MRI Safety Chapters 3 & 4; Read Chapters 1 & 2
1/931
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
932 Terms
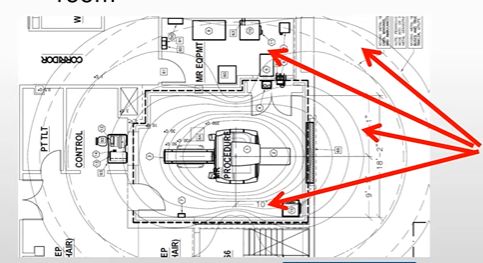
What are the arrows pointing to?
magnetic fringe field lines around the MRI scanner

What is the MRI Zone II?
MRI Patient Screening and Preparation

What is MRI Zone III?
Screened MRI Patients and Personal Only
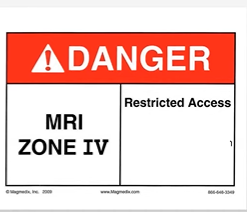
What is MRI Zone IV?
Screened MRI Patients Under Direct Supervision of Trained MRI Personnel Only

What does the image warn?
Restricted Access Strong Magnetic Field

What does the image show?
Ferromagnetic object being pulled into the magnet
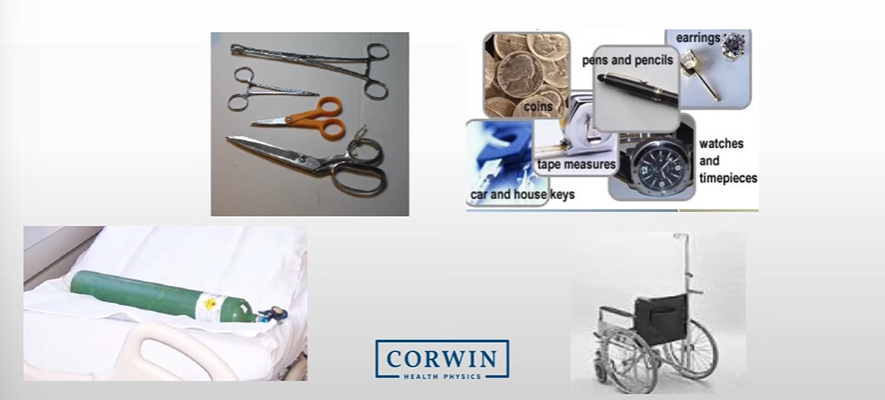
What does the image show?
Some Ferromagnetic Objects
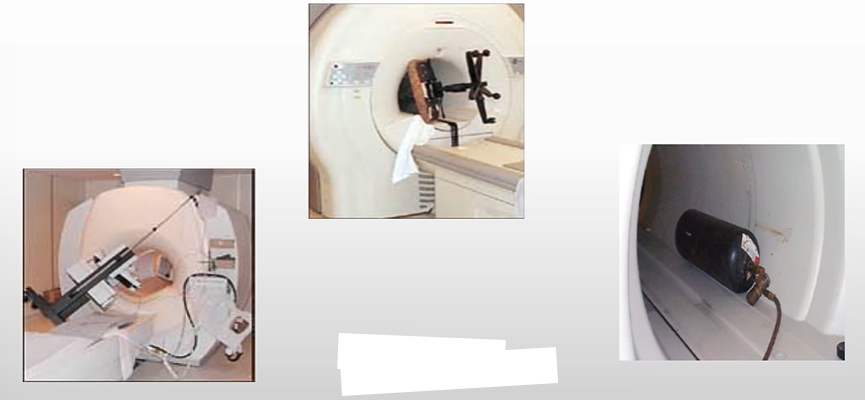
What does the image show?
Results of Missile Effect

What does the sign stand for?
MR Safe

What does the sign stand for?
MR Unsafe

What does the sign stand for?
MR Conditional
What are the guiding principles of MR safety?
MR personnel must be educated, remain vigilant in a dynamic environment, and apply that knowledge to screening and safety throughout time in the MR Suite
What defines Level 1 MR Personnel?
Individuals with minimal MR safety education who may work in Zone III and may enter Zone IV only with escort by Level II personnel
What defines Level 2 MR Personnel?
Individuals extensively trained in MR safety, including risks such as thermal loading, burns, and neuromuscular excitation, with authorized access to Zone IV
Who identifies Level II MR Personnel?
The MR Medical Director
What is the MRI scanner fundamentally?
A very large and powerful magnet
What is the typical field strength of clinical MRI scanners?
1.5 to 3.0 Tesla
What field strength is beginning to appear in MRI?
7 Tesla magnets
How many gauss is 3 Tesla?
30,000 gauss
How strong is Earth’s magnetic field?
Approximately 0.5 gauss
Is the MRI magnet ever turned off?
No, the MRI magnet is always on
Why is MRI unique compared to CT?
The magnetic field is always on and extends beyond the room
What is Zone I in MRI?
A publicly accessible area with no MRI restrictions
What is Zone II in MRI?
The interface between public Zone I and restricted Zone III, where patients are typically screened
What is Zone III in MRI?
A restricted area outside the scanner room where unscreened individuals may face serious risk; access requires training
Why is Zone III dangerous?
Unscreened individuals or equipment may interact dangerously with the MR environment
What must employees entering Zone III have?
Proper MRI safety training
What is a common issue with Zone III compliance?
Many sites cannot meet full engineering requirements
What should sites do if they cannot fully meet Zone III engineering requirements?
Make best effort to evaluate, comply, train personnel, and secure the scanner room
What is Zone IV in MRI?
The MRI scanner room
What must be done with the Zone IV door?
It must always be closed or monitored
What is required for Level 1 personnel entering Zone IV?
They must complete a screening form every time they enter Zone IV
Who are examples of Level II MR personnel?
MR technologists and MR radiologists
What is the role of the MR Medical Director regarding personnel?
They identify individuals who qualify as Level II MR personnel
What is the MRI scanner?
A very large and powerful magnet
What are typical clinical MRI field strengths?
1.5 to 3.0 Tesla
What higher field strength is becoming more common?
7 Tesla
How many gauss is 3 Tesla?
30,000 gauss
How strong is Earth’s magnetic field?
Approximately 0.5 gauss
Is the MRI magnet ever turned off?
No, the MRI magnet is always on
Why is MRI unique?
The magnetic field is always on and extends beyond the room
What is Zone I?
A general public area with no MRI restrictions
What is Zone II?
The interface between public Zone I and restricted Zone III where patients are screened
What is Zone III?
A restricted area outside the scanner room where unscreened individuals may face serious risk
Why is Zone III dangerous?
Unscreened individuals or equipment may interact dangerously with the MR environment
What is required for employees entering Zone III?
MRI safety training
What is a common Zone III compliance issue?
Many sites cannot meet full engineering requirements
What should sites do if they cannot meet Zone III engineering requirements?
Make best effort to evaluate, comply, train personnel, and secure the scanner room
What is Zone IV?
The MRI scanner room
What must be done with the Zone IV door?
It must always be closed or monitored
Who may enter Zone IV?
Only screened patients and screened personnel under proper supervision
Why must Level 1 personnel be escorted in Zone IV?
Because Level 1 personnel do not have sufficient MR safety training to enter Zone IV independently
What is required of all personnel entering Zone IV?
All personnel must be screened before entering Zone IV
What are the permanent bioeffects of static magnetic fields under 10T?
There are no permanent bioeffects from static fields under 10T
What causes most bioeffects from static magnetic fields?
Induced voltages in tissues due to motion through the magnetic field
What sensations may occur when moving through a static magnetic field?
Flashes of light, vertigo, and metallic taste
What is the projectile effect?
Ferromagnetic objects can be pulled violently into the magnet
What are possible results of the missile effect?
Injury to patients or staff and damage to the MRI scanner
What is the definition of an MR Safe item?
An item that poses no known hazards in all MR environments
What is the definition of an MR Unsafe item?
An item known to pose hazards in all MR environments
What is the definition of an MR Conditional item?
An item that poses no known hazards under specified conditions
What should you do if you are unsure whether an item is safe?
Do not guess; consult an MRI technologist for evaluation
What must be completed before an MRI exam can be scheduled?
The MRI Patient Screening Questionnaire
What items are screened for on the MRI questionnaire?
Ferromagnetic items, implants, conductive materials, metallic tattoos, and NSF risk
What must all staff entering the MRI room complete?
An MRI screening form
What is quenching the magnet?
The deactivation of the magnetic field, causing rapid cryogen boil‑off
When should a quench be performed?
Only when someone is pinned by a ferromagnetic object or during an uncontrollable fire requiring ferromagnetic firefighting equipment
Where are emergency quench buttons located?
In each scanner room and control room
Are pregnant healthcare workers allowed in the MR environment?
Yes, they may work in and around the MR environment throughout pregnancy
What activities may pregnant workers perform in MRI?
Positioning, scanning, archiving, injecting contrast, and emergency entry
Where should pregnant workers avoid being during actual MR acquisitions?
Zone IV
What is the purpose of knowing MRI Safety Team contacts?
To ensure staff can reach the MR Medical Director or MRI Safety Officer when safety concerns arise
Who is part of the MRI Safety Team?
The MR Medical Director and the MRI Safety Officer (MRSO)
Why must the MRI scanner room door remain closed or monitored?
To prevent unscreened individuals or unsafe items from entering Zone IV
What barrier is recommended if the Zone IV door is left open?
A caution barrier such as straps or plastic chains
How should technologists position themselves when approaching the patient in Zone IV?
From the far side of the scanner to view the door and avoid projectile paths
Who must supervise Level 1 personnel in Zone IV?
Level 2 personnel must directly supervise Level 1 personnel in Zone IV
Who may enter Zone IV?
Only screened patients and screened personnel under proper supervision
What is required of all personnel entering Zone IV?
All personnel must be screened before entering Zone IV
Are there permanent bioeffects from static magnetic fields under 10T?
No permanent bioeffects occur at clinical field strengths under 10T
What causes most static magnetic field bioeffects?
Induced voltages in tissues due to motion through the magnetic field
What sensations may occur when moving through the magnetic field?
Flashes of light, vertigo, and metallic taste
What is the projectile effect?
Ferromagnetic objects can be pulled violently into the magnet
What injuries can result from the missile effect?
Injury to patients or staff and damage to the MRI scanner
What is an MR Safe item?
An item that poses no known hazards in all MR environments
What is an MR Unsafe item?
An item known to pose hazards in all MR environments
What is an MR Conditional item?
An item that poses no known hazards under specified conditions
What should you do if unsure whether an item is safe?
Do not guess; consult an MRI technologist for evaluation
What must be completed before an MRI exam can be scheduled?
The MRI Patient Screening Questionnaire
What items are screened for on the MRI questionnaire?
Ferromagnetic items, implants, conductive materials, metallic tattoos, and NSF risk
What must all staff entering the MRI room complete?
An MRI screening form
What is quenching the magnet?
The deactivation of the magnetic field, causing rapid cryogen boil‑off
When should a quench be performed?
Only when someone is pinned by a ferromagnetic object or during an uncontrollable fire requiring ferromagnetic firefighting equipment
Where are emergency quench buttons located?
In each scanner room and control room
Are pregnant healthcare workers allowed in the MR environment?
Yes, they may work in and around the MR environment throughout pregnancy
What activities may pregnant workers perform in MRI?
Positioning, scanning, archiving, injecting contrast, and emergency entry
Where should pregnant workers avoid being during actual MR acquisitions?
Zone IV
What is the purpose of knowing MRI Safety Team contacts?
To ensure staff can reach the MR Medical Director or MRI Safety Officer when safety concerns arise
Who is part of the MRI Safety Team?
The MR Medical Director and the MRI Safety Officer (MRSO)
What is the MRI Safety Officer (MRSO) responsible for?
Overseeing MRI safety practices and serving as a point of contact for safety concerns