Ocular Anatomy: Intro to Eye
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
what does the visual system do
takes information from environment in the form of light and analyzes and interprets it so the organism can see
what tissues hold the eye and protect it
bony tissue
fatty tissue
connective tissue
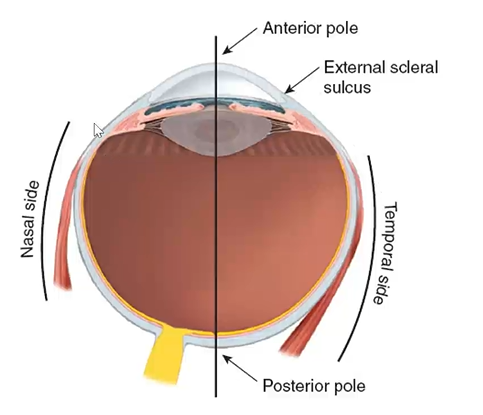
anatomical orientations of eye:
sides of eye/orientation of eye
nasal side/ temporal side
anterior pole/posterior pole
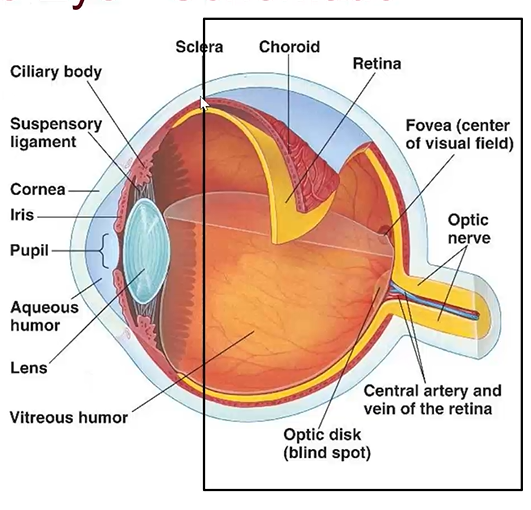
outer to inner layers of eye (superficial to deep):
outer fibrous tunic
middle vascular tunic
inner neural tunic
what does the fibrous tunic (outermost tunic) consist of
cornea - front has to be clear to see
limbus - transition zone
sclera - white of eye
(blue)
whats the function of the fibrous tunic
protection
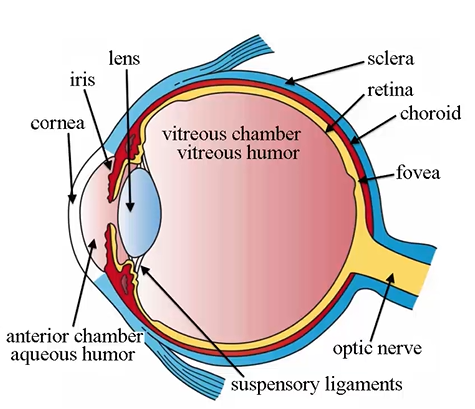
cornea
clear cap, so light can enter
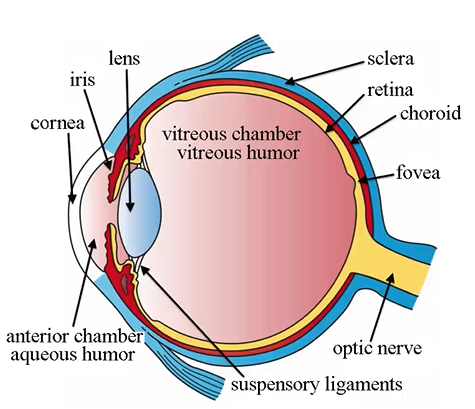
limbus characteristics
transition zone between cornea and sclera
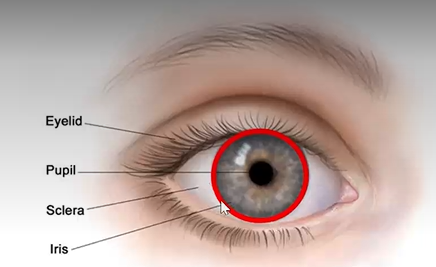
sclera characteristics
white of eye
opaque, fibrous, tough protective outer layer of the eye
continuous w the cornea and w the sheath covering of the optic nerve
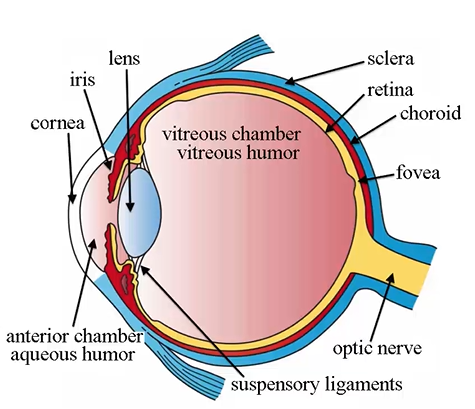
middle tunic (uveal/vacular tunic) components
iris
ciliary body
choroid
(red)
highly vascularized
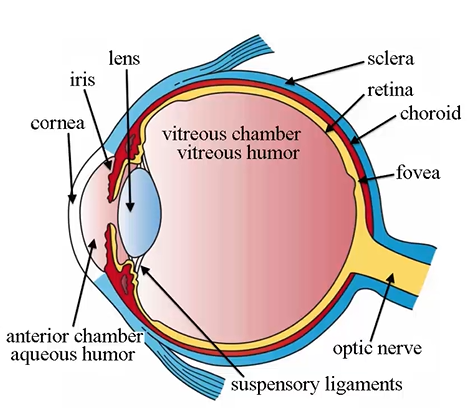
iris characteristics
gives eye color
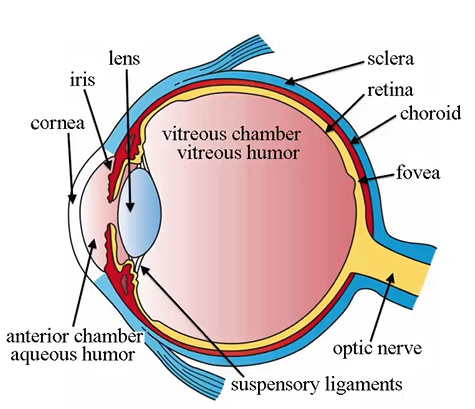
ciliary body characteristics
muscle; lets us focus light
continuous w iris and choroid, triangle shape
can not be seen unless patient is imaged
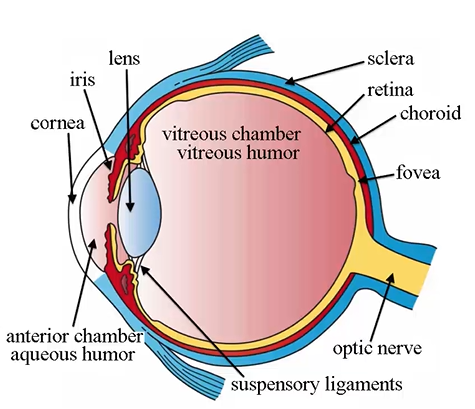
choroid
vascular layer of eye lying between retina and sclera
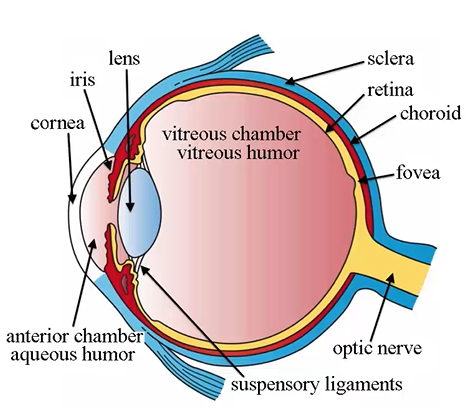
Inner tunic (Nervous Tunic) components
sensory retina
retinal pigmented epithelium - not shown
(yellow)
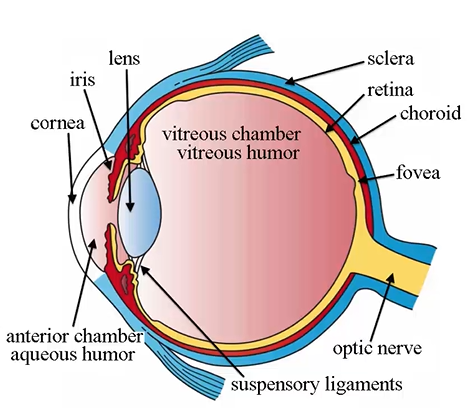
sensory retina characteristics
nervous tissue
converts light into a stimulus that is transmitted to the brain to be interpreted as an image
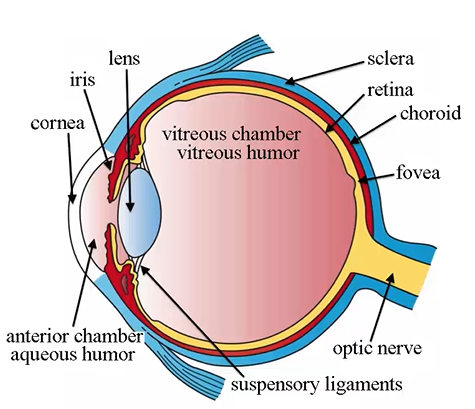
fovea
in inner tunic and is an indentation that gives us sharp vision
retinal pigmented epithelium
support layer to sensory retina
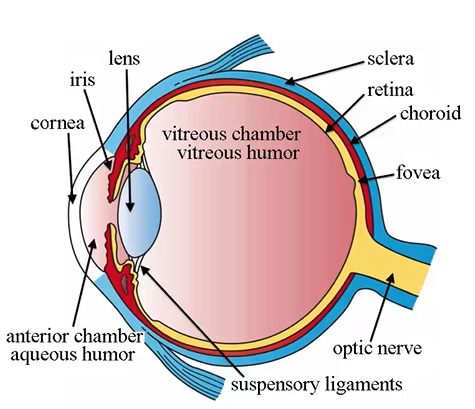
name the tunics and parts in the histological section
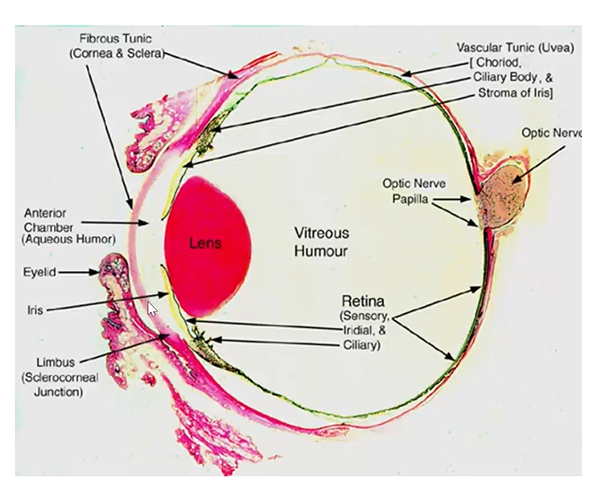
structures in anterior portion of the eye
cornea
limbus
anterior sclera
anterior chamber (aqueous humor)
iris
lens (suspensory ligament)
ciliary body
posterior chamber (aqueous humor)
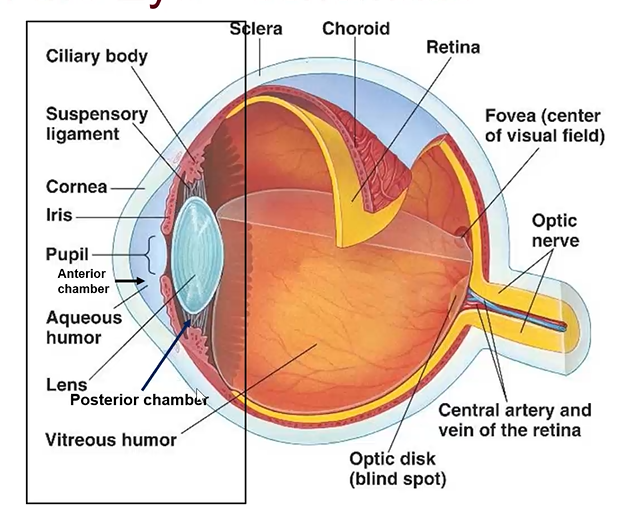
anterior chamber
behind cornea and in front of lens
filled w aqueous
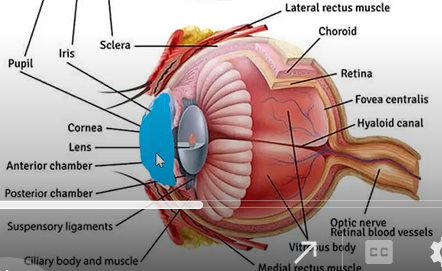
zonules
fine fibers that attach to lens, do not pick up stain
lens characteristics
transparent football shaped
posterior chamber
behind iris and adjacent to lens
filled w aqueous
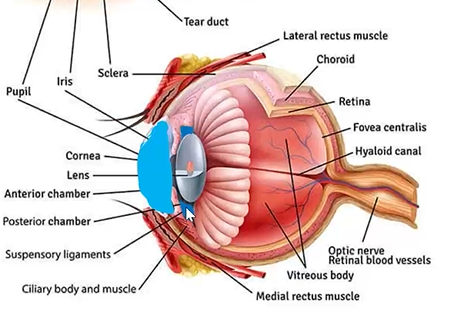
anterior sclera
forward part of sclera
posterior region of eye components
sclera - posterior region
choroid
retina
vitreous humor - filling vitreous chamber
fovea
optic nerve
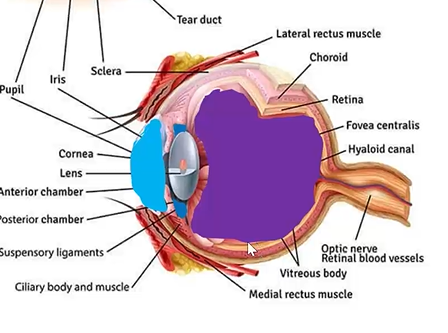
chambers of the eye include:
anterior chamber
posterior chamber
vitreous chamber
aqueous
fluid, gives avascular tissues nutrients and removes waste
vitreous chamber
behind lens
largest chamber
filled w vitreous gel
maintains eye shape
eyelids
protect the eyes
thin layer of epithelial tissue - skins of upper and lower eyelids are the thinnest layers of skin in the body
eyelid fxns
protect eye from foreign bodies
blinks as a reflex
helps to spread tears
limit light entering the eye
nasolacrimal system function
produce tears via the lacrimal gland
drain the tears via the drainage system —> empties into nasal cavity
—> when you cry your nose runs
functions of cornea
transparency - to focus light
refractive power
protection
conjunctiva characteristics
thin, transparent layer of cells which cover the sclera and inner eyelid
conjunctiva function
protect the sclera from organisms
produce part of the tear film
provide nutrition and lubrication to the cornea
sclera fxn
provide protection
maintains shape of eye
eye muscles attach to sclera
limbus fxn
area where fluid of eye drains
via the canal of schlemm
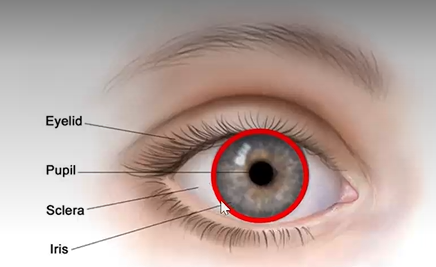
iris functions
controls the size and shape of the pupil (and illumination to the retina)
gives eyes their color
ciliary body fxn
produces aqueous or fluid of the anterior and posterior chambers
ring of muscle that changes shape of lens to maintain focus
lens fxn
focuses light rays onto retina
can become cloudy and develop cataracts
choroid fxn
nourishes the outer layers of the retina
prevents reflection of light (highly pigmented)
retina fxn
receives light - has light sensitive cells (rods and cones)
converts light to visual energy
transmits light
fovea characteristics
area of retina where light is focused for clear vision
fovea fxn
gives us our clear vision and color vision(cones)
optic nerve characteristic
extension of the last layers of the retina
optic nerve fxn
transmits nerve impulses from retina ultimately to visual cortex
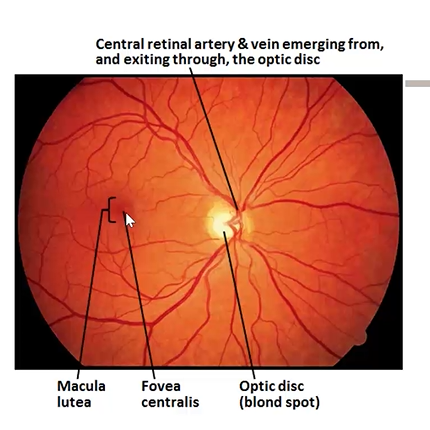
where is the blind spot?
at the optic disc - where the optic nerve leaves the eye
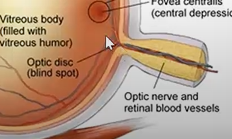
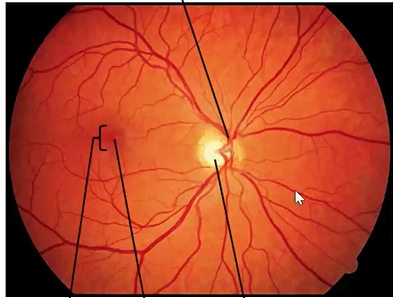
name the parts
red is the sensory retina w the blood vessels