Aice Environmental Management Unit 6: Managing water supplies
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
distribution of the Earth's water
salt water in oceans 97%
Freshwater 3%:
• surface fresh water - ice sheets, glaciers, lakes, rivers, swamps, marshes, permafrost
• sub-surface fresh water - soil moisture, ground water, permafrost
• atmospheric water
water security
the ability to access sufficient quantities of clean water to maintain adequate standards of food and manufacturing of goods, adequate sanitation and sustainable health care
causes of water insecurity
• climate change, including changes in rainfall
• natural disasters, including drought and flooding • pollution events
• inadequate sanitation
• population growth, changes in land usage including deforestation and urbanisation
• competing demands from agricultural, industrial, energy and domestic sectors
• mismanagement of irrigation, including salinisation
• international competition over water sources
• inequality of availability between water-rich and water-poor regions
• differing access to safe drinking water in urban and rural area
Aral Sea Disaster
1950s, when the Soviet Union diverted two rivers that fed the Aral Sea in Central Asia, dramatically decreased freshwater input into the Aral Sea, salinity of the remaining lake water increased, destroying the local fish populations, diversion project reduced its surface area by more than 60 percent, dust storms have eroded soil, salt, and pesticide residues from the dry lake bed and carried particles of these substances into the atmosphere, summers in the region are now hotter and winters are colder
impacts of water insecurity
• reduced crop yield and crop failure • livestock death • food shortages, malnutrition and famine • illness caused by contaminated drinking water, limited to diarrhoea and cholera
describe and evaluate strategies for managing water security
• sustainable water extraction and improved supply (piped supply, aquifers and artesian wells, boreholes, gravity-fed schemes, reservoirs and dams)
• reduction in water usage (improved irrigation techniques, growing crops less dependent on high water supply, recycling and rainwater catchment)
• education on sustainable water use
• poverty reduction
• international agreement and water-related aid (detailed knowledge of international agreements is not required)
• rationing
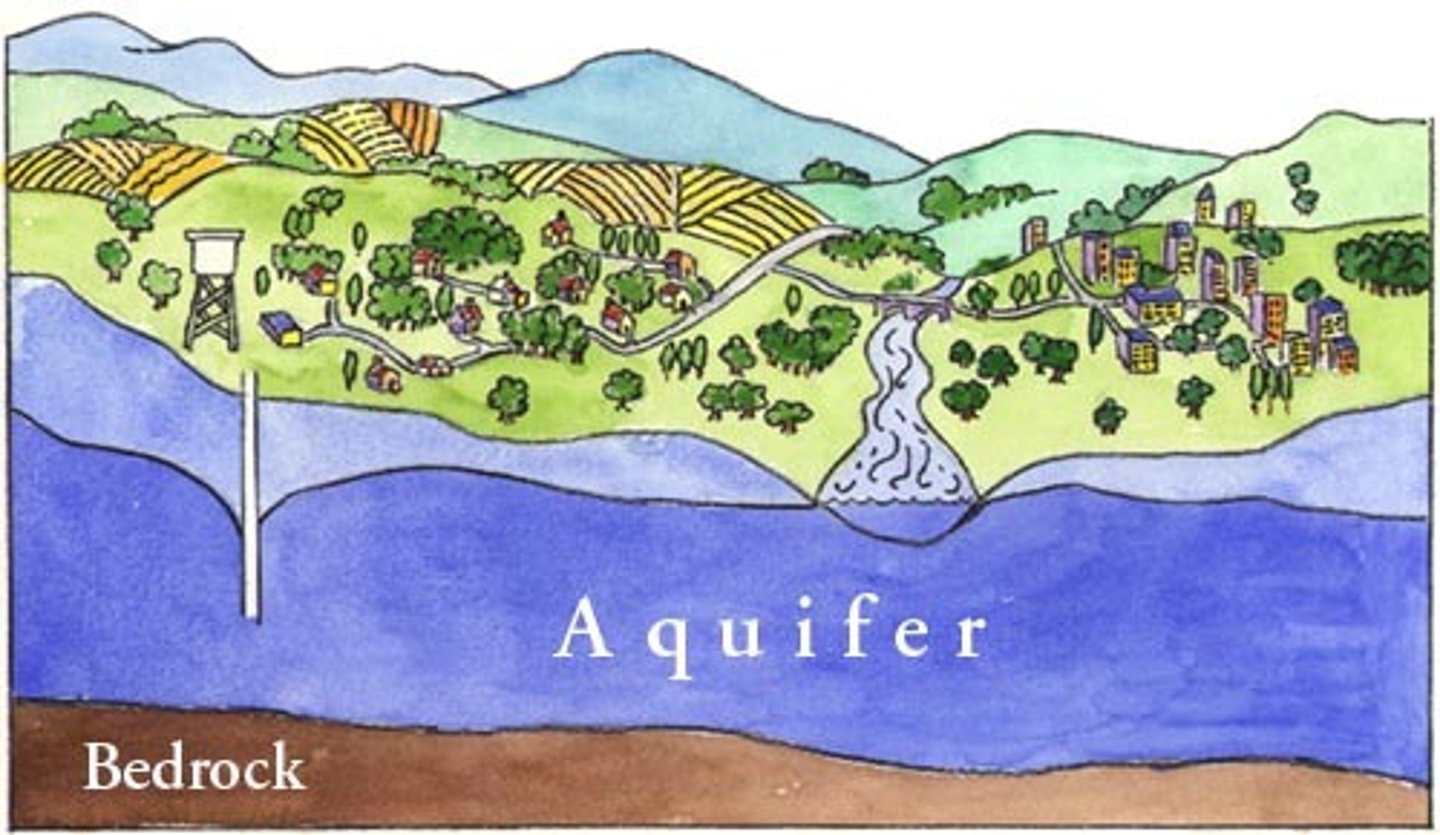
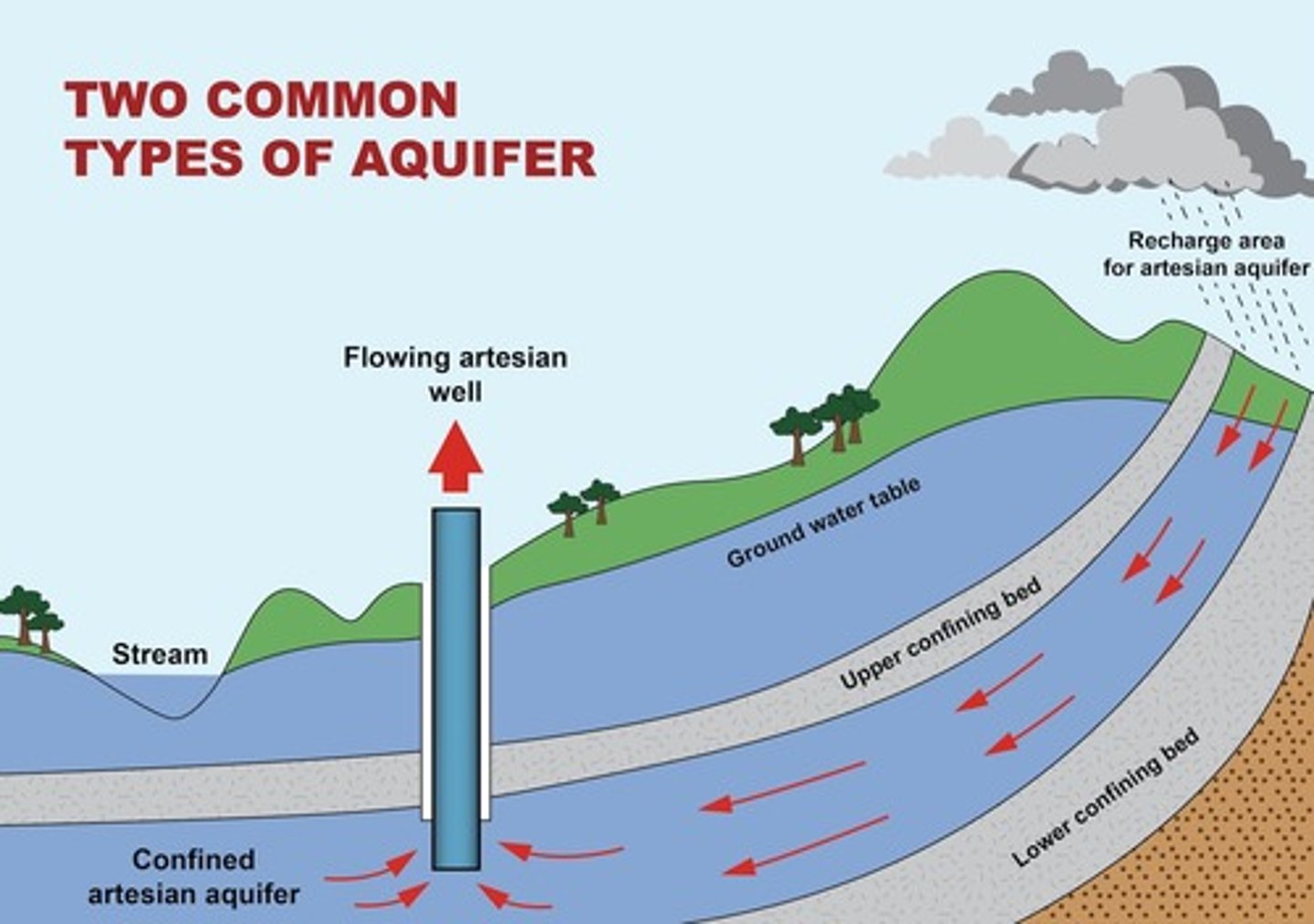
Aquifer
A body of rock or sediment that stores groundwater and allows the flow of groundwater.
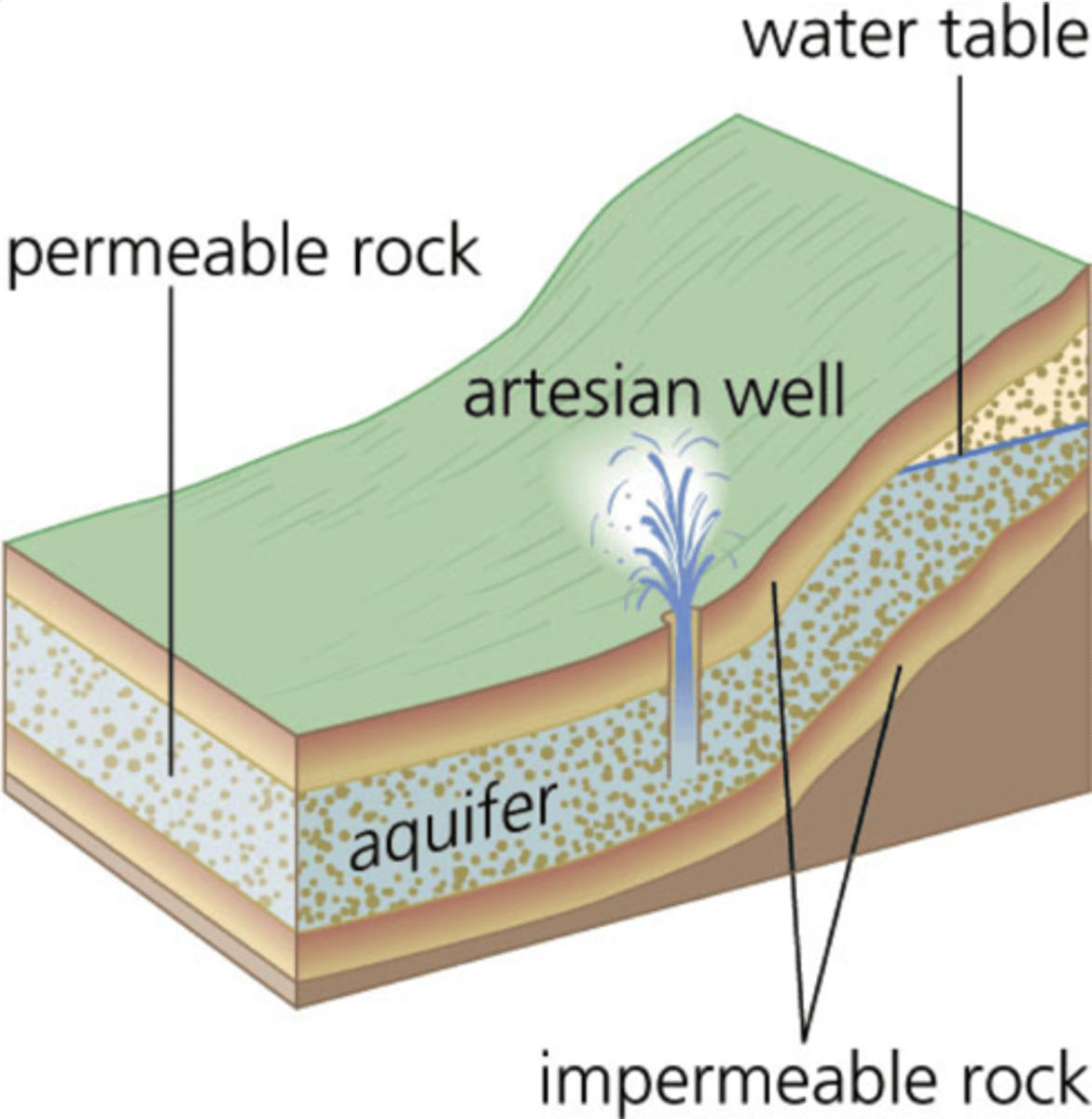
Artesion Well
a welling created by drilling a hole into a confined aquifer, releases pressure
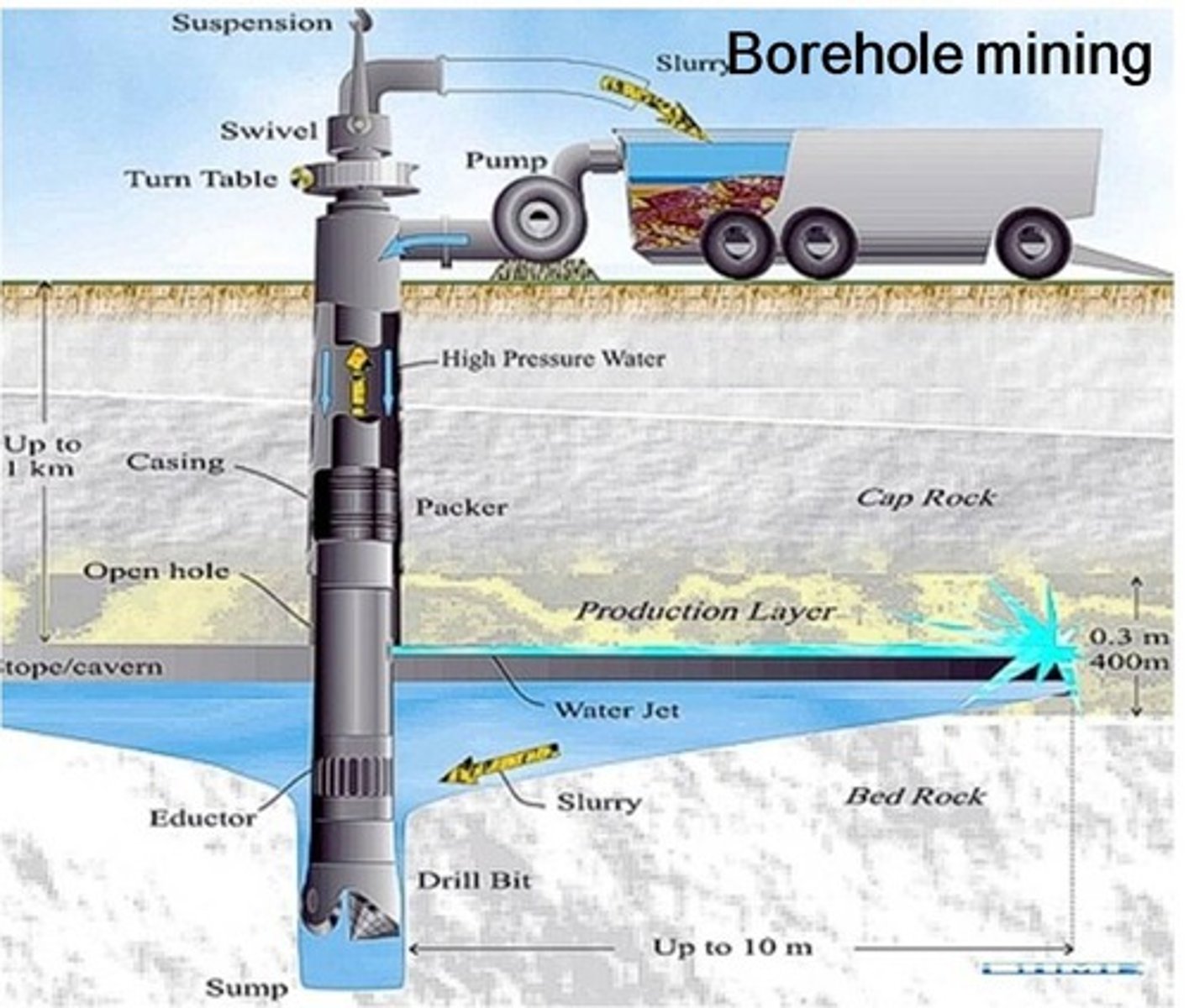
borehole
a very deep narrow hole in the ground made in order to get water or oil
reservoir
a large natural or artificial lake used as a source of water supply.
Dams
Built across a body of water, slows the movement of water behind it, creates large reservoir for water supply, decreases erosion
pros and cons of dams and reservoirs
pros:
-reliable water supply
-recreation
-flood control
cons:
-flooded land
-greatly altered stream flow
-siltation behind the dam
-very costly
Gravity fed schemes
supply from a small upland river, stream or spring, impounded within a protected catchment, is an example of a sustainable water supply technology requiring no treatment
Rationing
A system of allocating scarce goods and services using criteria other than price
sustainable water use
• Waste less water and subsidize water conservation
• Do not deplete aquifers
• Preserve water quality
• Protect forests, wetlands, mountain glaciers, watersheds, and other natural systems
• Get agreements among regions and countries sharing surface water resources
• Raise water prices
• Slow population growth
Cholera
an acute intestinal infection caused by ingestion of contaminated water or food
diarhea
- a gastrointestinal disturbance characterized by decreased water absorption and increased peristaltic activity of the large intestine.
-not enough water absorbed
Water Aid
Water Aid is an international non-government organisation dedicated to the provision of safe and clean domestic water, sanitation and hygiene education to the world's poorest people. Water Aid envisions a world where all people have access to safe water and sanitation, with a mission to transform the lives of the poorest and most marginalised by increasing access to safe water, sanitation and hygiene.

UN Sustainable Development Goals
17 goals, examples: no poverty, zero hunger, good health and well being, quality education and WATER AND SANITATION

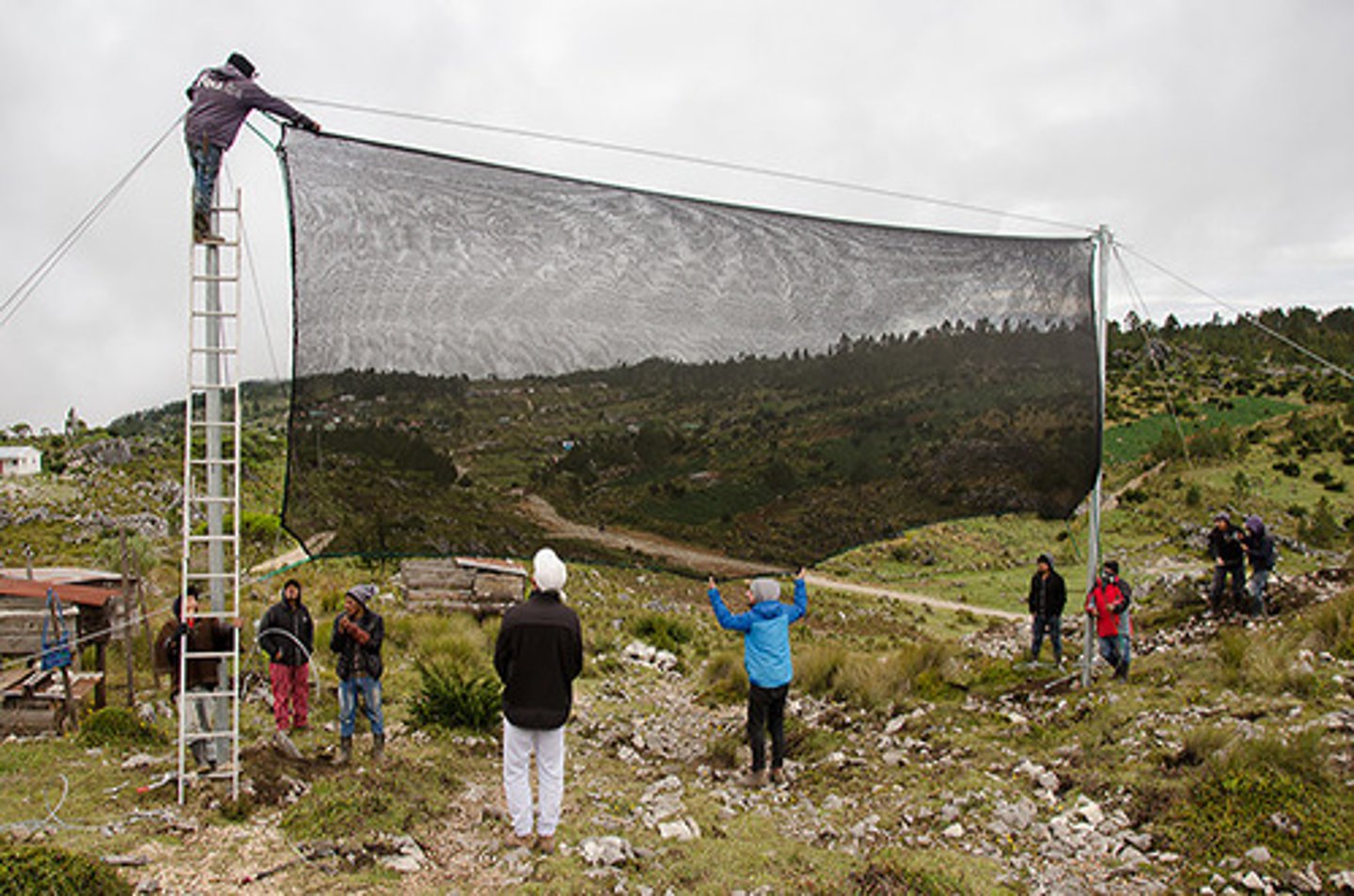
fog nets
Used in desert areas with fog (chile and peru) to capture drinking water through fog drip phenomenon

piped water supply
moving water into an area with large water pipes typically consists of a centralized pumping station, often with elevated storage tanks, that transports water via underground pipes to shared or private spaces such as yards near houses.
Piped water systems with shared and private household taps decrease the distance to the water source and the time spent fetching water.

Desalination
the removal of salt from seawater to make it usable for drinking and farming

pros and cons of desalination
-Pros: ample supply
-Cons: expensive, energy-intensive process, toxic wastewater, damages aquatic food webs
drip irrigation systems
deliver small amounts of water directly to plant roots by using perforated tubing, water is released to plants as needed and at a controlled rate

irrigation cons
-deplete groundwater
-saltwater intrusion
-waterlogging
-salinization

alfalfa
a plant widely grown for animal feed; highly water intensive

drought-tolerant crops
this kind of crop can reduce the consumption of water
growing native crops
Salt water intrusion
near the coast, sea-level rise and overpumping of groundwater causes saltwater to move into the aquifer.
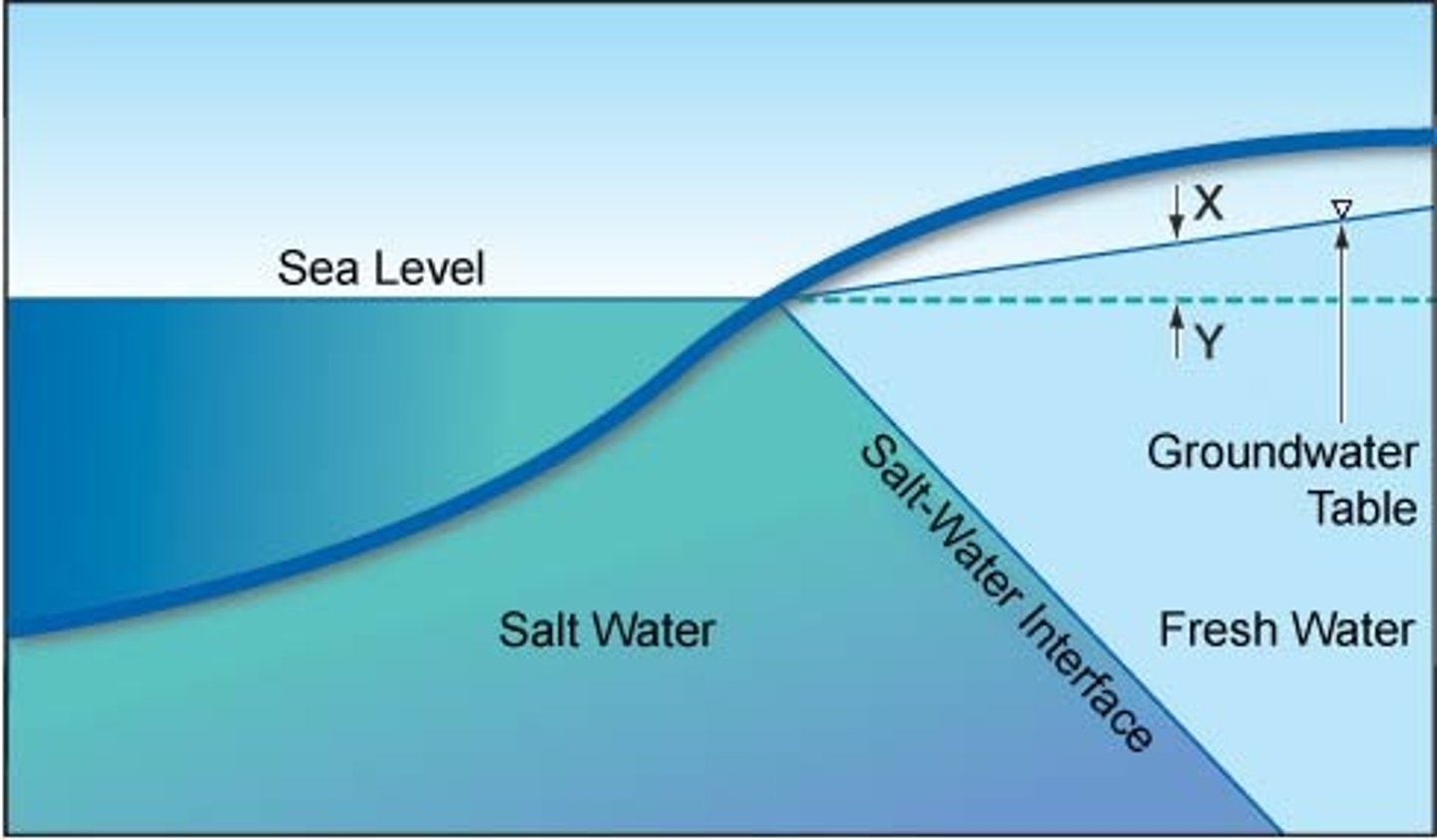
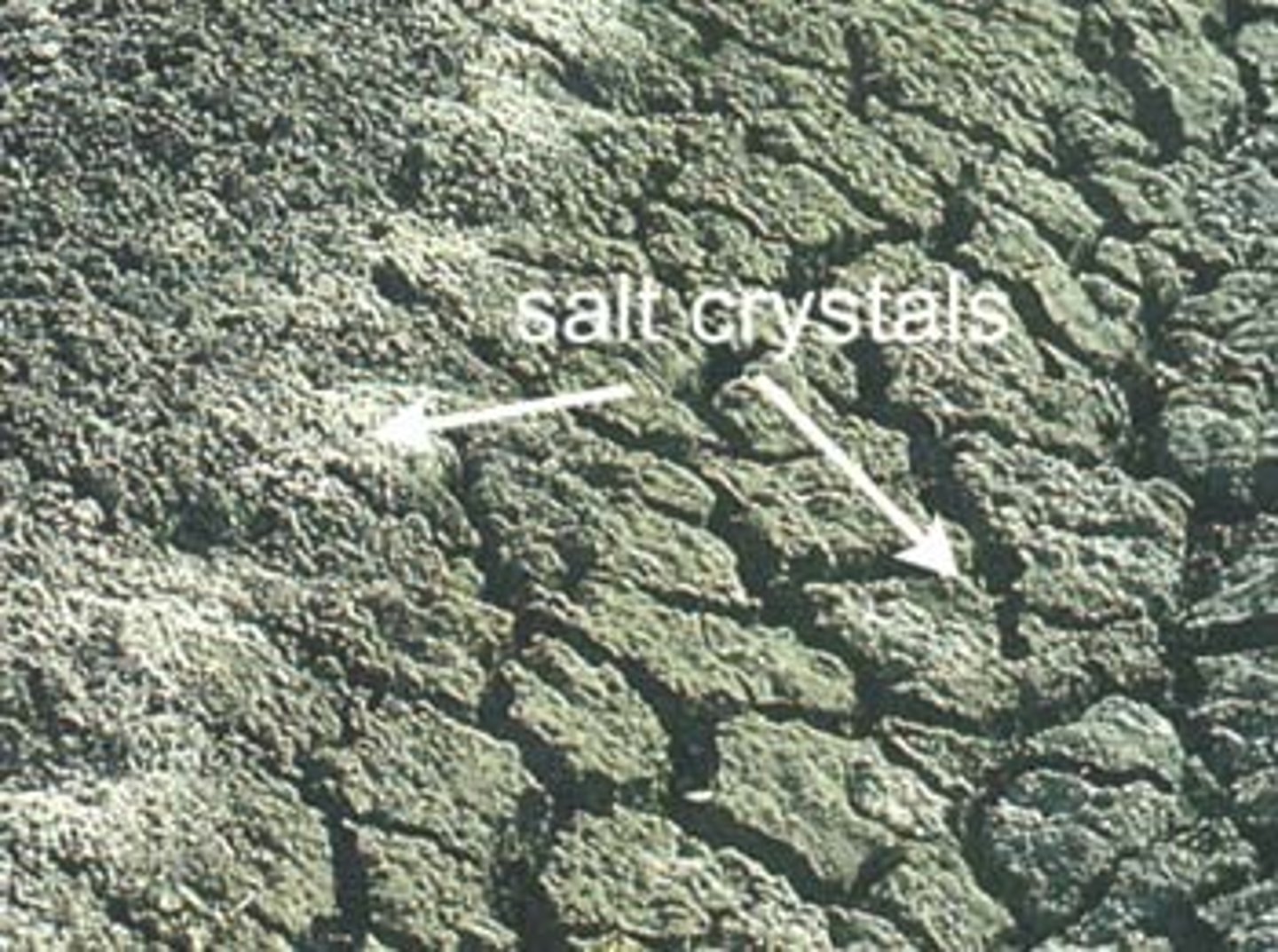
Salinization
A process in which mineral salts accumulate in the soil, killing plants; occurs when soils in dry climates are irrigated profusely

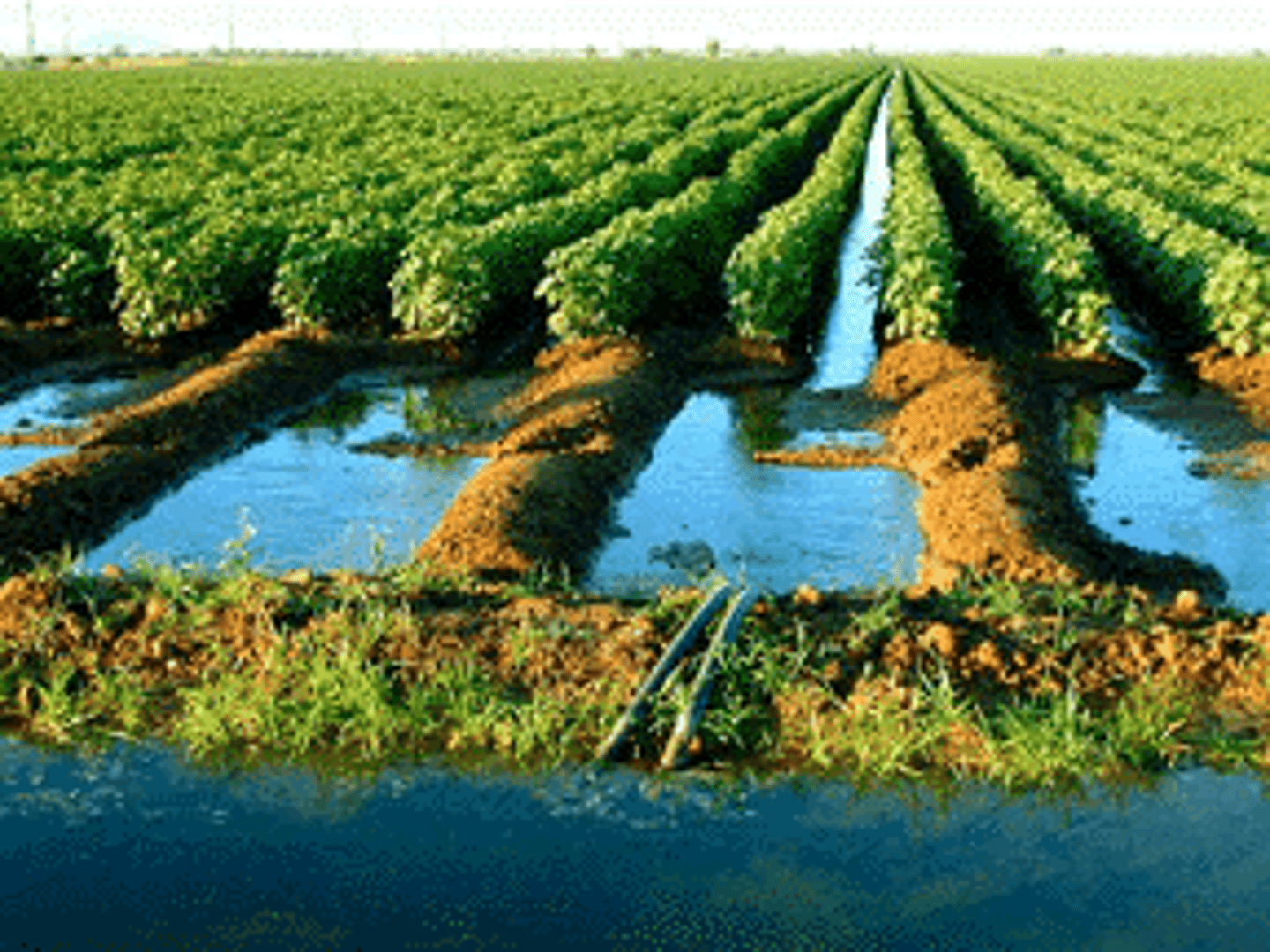
Types of irrigation
drip irrigation, flood irrigation, furrow irrigation, and spray irrigation

Cape Town Day Zero
first modern major city in the world to almost completely run out of water
confined aquifer
A groundwater storage area trapped between two impermeable layers of rock.
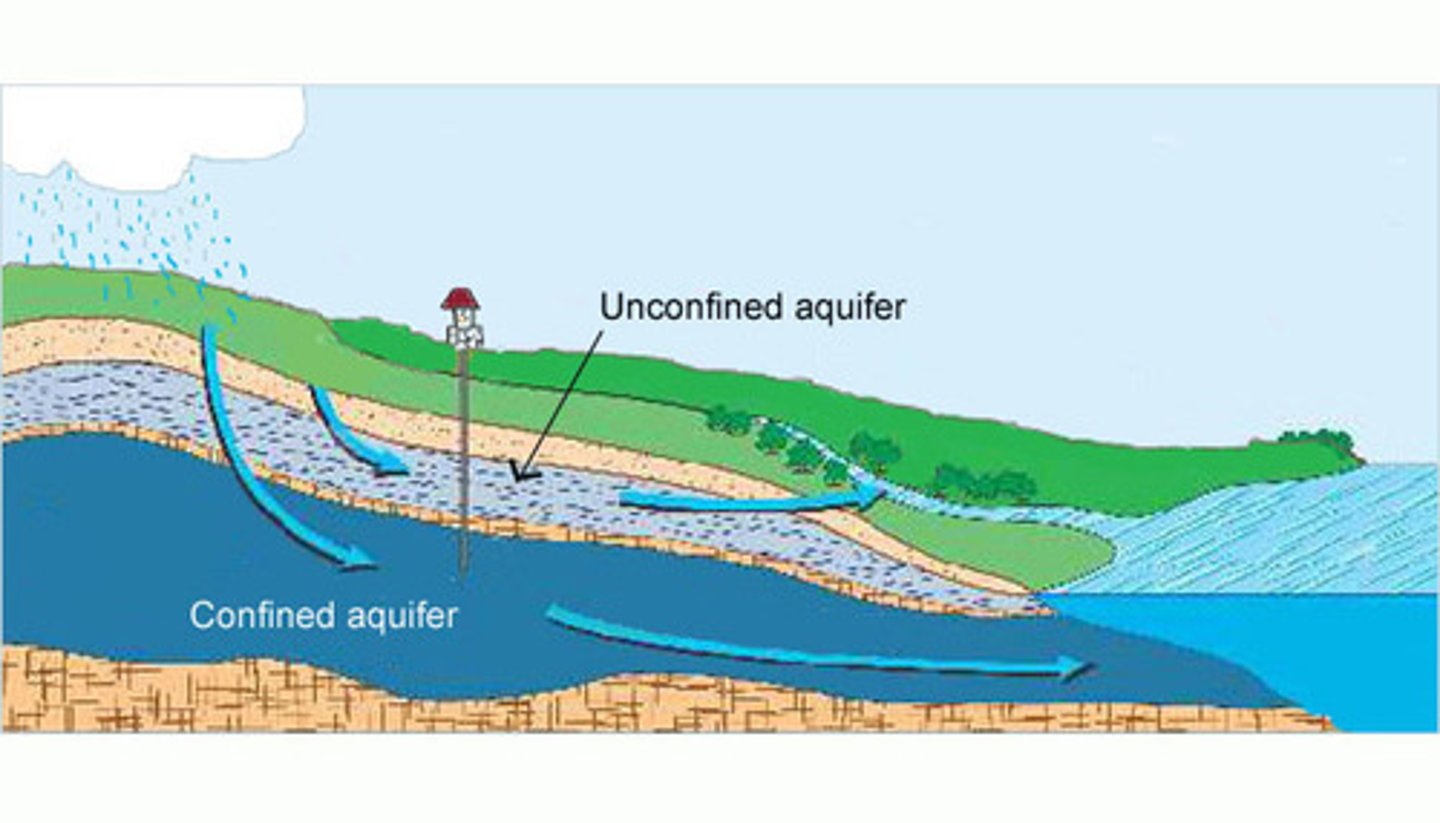
unconfined aquifer
An aquifer made of porous rock covered by soil, which water can easily flow into and out of.
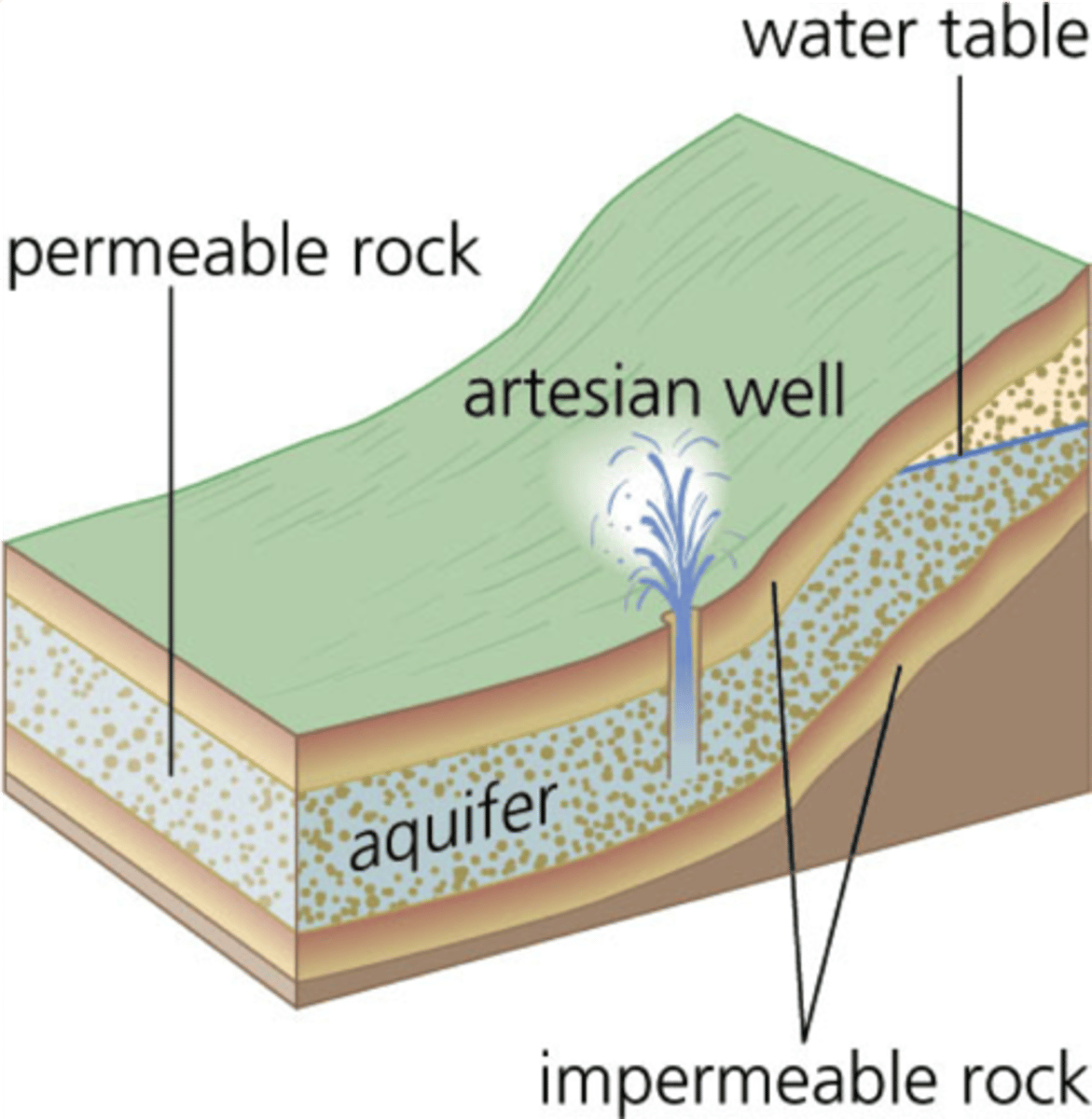
artesian well
A well in which water rises because of pressure within the aquifer
Open defecation
using open spaces rather than a toilet to pass human waste
