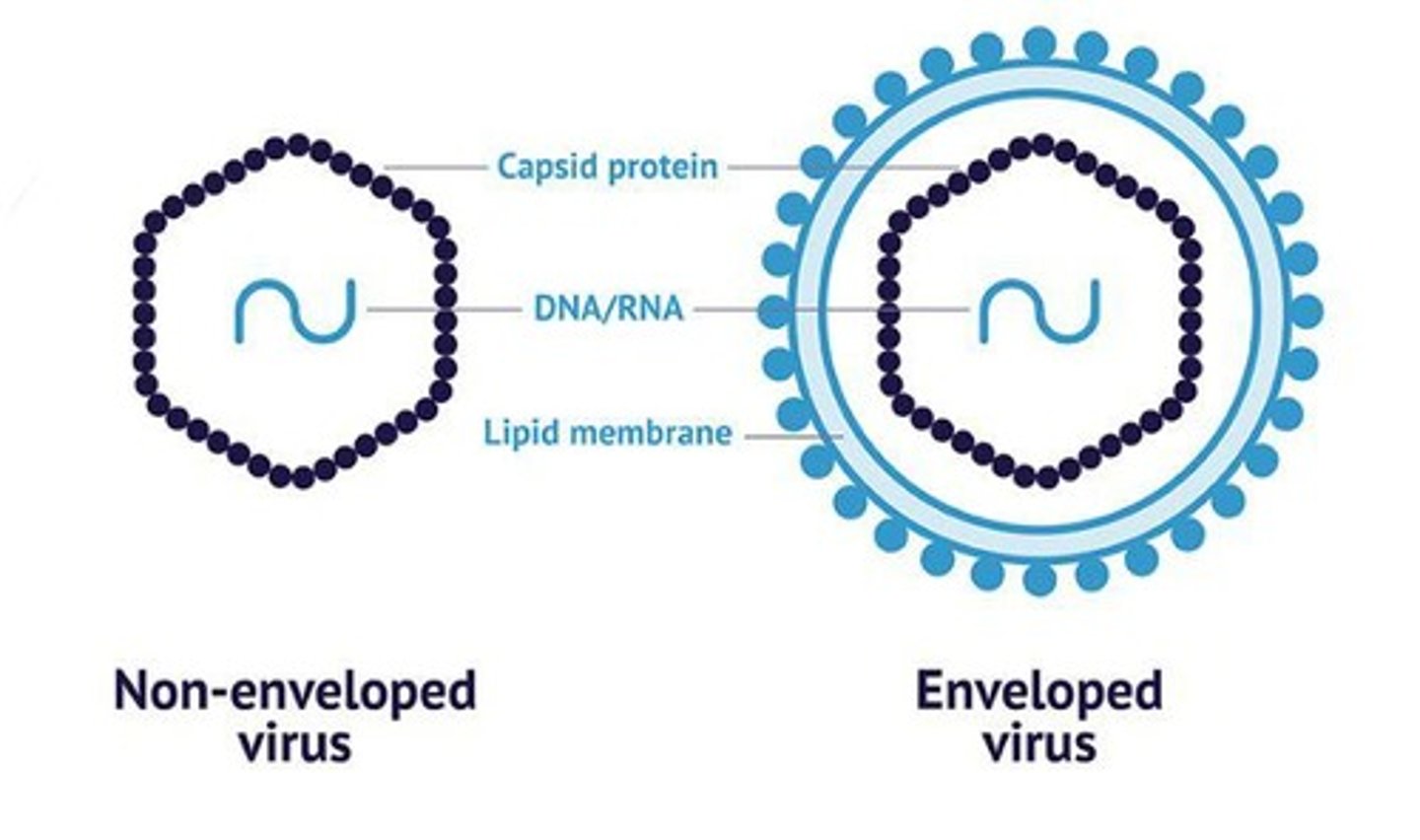
Non-enveloped viruses
Viruses without a lipid membrane, e.g., bacteriophages.
Positive-sense RNA
RNA can directly act as mRNA for translation.
Negative-sense RNA
RNA must be transcribed into mRNA first.
Retroviruses
Contain ssRNA and use reverse transcriptase to make DNA.
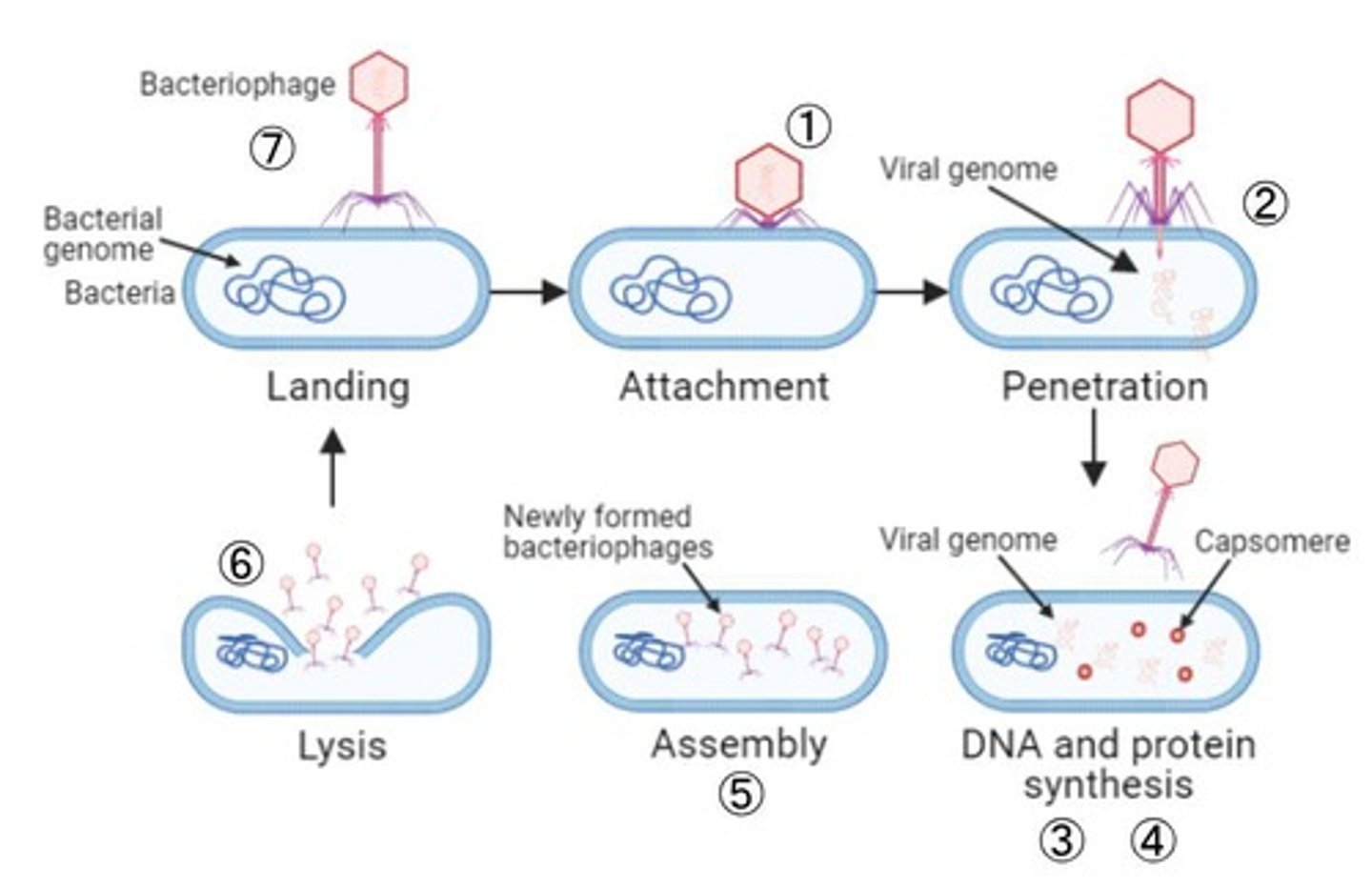
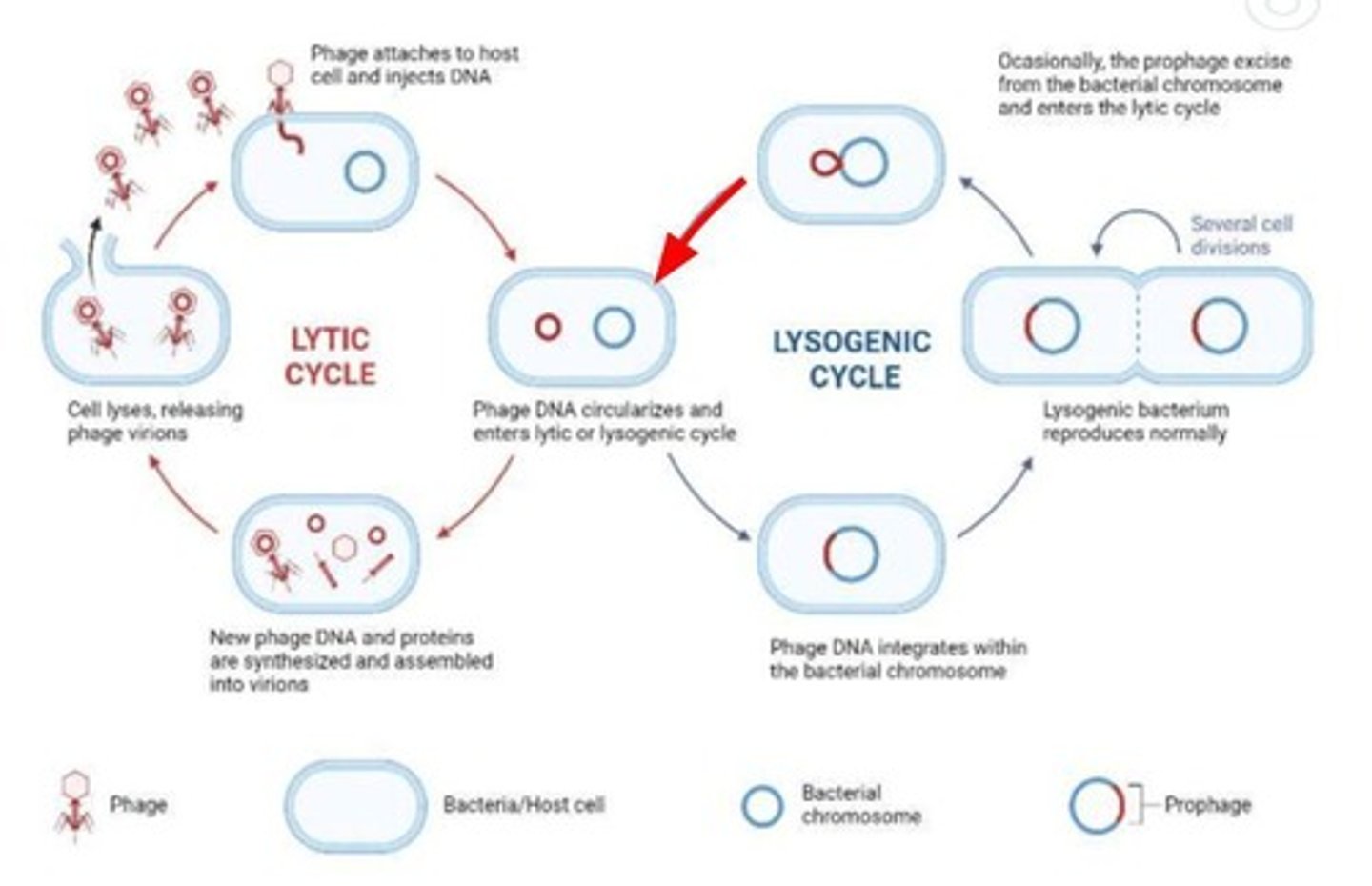
Lytic cycle
Viral reproduction involving host cell lysis.
Lysogenic cycle
Viral genome integrates into host genome without killing.
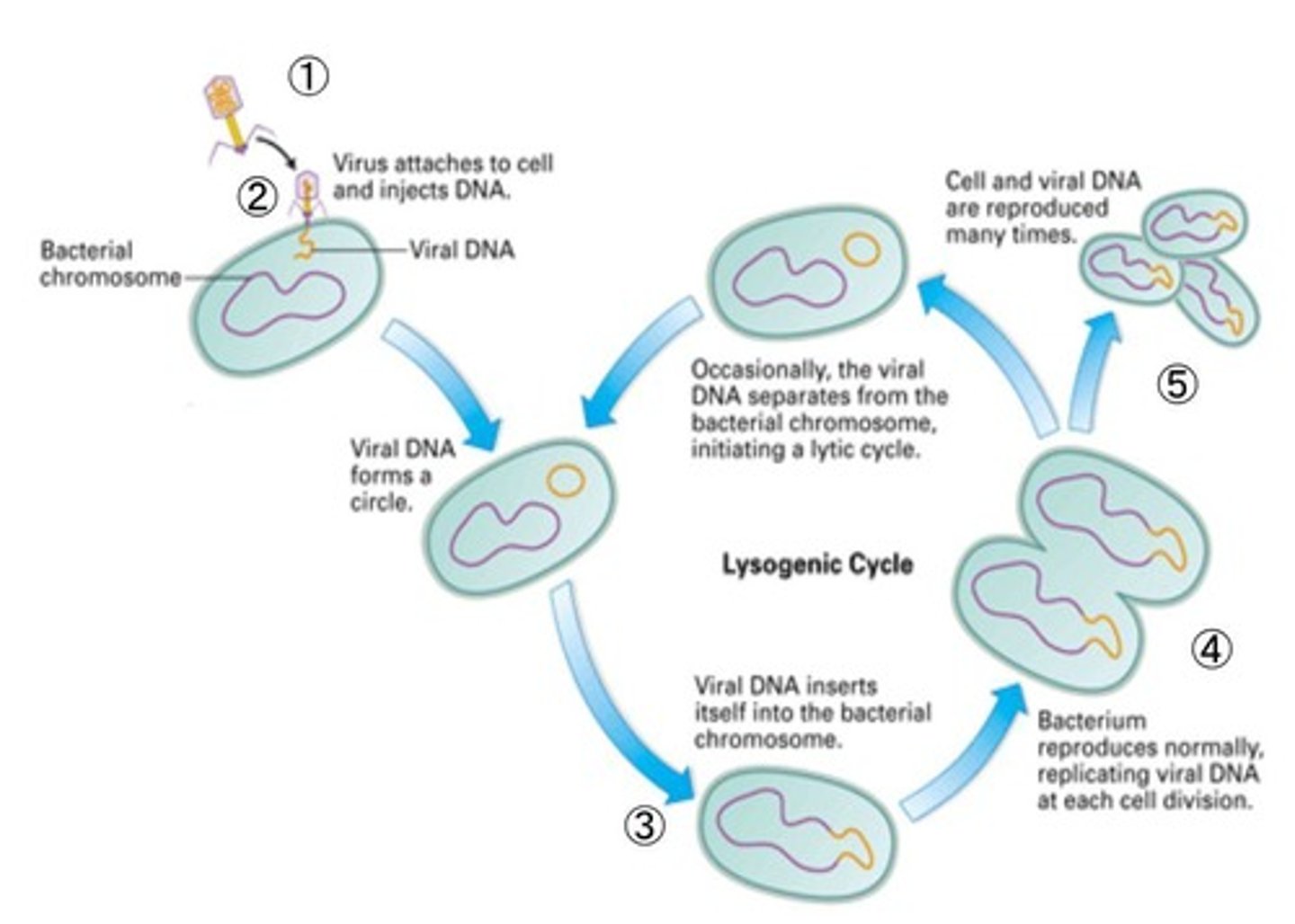
Viral attachment
First step in both lytic and lysogenic cycles.
Viral genetic material entry
Second step where virus injects its genome.
Viral replication
Host cell replicates viral genetic material.
Viral protein synthesis
Host cell synthesizes viral proteins.
Viral assembly
New virus particles are assembled within host.
Host cell lysis
Host cell bursts, releasing new viruses.
Convergent evolution
Unrelated viruses share features due to similar lifestyles.
High mutation rates
RNA viruses mutate rapidly, aiding evolution.
Recombination
Swapping genetic material between co-infecting viruses.
Short generation times
Eclipse periods range from 8 to 72 hours.
Large population sizes
High numbers increase variation and mutation chances.
Antigenic drift
Small changes in virus proteins evade immune detection.
HIV drug resistance
HIV mutates quickly, requiring drug cocktails for treatment.