spinal cord, brainstem, forebrain 1/30
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
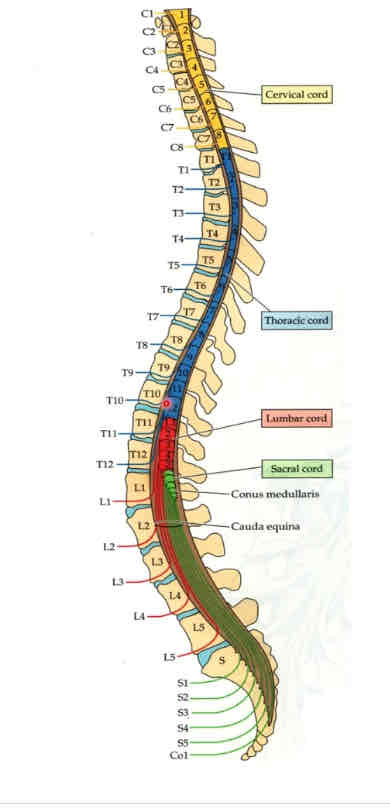
spinal cord
located within vertebral canal
7 cervical vertebrae
12 thoracic vertebrae
5 lumbar vertebrae
5 sacral vertebrae
extends from foramen magnum to first lumbar vertebra
what is a spinal cord segment?
a part of the spinal cord with a pair of spinal nerves branching off of it
how many spinal cord segments?
31 total
how many cervical spinal cord segments?
8
how many thoracic spinal cord segments?
12
how many lumbar spinal cord segments?
5
how many sacral spinal cord segments?
5
how many coccygeal spinal cord segments?
1
what attaches to each spinal cord segment?
a pair of spinal nerves
C1-C7 spinal nerves
emerge above their respective vertebra
C8 spinal nerve
emerges between CV7 and TV1
how do you classify the level of spinal cord lesions?
according to spinal cord segment, not vertebral level
as you progress through development, what does the spinal cord do?
ascends in the vertebral canal
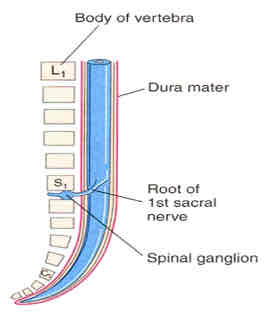
how old?
8 weeks gestation
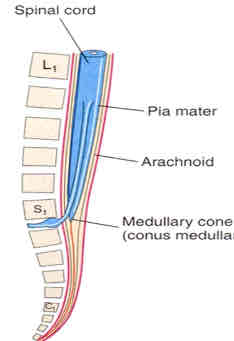
how old?
24 weeks gestation
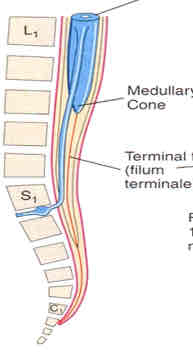
how old?
newborn
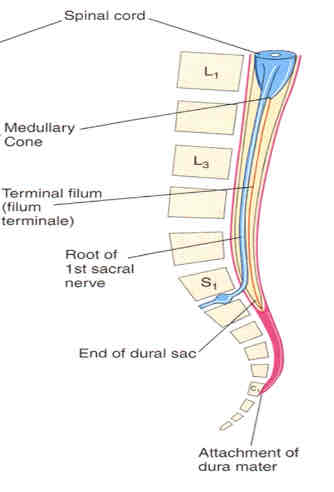
how old?
adult
dural sac
extends from conus medullaris to SV2
composed of caudal equina
filum terminale
CSF
site of lumbar needle tap
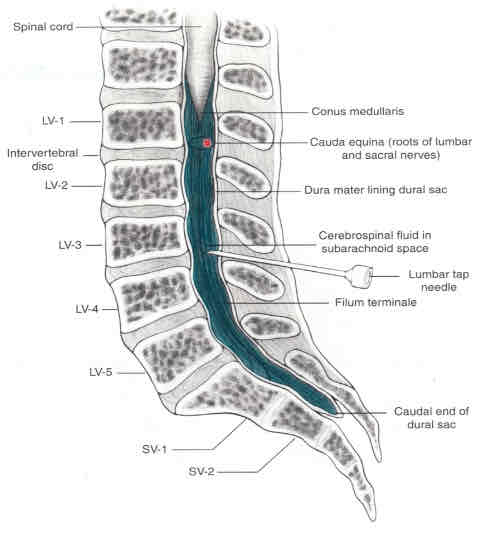
lumbar needle tap
drains CSF for analysis below LV1 so as to avoid puncturing the spinal cord—typically at LV3
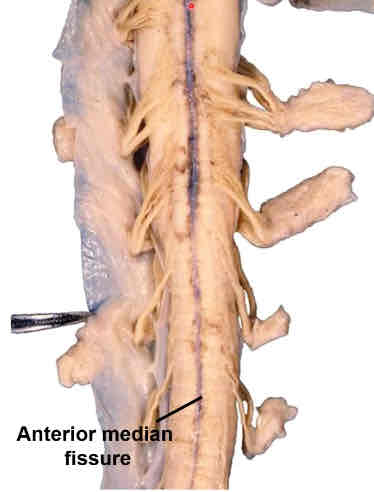
ventral midline of spinal cord
anterior median fissure (artery removed)
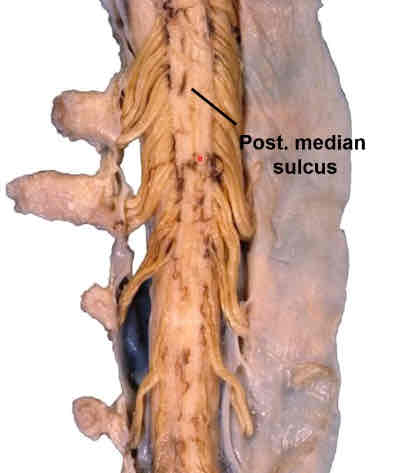
dorsal surface of spinal cord
posterior median sulcus
white matter
3 funiculi—anterior, lateral, and posterior
4 parts of gray matter
dorsal, ventral, lateral horns; intermediate zone
what does white matter contain?
myelinated structures (axons)
what does gray matter contain?
unmyelinated structures (soma, dendrites)
lateral horn
only found in segments T1-L2
origin of preganglionic sympathetic fibers
dorsal and ventral roots form
proper spinal nerves
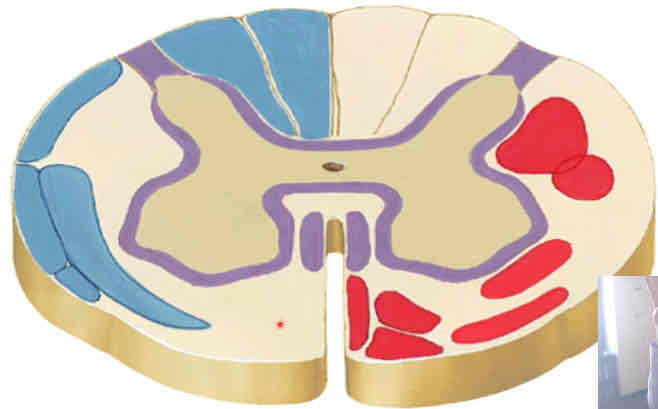
blue
ascending pathways
red
descending pathways
purple
fibers passing in both directions
dorsal horn
receives sensory impulses
ventral horn
origin of somatic efferent/motor neurons
cervical segments
have the most white matter
relatively large horns for UE innervation
thoracic segments
less gray matter bc trunk doesn’t require much innervation
lumbar and sacral segments
most gray matter bc LEs require more innervation
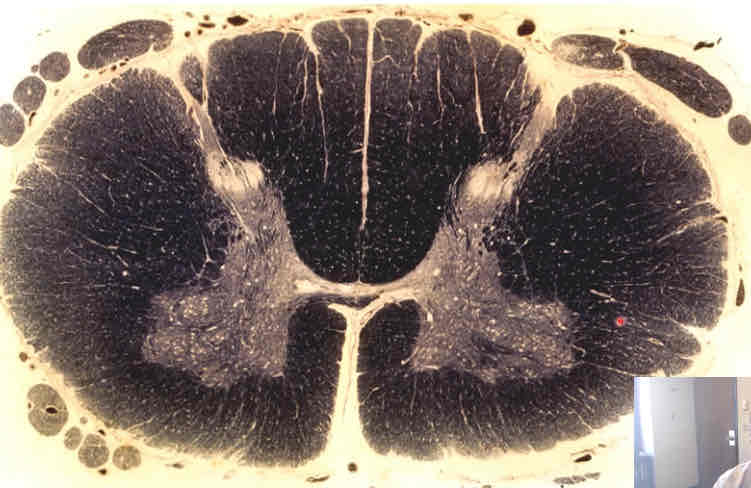
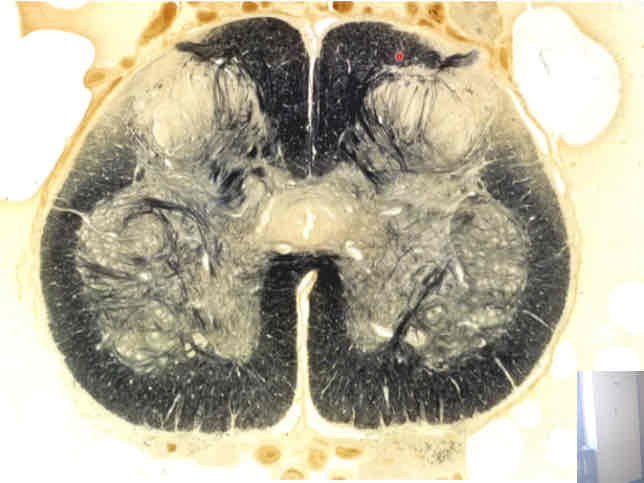
what does this weigert stain depict?
cervical cord
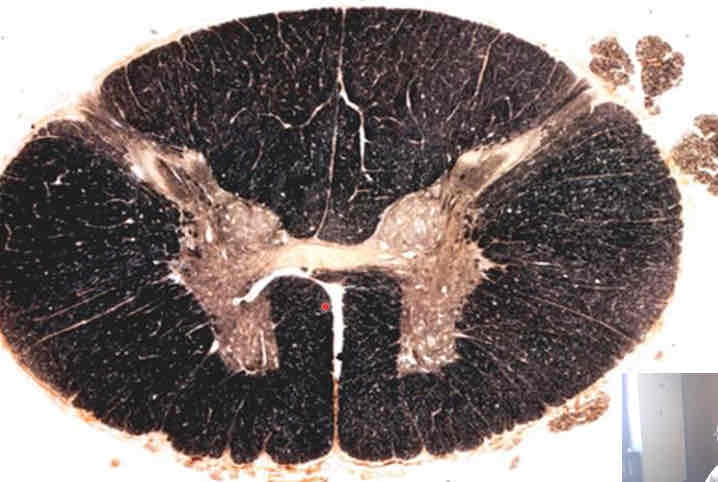
what does this weigert stain depict?
thoracic cord
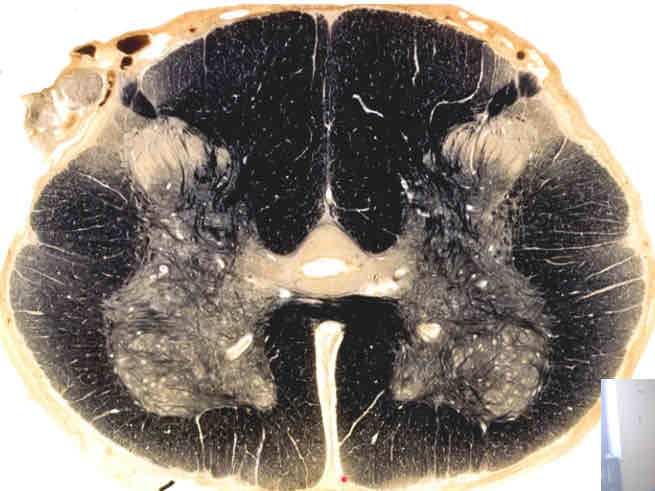
what does this weigert stain depict?
lumbar cord
what does this weigert stain depict?
sacral cord
brainstem contents
functional centers for all but one of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves
long tracts (CNS axon bundles) that transmit ascending impulses from all parts of the body to the forebrain and impulses that originate in the forebrain
vital functional centers (cardiac, respiratory)—so, lesions are often fatal
how is brainstem damage manifested?
by functional loss (somatosensory, motor, etc.) and abnormalities in cranial nerve functions due to their origin here
neural tube
one end develops into the brain, the other into the spinal cord
medulla
inferior part of the brainstem
contains superior open part (associated with fourth ventricle) and inferior closed part
pons
intermediate part of the brainstem
midbrain
superior part of the brainstem
what is the cavity between the pons and cerebellum?
fourth ventricle—continuous with cerebral aqueduct
medulla (ventral surface)
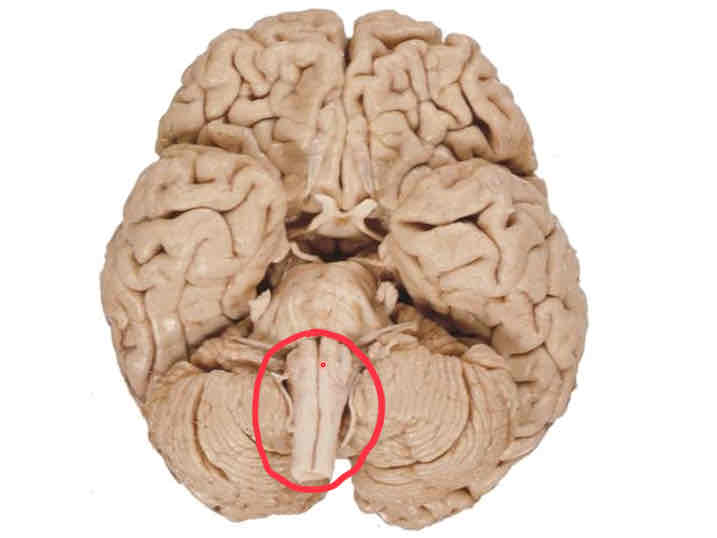
midbrain (ventral surface)
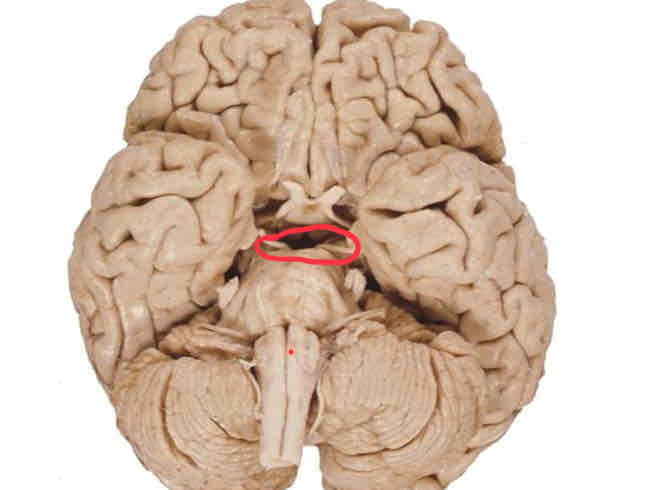
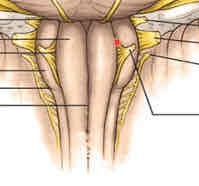
medulla ventral surface features
medial to lateral: anterior median fissure (continuous with spinal cord), medullary pyramids, preolivary sulci, olives, postolivary sulci
preolivary sulcus
CN 12 emergence point
postolivary sulcus
CN emergence from superior to inferior: CN 9, 10, 11
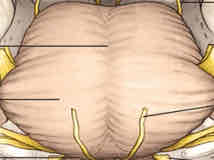
pons ventral surface (basilar pons) features
most inferior: pontomedullary sulcus (separates pons from medulla)
down midline: basilar sulcus (with basilar artery)
transverse fibers extending from basilar sulcus
pontomedullary sulcus
CN 6 (medial), CN 7, and CN 8 (lateral) emergence point
midpontine level of basilar pons
CN 5 emergence point—motor root more medial than sensory, sensory root is larger
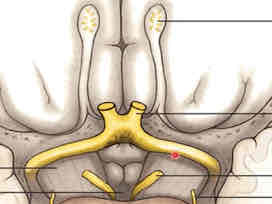
midbrain ventral surface features
cerebral crus, separated by interpeduncular fossa
cerebral crus
CN 4 (emerges from dorsal surface of brainstem, but wraps around lateral sides and can be seen anteriorly) decussation point on lateral/superior sides of pons
CN 3 on medial sides (from interpeduncular fossa)
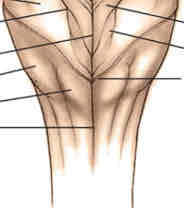
medulla dorsal surface features
closed (medial to lateral): posterior median sulcus, gracile tubercles, cuneate tubercles
open (medial to lateral): hypoglossal trigones, vagal trigones (slightly inferior; both with nuclei deep to them), vestibular area
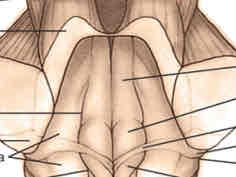
pons dorsal surface features
medial to lateral: posterior median sulcus (continued from spinal cord), facial colliculi, vestibular area (continued from open medulla), cerebellar penducles (superior, middle, and inferior)
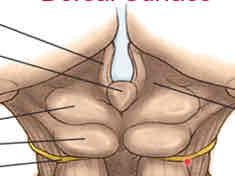
midbrain dorsal surface features
medial to lateral: corpora quadremina (inferior and superior colliculi)
cerebellar peduncles
attachment site for cerebellum
consist of white matter
inferior colliculi
superior to CN 4 emergence point (before it wraps around laterally)
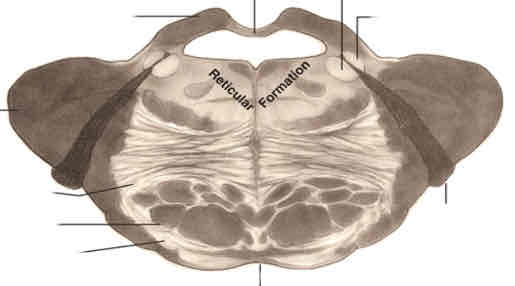
closed medulla cross section stain
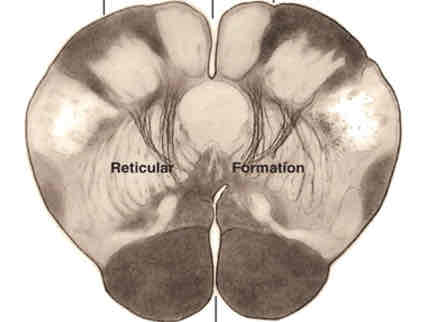
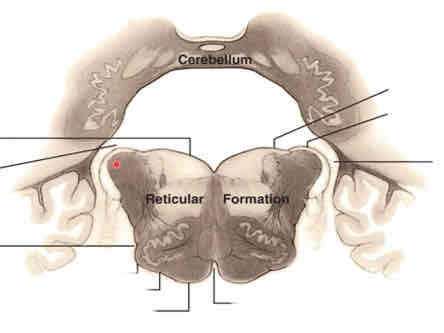
caudal open medulla cross section stain
rostral open medulla cross section stain
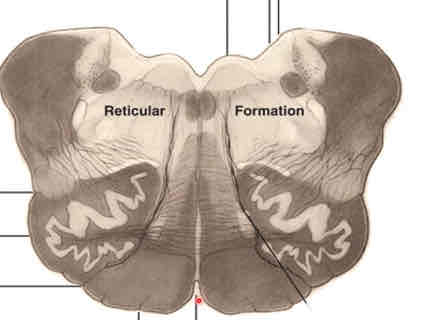
caudal pons cross section stain
middle pons cross section stain
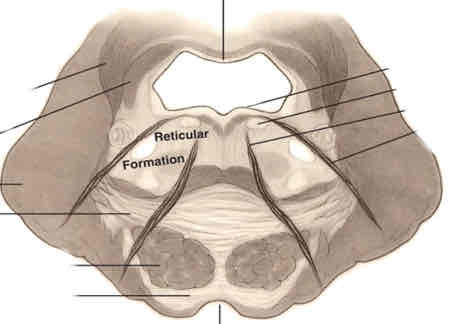
rostral pons cross section stain
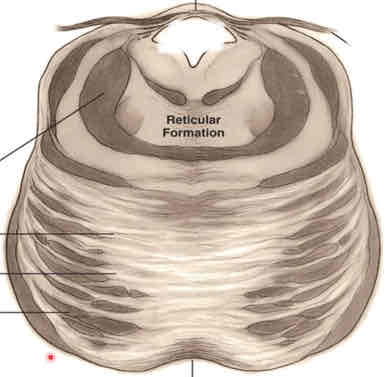
caudal midbrain cross section stain
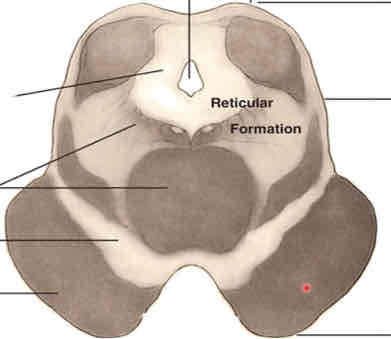
rostral midbrain cross section stain
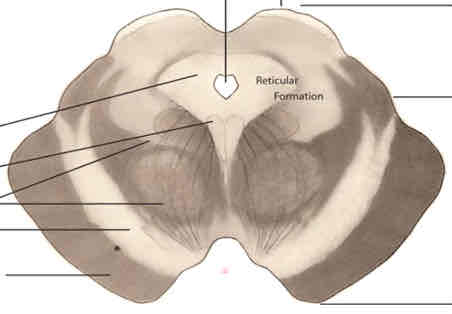
forebrain
consists of telencephalon and diencephalon
superior to the brainstem
diencephalon
contains functional centers for the integration of all info passing from brainstem and spinal cord to cerebral hemispheres, and centers for motor and visceral activity integration
telencephalon
paired cerebral hemispheres that integrate the highest mental functions (ex. sensory and emotional awareness, learning and memory, intelligence and creativity, and language)
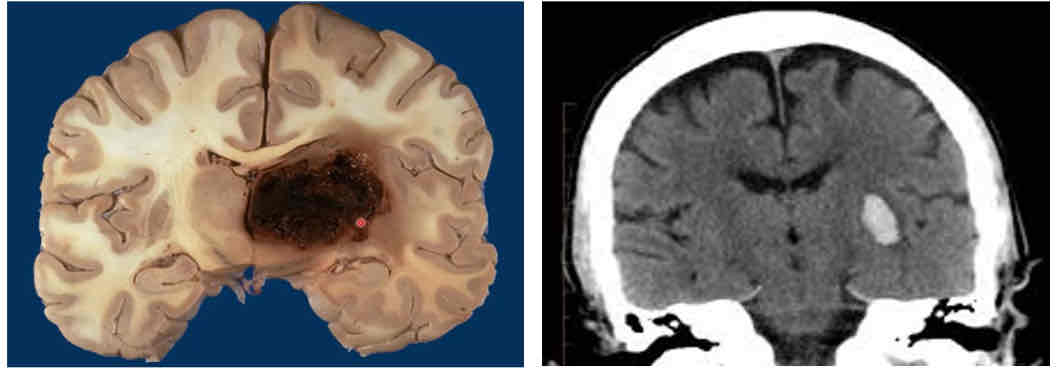
most common vascular lesions
“capsular strokes” or bleeds that occur deep in the brain, in the internal capsule of the forebrain within the white matter
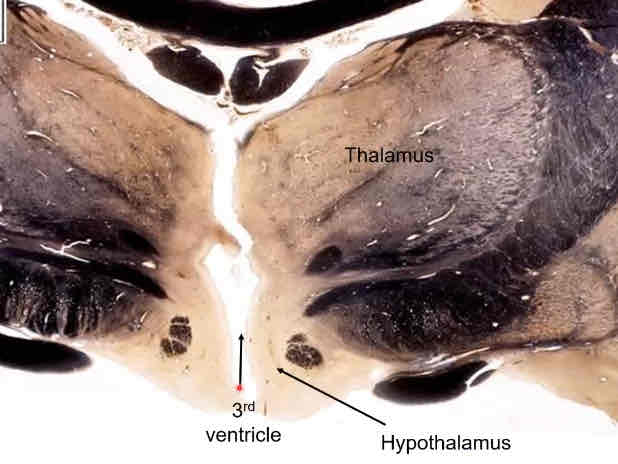
third ventricle
cavity of the diencephalon, continuous with cerebral aqueduct
structures of the telencephalon
corpus callosum, interventricular foramen, septum pellucidum, cerebral cortex
corpus callosum
white matter connecting left and right hemispheres
structures of the diencephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, epithalamus
thalamus
egg shaped, superior to hypothalamus
hypothalamus
inferior to thalamus
controls a lot of autonomic functions
subthalamus
inferior to thalamus and posterior/inferior to hypothalamus
epithalamus
posterior to thalamus
consists of pineal gland
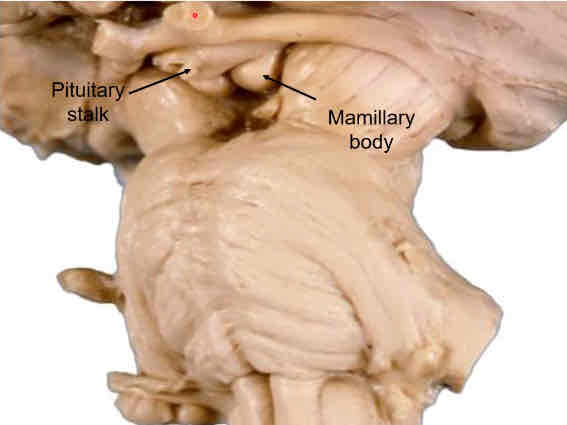
ventral (inferior) surface of diencephalon
mammillary bodies
stalk of pituitary gland (infidibulum)
optic chiasm
coronal myelin stain of diencephalon
telencephalon lateral surface
cerebral cortex—twists and turns to form a gyri with sulci (fissures) in between
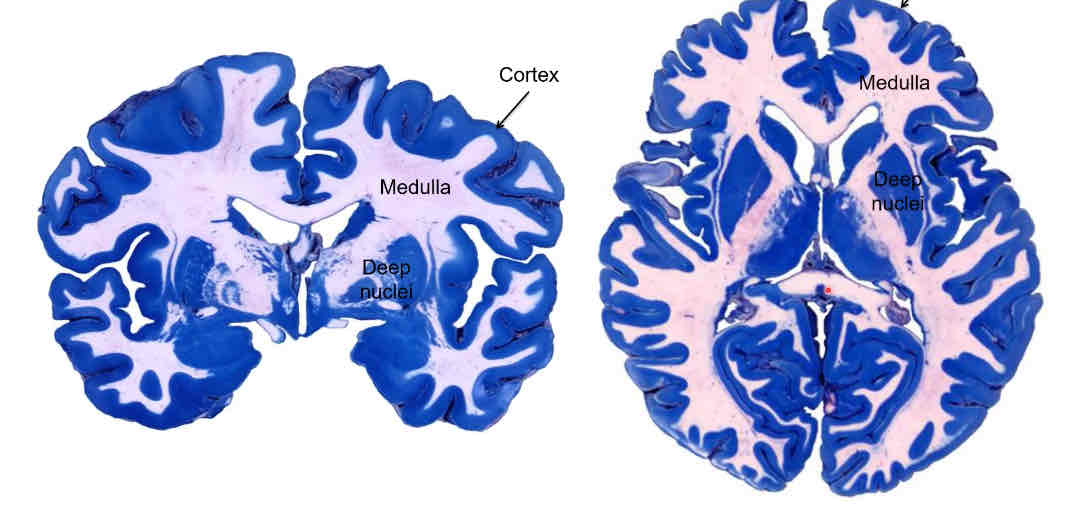
components of the telencephalon
cortex, medulla, deep nuclei
lateral ventricles
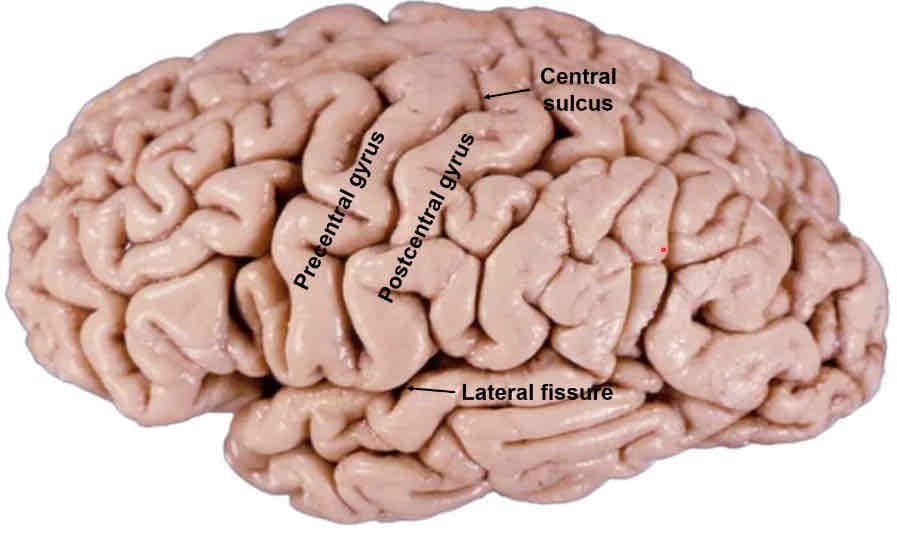
lateral fissure
starts anteriorly and ends about 2/3 through the brain (ant-post direction)
separates frontal and temporal lobe and parietal and temporal lobe
central sulcus
begins superiorly, goes inferiorly down middle of the brain and stops when it intersects w/ lateral fissure
separates frontal lobe from parietal lobe
precentral gyrus
anterior to central sulcus
primary motor cortex
postcentral gyrus
posterior to central sulcus
primary somatosensory cortex
occipital lobe
most posterior lobe, no clear boundary between it and the parietal & temporal lobes
paracentral lobule
region of the frontal lobe consisting of gyri and sulci and the medial extension of the central sulcus
parieto-occipital sulcus
separates the parietal lobe from the occipital lobe
inwardly curved sulcus on the posterior medial side of the brain
cortical stroke
a bleed (ischemic response to blockage) that occurs in the cerebral cortex
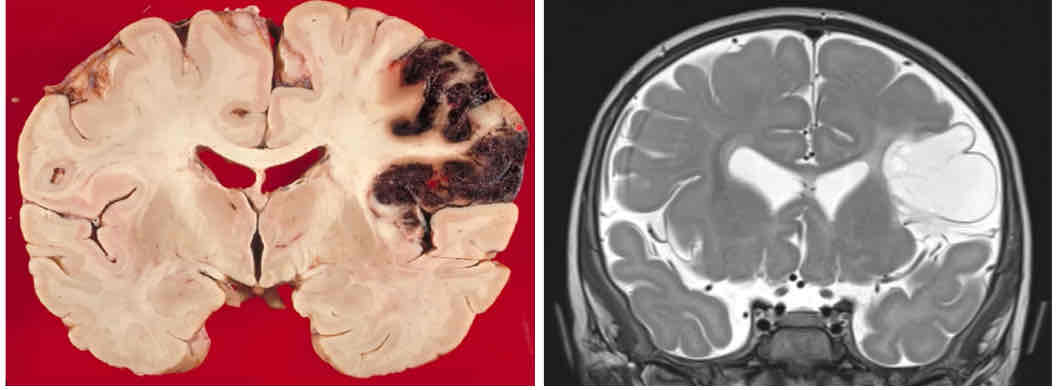
multiple sclerosis
paraventricular plaques within the medulla of the forebrain along the lateral ventricles
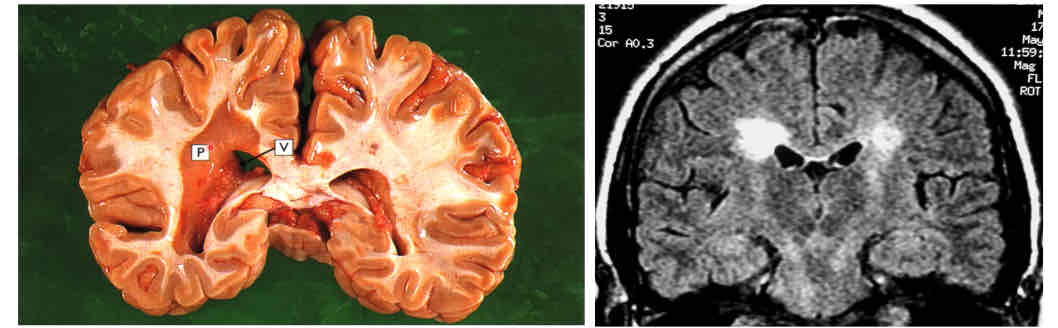
PI: the C7 spinal nerve emerges between which vertebrae?
CV6 and CV7
why do we classify lesions in the spinal cord according to spinal cord segment and not vertebral level?
because the spinal cord is not found at all vertebral levels
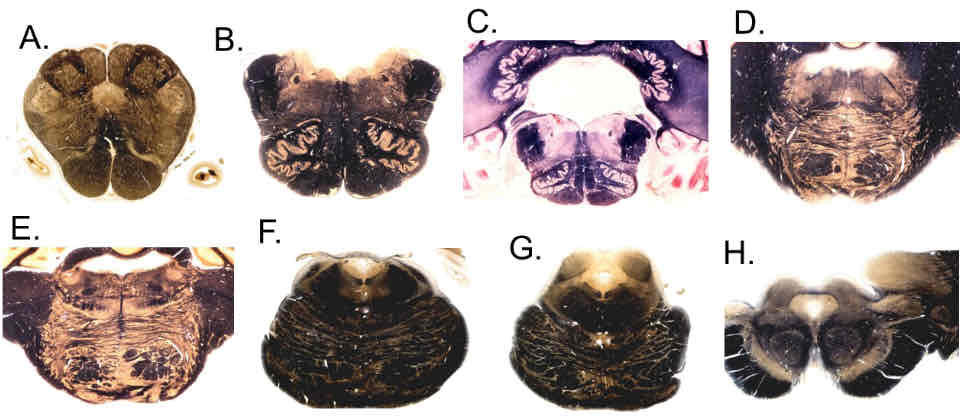
PI: which of the following brainstem levels includes the decussation of the trochlear nerve?
F
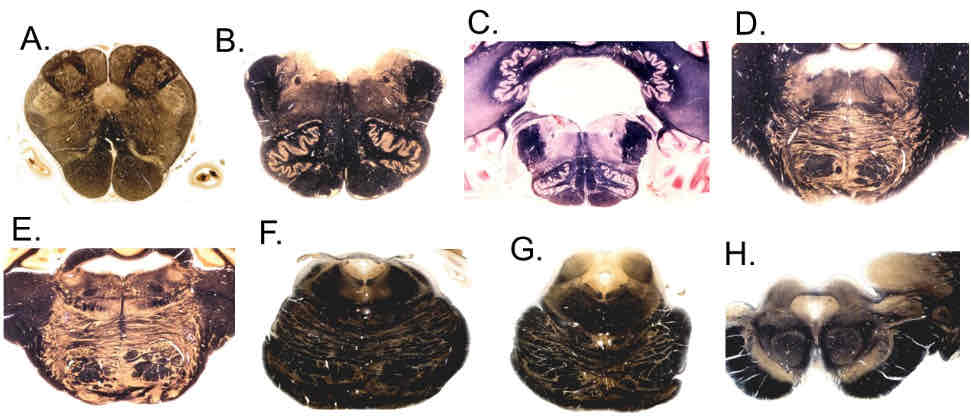
PI: which of the following brainstem levels includes the facial colliculus?
D
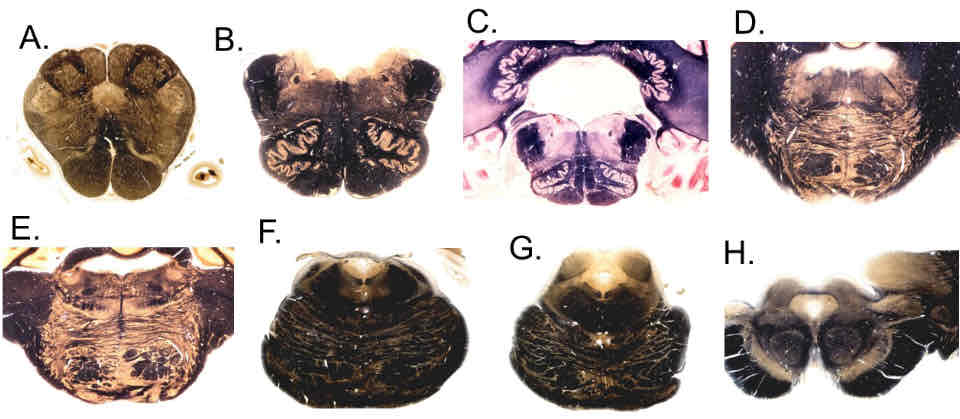
PI: which of the following brainstem levels includes the cerebral crus?
H
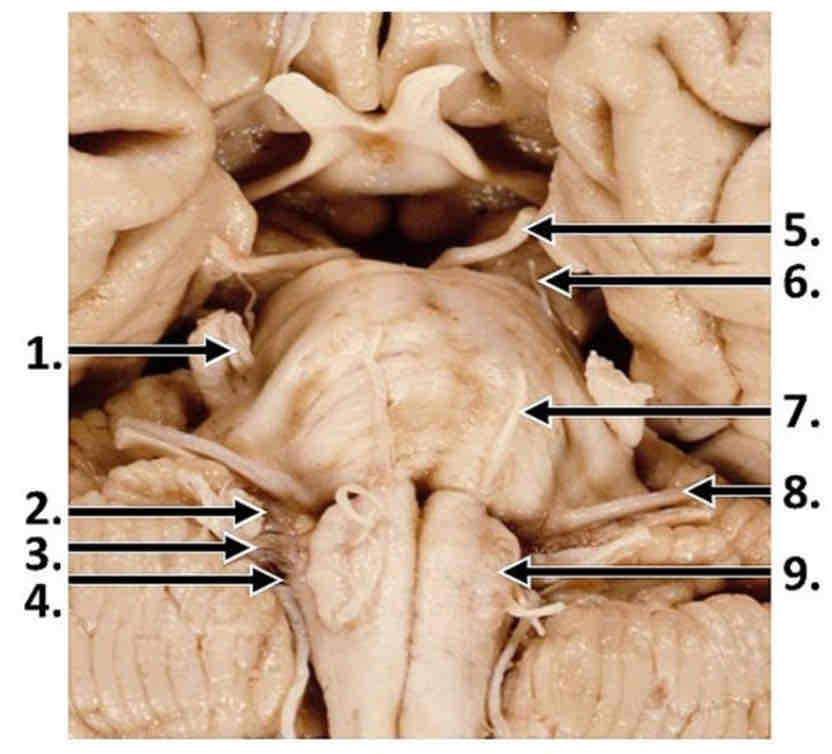
PI: which labeled cranial nerve emerges from the interpeduncular fossa, near the cerebral crus?
5