Plate Tectonics Study Guide
1/73
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
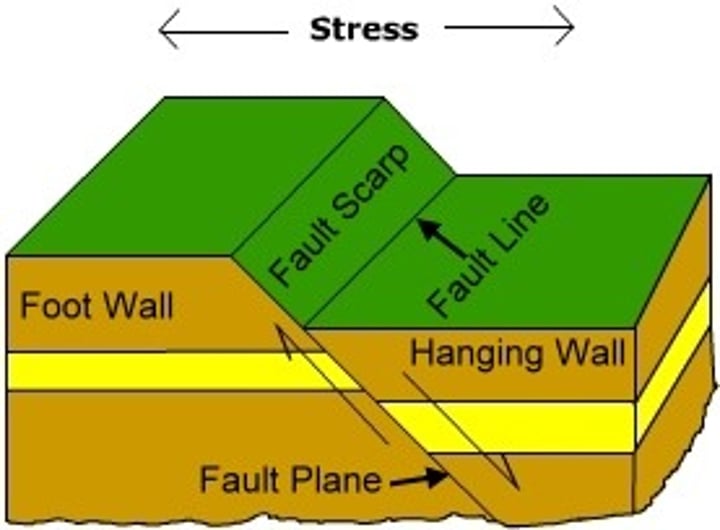
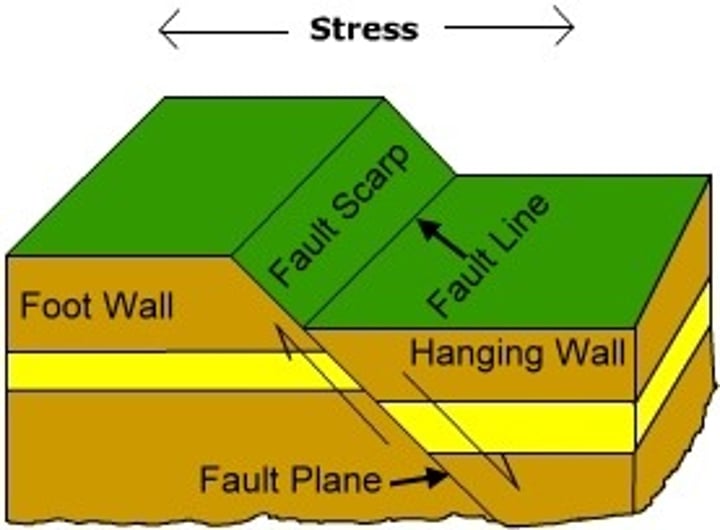
fault
The surface along which rocks break and slide past each other.
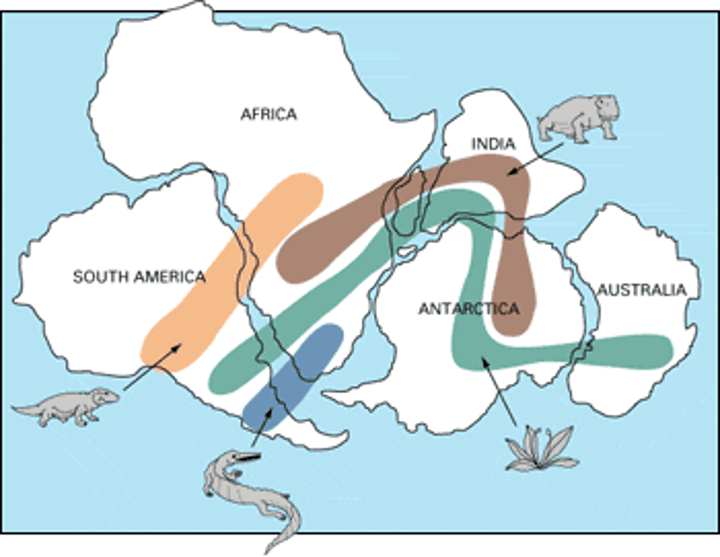
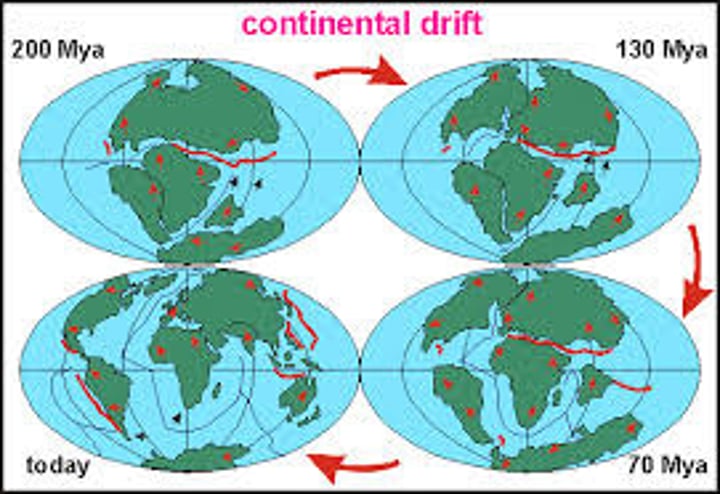
continental drift
the gradual movement of the continents across the earth's surface through geological time.
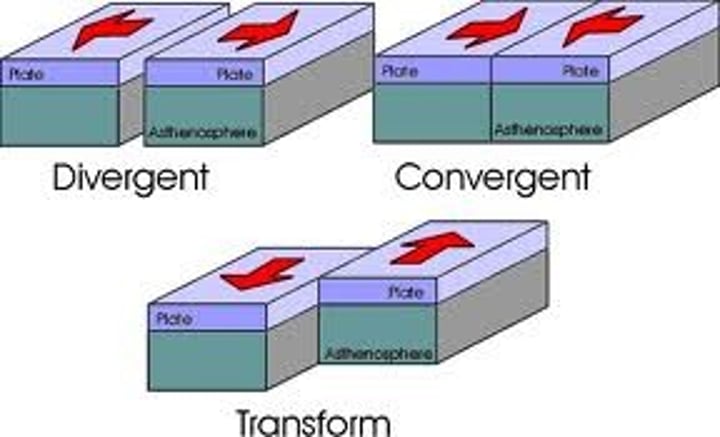
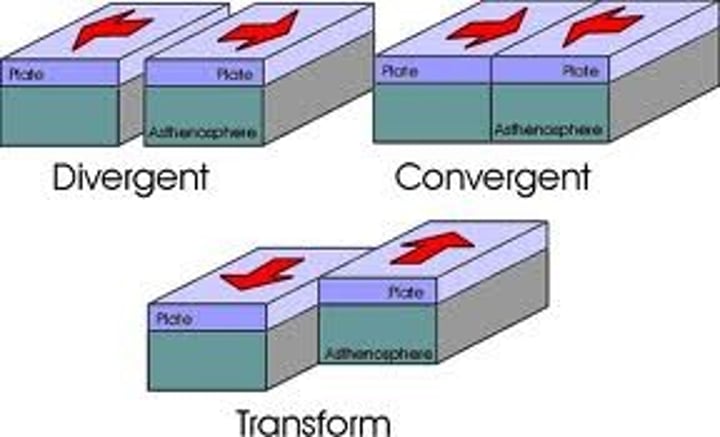
divergent boundary
Place where two tectonic plates move away from each other
mid-ocean ridge
an underwater mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced
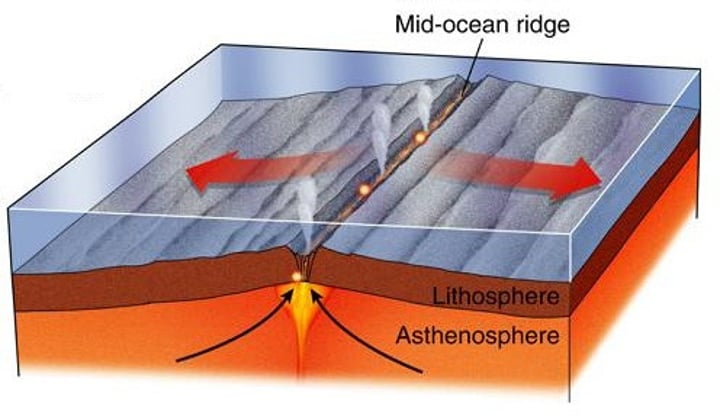
plate tectonics
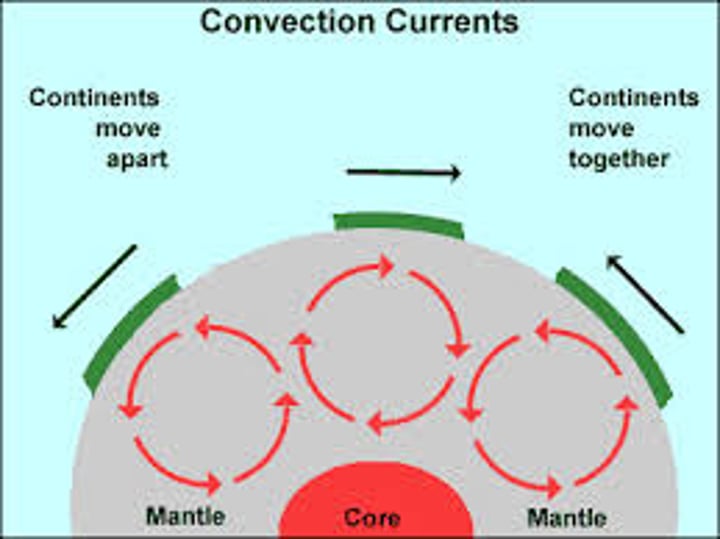
The theory that the earth is broken into plates and are in motion due to convection currents in the asthenosphere (upper mantle)

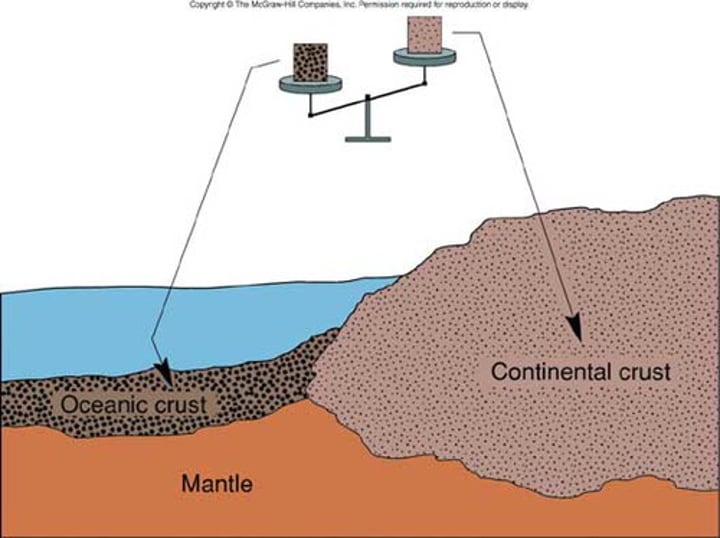
oceanic crust
thinner, more dense, younger crust making ocean floor/Large pieces of earths crust and upper mantle that move due to convection currents.
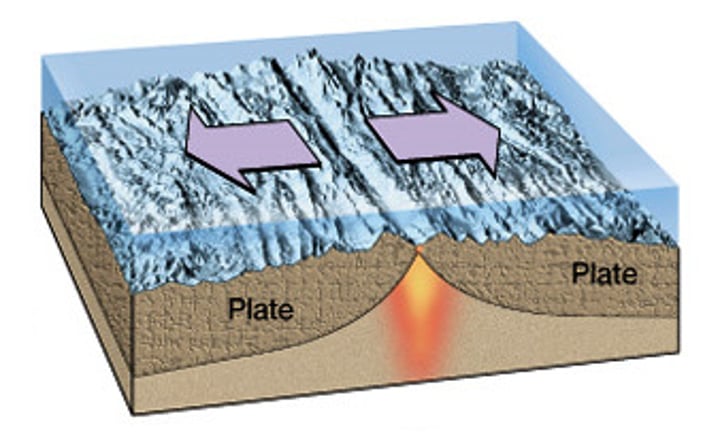
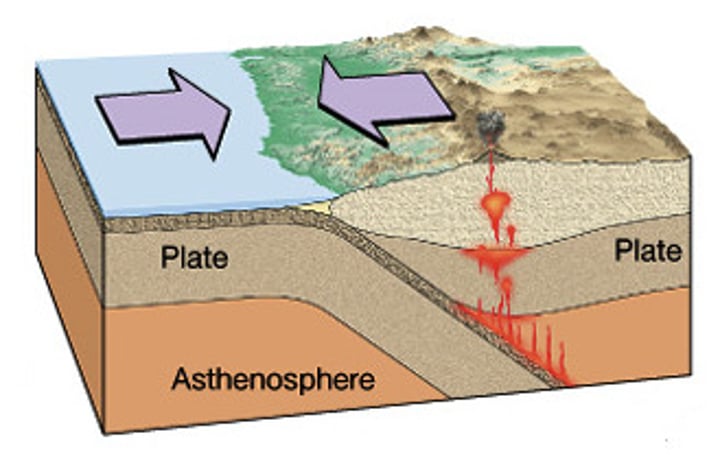
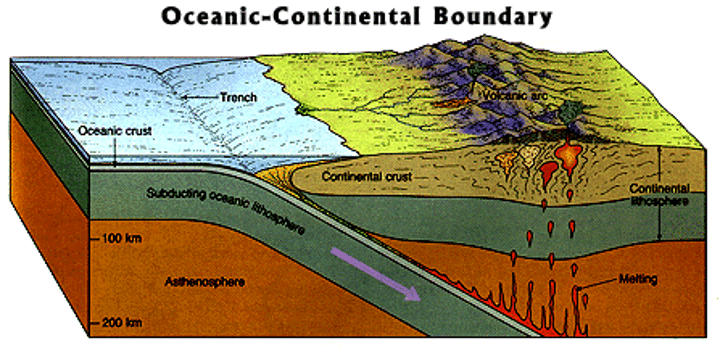
convergent boundary
The boundary formed by the collision of two plates
deep-ocean trench
deep valley or underwater canyon where the oceanic crust sinks back toward the mantle
cynognathus, mesosaurus, lystrosaurus, and glossopteris
What fossils did Wegener use for his theories?
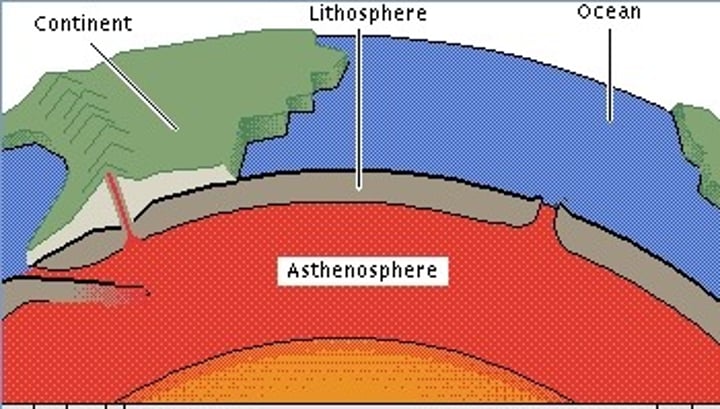
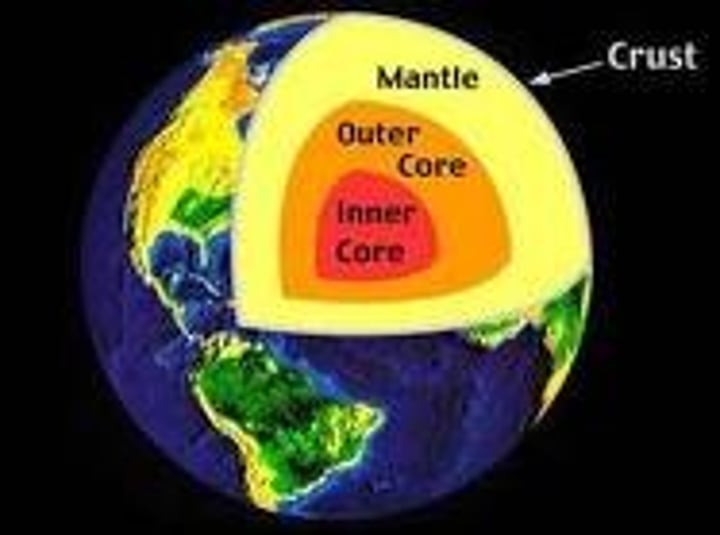
asthenosphere
The soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats
continental crust
The portion of the earth's crust that primarily contains granite, is less dense than oceanic crust, and is 20-50 km thick/Large pieces of earths crust and upper mantle that move due to convection currents.
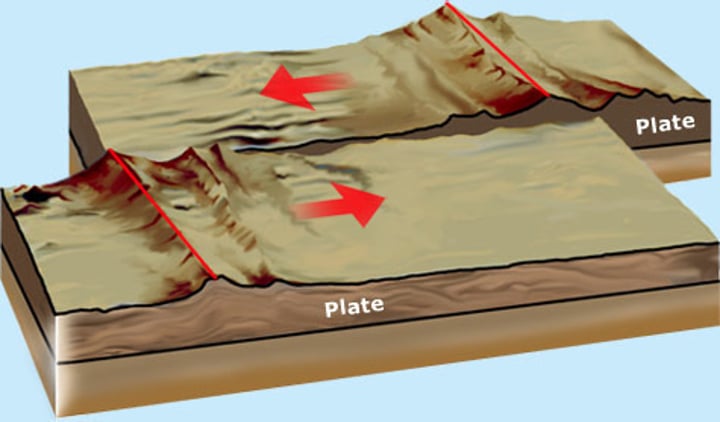
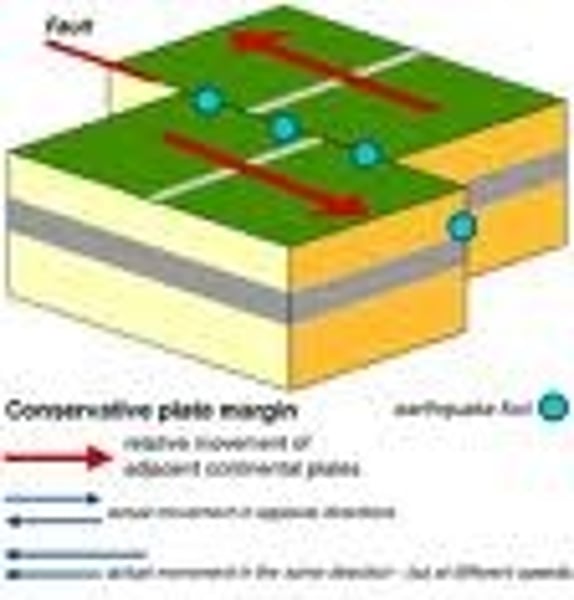
transform boundary
The boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally
sonar
Sound waves from ships bounce off the ocean floor to tell how deep the water is.
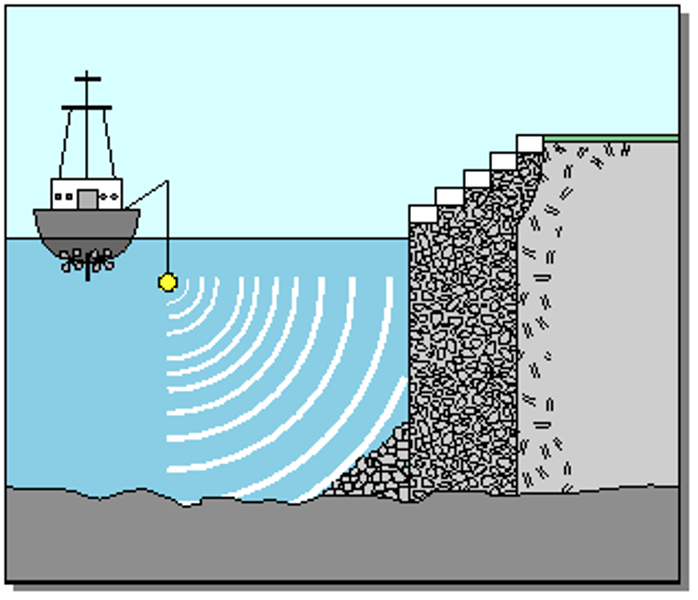
plate boundary
the region where two tectonic plates are in contact
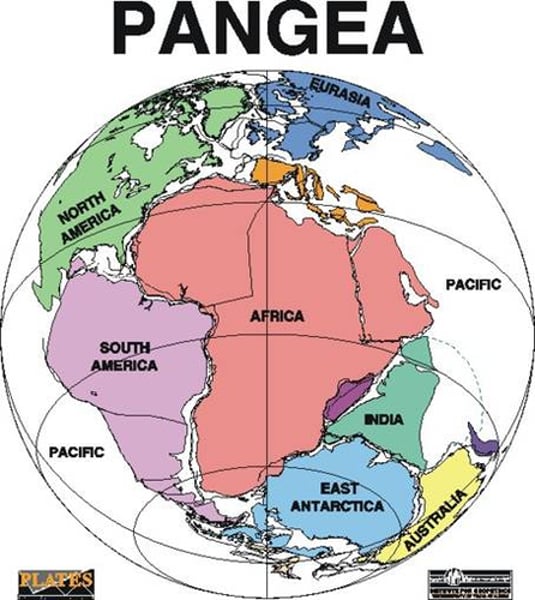
Pangaea
the name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to today's continents.
land features, fossils, past climate, coastlines
Explain the evidence supporting the hypothesis of Alfred Wegener
He didn’t know how plates moved
Why was Wegener's hypothesis rejected (reason 1 - explanation)?
He was a weatherman
Why was Wegener's hypothesis rejected (reason 2 - job)?
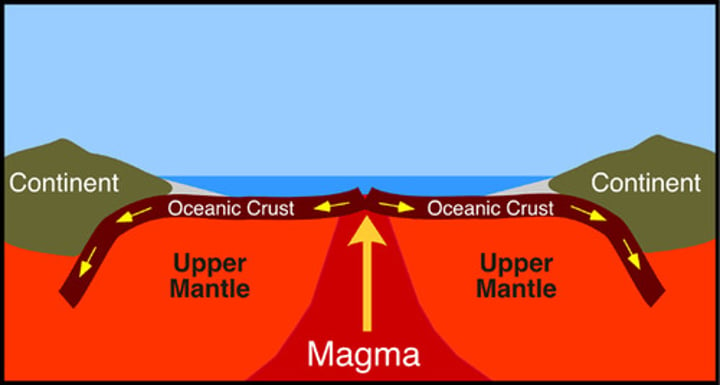
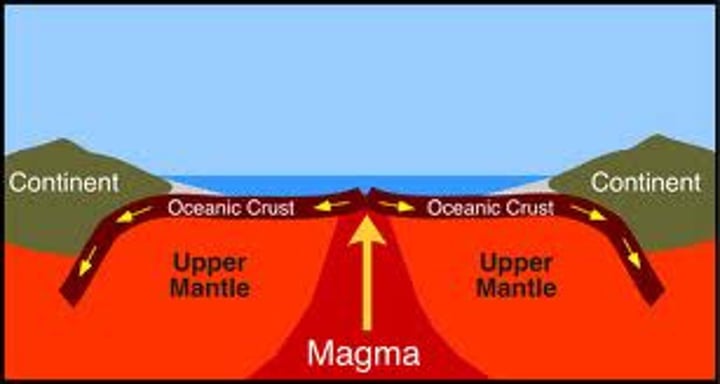
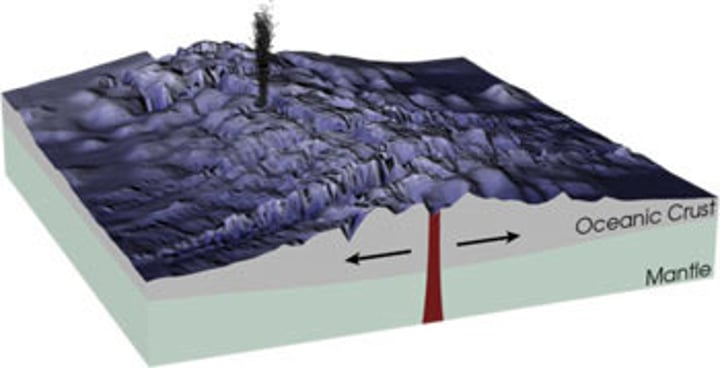
sea-floor spreading
The process of adding more crust to the ocean floor. We know this occurs because of ocean-floor material, magnetic stripes, and drilling samples.
Ocean material
Seafloor spreading evidence: Pillow lava, rocks on the ocean floor form in the shape of a pillow when it cools and hardens very quickly underwater
Magnetic stripes
Seafloor spreading evidence: When molten material erupts it brings magnetic material with it and lines up in the direction of the magnetic field at the time..the magnetic field changes over time and the stripes reflect those changes
Seafloor age
Seafloor spreading evidence: At oceanic spreading centres, new oceanic crust is formed from magma upwelling. This new crust emerges from the ridge and pushes the pre-existing rocks away from the ridge laterally. This results in a strip of new rock cutting through the older rock. As the formation of the crust continues, the older rocks will be pushed further away from the ridge, while younger, newly produced rocks will occupy the area closest to the ridge.
the force that moves the plates
Seafloor spreading supports Wegener's hypothesis because it explains _______________.
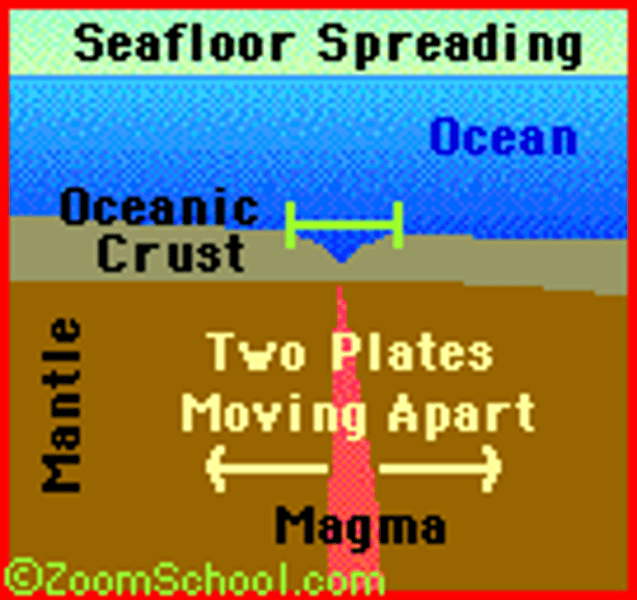
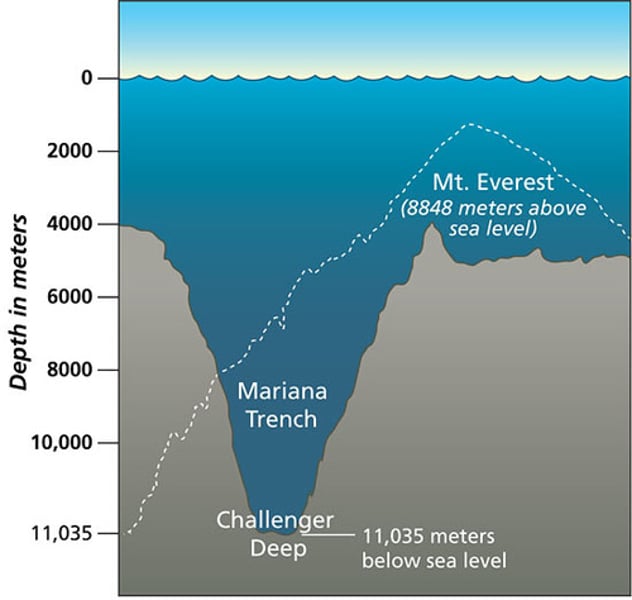
deep-ocean trench
A deep underwater canyon where the ocean crust bends downward. The Pacific Ocean has the most deep of these.
Ex. Mariana Trench 😱
subduction
The process of the ocean floor sinking beneath a deep ocean trench and back into the mantle. When new crust is formed, the older crust is pushed further away from the trench, it cools and becomes more dense. This dense crust can sink back into the mantle when it reaches an ocean trench.
smaller
Because the Atlantic Ocean is opening and North America and South America are moving westward, we know that the Pacific Ocean is getting ________ (larger/smaller).
larger
Because of the presence of spreading centres (divergent plate boundaries), we can tell that the Atlantic Ocean is getting __________ (larger/smaller).
stay the same
Subduction and seafloor spreading balance each other out, allowing Earth’s size to _______ (increase/decrease/stay the same).
4 billion years old
How old is the oldest continental crust?
Remember: because continental crust is lighter than oceanic crust, continental crust cannot subduct. We therefore still have some very old continental rocks at the surface of the Earth.
180 million years old
How old is the oldest oceanic crust in the Atlantic?
Remember: oceanic crust tends to get colder and denser with age as it spreads off the mid-ocean ridges. It gets so dense, that it sinks in the upper mantle (subduction). This is like a giant recycling system for oceanic lithosphere!
tectonic plate
A ________ is the name for the pieces of the earth's crust (lithosphere)
lithosphere
What layer of Earth contains tectonic plates?
Hint: The solid, outer layer of the Earth that consists of the the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle
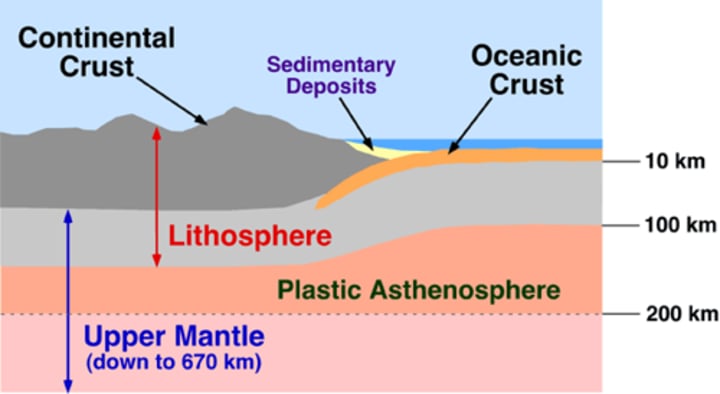
Oceanic and continental plates
What are the two kinds of plates?
fault
The surface along which rocks break and slide past each other.
convection currents
What drives plate movement?
2 to 5 cm per year
How fast do plates move on average?
fingernails
What grows just as fast as plates move?
73 miles
How long is Hadrian's wall?
sure
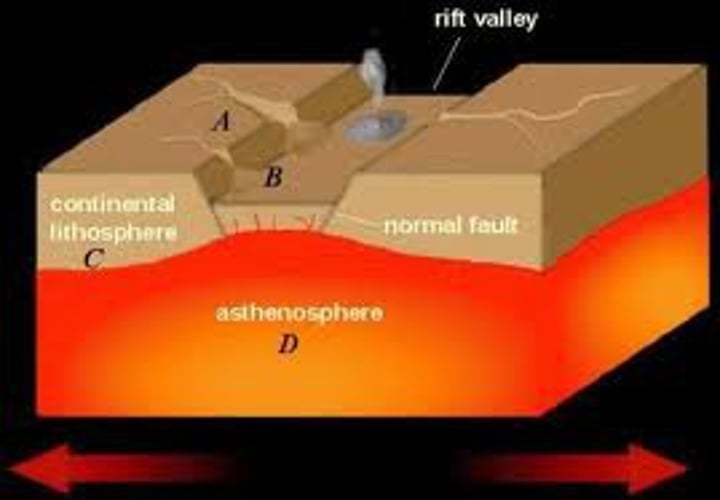
Read this and type sure (how are sea-floor spreading and rift valley forming alike):
Sea-floor spreading and rift valleys both involve plates diverging (moving apart)
yes
Read this and type yes (how are rift valleys and sea floor spreading different):
Sea-floor spreading occurs underwater, rift valleys occur on land; the new crust is formed by sea-floor spreading, rift valleys don't create new land
transform boundaries
What plate boundary doesn't change the mass or composition of the sea floor (ex. through subduction or creating new crust)?
ok
Read this and write/click “ok” hehe:
Layers that are less dense, such as the crust, float on layers that are denser, such as the mantle. Both oceanic crust and continental crust are less dense than the mantle, but oceanic crust is denser than continental crust. This is partly why the continents are at a higher elevation than the ocean floor.
earthquakes and volcanic eruptions
What catastrophic events can plate movements cause?
Laurasia
top part of pangaea
Gondwana
bottom part of pangaea
Panthalassa Ocean
ocean in Pangaea
James Hutton
father of geology
Eurasian Plate and Indian Plate
What two plates created the Himalayas (hint: C-C convergent boundary)?
Nazca Plate and South American Plate
What two plates created the Andes (hint: O-C convergent boundary)?
Pacific Plate and North American plate
What two plates created the San Andreas Fault (hint: transform boundary)?
James Ussher
The man who calculated the age of the Earth to have been formed on October 23, 4004 BC.
Catastrophism
A theory on Earth’s formation and the diverse landscapes of our planet based on James Ussher’s timeline.
Hint: Involved landforms being quickly created by various natural disasters.
Uniformitarianism
A theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted from the action of continuous and uniform processes.
Hint: this theory was formed by Hutton’s timeline.
Hadrian’s wall
A very old wall that was in very good condition, whilst the same type of rock that was part of the ground was worn and eroded. It inspired Hutton’s theories on the timeline of the Earth.
seven
How many major plates are there?
ten
How many minor plates are there?
C-C convergent
Subduction doesn’t occur at ______________ boundaries. (hint: folded mountains are here!)
over 45,000 miles long
How long is the global ridge system?
Cascade Mts and Andes Mts
List some O-C convergent boundary examples :)
Aleutian Islands and Marianas Trench
List some O-O convergent boundary examples :)
Alps, Urals, and Appalacians
List some C-C convergent boundary examples :)
East African Rift
Name an example of continental rifting
Playa
shallow, short-lived lake
Racetrack Playa
a basin and range system in Death Valley; one of the flattest places on Earth
Hint: the rolling stones 🫨
410-620 miles deep
In the layer cake model, at what depth is the mantle divided
layer-cake model
Convection Model:
Two layers: thin upper mantle and thick lower mantle
subducted slabs go no deeper than 620 miles
melted plates cause hotspots
very little mixing between sections
heat slowly rises from lower mantle
whole-mantle convection
Convection Model:
aka the plume model
narrow tube-like plumes and large mega plumes
heat comes from the core
convective flow is driven by lithosphere subduction
subducted slabs rest on the core-mantle boundary
Vine and Mathews
Who interpreted the magnetic stripes of the mid-atlantic ridge as products of steady creation of new crust?
Olympus Mons
If there were no plate tectonics, Hawaii would be the size of ______.
Marie Tharp and Bruce Heezen
Who released the first ocean floor map in 1957?
Harry Hess
Who theorised that the oceanic mountain ranges were caused by tectonic plates that were spreading apart and creating new crust?
Marie Tharp and Harold Foster
Who discovered the correlations between the mid-atlantic ridge and earthquakes?
Alfred Wegener
Who proposed the theory of continental drift in 1915?
thicker
Sediments became ______ (thicker/thinner) the older the rock got (further from the ridge)