Renaissance & Reformation
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Renaissance
“The activity, spirit, or time of the great revival of art, literature, and learning in Europe beginning in the 14th century and extending to the 17th century, marking the transition from the medieval to the modern world” (Unit 8 Slideshow).
Humanism
“An intellectual and philosophical movement focused on human potential and achievements” (Unit 8 Slideshow).
Patron of the arts
a wealthy person who funds/supports artists
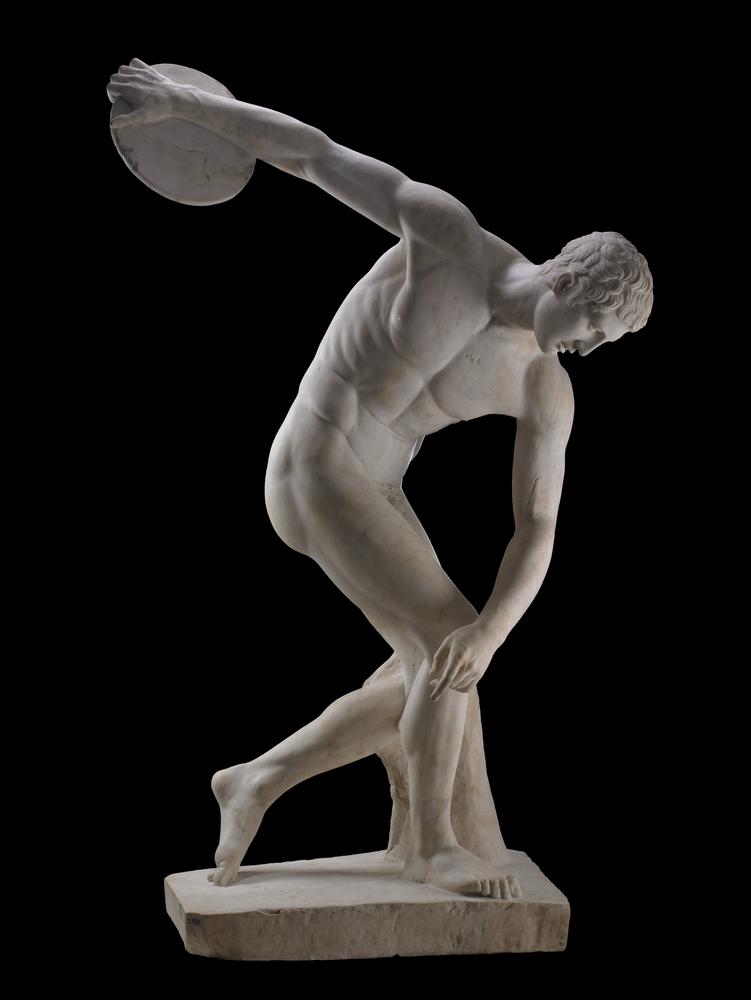
Characteristics of Classical Art
often carved in marble
realism
most figures from the time have similar-looking faces

Characteristics of Medieval Art
disproportionate figures
not very strong attempts at perspective
appear 2D
castles are often in the background
plain/patterned background

Characteristics of Renaissance Art
excellent use of perspective
high detail
portraits and religious art
realism
frescos and canvas paintings

Church Response to Reformation
Pope Paul III (or simply The Pope)
investigated indulgences and other possible offenses towards the Church
approved the Jesuits
use inquisition to find heretics
Council of Trent
the Church was the only authority that could interpret the Bible and anyone who made their own interpretation was guilty of heresy
unlike Luther’s preachings, Christians could not achieve salvation on faith alone, and also needed to perform “good works”
The Church and the Bible had equal authority
Indulgences were fine, as long as they were sold honestly
Jesuits
founded schools that taught both classical subjects and theology
converted people to Christianity
tried to stop the spread of Protestantism
Inquisition
the punishing/killing of heretics
Index of Prohibited Book
the burning of texts “dangerous” to the Church
Causes of Reformation
Renaissance values of humanism made people question the Church
printing press allowed critical ideas about the Church to spread
Political leaders were not happy with the power the Church held
People were tired of the taxes they had to pay to the Church despite the Church’s extreme wealth
Church leaders became corrupt and sinful
People disapproved of the selling of indulgences
Secular
Relating to the present and worldly rather than spiritual. Often used to describe the Renaissance.
Perspective
the artistic technique of making a 2D image appear 3D
Vernacular
a dialect/language spoken but the ordinary people
Utopia
A book written by humanist Thomas More about a perfect fictional world. It has no greed, corruption, or war.
William Shakespeare
A famous playwright and poet known for works such as Romeo and Juliet, Macbeth, and Hamlet. He was influenced by the Renaissance when it spread to England.
Johann Gutenberg
German craftsman who developed the printing press that could print faster and cheaper. This new press helped spread new ideas quickly and to a broader audience.
Albrecht Dürer
famous German artist of the Northern Renaissance
Legacy of the Renaissance
(taken directly from the textbook)
Changes in the Arts
• Art drew on techniques and styles of classical Greece and Rome.
• Paintings and sculptures portrayed individuals and nature in more realistic and lifelike ways.
• Artists created works that were secular as well as those that were religious.
• Writers began to use vernacular languages to express their ideas.
• The arts praised individual achievement.
Changes in Society
• Printing changed society by making more information available and inexpensive enough for society at large.
• A greater availability of books prompted an increased desire for learning and a rise in literacy throughout Europe.
• Published accounts of new discoveries, maps, and charts led to further discoveries in a variety of fields.
• Published legal proceedings made the laws clear so that people were more likely to understand their rights.
• Christian humanists’ attempts to reform society changed views about how life should be lived.
• People began to question political structures and religious practices.
Indulgence
A pardon that was sold by the church in order to guarantee a peasant’s salvation. Took advantage of scared peasants.
Reformation
A movement to reform the Catholic church
Martin Luther
German monk who was disturbed by the indulgences being sold by church officials and wrote the 95 Theses which were ideas critical of the Church. He served as a catalyst for the Reformation. Believed that people should have a personal connection with God and shouldn’t need an official’s interference.
Lutherans
the name for Luther’s followers; a sect of Protestantism
Protestant
a Christian religion that is not Catholicism
Annul
to remove the record of a marriage completely
Church of England
Formed by Henry VIII after the pope refused to annul his marriage to Catherine of Aragon. Was a Protestant church but was later turned back to Catholic by Catherine’s daughter. Anne Boelyn’s daughter, Elizabeth I, turned the Church (now called the Anglican Church) back to Protestantism but kept it mild enough that both Catholics and Protestants could attend.
Predestination
the idea that God chose who would be saved at the beginning of time and this can not be changed
Calvinism
A religion that followed John Calvin’s ideas. Believed in predestination and that governments should be theocracies.
Theocracy
government run by or closely tied to religion
Presbyterians
John Knox put Calvin’s ideas into practice in Scotland. His followers were called Presbyterians.
Anabaptists
Believed that people should choose if they wanted to be baptized, so they only baptized people old enough to decide. Did not approve of theocracy and they did not believe in wars. Anabaptists were persecuted by Protestants and Catholics.
Catholic Reformation
the reformation of the Catholic church in response to the Protestant movement in order to keep Catholics loyal
Jesuits
a group of Catholics who helped reform the Catholic Church by founding schools that taught both classical subjects and theology, converting people to Christianity, and stopping the spread of Protestantism
Council of Trent
a group of Catholic cardinals and bishops who investigated indulgences and agreed on some basic doctrines:
the Church was the only authority that could interpret the Bible and anyone who made their own interpretation was guilty of heresy
unlike Luther’s preachings, Christians could not achieve salvation on faith alone, and also needed to perform “good works”
The Church and the Bible had equal authority
Indulgences were fine, as long as they were sold honestly
Heresy
the crime of disagreeing with a religion’s ideas
Index of Prohibited Book
the burning of texts “dangerous” to the Church
Causes for Renaissance
distrust and waning faith in the Church, allowing for the return of individuality and appreciation for worldly pleasures
people wanted to appreciate the value of humanity (humanism) after the plague took so many lives
rediscovery of classical texts
the Middle Ages brought wealth to many merchants who would later serve as patrons of the arts
more people were moving from manors to cities in search of freedom from their feudal lords; cities were centers of cultural and intellectual development
the printing press allowed ideas to spread more quickly, including ideas about the Renaissance
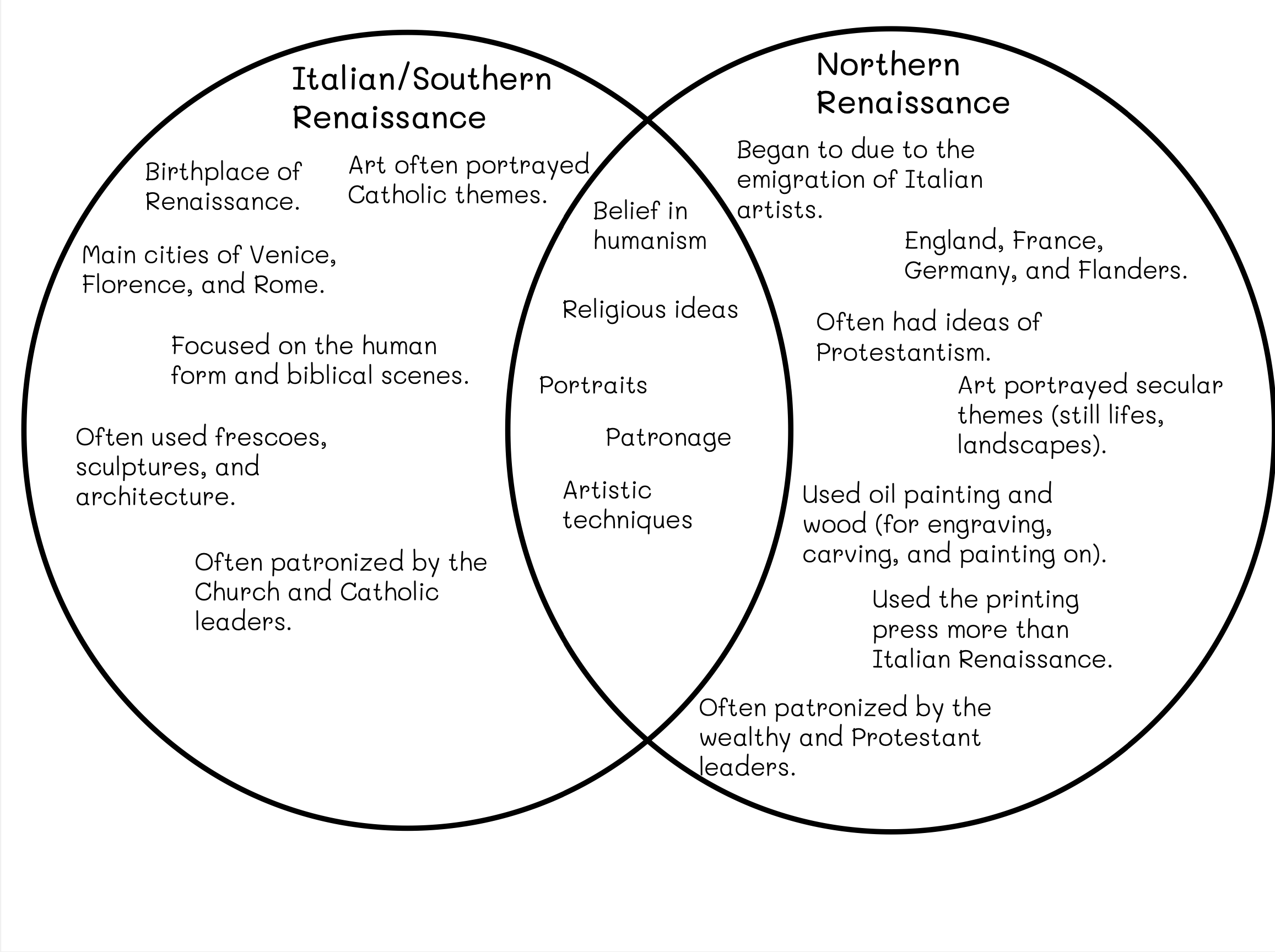
Northern vs. Southern Renaissance