AQA GCSE Music: Harmony and Tonality
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Tonal
Music arranged wherein all the tones and semitones used relate to a tonic.
Major
Music based on a major scale, where the tones (T) and semitones (S) come in this order TTSTTTS
Minor
Music based on a minor scale. In a melodic minor scale, the order is T-S-T-T-T-T-S going up, and T-T-S-T-T-S-T coming down.
Modal
Music based on one of the scales of seven pitch classes commonly found in western music, but excluding the major and minor scales.
Modulation to the Dominant (what, give bog standard basic key example)
Where the music changes to the key of the 5th note of the scale (e.g., in the key of C major, it would go to G major).
Modulation to the Subdominant
Where the music changes to the key of the 4th note of the scale (e.g., in the key of C major, it would go to F major).
Modulation to the Relative Major/Minor (include examples)
Where the music changes to the key that shares the same key signature (e.g., C major to A minor, or G minor to Bb major).
Atonal
Music that is unrelated to a tonic note and therefore has no sense of key.
Diatonic
Music written using the major and minor keys; a major or minor scale, or the notes from such a scale. (Using the notes of the prevailing key, usually major or minor)
Chromatic
Where notes in the scale of the prevailing key are altered (e.g., G sharp in the scale of C major).
Consonant
Sounds which fit well together (though the range of these chords or combinations of sound is not fixed).
Dissonant
Sounds which clash when played together.
Pedal
A sustained or repeated note, usually but not necessarily in the bass, sounding against changing harmonies. ( Sustained or repeated note played whilst harmonies change, usually in the bass)
Drone
A continuous, sustained sound. (Sustained or repeated note, often with another note, whilst harmonies do not change)
Cadence
A cadence is formed by 2 chords that come at the end of a musical phrase. Cadences are like “musical punctuation”, like full stops or commas.
Perfect Cadence
Chord V-I (dominant-tonic), like a musical full stop.
Plagal Cadence
Chord IV-I, like a weaker musical full stop, “amen” cadence, used at the end of hymns
Imperfect Cadence
Typically Chord I,II, or IV - Chord V (always ends on dominant chord V), acts like a musical comma
Interrupted Cadence
Chord I-VI, often called the “surprise cadence”, acts like a musical comma
What’s so special about Chord VI?
In a major key it’s a minor chord and in a minor key it’s a major chord!
Tierce de Picardie
When the final chord of a piece or movement in a minor key is a tonic major chord instead of the expected minor chord.
C minor example of Tierce de Picardie
If a piece or movement is in C minor, the last chord, unexpectedly would be C major.
Key Signature
Sharps/flats at the start of the stave that indicate what key a piece is in.
Relative minor
A minor key with the same key signature as a major key.
Modes
Ancient Scales, sound like a mixture of major and minor, there’s a tone between the 7th and 8th notes of these scales. Not major/minor
Modulation
When the music changes key.
How to work out a relative minor from a major key:
they are always a 3rd lower than their relative major, so transpose the tonic of the relative major a 3rd lower to get the relative minor.
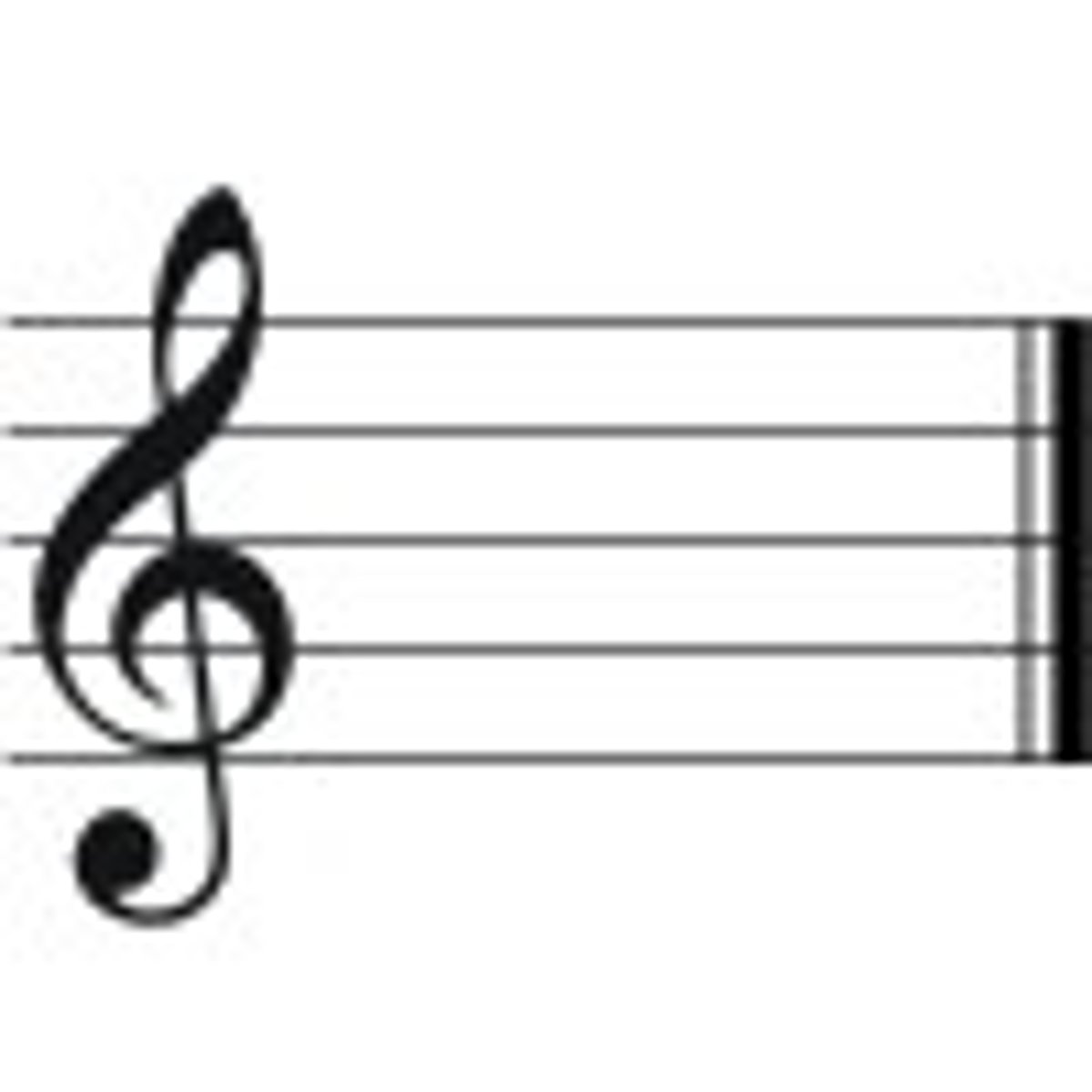
C Major

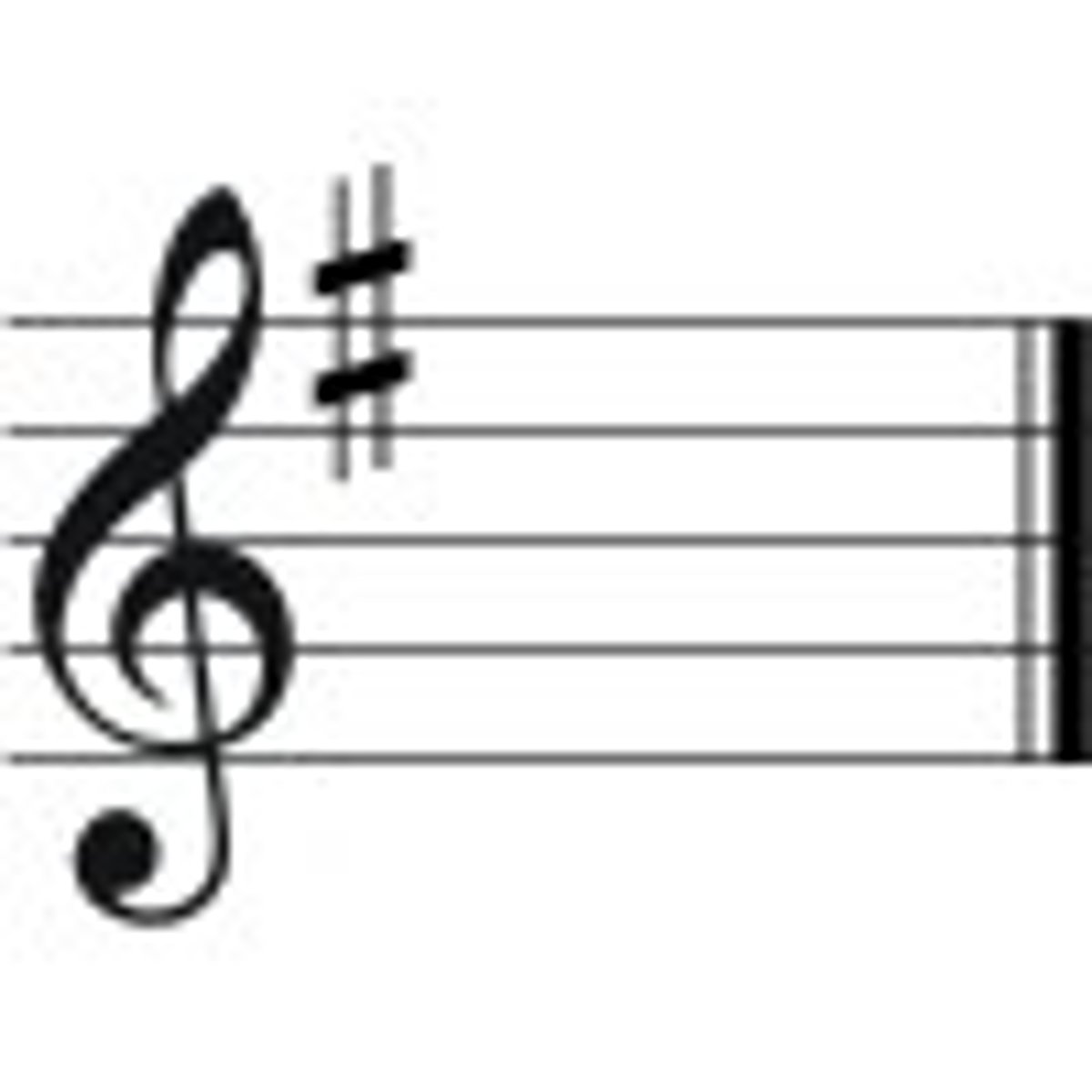
G Major

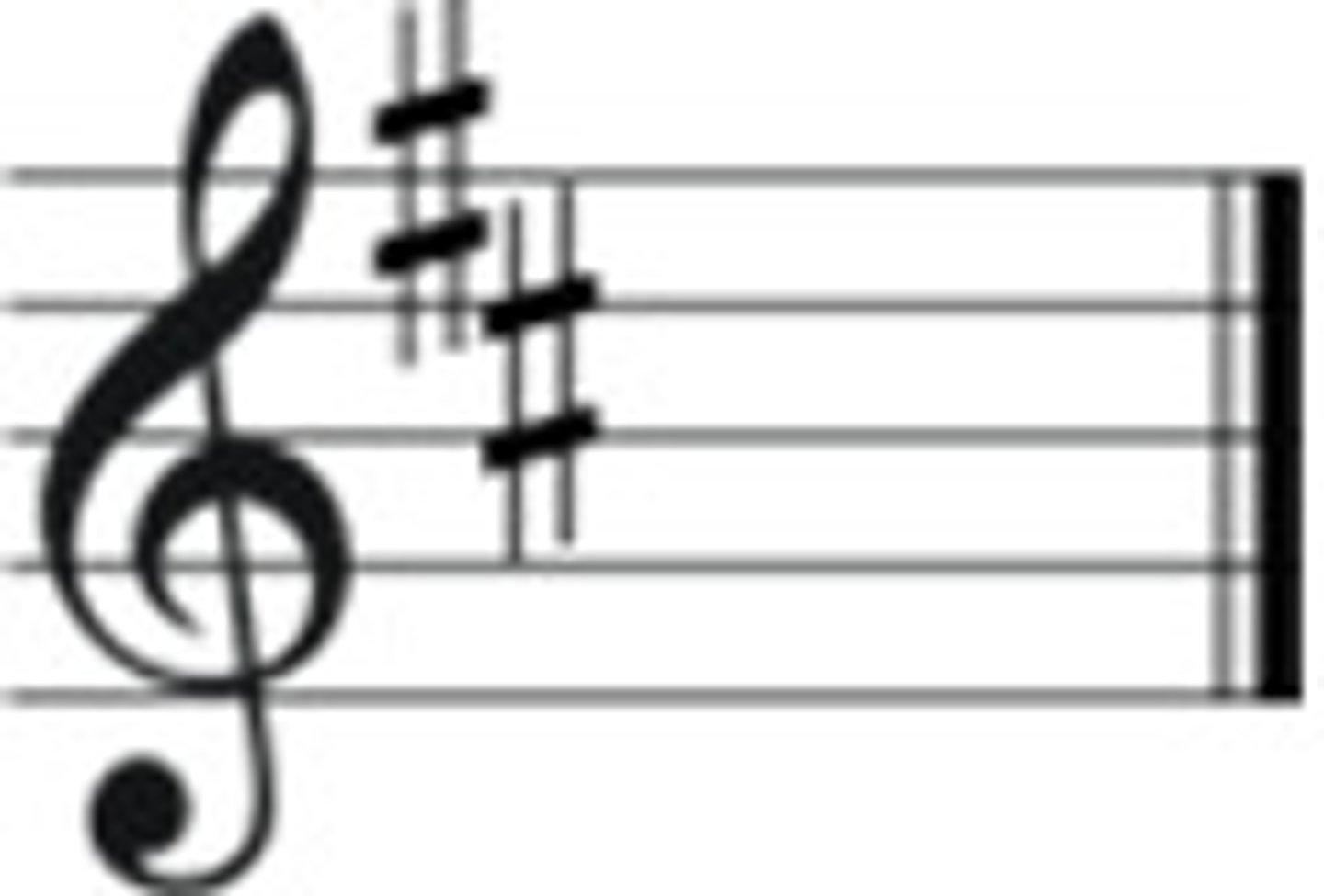
D Major

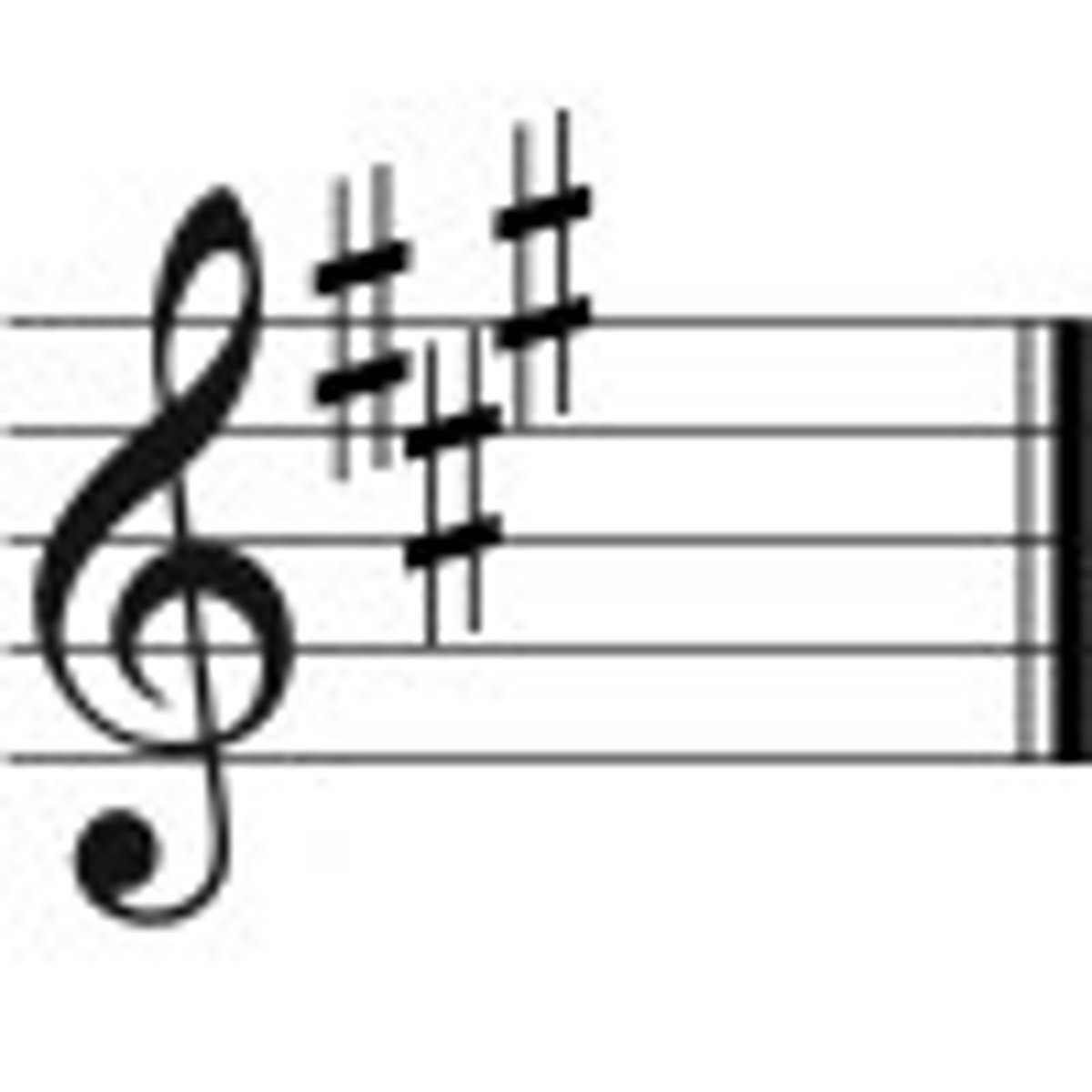
A Major

E Major
F#,C#,G#,D#
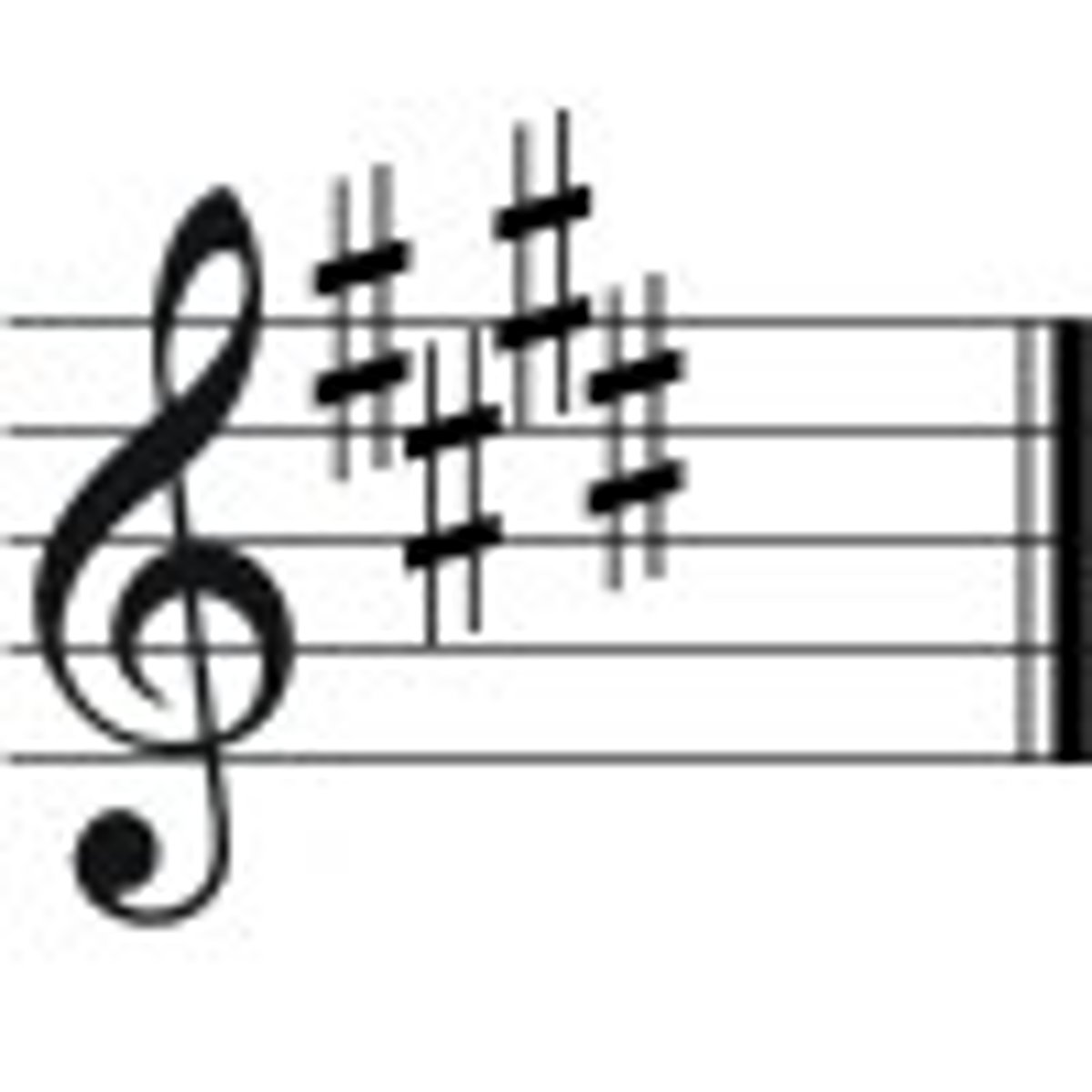

F Major
B flat
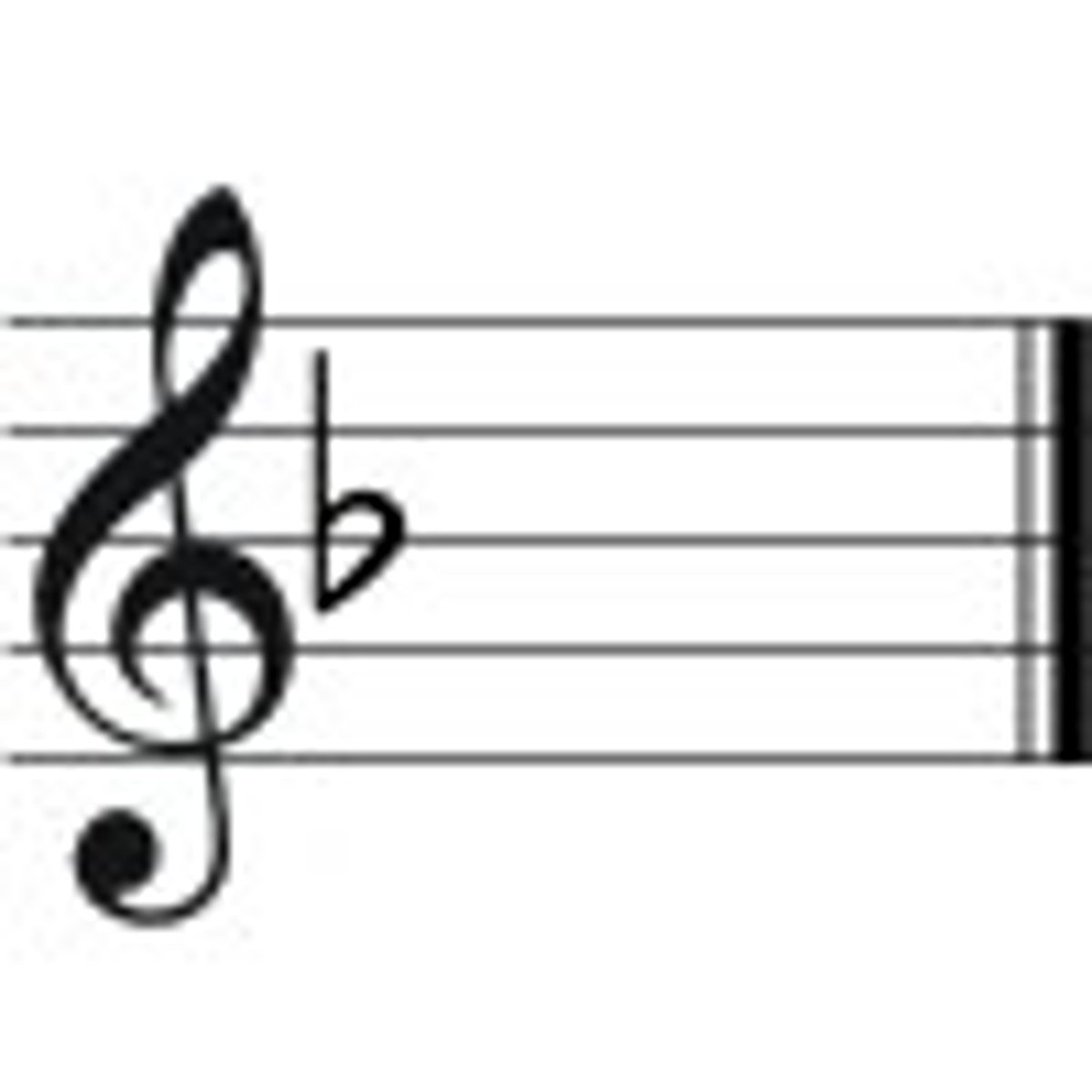

Bb Major
B flat and E flat
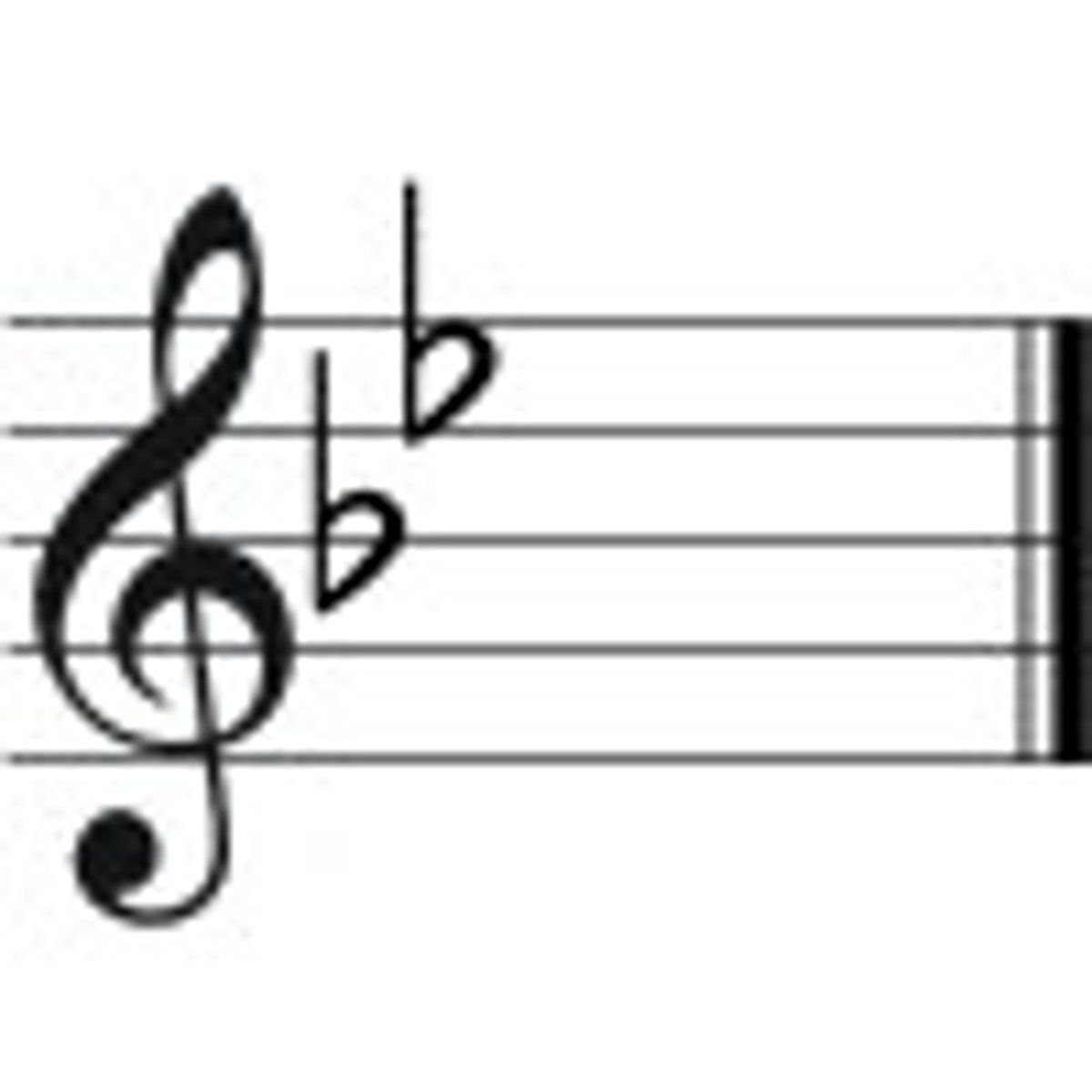

Eb Major
B flat, E flat, A flat
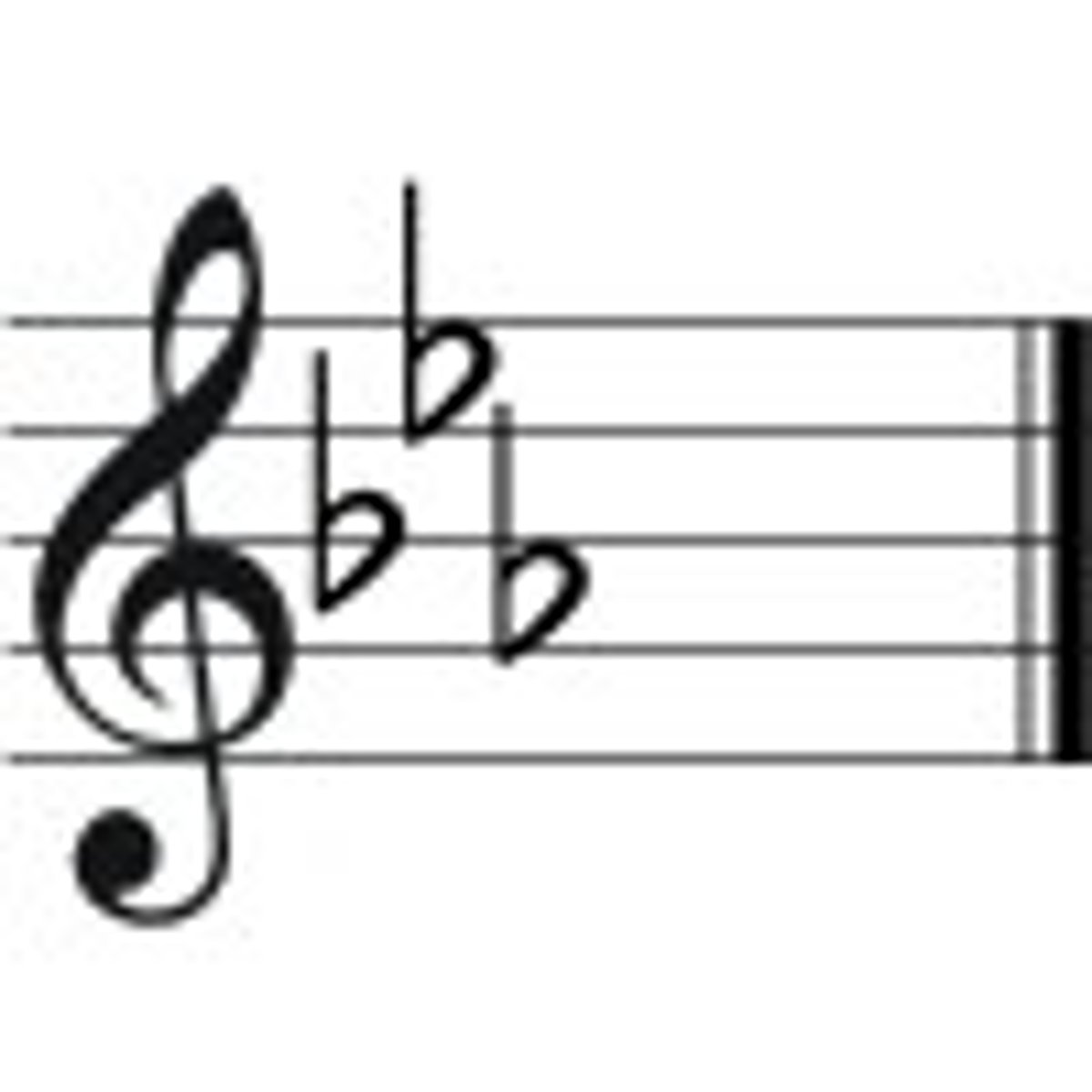

Ab Major
B flat, E flat, A flat, D flat

Rule for Sharp Keys
Look at the last sharp and go up one
Rule for Flat Keys
Look at the 2nd to last flat - that's the key
Rule for Relative Minor
Go down 3 semitones
Accidental for minor scales
Sharpen the 7th note
Tonic
1st note of a scale
Supertonic
2nd note of a scale
Mediant
3rd note of a scale
Subdominant
4th note of a scale
Dominant
5th note of a scale
Submediant
6th note of a scale
Leading note
7th note of a scale
Octave
8th note of a scale
Interval of a 2nd
Distance between note 1 and note 2 of a scale

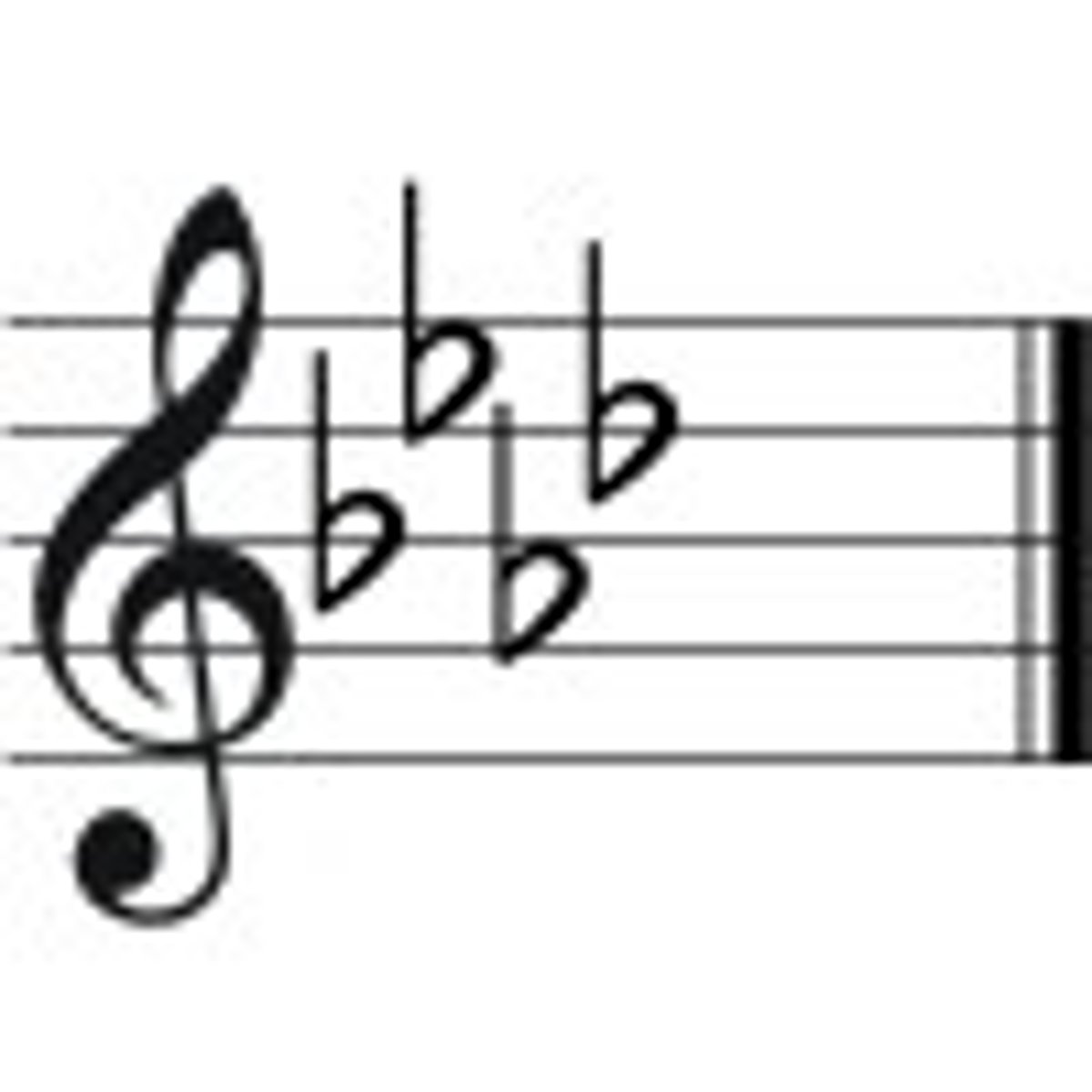
Interval of a 3rd
Distance between note 1 and note 3 of a scale

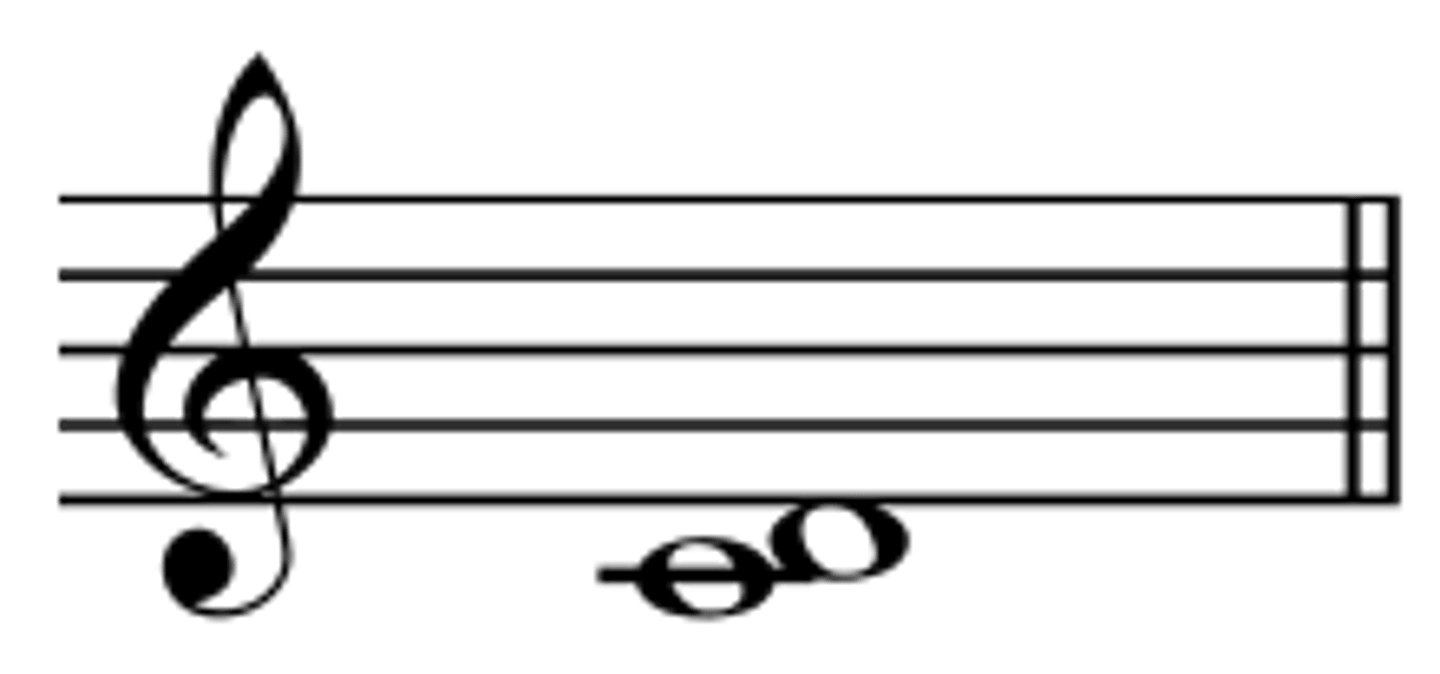
Interval of a 4th
Distance between note 1 and note 4 of a scale

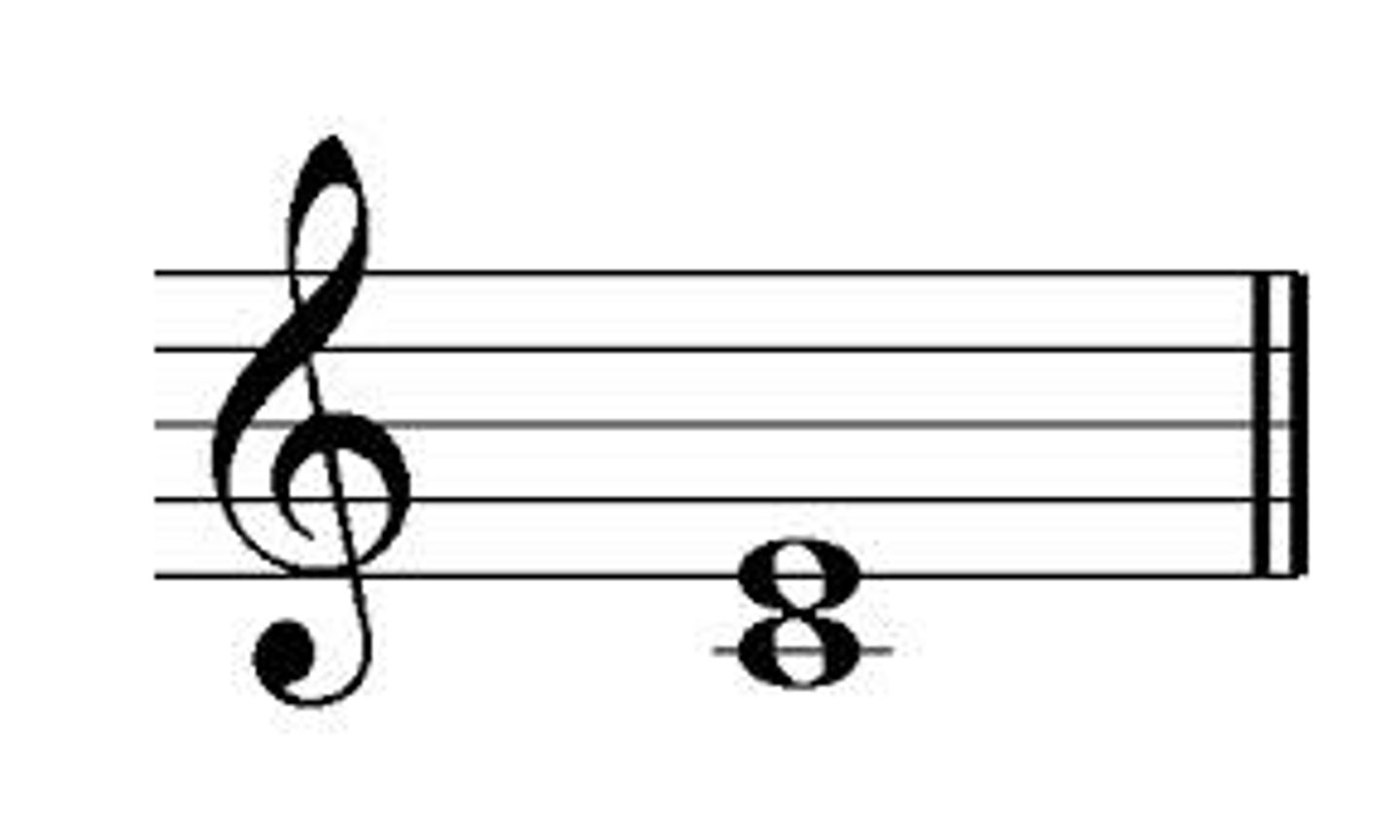
Interval of a 5th
Distance between note 1 and note 5 of a scale
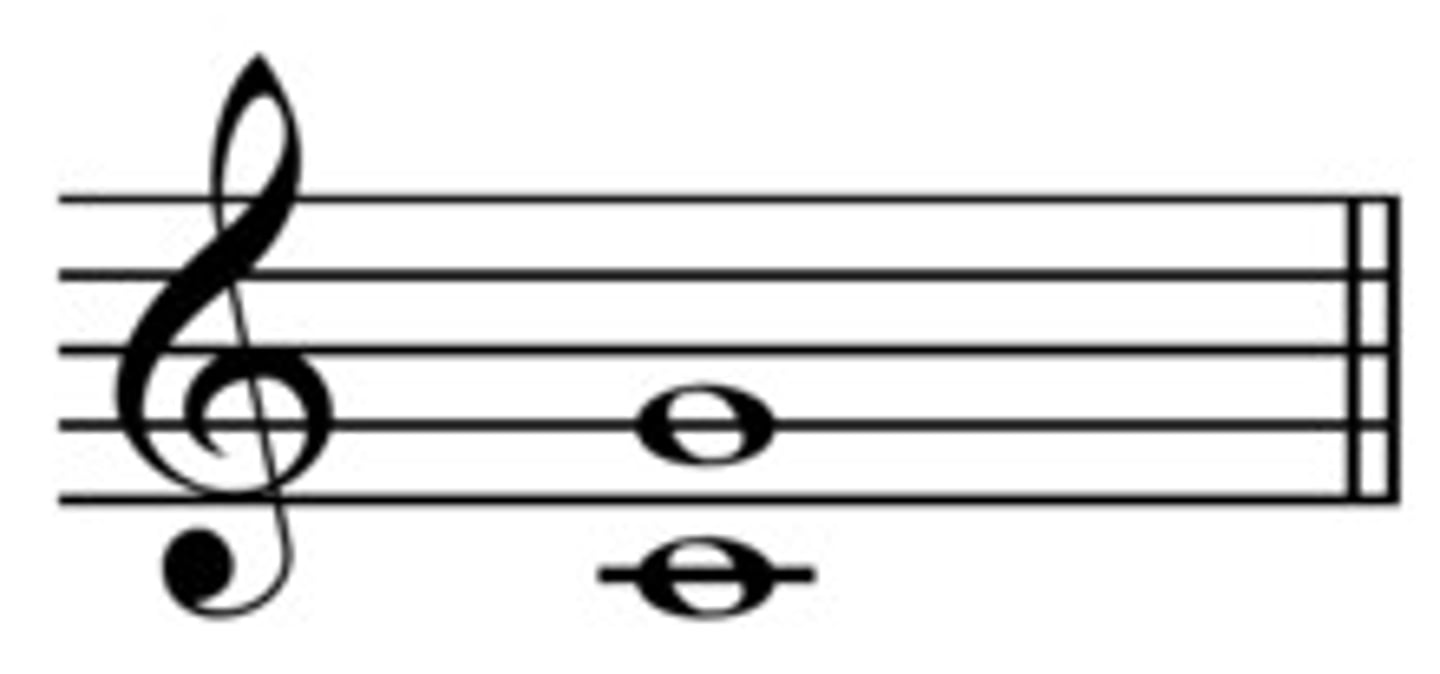
Interval of a 6th
Distance between note 1 and note 6 of a scale
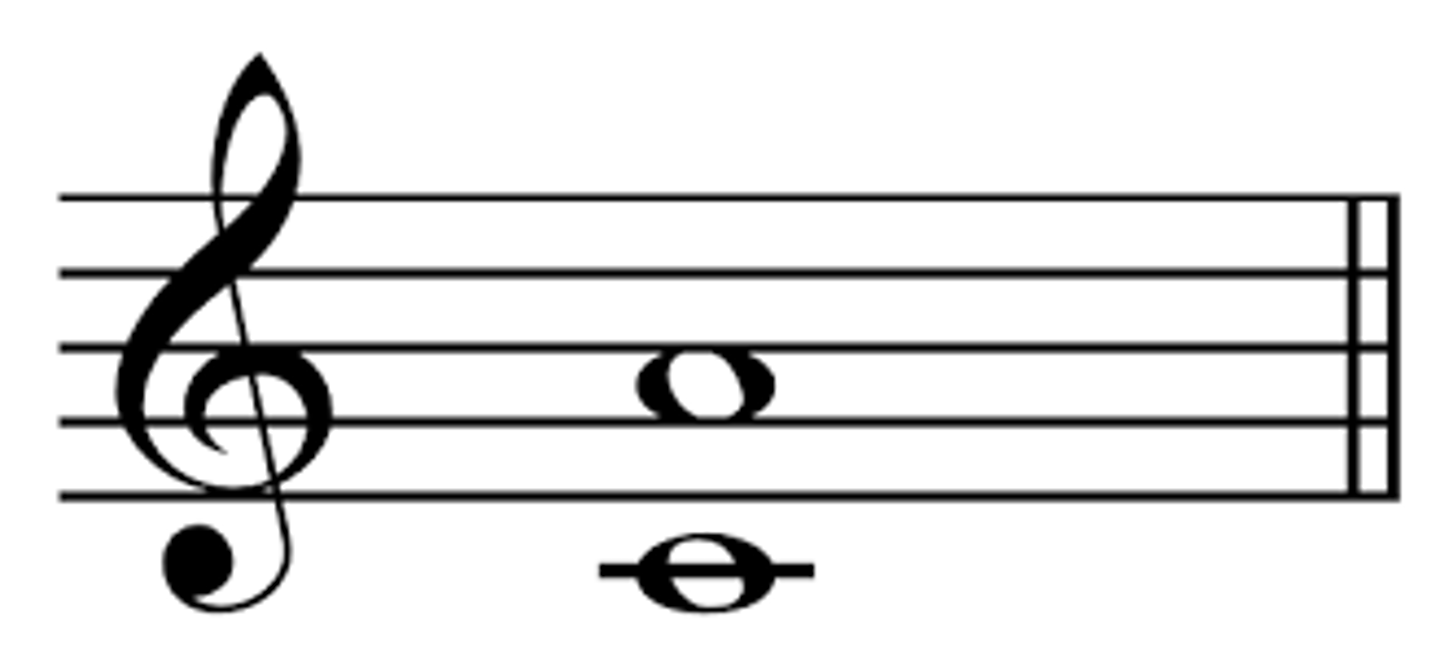
Interval of a 7th
Distance between note 1 and note 7 of a scale
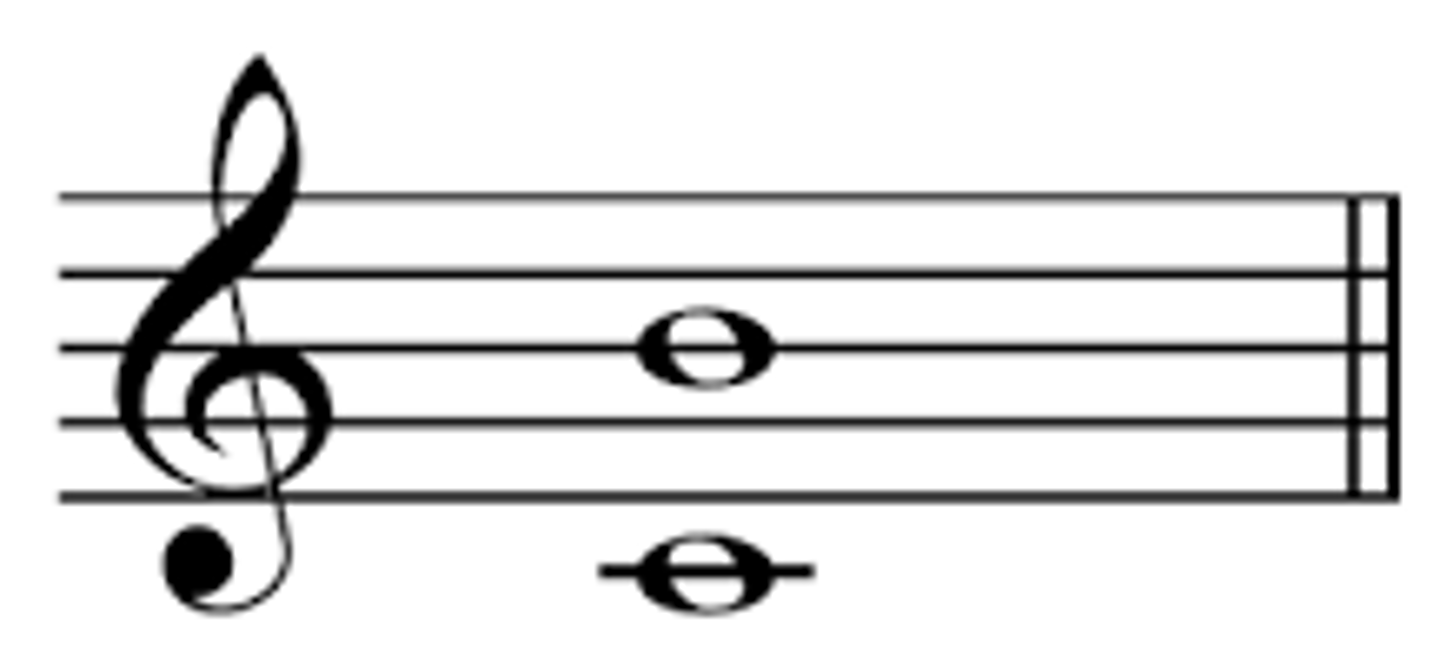
Interval of an octave
Distance between note 1 and note 8 of a scale
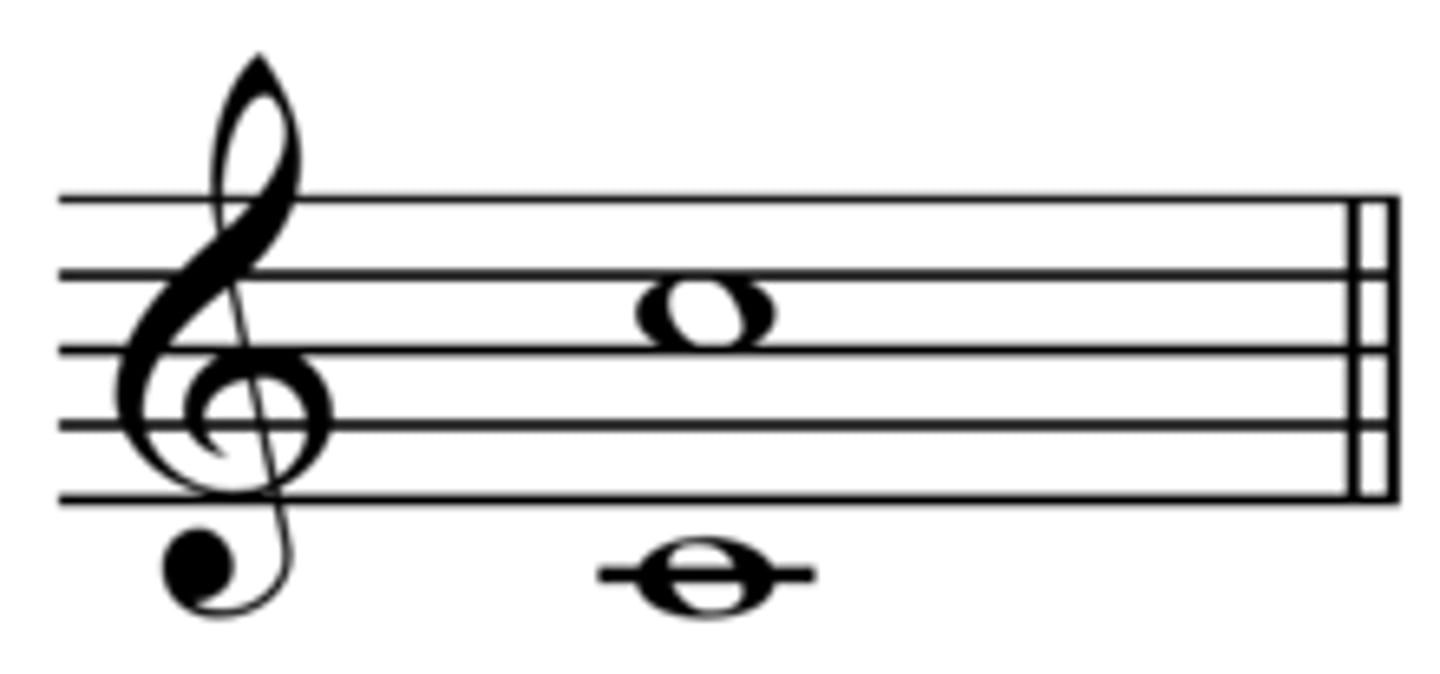

What harmony involves
Combining more than one note
Two factors to consider when combining multiple notes to make a pleasant sound
Chords and keys
Three of many different types of compositions a chord sequence can be the starting point for
Song, instrumental piece or film track
Two things a chord sequence can evoke
A particular mood or atmosphere
Semitone
smallest interval between 2 notes; a half step
Chromatic Scale (how played)
When semitones are played one after another in order, up and down
Number of semitones between root and third in a minor triad
3
What augmented and diminished chords sound more than major and minor triads
Unstable (augmented: eerie sinister moods)
Order for Sharps (very important!)
Father Charles Goes Down And Ends Battle
Order for flats
Battle Ends And Down Goes Charles' Father
What diminished and augmented chords add can be used to add to your music
Harmonic interest and tension
Augmented triad
Major triad with the fifth moved up by a semitone
Notation for augmented triad with root R
R aug
Three ways an augmented chord can be used:
As a 'stepping note' between other chords, a substitute for chord V and to add a sense of ambiguity or unpredictability
Root
note that is the basis for a chord, regardless of its inversion(root position is the strongest position and most common for a chord, 2nd and 3rd inversions of a chord are less used)
Inversion
Chord with notes rearranged so that a different note is in the bass
Purpose of inversion
Makes a chord sequence easier to play and can give a smoother bass line which can be more pleasant to listen to
What you do to a minor scale to make it melodic minor when ascending
Sharpen 6th
What you do to a minor scale to make it melodic minor when descending
No sharp 7th like in harmonic, so effectively flatten it
Accidentals
An accidental is a symbol in music notation that raises or lowers a natural noteby one or two half steps.
Dorian mode
Flattened third and seventh compared to major scale starting on the same root
Phrygian mode
Flattened 2nd compared to natural minor scales beginning on the same root
Aeolian mode
Same as the natural minor with the same root! (e.g A minor)
What the tone interval between 7th and 8th notes in a mode gives the music
A distinctive character which you should listen for
Mode
Very distinctive ancient scale, each with a different structure of tones and semitones, unlike major and minor scales - though they sometimes sound like a mixture of the two
Tonal Centre
Specific note around which a piece of music is organized
What you need in the new key when you modulate
A perfect cadence
Notes when adding seventh to the dominant in key of C. This is great to use in compositions
G, B, D and F
Notes in a dominant seventh chord
Root, third, fifth and minor seventh
Pretty much all (except maybe atonal) pieces of music are based on:
A scale!
Chromatic writing
When other notes as well as notes belonging to a prevailing key or scale are used