D426 - Data Management Foundations
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
database application
software that helps business users interact with database systems
database administrator
responsible for securing the database system against unauthorized users. A _____ enforces procedures for user access and database system availability.
Authorization
Many database users should have limited access to specific tables, columns, or rows of a database. Database systems authorize individual users to access specific data.
Rules
Database systems ensure data is consistent with structural and business rules
query processor
interprets queries, creates a plan to modify the database or retrieve data, and returns query results to the application.
Storage Manager
translates the query processor instructions into low-level file-system commands that modify or retrieve data. Database sizes range from megabytes to many terabytes, so the _____ uses indexes to quickly locate data.
Transaction Manager
ensures transactions are properly executed. The ______ prevents conflicts between concurrent transactions. The _______ also restores the database to a consistent state in the event of a transaction or system failure.
INSERT
inserts rows into a table.
INSERT INTO table_name (column_name1, column_name2, ...) VALUES (DEFAULT, 'bob', 30, 150);
SELECT
retrieves data from a table
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name; -- return all data from those columns.
UPDATE
modifies data in a table
UPDATE table_name SET column_name = 2 WHERE column_id = 3;
Delete
deletes rows from a table
DELETE FROM table_name; -- all rows deleted! DELETE FROM table_name WHERE column_name = 'value'; -- delete row
CREATE TABLE
creates a new table by specifying the table and column names.
DDL
Data Type
Each column is assigned a ____ that indicates the format of column values. ____ can be numeric, textual, or complex
INT, DECIMAL, VARCHAR, DATE
stores integer values
stores fractional numeric values
stores textual values
stores year, month, and day
Analysis Phase
specifies database requirements without regard to a specific database system. Requirements are represented as entities, relationships, and attributes.
entity
Is a person, place, activity, or thing. Singular.
relationship
is a link between entities, and an attribute is a descriptive property of an entity.
Analysis alternate names
conceptual design, entity-relationship modeling, and requirements definition.
logical design phase
implements database requirements in a specific database system. For relational database systems, ____ converts entities, relationships, and attributes into tables, keys, and columns.
physical design phase
adds indexes and specifies how tables are organized on storage media. _____ affects query processing speed but never affects the query result. The principle that _____ never affects query results is called data independence.
API
To simplify the use of SQL with a general-purpose language, database programs typically use an application programming interface
MySQL Command-Line Client
text interface included in the MySQL Server download. MySQL Server returns an error code and description when an SQL statement is syntactically incorrect or the database cannot execute the statement.
tuple
s an ordered collection of elements enclosed in parentheses. Ex: (a, b, c) and (c, b, a) are different, since tuples are ordered.
Table Data Structure
has a name, a fixed tuple of columns, and a varying set of rows
Column Data Structure
has a name and a data type
Row Data Structure
an unnamed tuple of values. Each value corresponds to a column and belongs to the column's data type
Data Type Data Structure
is a named set of values, from which column values are drawn
Data Structure Synonyms:
Table, File, Relation
Row, Record, Tuple
Column, Field, Attribute
Business rules
are based on business policy and specific to a particular database
Literals
Explicit values that are string, numeric, or binary.Strings must be surrounded by single quotes or double quotes.Binary values are represented with x'0' where the 0 is any hex value.
EX. 'String' "String" 123 x'0fa2'
Keywords
Words with special meaning
Ex. SELECT, FROM, WHERE
Identifiers
Objects from the database like tables, columns, etc.
Ex. City, Name, Population
Comments
Statement intended only for humans and ignored by the database when parsing an SQL statement.
Ex. -- single line comment. / multi-line Comment /
SQL Sublanguages
Data Definition Language (DDL) defines the structure of the database.
Data Query Language (DQL) retrieves data from the database.
Data Manipulation Language (DML) manipulates data stored in a database.
Data Control Language (DCL) controls database user access.
Data Transaction Language (DTL) manages database transactions
CREATE TABLE statement
creates a new table by specifying the table name, column names, and column data types
INT or INTEGER
integer values
VARCHAR(N)
Values with 0 to N Characters
Date
Date Values YYY-MM-DD
TIME
hh:mm:ss
DATETIME
YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SS
Decimal(M,D)
numeric values with M digits, of which D digits follow the decimal point
DROP TABLE
deletes a table, along with all the table's rows, from a database
DDL
ALTER TABLE statement
adds, deletes, or modifies columns on an existing table
DDL
Integer Data Types
Ex. 34 and -739448
TINYINT Signed Range: -128 to 127 Unsigned Range: 0 to 255
SMALLINT Signed Range: -32,768 to 32767 Unsigned Range: 0 to 65535
MEDIUMINT Signed Range: -8,388,608 to 8,388,607 Unsigned Range: 0 to 16,777,215
INT Signed Range: -2,147,483,647 to 2,147,483,647 Unsigned Range: 0 to 4,294,962,95
BIGINT Signed Range: -2^63 to 2^63 -1 Unsigned Range: 0 to 2^64 -1
Arithmetic Operators
+: Adds two numeric values
- (unary): Reverses the sign of one numeric value
-(binary): Subtracts one numeric value from another
*: Multiplies two numeric values
/: Divides one numeric value by another
%(modulo): Divides one numeric value by another and returns the integer remainder. Ex. 5%2 = 1
^: Raises one numeric value to the power of another
Comparison Operators
=: compares two values for equality
!=: compares two values for inequality
<: Compares two values with <
<=: Compares two values with ≤
>: Compares two values with >
UPDATE statement
_____ modifies existing rows in a table. The _____ uses the SET clause to specify the new column values. An optional WHERE clause specifies which rows are updated. Omitting the WHERE clause results in all rows being updated.
DELETE statement
_____ deletes existing rows in a table. The FROM keyword is followed by the table name whose rows are to be deleted. An optional WHERE clause specifies which rows should be deleted. Omitting the WHERE clause results in all rows in the table being deleted.
TRUNCATE statement
deletes all rows from a table. _____ is nearly identical to a DELETE statement with no WHERE clause except for minor differences that depend on the database system.
MERGE statement
selects data from one table, called the source, and inserts the data to another table, called the target.
primary key
is a column, or group of columns, used to identify a row. The _____ is usually the table's first column
simple primary key
consists of a single column
composite primary key
consists of multiple columns.
auto-increment column
is a numeric column that is assigned an automatically incrementing value when a new row is inserted.
Database users occasionally make the following errors when inserting primary keys:
Inserting values for auto-increment primary keys.
Omitting values for primary keys that are not auto-increment columns.
MySQL allows insertion of a specific value to an auto-increment column. However, overriding auto-increment for a primary key is usually a mistake.
foreign key
s a column, or group of columns, that refer to a primary key
FOREIGN KEY constraint
A _____ is added to a CREATE TABLE statement with the FOREIGN KEY and REFERENCES keywords. When a _____ is specified, the database rejects insert, update, and delete statements that violate referential integrity
Referential integrity actions
RESTRICT rejects an insert, update, or delete that violates referential integrity.
SET NULL sets invalid foreign keys to NULL.
SET DEFAULT sets invalid foreign keys to the foreign key default value.
CASCADE propagates primary key changes to foreign keys.
constraint
A _____ is a rule that governs allowable values in a database. ______ are based on relational and business rules,
Adding and dropping constraints
ALTER TABLE TableName followed by an ADD, DROP, or CHANGE clause
BETWEEN operator
Provides an alternative way to determine if a value is between two other values
LIKE operator
When used in a WHERE clause, matches text against a pattern using the two wildcard characters % and _.
% matches any number of characters. Ex: _____ 'L%t' matches "Lt", "Lot", "Lift", and "Lol cat".
ORDER BY clause
orders selected rows by one or more columns in ascending (alphabetic or increasing) order. The DESC keyword with the _____ orders rows in descending order.
Functions:
ABS(n): Returns the abzolute value of n
LOWER(s) Returns the lower case s
TRIM(s): Returns the strong s without leasing and trailing spaces
HOUR(t), MINUTE(t), SECOND(t): Returns the hour, minute or second from time t
Aggregate functions
COUNT() counts the number of rows in the set.
MIN() finds the minimum value in the set.
MAX() finds the maximum value in the set.
SUM() sums all the values in the set.
AVG() computes the arithmetic mean of all the values in the set.
HAVING clause
The _____ is used with the GROUP BY clause to filter group results.
JOIN
is a SELECT statement that combines data from two tables, known as the left table and right table, into a single result. The tables are combined by comparing columns from the left and right tables, usually with the = operator.
Alias
a column name can be replaced with an ____. The _____ follows the column name, separated by an optional AS keyword.
Join
Is a SELECT statement that combines data from two tables, known as the left table and right table, into a single result.
The tables are combined by comparing columns from the left and right tables, usually with the = operator.
INNER JOIN
combine records from two tables whenever there are matching values in a field common to both tables
FULL JOIN
selects all left and right table rows, regardless of match
Equijoins
An _____ compares columns of two tables with the = operator. Most joins are _____.
A _____ compares columns with an operator other than =, such as < and >.
Self-joins
joins a table to itself.
Cross-joins
combines two tables without comparing columns. A _____ uses a ______ clause without an ON clause.
subquery
sometimes called a nested query or inner query, is a query within another SQL query.
materialized view
a view for which data is stored at all times. Whenever a base table changes, the corresponding view tables can also change, so _____ must be refreshed.
WITH CHECK OPTION
When _________ is specified, the database rejects inserts and updates that do not satisfy the view query WHERE clause
entity-relationship model
Is a high-level representation of data requirements, ignoring implementation details
reflexive relationship
A ______ relates an entity to itself
ER diagram
Is a schematic picture of entities, relationships, and attributes. Entities are drawn as rectangles.
Attributes drawn as circles
Relationships drawn as lines
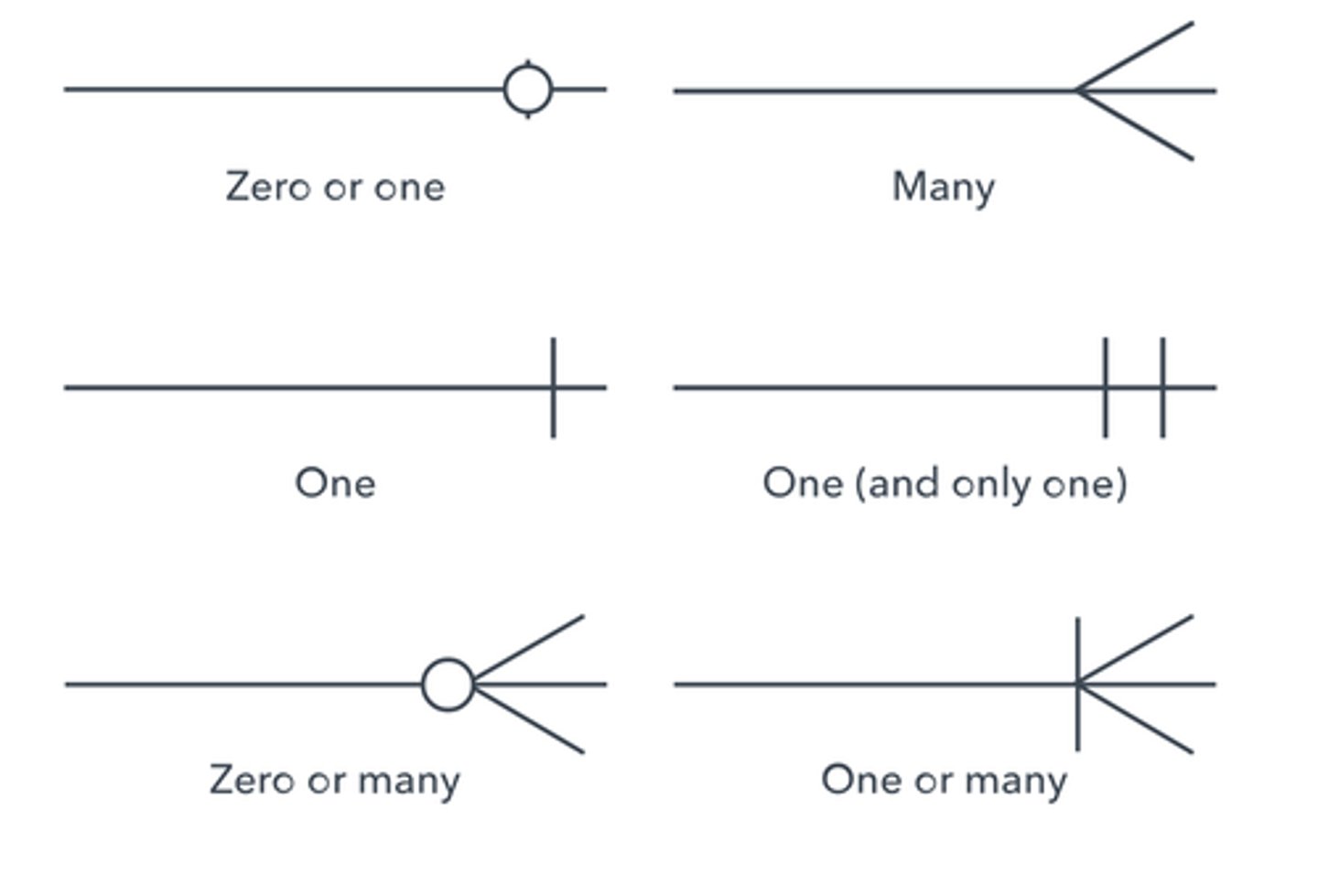
Minimum appears in parentheses
1 required
0 optional
entity type
An _____ is a set of things. Ex: All employees in a company.
Relationship Type
A _____ is a set of related things. Ex: Employee-Manages-Department is a set of (employee, department) pairs, where the employee manages the department
attribute type
An ______ is a set of values. Ex: All employee salaries.
Logical design
_____ converts the entity-relationship model into tables, columns, and keys for a particular database system.
Physical Design
_____ adds indexes and specifies how tables are organized on storage media.
Analysis steps
1. Discover Entities, relationships, and attributes
2. Determine Cardinalality
3. Distinguish strong and weak entities
4. Create supertype and subtype entities
Logical Design Steps (After Analysis Steps)
5. Implement Entities
6. Implement relationships
7. Implement Attributes
8. Apply normal form
cardinality
refers to maxima and minima of relationships and attributes.
Relationship maximum
is the greatest number of instances of one entity that can relate to a single instance of another entity.
Relationship minimum
is the least number of instances of one entity that can relate to a single instance of another entity.
subtype entity, supertype entity
A _____ is a subset of another entity type, called the _____ Ex: Managers are a subset of employees, so Manager is a _____ of the Employee _____. On ER diagrams, _____are drawn within the _____. Vehicle _____ and "car" "truck" "motorcycle" _____
IsA relationship
The identifying relationship
Partitions
A _____ of a supertype entity is a group of mutually exclusive subtype entities
crow's foot notation
depicts cardinality as a circle (zero), a short line (one), or three short lines (many). The three short lines look like a bird's foot, hence the name "_____".
intangible entity
is documented in the data model, but not tracked with data in the database
PRIMARY KEYS SHOULD BE:
Stable. Primary key values should not change. When a primary key value changes, statements that specify the old value must also change. Furthermore, the new primary key value must cascade to matching foreign keys.
Simple. Primary key values should be easy to type and store. Small values are easy to specify in an SQL WHERE clause and speed up query processing. Ex: A 2-byte integer is easier to type and faster to process than a 15-byte character string.
Meaningless. Primary keys should not contain descriptive information. Descriptive information occasionally changes, so primary keys containing descriptive information are unstable.
Artificial Key
An _____ is a single-column primary key created by the database designer when no suitable single-column or composite primary key exists. Usually _____ values are integers, generated automatically by the database as new rows are inserted to the table. _____ are stable, simple, and meaningless.
Functional Dependence
Dependence of one column on another
Redundancy
Is the repetition of related values in a table.
Normal Forms
_____ are rules for designing tables with less redundancy