1 General Evaluation of the Gastrointestinal System
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Looking at or biting sides, stretching out, kicking at belly, excessive rolling and lying down, lip curling, not eating, pawing
Name some (8) general colic symptoms in horses:
Lactate (normal less than 2 mmol/L)
Poor prognosis:
Serum lactate: > 6 mmol/L
Peritoneal lactate: 2x serum
Glucose (normal 80-100 mg/dL)
Poor prognosis: > 300 mg/dL
Electrolytes (acidosis)
BUN/Creatinine (dehydration)
GGT (right dorsal displacement)
Name some specific things you can look at on chemistry which will tell you there is colic going on in horses
Endotoxemia
Severe neutropenia or diverging PCV/TP in a horse with colic symptoms tells you WHAT is going on?
Because with abdominal pain, horses cannot vomit and will acquire more fluid in the stomach to the point at which it may rupture
Why do we care to pass a naso-gastric tube in horses with colic?
Angle the head down and encourage the horse to swallow, blow into the tube while it moves down
How should the horse's head move to easily pass a naso-gastric tube?
Ventral nasal meatus
Ideally, which part do you pass the nasogastric tube thru in horse's nasal cavity?
d. pancreas when palpating dorsally
Which is NOT normal to feel in an equine rectal palpation?
a. spleen at the left abdominal wall
b. band of cecum at the upper right
c. caudal border of the left kidney on the left
d. pancreas when palpating dorsally
e. ventral part of the vertebrae and pulse of the aorta when palpating dorsally
Rectal tears
What is a possible complication if you palpate too aggressive rectally in horses?
Pelvic flexure and Impaction
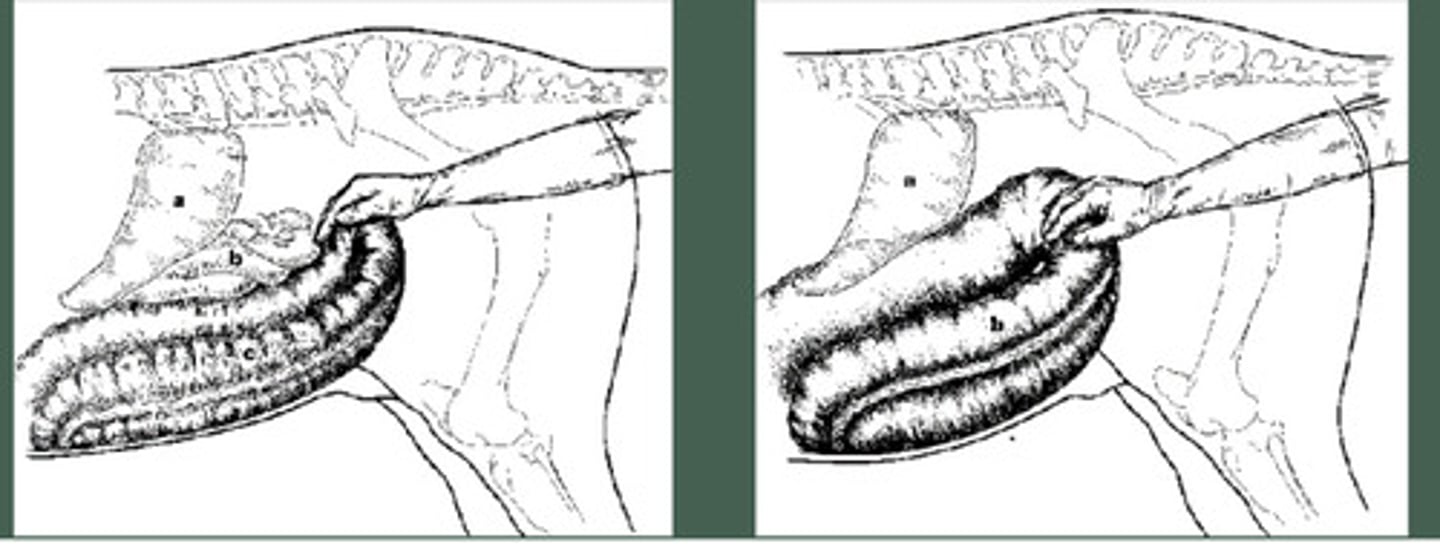
TWO PART QUESTION: What is being palpated in this picture, and if the horse had a hoof abscess and is stabled in straw, what is the most likely problem in picture B?
Long needle versus teat cannula (both on ventral midline)
What are the two techniques you can use to do an abdominocentesis in horses?
Needle abdominocentesis
Which must be at least two inches long, performed at ventral midline at the lowest portion of the abdomen in horses, needle abdominocentesis or teat cannula abdominocentesis?
Teat cannula abdominocentesis
Which is more complicated, needing the use of a #15 blade and a bleb of lidocaine, performed on right of ventral midline to avoid the spleen in horses, needle abdominocentesis or teat cannula abdominocentesis?
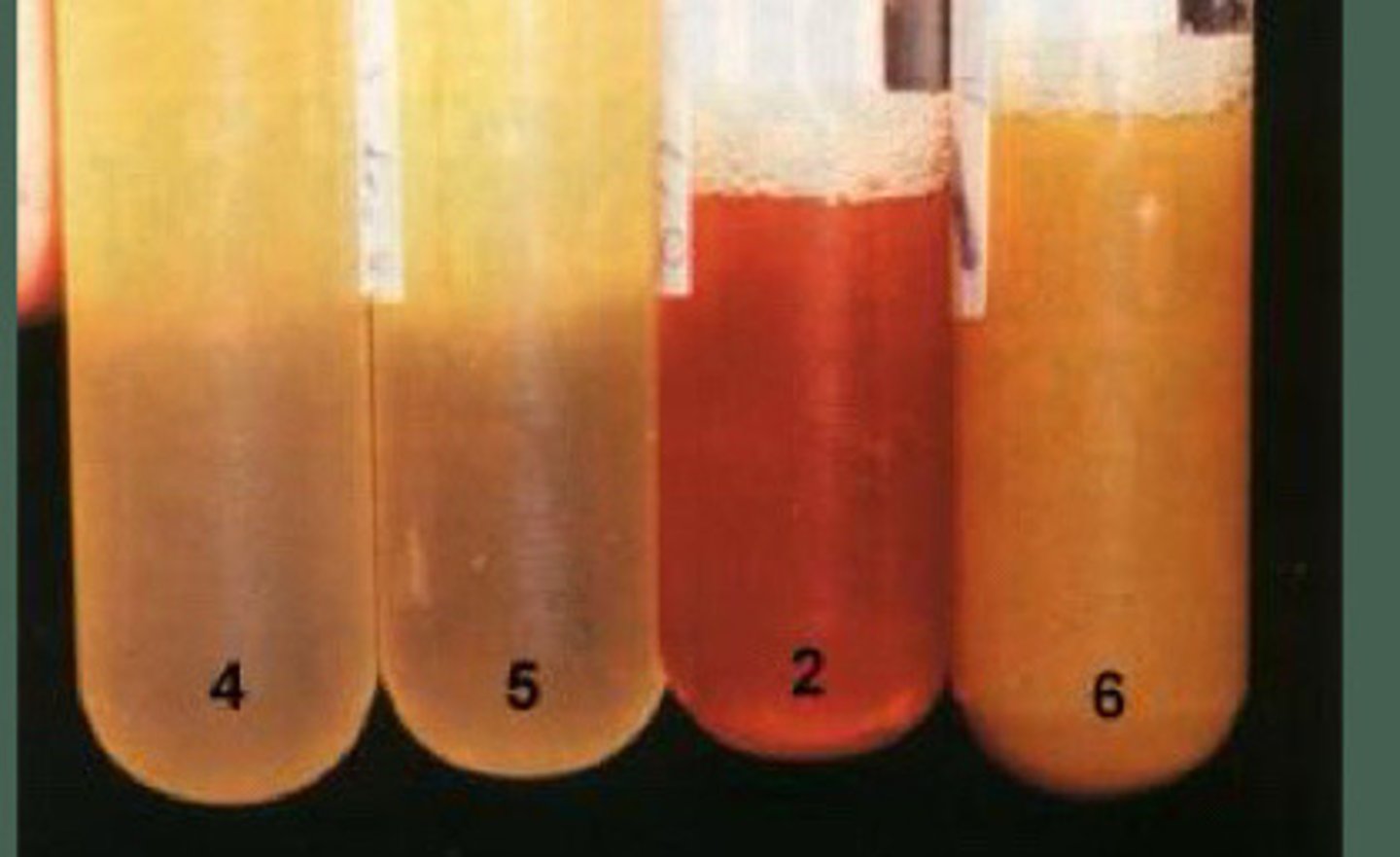
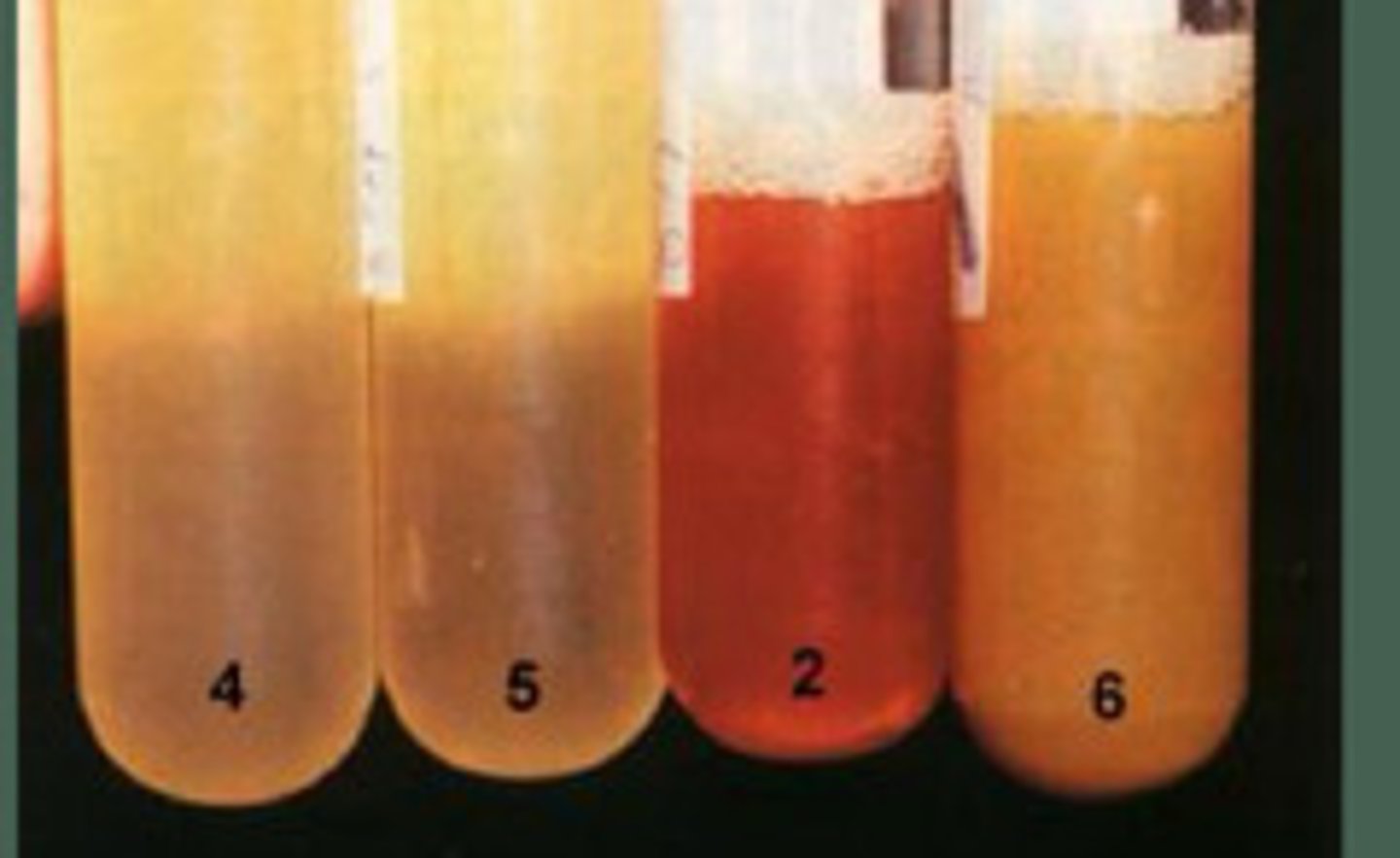
If there is red fluid, such as that in the image labeled "2", then there is compromised intestine and the horse may need to go to surgery (to do an exploratory)
What information can be obtained from abdominocentesis color in horses?
Yes
You are an equine surgeon and a colleague referred you a horse with colic. He felt small intestinal distention on rectal exam and got the peritoneal fluid which is in the "4" image. You see the horse a couple hours later and get the sample labeled "2". Does this horse need surgery?
2-5 MHz
Is it more likely you will use a 2-5 MHz or 12-16 MHz curvilinear transducer to do abdominal ultrasound of a horse?
1. ventral
2. gastric
3. spleno-renal
4. left middle third
5. duodenal
6. right middle third
7. thoracic
Name the 7 locations which are assessed in a FLASH (fast localized abdominal sonography) ultrasound in horses
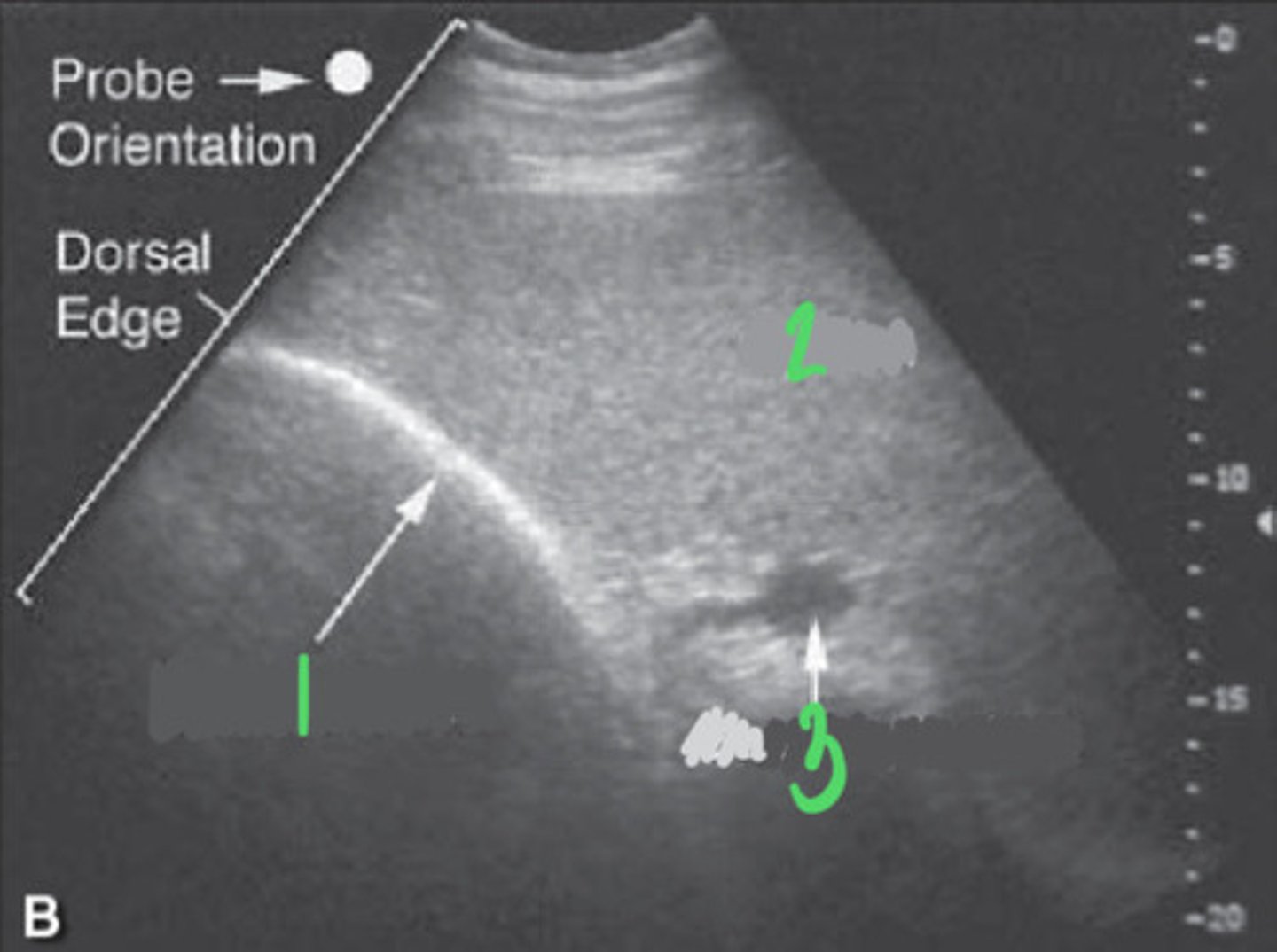
LEFT ABDOMEN GASTRIC:
1. stomach wall
2. spleen
3. gastrosplenic vein
What FLASH view is this in horses and what are the numbers showing you?
LEFT ABDOMEN NEPHROSPLENIC:
1. Spleen
2. kidney
What FLASH view is this in horses and what are the numbers showing you?
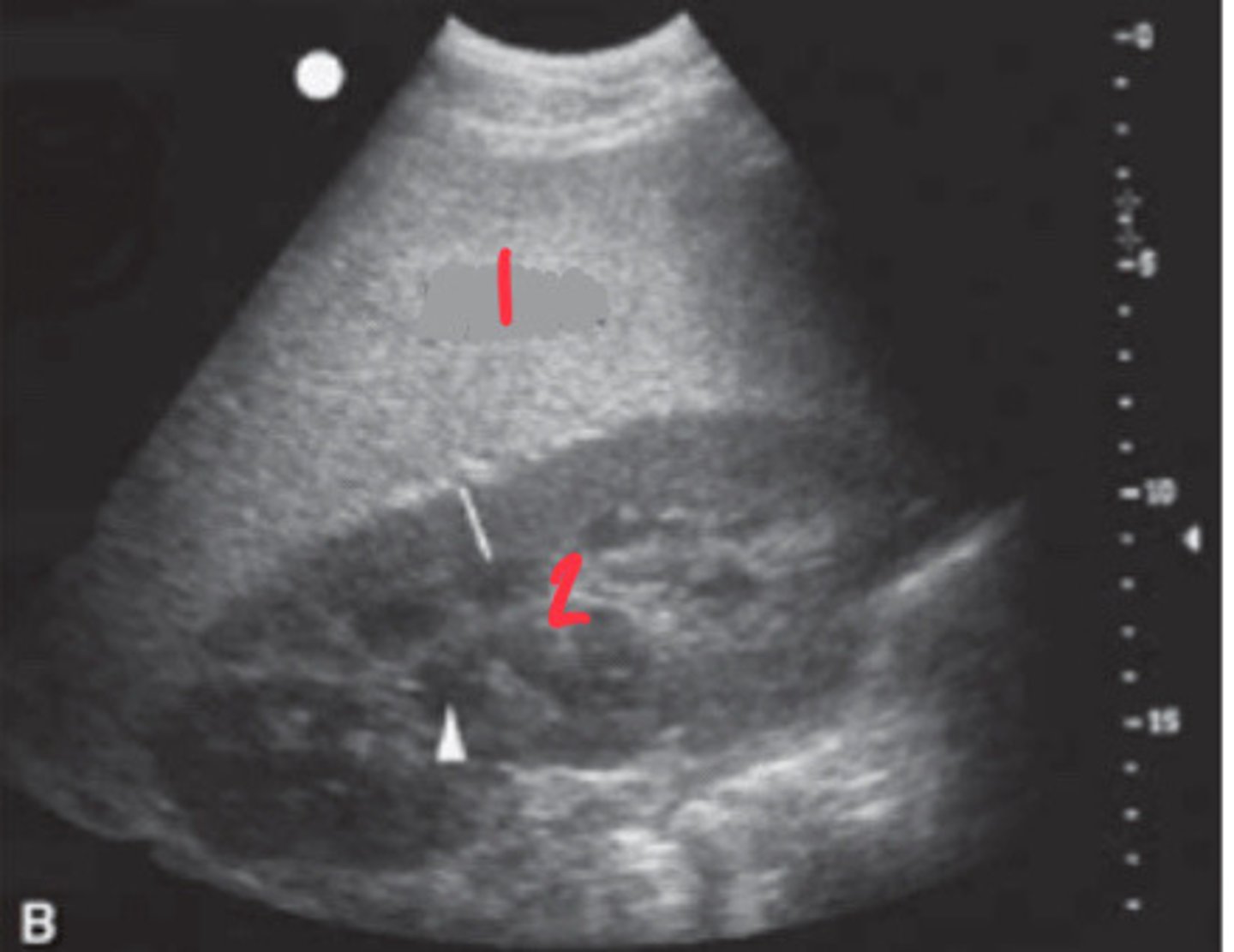
LEFT ABDOMINAL VENTRAL:
1. Spleen
2. Sacculations
3. Left ventral colon
What FLASH view is this in horses and what are the numbers showing you?
LEFT ABDOMINAL VENTRAL:
1. Left dorsal colon
2. spleen
3. left ventral colon
What FLASH view is this in horses and what are the numbers showing you?
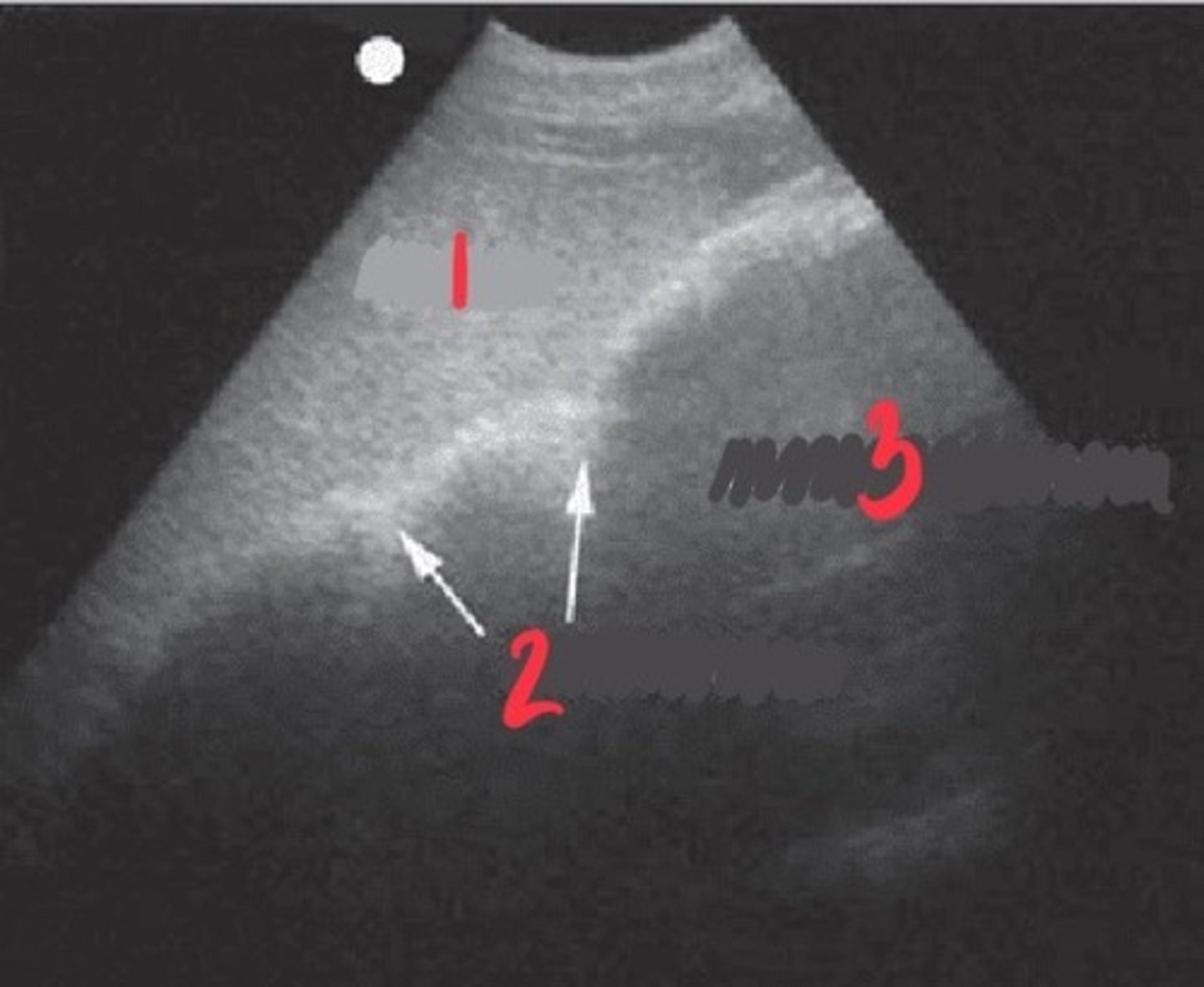
LEFT ABDOMINAL:
Individual loops of small colon
What FLASH view is this in horses and what are the arrows showing you?
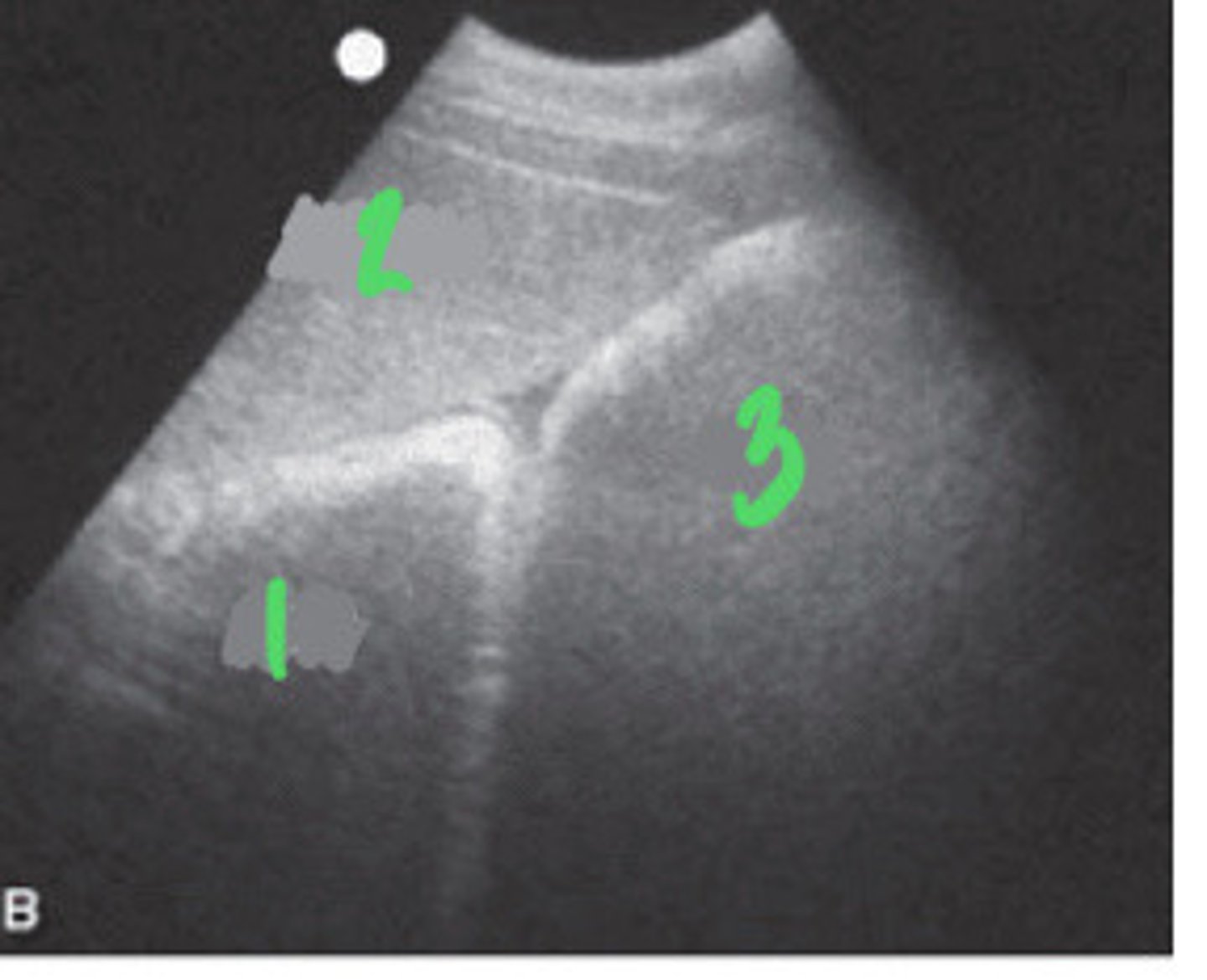
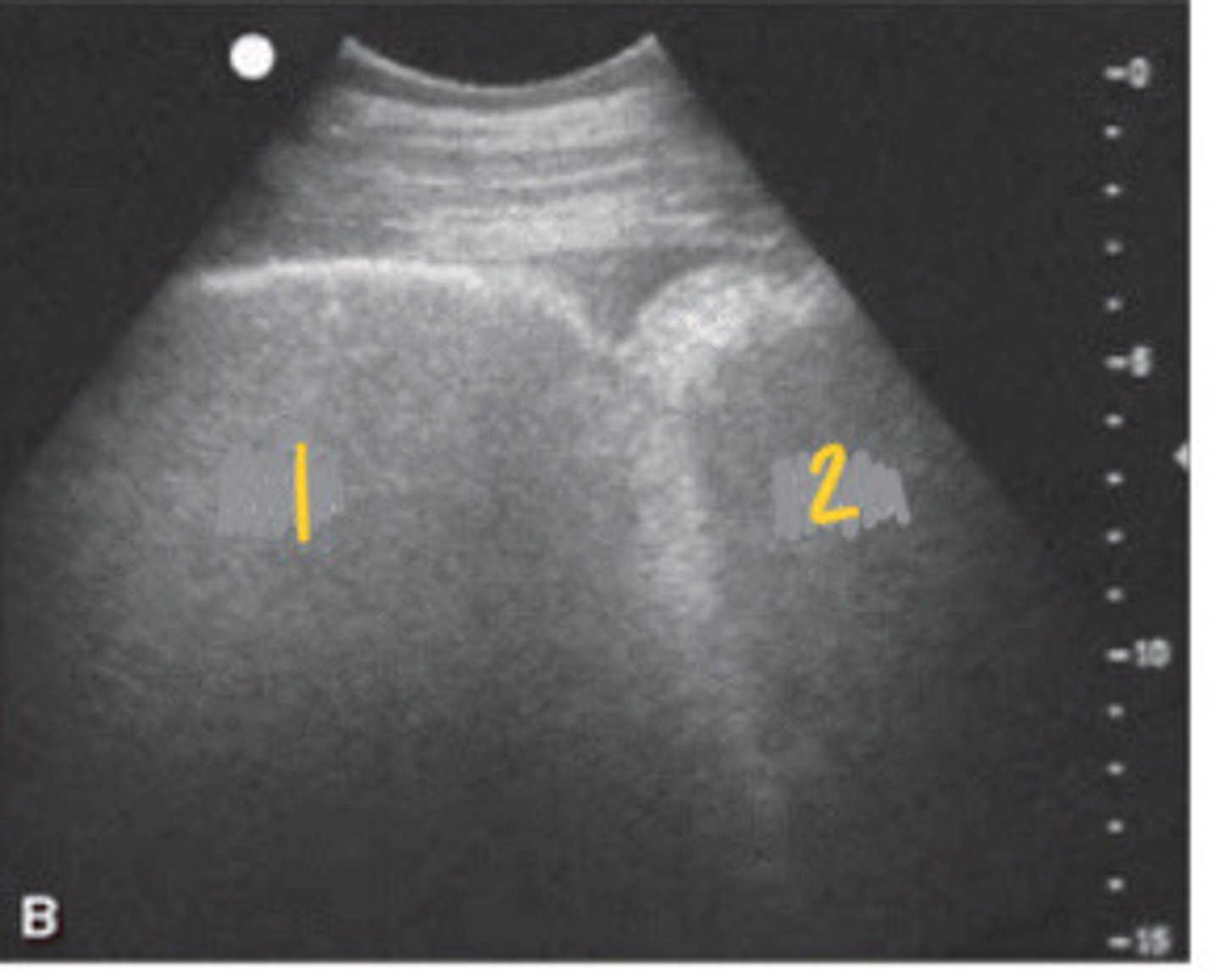
RIGHT ABDOMINAL
1. liver
2. duodenum
3. right dorsal colon
What FLASH view is this in horses and what are the numbers showing you?
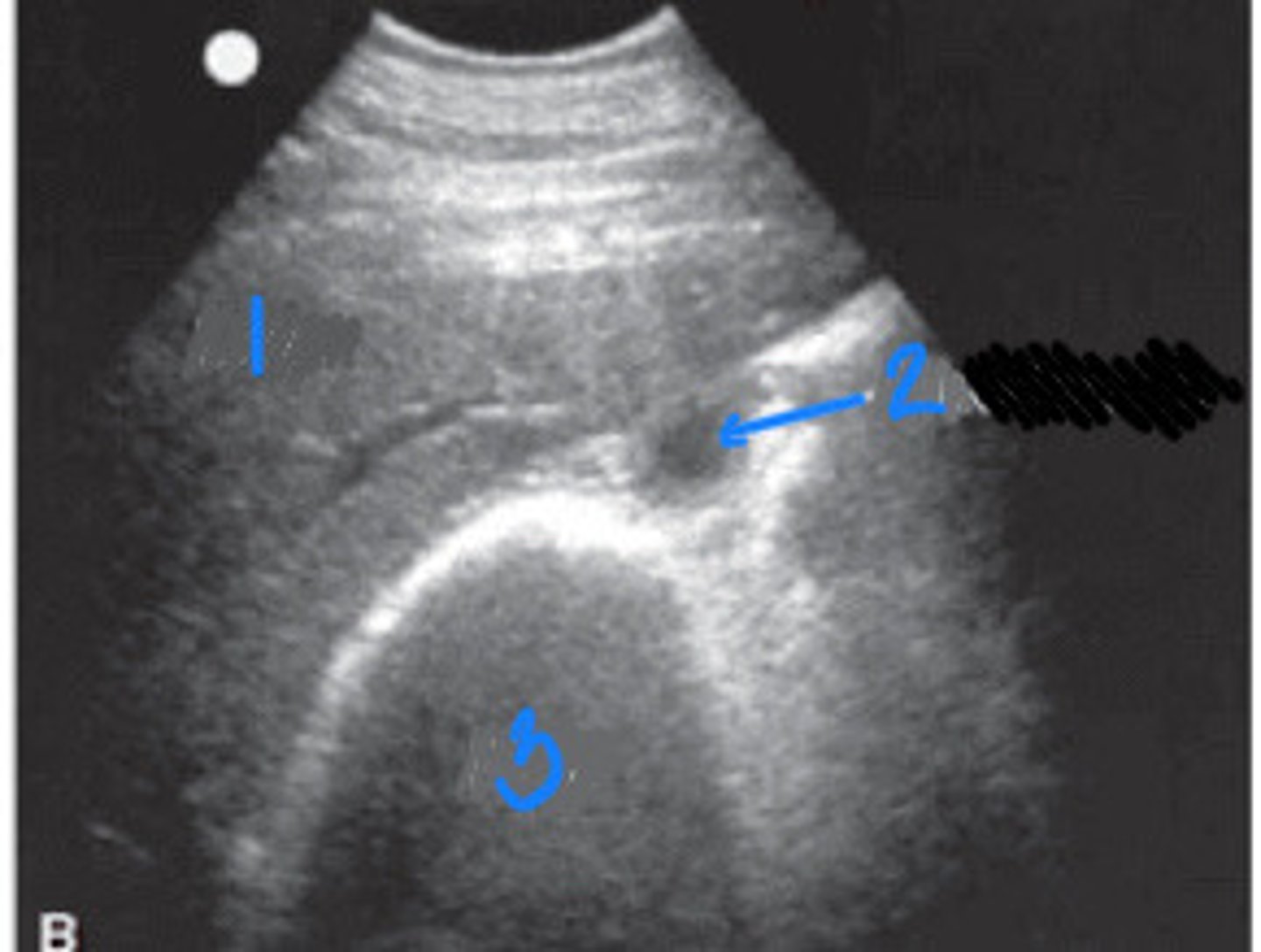
RIGHT ABDOMINAL:
1. kidney (right kidney is NOT FELT ON PALPATION)
2. cecum
3. duodenum
What FLASH view is this in horses and what are the numbers showing you?
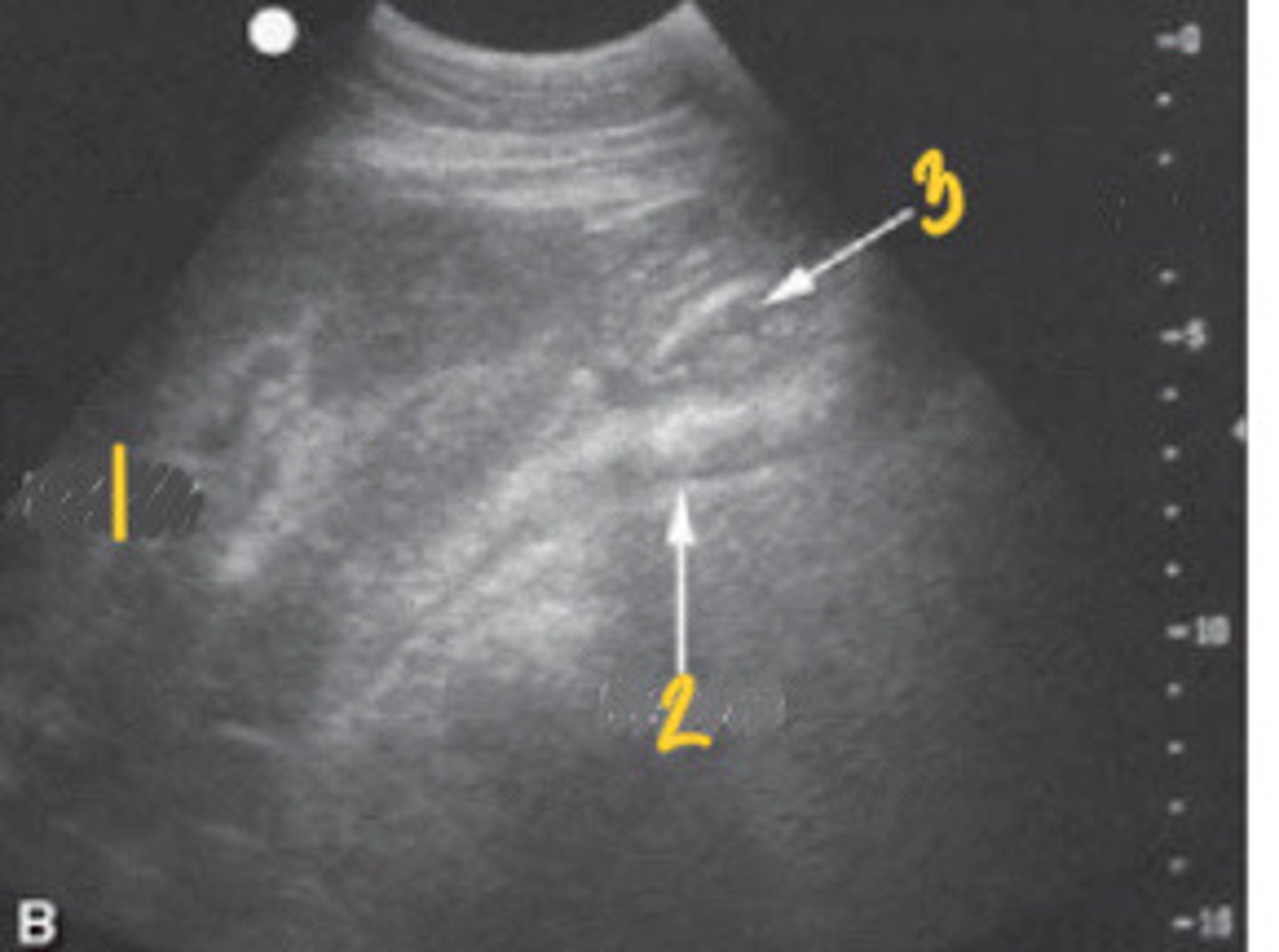
RIGHT ABDOMINAL:
1. right dorsal colon
2. right ventral colon
What FLASH view is this in horses and what are the numbers showing you?
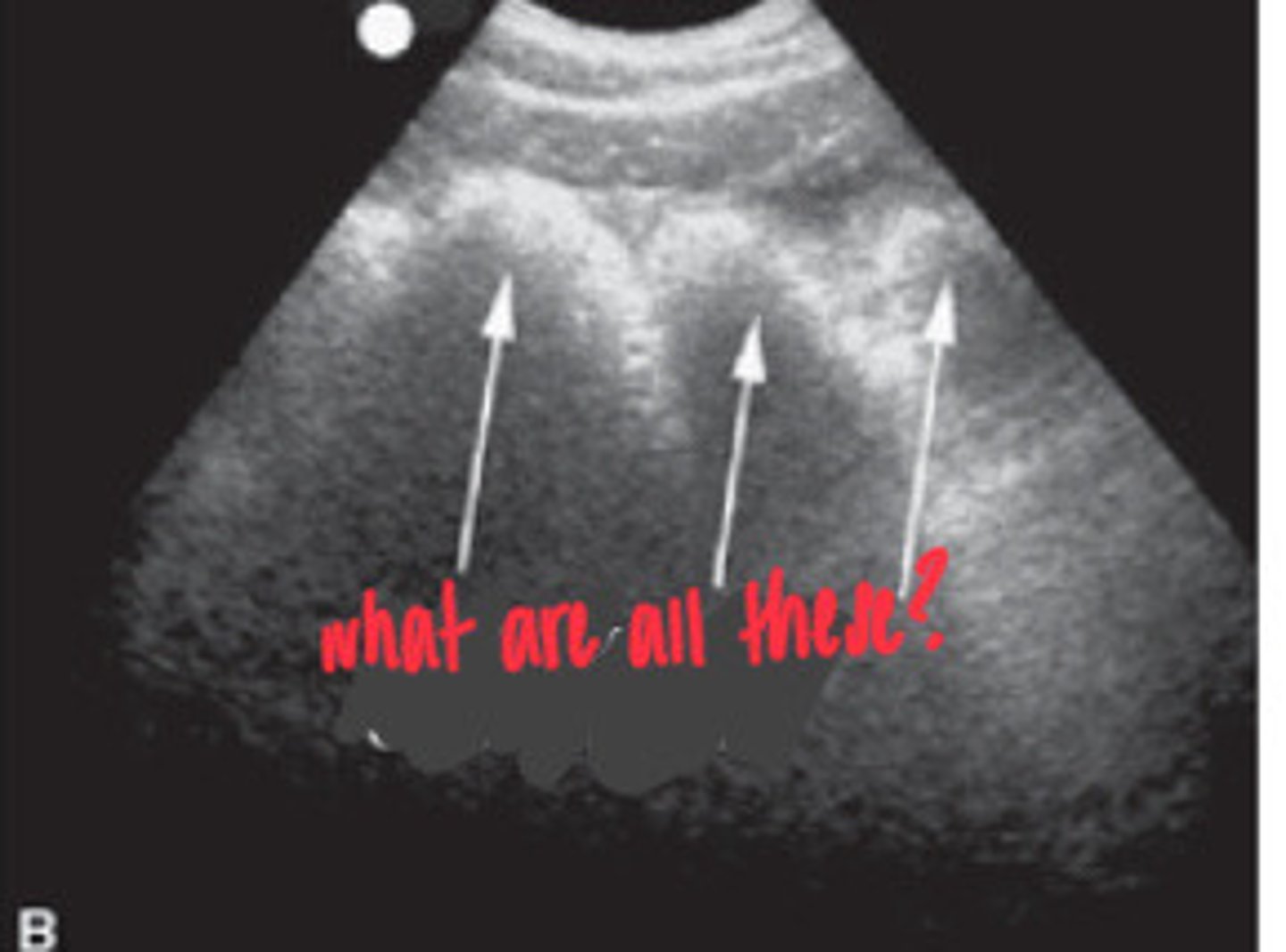
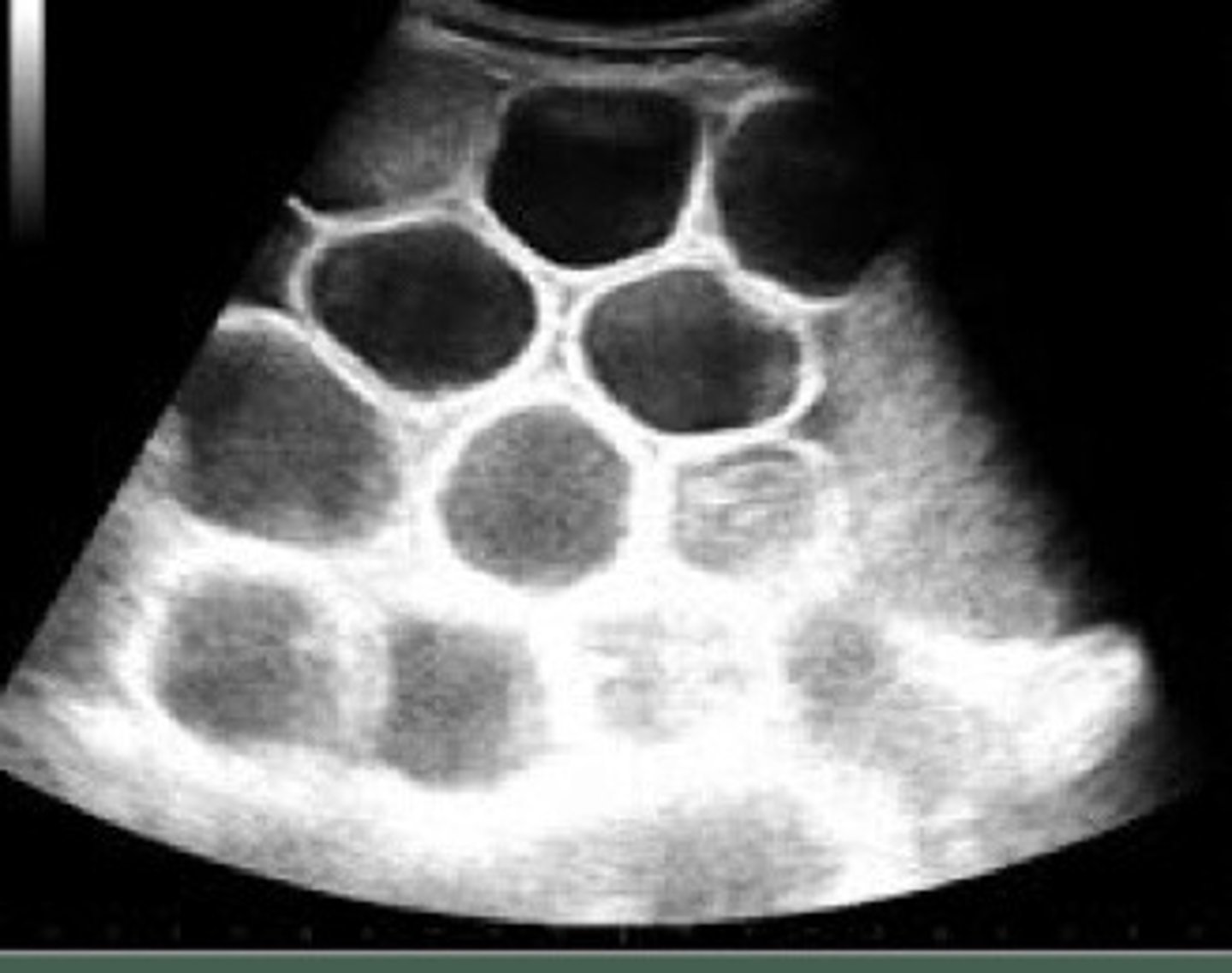
Small intestine
What part of the intestine is distended here?
Pain control and sedation
Note: majority of cases can be medically managed
What are the two biggest parts of controlling colic?
Phenylephrine
What medication can you give for colic horses with nephrosplenic issues?
Buscopan
What medication can you give for colic horses as an anti-spasmodic?
1. severe uncontrolled pain
2. heart rate over 60
3. abnormal rectal exam (but not an impaction)
4. reflux in nasogastric tube
5. dehydration/toxemia
6. abnormal abdominal fluid
Name a few conditions which would cause you to refer a colic in horses