Chapter 5: The Human Tissues
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Merged flashcards from Chapter 5, McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Tissue growth
Increasing the number (hyperplasia) or size (hypertrophy) of existing cells
Hyperplasia
Growth through cell multiplication
Hypertrophy
Enlargement of preexisting cells
Neoplasia
Development of a tumor; benign or malignant
Differentiation
The development of a more specialized form and function by unspecialized tissue; often seen in embryonic development
Metaplasia
Changing from one type of mature tissue to another; pseudostratified columnar epithelium to stratified squamous in the bronchi of smokers
Embryonic stem cells
Undifferentiated cells that are not yet specialized and can turn into many others
Developmental plasticity
The ability of a stem cell to give rise to many cell types
Pluripotent embryonic stem cells
Stem cells that can develop into any type of cell in the embryo, not the organs
Totipotent embryonic stem cells
Stem cells that can develop into any type of a fully differentiated stem cell; very early
Adult stem cells
Undifferentiated cells in mature organs
Multipotent adult stem cells
Adult stem cells that can develop into two or more cell lines, like bone marrow
Unipotent adult stem cells
Adult stem cells that produce only one cell type, like cells producing sperm
Regeneration
The replacement of dead or damaged cell by the same type of cell as before
Fibrosis
The replacement of damaged cells with scar tissue; no function is restored
Stages of healing skin
Vessels bleed into cut, releasing histamine and allowing plasma to flow better with antibodies and proteins
Blood clot forms, protecting healing and blocking infection while leukocytes digest debris
Blood capillaries sprout from nearby vessels, and the tissue heals with soft granulation tissues and new collagen as the blood clot is removed over 2 weeks
Epithelial tissue multiplies and regenerates beneath the scab; connective tissue undergoes fibrosis which may show a scar for up to 2 years
Atrophy
The shrinkage of a tissue through loss in cell size or number; occurs in normal aging or lack of use
Necrosis
Tissue death due to trauma, toxins, or infections
Infarction
Sudden tissue death when blood supply is cut off
Gangrene
Tissue necrosis due to insufficient blood supply; often paired with infection—types include decubitus ulcers (bed sores), dry gangrene, wet gangrene (organ liquefaction), or gas gangrene (hydrogen bubbles in tissues)
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death to maintain optimal tissue function
Stem cell controversy
While embryonic stem cells have lots of potential, they are also limited by their ability to give rise to living beings
Cell junctions
The connections between two cells; they are usually anchored with each other or the matrix for communication, strength, and transfer
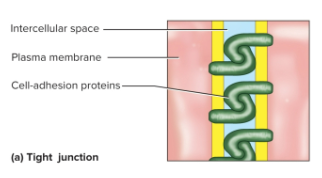
Tight junction
A zipper-like, interlocking linkage between cells by trans membrane adhesion proteins
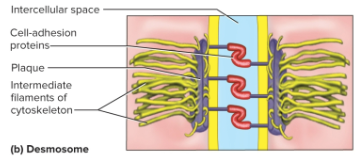
Desmosome
A Velcro-like patch that holds cells together and resists mechanical stress, has hook-shaped proteins with more space in between
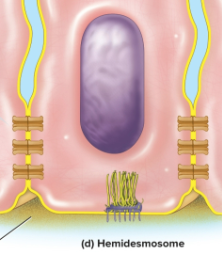
Hemidesmosome
A half-desmosome that anchors basal cells of an epithelium to the basement membrane
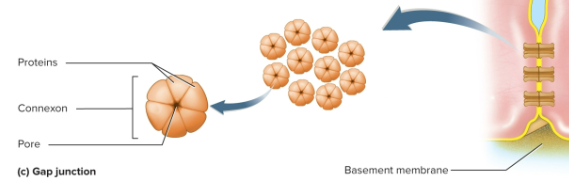
Gap junction
Junction formed by orange-like connexons, these transfer substances like a bridge and are located in cardiac and smooth muscle as well as the embryo, lens, and cornea
Connexon
Six trrans membrane proteins arranged like segments around a water-filled pore
Gland
A cell or organ that secretes substances for use in the body or releases them
Secretion
Keeping a product useful to the body
Excretion
Removing a product not useful to the body (waste products)
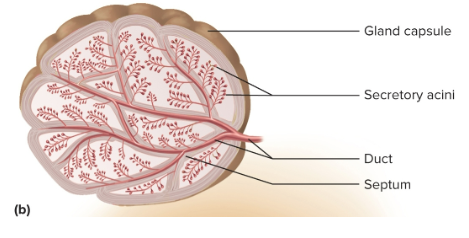
Exocrine glands
Glands that maintain their contact with the surface of the epithelium via a duct
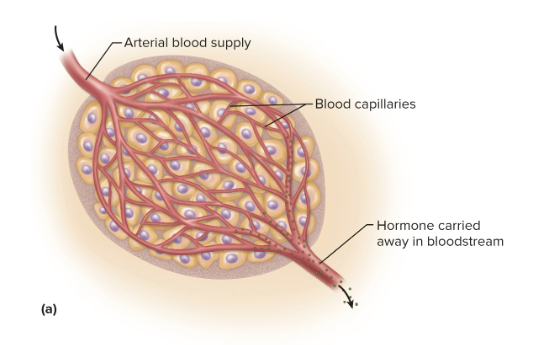
Endocrine glands
Glands that have no ducts or contact with the outside, they secrete hormones directly into the blood
Hormones
Chemical messengers that stimulate cells elsewhere in the body
Unicellular glands
Found in an epithelium that is predominantly non-secretory; can be endocrine or exocrine
Capsule
The connective tissue covering of the exocrine gland
Septa (trabeculae)
Extensions of a capsule that divide into compartments
Stroma
The connective tissue framework of the gland; supports and organizes glandular tissue
Parenchyma
Cells that perform both the tasks of synthesis and secretion
Classification of glands
By duct (simple and unbranched, or compound and branched) or by gland shape (tubular with narrow secretory portion, acinar with multiple secretory cells, or tubuloacinar with both characteristics)
Serous glands
Produce thin, watery secretions (perspiration, milk, tears, digestive juices)
Mucous glands
Produce glocyoprotin, mucin, to absorb water from mucous
Mixed glands
Contain both serous and mucous cell types and produces a mixture
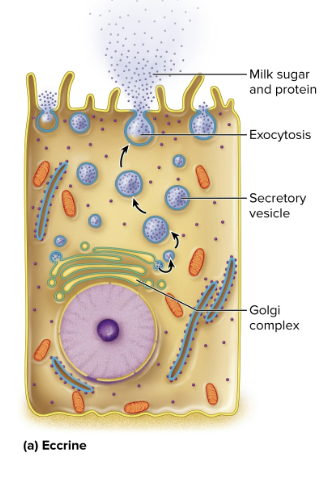
Eccrine glands
Uses vesicles that release secretion by exocytosis, like tears, the pancreas, etc

Apocrine glands
A liquid droplet covered by the membrane and cytoplasm from the cell surface; used to make milk
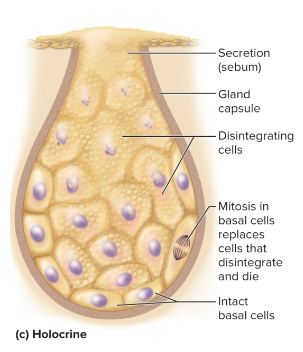
Holocrine secretion
Cells accumulate a product until they disintegrate, secretes cell fragments and substances
Membranes
Only epithelial, only connective or a mix of epithelial, connective, and muscular tissues
Cutaneous membrane
The skin (the largest membrane in the body), made up of stratified squamous epithelium on connective tissue
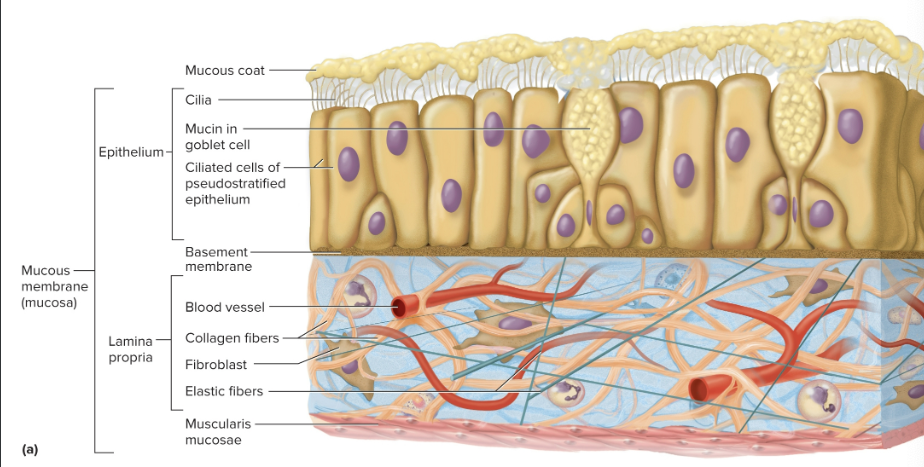
Mucous membrane
Lines passages that open to the external environment (like the digestive tract); absorbs, secretes, and protects often with goblet cells
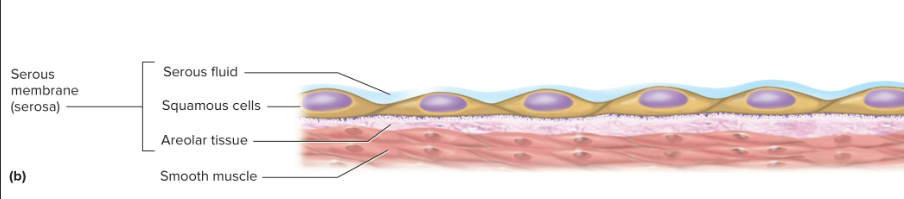
Serous membrane
Internal membranes of simple squamous epithelium on areolar tissue; produces serous fluid that arises from blood and lines organs and body cavities (endothelium to the heart, mesothelium on cavities)
Excitability
The ability to respond to stimuli by changing membrane potential; most developed in nervous and muscular tissues
Membrane potential
The electrical difference in voltage that occurs across the cell membrane; neurons transmit signals while muscles contract
Nervous tissue
Tissue specialized for communication by electrical and chemical signals
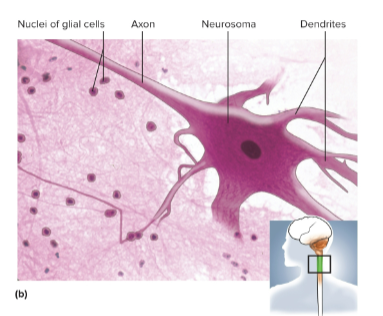
Neurons (nerve cells)
Cells in nervous tissue that detect stimuli, respond quickly, and transmit coded information
Neuroglia (glial cells)
Cells in the nervous tissue that protect and assist the neurons
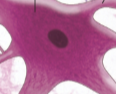
Neurosoma
The cell body of the neuron; it houses the nucleus and controls protein synthesis
Dendrites
Short, branched processes that receive signals from other cells and transmit messages to the neurosoma
Axon (nerve fibers)
Sends outgoing signals to other cells and can be more than a meter long
Muscular tissue
Elongated cells that are specialized to contract in response to stimulation; made to exert physical force on tissues, move the body, and create body heat
Types of muscular tissue
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
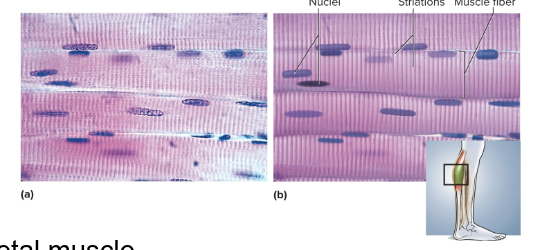
Skeletal muscle
Type of muscular tissue made up of long, thin muscle fibers that attach to bone, contrains multiple nuclei and striations and are voluntarily controlled

Striations
Alternating dark and light bands
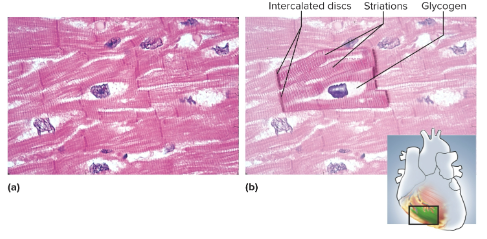
Cardiac muscle
Type of involuntary muscular tissue that is limited to the heart wall; they are short and branched with a centrally located nucleus, intercalated discs that provide electrical connection
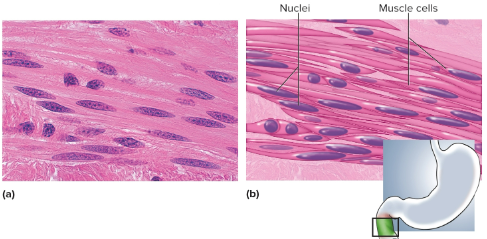
Smooth muscle
Type of involuntary muscular tissue usually found in the stomach, it lacks striations, is short, and has one central nucleus
Epithelia
Sheets of closely adhering cells that cover body surfaces and life body cavities; they have a high rate of mitosis
Avascularity
Lacking blood vessels; epithelia have this quality and are nourished by underlying connective tissue
Functions of epithelia
Protect deeper tissues from injury and infection
Produce and release chemical secretions
Excrete wastes
Absorb and filter substances
Sense stimuli
Basement membrane
The layer between epithelium and the underlying connective tissues; comprised of collagen and glycorproteins to anchor it down
Basal surface
Cell surface facing the basement membrane; the bottom
Apical surface
Cell surface that faces away from the basement membrane; the top
Lateral surface
Cell surface between the basal and apical surface; the sidewall
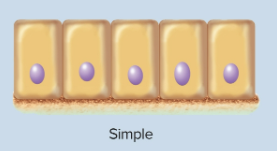
Simple epithelia
Contains one layer of cells and are named by their shape; all touching the basement membrane
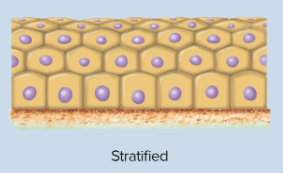
Stratified epithelia
Contains many layers of cells are named by their topmost (apical) shape; some may not touch the basement membrane and can rest on others
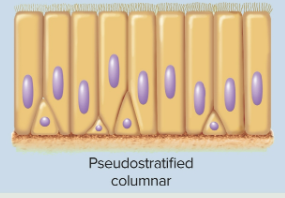
Pseudostratified columnar epithelia
Epithelia that may appear to be stratified but only differentiated by height of cells—located in the respiratory tract, sex cells, and male urethra, as it secretes and propels mucus
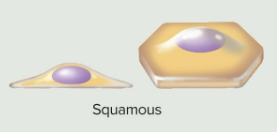
Squamous epithelia
Cells that are thin and scaly, flattened
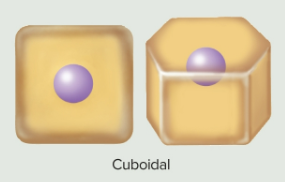
Cuboidal epithelia
Epithelia that are cube-shaped, square, or round
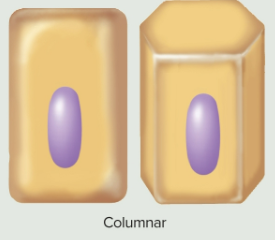
Columnar epithelia
Epithelia that are tall or narrow, shaped like columns
Goblet cells
Wineglass-shaped mucus-secreting cells in simple columnar and pseudostratified epithelia
Simple squamous epithelium
A single row of thin cells with nuclei near the basement membrane; they permit rapid diffusion or transport of substances and secrete serous fluid—located in the alveoli (air sacs), capillaries, and endothelium
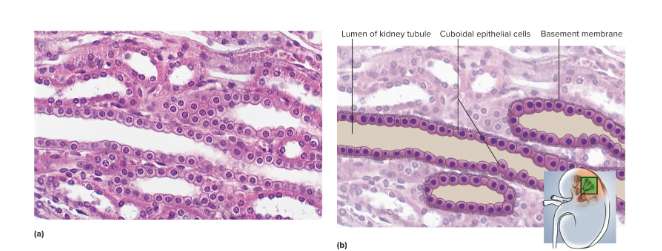
Simple cuboidal epithelium
A single layer of square or round cells; they absorb and secrete substances and aid mucus production and movement—located in the liver, thyroid, salivary glands, and kidney tubules
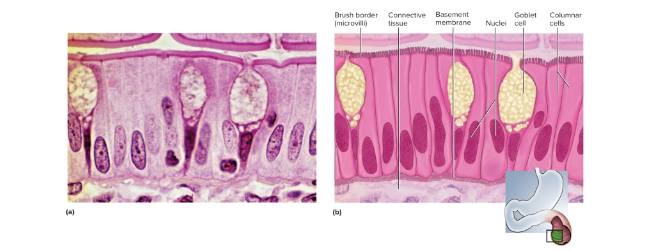
Simple columnar epithelium
A single row of tall, narrow cells; they are in the border of microvilli and aid in absorption and secretion of mucus—located in the GI tract as part of cilia and lining for absorption
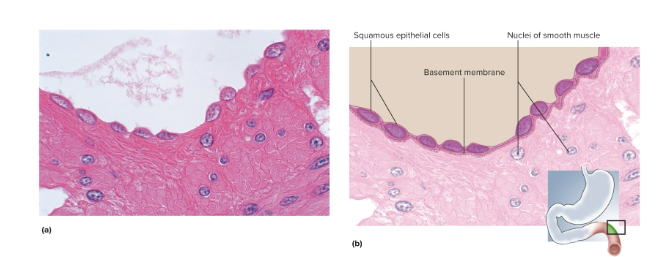
Stratified squamous epithelium
The most widespread epithelium in the body; the deepest layers undergo continuous mitosis as cells are pushed up and die or flake off—lines oral cavity and anal canal
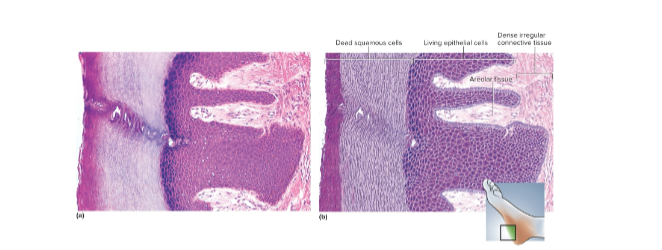
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Multiple cell layers, the cells become flat and scaly toward the surface; protects from outside by resisting abrasion, preventing water loss, and penetration by organisms—located in epidermis, palms, and soles
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
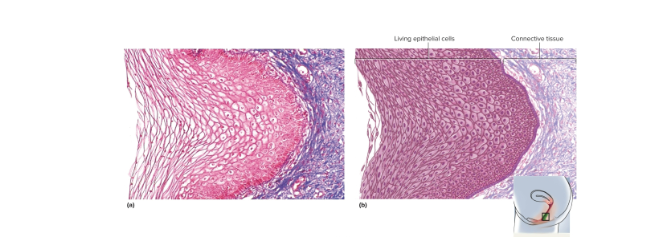
Same as keratinzed epithelium without surface layer of dead cells, also resists abrasion and penetration—located on tongue, esophagus
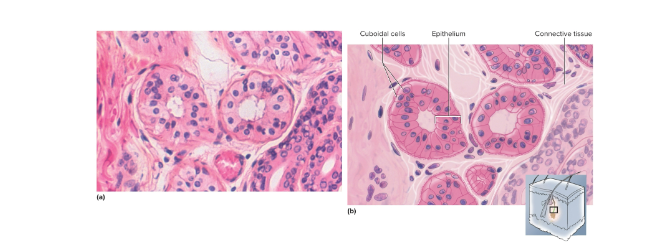
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Two or more layers of square or round surface cells; secretes sweat, produces sperm, and hormones in sweat glands and reproductive organs
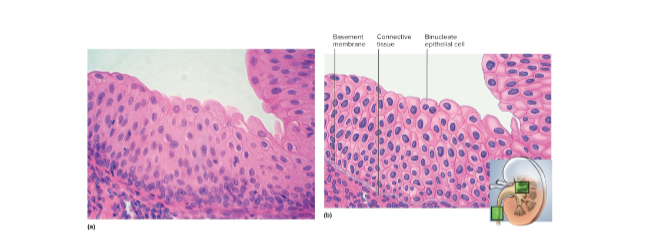
Urothelium (transitional epithelium)
Multilayered epithelium that can stretch between round and flat; located in ureter and bladder for filling of urinary tract
Connective tissue
Abundant type of tissue where cells may not be in direct contact; supports, connects, and protects organs with varying avascularity
Functions of connective tissue
Connecting organs
Support and movement
Physical and immune protection
Heat production
Internal transport and storage
Fibrous connective tissue
Connective tissue made up of many types of cells; types include loose, dense regular/irregular, areolar, and reticular
Fibroblasts
Fibers in fibrous connective tissue; the ground substance of the matrix
Macrophages
Cells in fibrous connective tissue that phagocytize (eat) foreign material and activate immune system
Leukocytes
White blood cells in fibrous connective tissue; made of up neutrophils and lymphocytes (anti-bacteria, toxins, and foreign agents)
Mast cells
Cells in fibrous connective tissue that secrete substances to inhibit blood clotting and dilate blood cells
Adipocytes
Cells in fibrous connective tissue that store triglycerides, or fat molecules
Collagenous fiber
A fiber in fibrous connective tissue; makes up 25% of the body’s proteins and is tough, flexible, and stretch-resistant to make up tendons, ligaments, and deep skin layers
Reticular fiber
A fiber in fibrous connective tissue; made up of collagen fibers coated with glycoprotein to make up spleen and lymph nodes
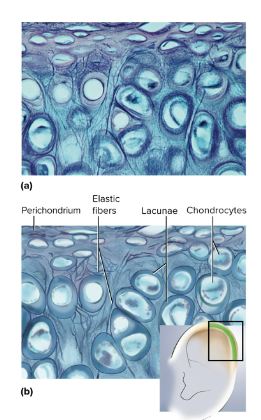
Elastic fiber
A fiber in fibrous connective tissue; made up of elastin to allow stretching and recoiling particularly in elastic cartilage in external ears
Proteoglycans
Part of ground substance in fibrous connective tissue made of brush-shaped molecules; holds tissues together with gravy-like colloids
Adhesive glycoproteins
Part of ground substance in fibrous connective tissue made of protein-carbohydrate complexes; binds tissue components
Loose connective tissue
Fibrous connective tissue with gel-like ground substance between cells; includes areolar and reticular loose tissue