Biology- Med Connect Past Papers Set 1
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
highest arterial pressure
in aorta
trypsin
degrades proteins to amino acids
small intestine
trypsinogen
inactive form of trypsin
activated by enteropepridase
exocrine
secrete WITH ducts
endocrine
directly into blood stream
location of prostate
inferior to the bladder neck in males
prostate
exocrine gland
secretion contributes to semen and plays a role in sperm activation
fluid contains nutrients enzymes and prostate specific antigens
location of vocal cords
larynx
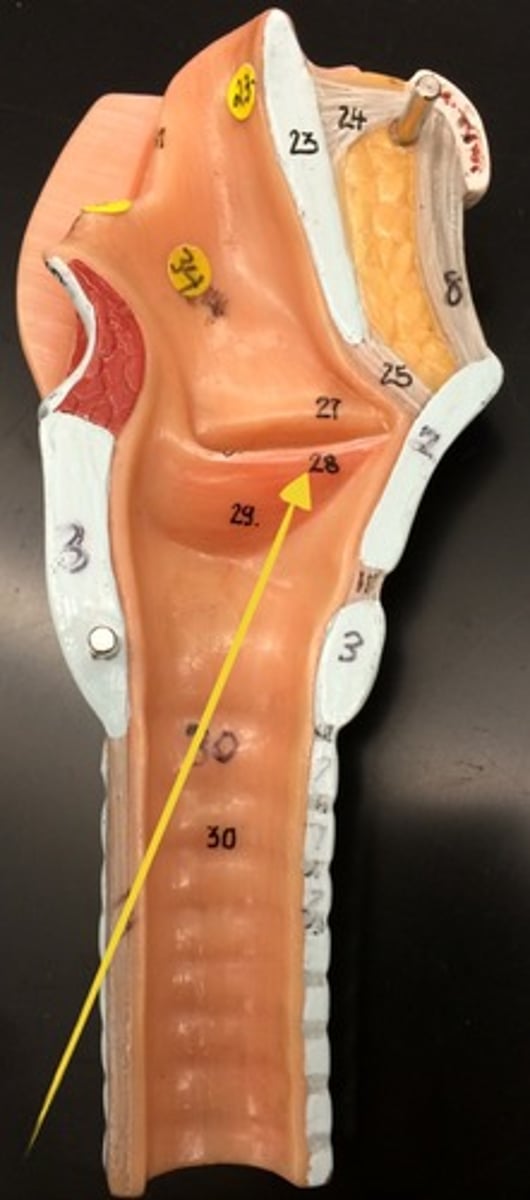
2 types of vocal cords
-true
-false vocal cords/ vestibular folds are superior to the true ones a
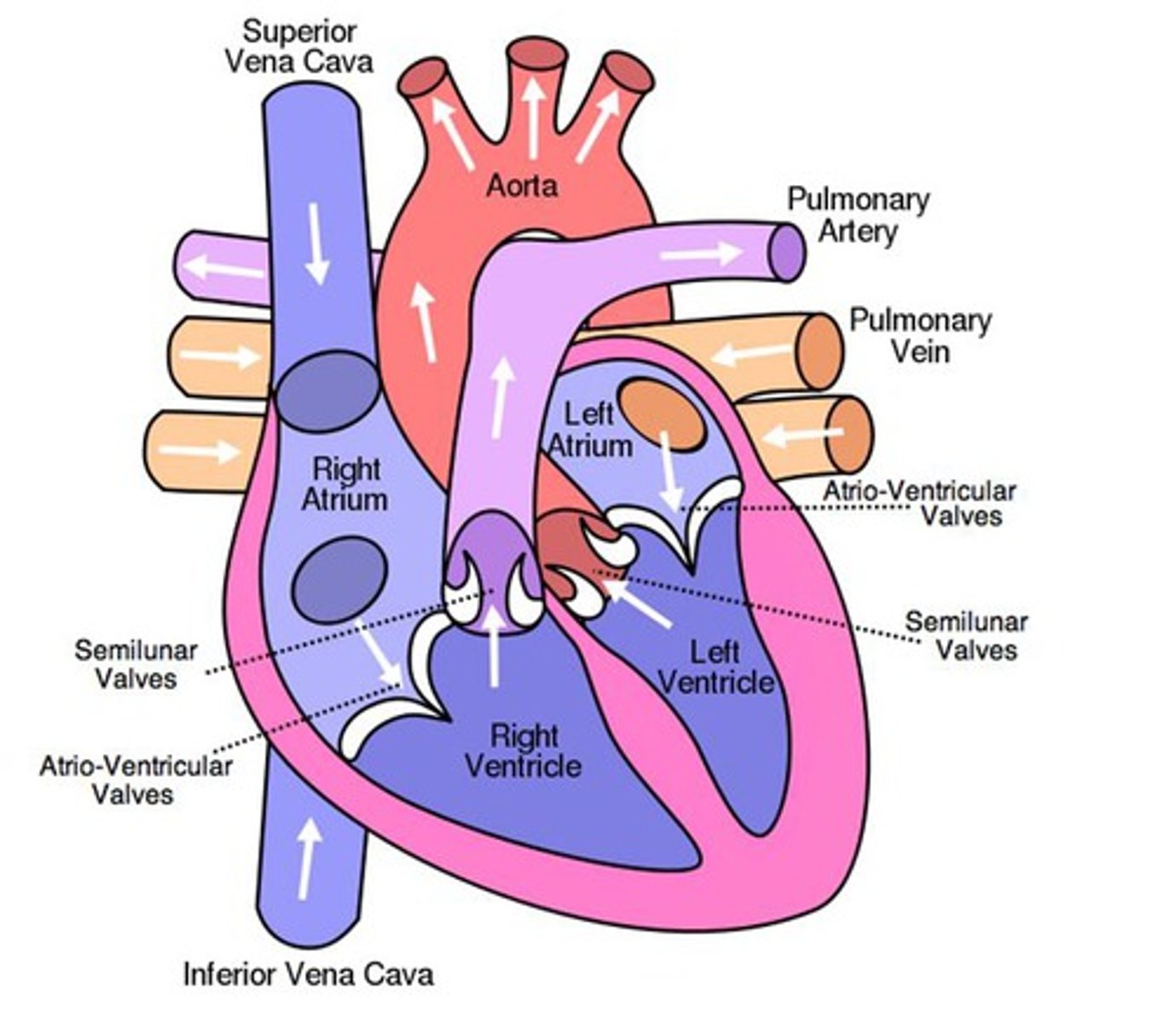
start of systemic circulation
starts at left ventricle
which walls are thicker in the heart
left ventricle walls are slightly thicker than the right because the left needs to pump blood to the entire body ( further distance)
systemic circulation
1.oxygenated blood from the left ventricle
2. through the arteries, to the capillaries in the tissues of the body
3.from the tissue capillaries, the deoxygenated blood returns through a system of veins
4. to the right atrium of the heart.
labelled heart
Immiscible
incapable of mixing
because the force of attraction between molecules of the same liquid are greater than the force of attraction between the 2 different liquids
polypeptide chains are
linear and unbranched
smallest organelle
ribosome
albinism
-defect in melanin synthesis
-caused by absence of
-tyrosinase enzyme
inheritable
when do mammals only secret sperm
process of ejaculation
ejaculation
ejection of semen from the reproductive tract
double membrane organelles
plastids
( plastic fake 2 layers)
general function of plastids
manufacturing and storing of food
replication
-DNA synthesis
- producing identical replicas of DNA from one original strand
eustachian
-tube
-a canal
-connects middle ear to nasopharynx
-function : control pressure within the middle of the ear so its equal to air pressure external to body
nasopharynx consists of
upper throat and back of nasal cavity
accommodation
is the adjustment of the optics ( light orientation mechanics) of the eye to keep in focus on the retina as distance varies
process of adjusting focal length of lens
exocrine function of pancreas
produces substances like enzymes and releases them into ducts
endocrine function of pancreas
produces insulin and glucagon, regulates blood sugar
secreted directly into the blood
( D DIRECTLY)
why is the epidermis nourished almost exclusively by diffused oxygen from the surrounding air
no blood supply ( avasular)
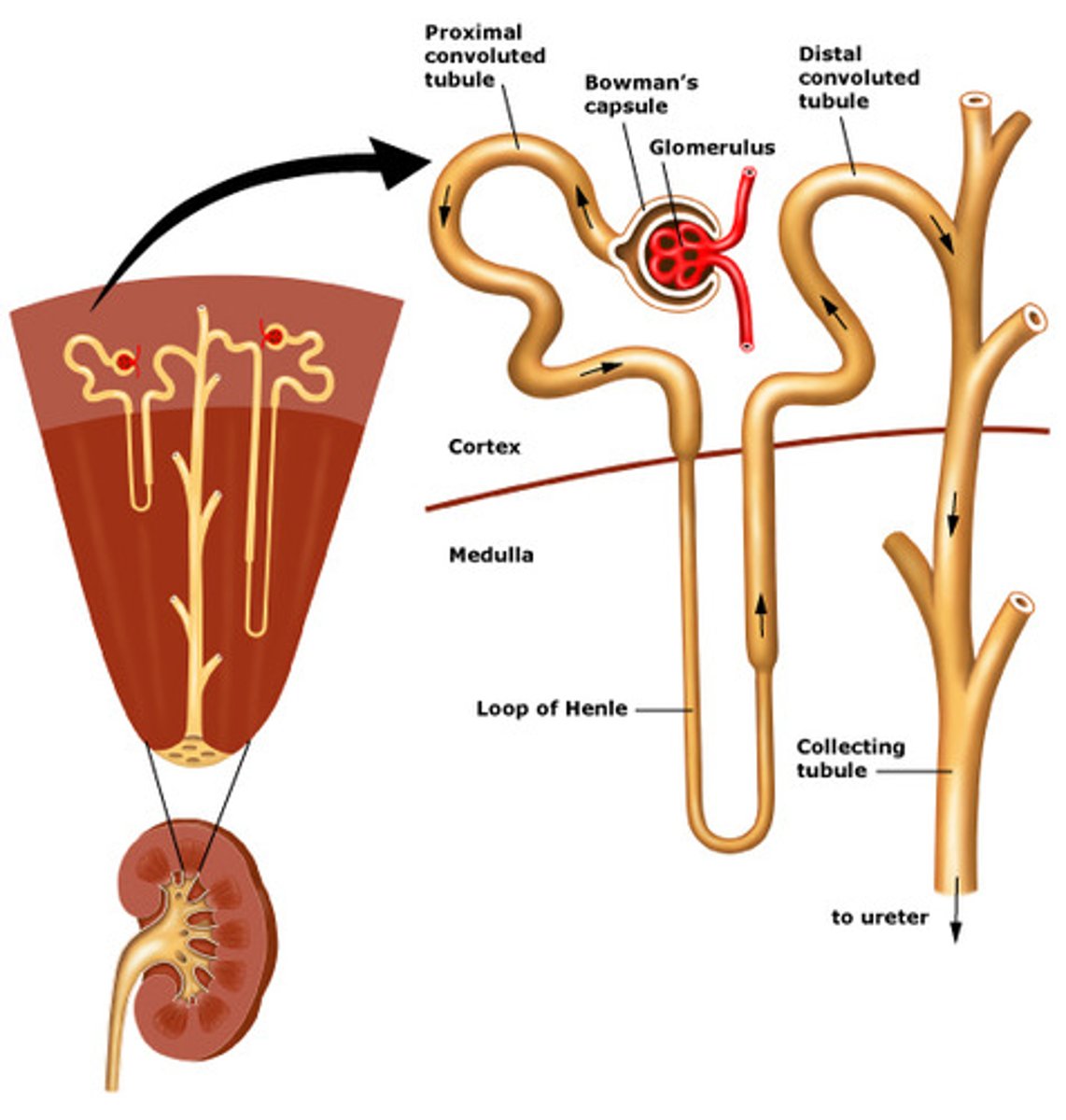
nephron functions
filtration , reabsorption and secretion
upmost function is to regulate H2O and ion concs
Amylase location
saliva and pancreas
function of amylase
breaks down carbohydrates
Colloid
a mixture in which one substance of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance
name can be given to the dispersed substance alone
what doe peroxisomes contain that allow them to carry out the oxidation of various substances
oxidases
hameoglobin
red protein
responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood of vertebrates
molecule is comprised of subsunits
each subunit contains an iron atom bound to a haem group
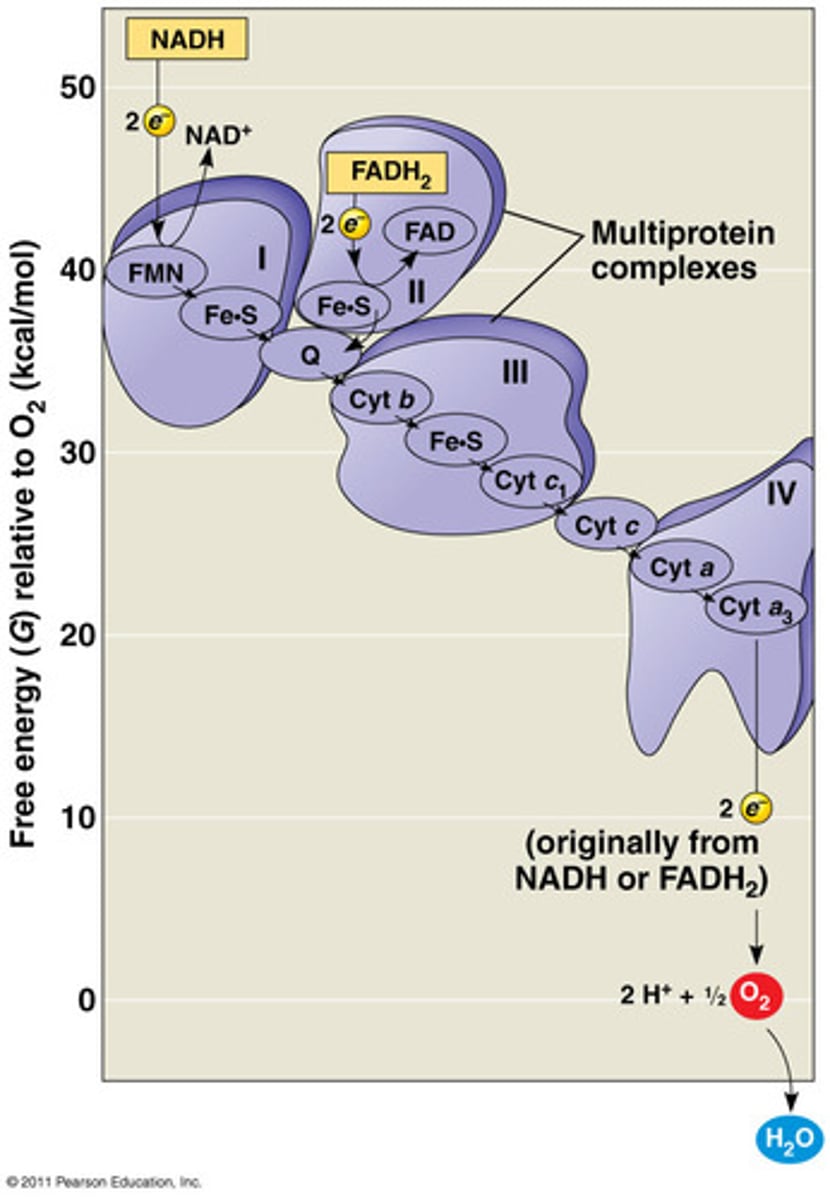
oxidative phosphorylation
The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain; the third major stage of cellular respiration.
fertillisation
-generative ferrillisation
-conception
-fecundation
-syngamy
-impregnation
-fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism
-new diploid cell called a zygote is formed
larynx
-voice box
-organ in the neck of tetra pods
- breathing
-sound production
-protecting trachea against food aspiration
-house vocal cords , manipulate pitch and volume
-phonation
the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration
phonation
thyroid hormones
thyroxine and triiodothyronine
adrenal gland releases
mineeralocorticoid
gulcocorticoids
androgens
eg prokaryotic cell
bacteria
archaea
genetic description
pro vs eu
pro- single circular chromosome
typically lacks chromosomes
eu- multiple linear chromosomal DNA with histones
both- can have plasmids naturally in bacteria
name of first vertebrae
atlas
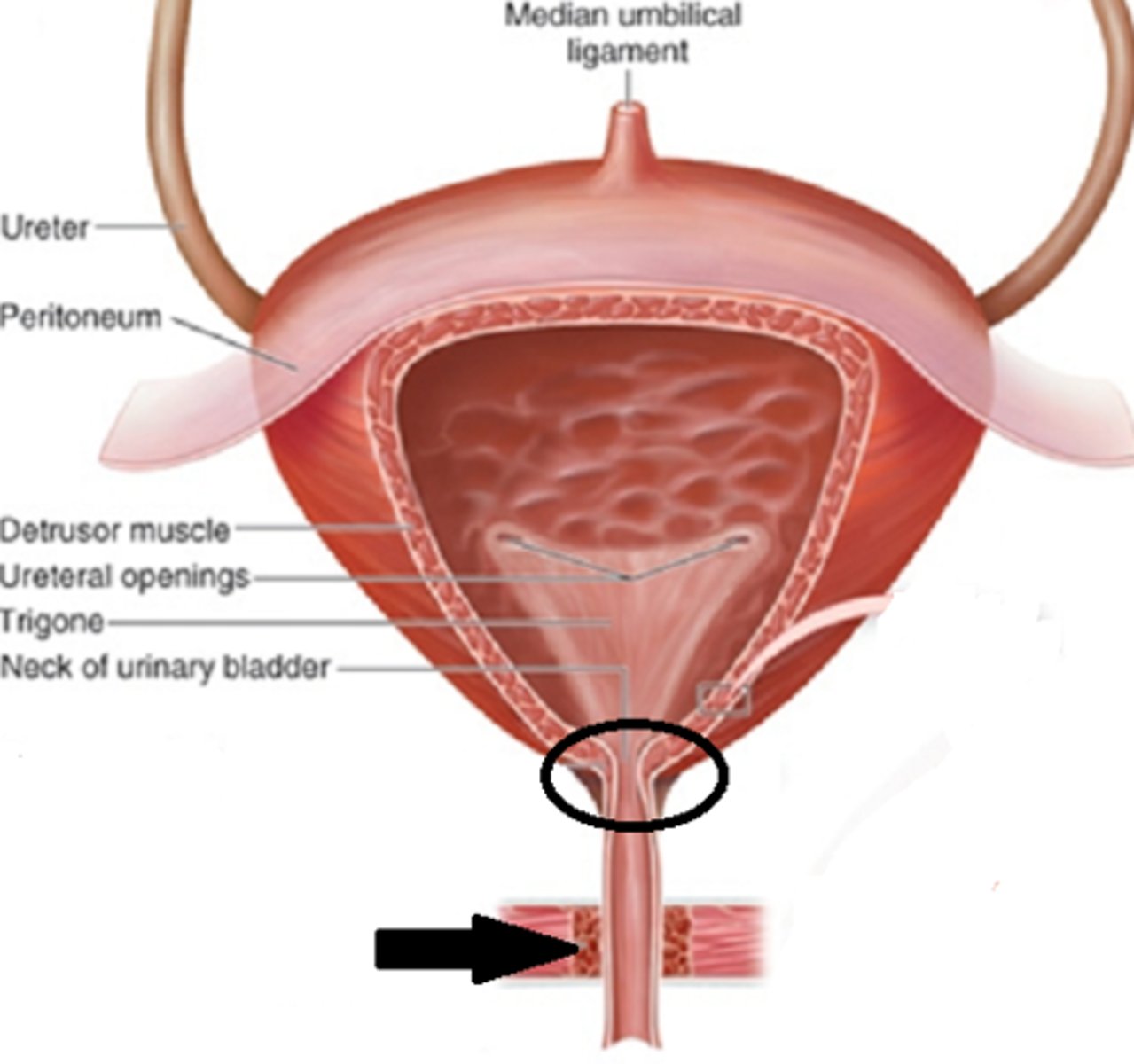
properties of the urinary bladder
smooth collapsible muscular sac
location of urinary bladder
above and behind pubic bone
empty bladder
size and shape of a pear
capacity of bladder
400-600mL
layers of muscle tissue in the bladder allow it
to stretch
during urination
-bladder muscles squeeze
-2 sphincters( valves) open
-exit via urethra, to which it is funnelled to
urethra is longer in
men than women because it passes the penis
rugae
-tiny wrinkles lining the inner surface of the bladder
-allows it to stretch
layers of the urinary bladder
- innermost mucosa
-submucosa
-visceral muscles of muscularis layer surround submucosa
mucosa
-inner most layer of urinary bladder
-unlike other hollow organs the urinary bladder is lined with transitional epithelial tissue
advantage of transitional epithelial tissue
-stretch
-protection to underlying tissues from acidic / alkaline urine
submucosa
layer of connective blood vessels and nervous tissue
function of visceral muscles
-make up muscularis layer, outermost layer
-expand and contract during urination
detrusor muscle
another name for muscularis
internal urethral sphincter
-made by muscularis layer
-ring of muscle
-surrounds urethra opening
-relaxes to allow urine to flow into urethra
( gates to urethra- border control)
vesicles
small spheres of fluid surrounded by a lipid bilayer mebrane
vesicles functions
transporting intracellularly
lysosomes -digestion + waste control
recycle
how many different enzymes can be found in lysosomes
60 different enzymes
hydrolytic enzymes
optimum pH for lysosomes
acidic
hydrolytic enzyme makes it acidic
unlike neutral cell
process hydrolytic enzymes use
hydrolysis
addition of water molecule which cause substance to cleave ( split)
endocytic vesicle
-type of lysosome
-digest food into smaller pirces that can enter the cell
-brings particles into the cell
autophagy
- possible function of lysosomes
-destruction of improperly functioning organelles
phagocytosis
-lysosomes involved
-cell engulfs a molecule in order to break it down
lysosome size
- micrometres
why so lysosomes form double layered membranes in aqueous solutions
have a phospholipid membrane
organelles with a phospholipid membrane
cell membrane
nuclear membrane
nucleus
golgi apparatus
endoplasmic reticulum
formation of lysosomes
1.hydrolytic enzyme is formed in endoplasmic reticulum ( ROUGH)
2. enzymes tagged
3. enzymes transported to golgi
4.packaged
5.budding off gogi apparatus
proteases break down
proteins
during exocytosis the cell
released cellular secretions
which cells have the largest nucleus
monocytes
duplication is
an intrachromosomal aberration
Intra vs Inter
within vs between
true organ of hearing is
organ of corti
mid brain is involved in the
vision and hearing
progesterone is secreted from
corpus luteum of ovary
second heart sound is
diastolic as it represents the closure of semilunar valves
the first cervical vetebrais is called
atlas and connects the spine to the skull
function of sclera
acts as a tough protection from injury, and provides attachment for the extraocular muscles that move the eye
PROTECTION
ureter
upper half located in the abdomen
2- connect to each kidney
tube which urine passes through drom kidney to urinary bladder
excretion of fluids
virion
complete virus particle, replicates only inside living cells of an organism
mitosis
-cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
-a type of cell division that results in 2 daughter cells having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus typically of ordinary tissue growth
acrynom remember 4 lobes of brain
FTPO
fk terry priya overweight
main enzyme in translation
peptidyl-transferase
disease agents consisting of only naked RNA are known as
vironids
viroids
Infectious particles that cause disease in plants
viroids
Consist only of RNA; no protein coat. Obligate intracellular agents that use the machinery and nutrients of host cells to replicate.
single stranded RNA molecules
prions are infectious particles that only contain ------- molecules
protein
the eye lens is
double convex
facial bones are
mandible
the triceps of the lower limb
flexes the ankle
meiosis is typical of
germ cell
glycolysis is the process of degradation of
gulcose
the bonds between phosphate residues in molecule of atp are
macroergic
chromatin is a
complex of proteins and DNA
bone are the active part of the locomotor system
no false
can the cell nucleus function independently of the cytoplasm
no the cell nucleus could not
where is the pituitary gland located
in the cavity of the skull