dental occlusion quiz 2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Occlusion
the static relationship between the incising or masticating surfaces of the
maxillary or mandibular teeth or tooth
Articulation
the static and dynamic contact relationship during function
TMJs with their surrounding tissues
Posterior Determinants of occlusion
Teeth and their guidance or articulation
Anterior Determinants of Occlusion
even/simultaneous contact, force through long axis (of tooth), horizontal movement towards anterior
characteristics of stable occlusion
rotation
occurs in inferior cavity
sliding movement
occurs in superior cavity
articular disc
functionally acts like third bone of TMJ
External lateral ligament
Prevents from posterior dislocation of the joint
sphenomandibular ligament
primary passive support of mandible, along with muscles of mastication
stylomandibular Ligament
Limits the opening and protrusion movements of the jaw
posterior border
thickest portion of articular disc
intermediate zone
thinnest portion of articular disc
transverse horizontal axis
imaginary line around which the mandible may rotate within the sagittal plane
reproducible, determined by ligaments and TMJ
properties of terminal hinge position
point of initial contact (PIC)
the first occlusal contact between opposing teeth during closure.
centric relation
purely rotary movement about transverse horizontal axis, tooth independent, CONDYLE DEPENDENT
centric occlusion
occlusion of opposing teeth when in centric relation, may or may not coincide with MIP
maximal intercuspal position
complete intercuspation of opposing teeth, INDEPENDENT of condylar position, ie. best fit of teeth regardless of condylar position
long centric/freedom in centric
CO to M IP slde with no vertical dimension change and no interferences
2-4 mm
normal interocclusal rest space (space between teeth at rest)
most anterior superior position of inferior space
position of condyles in central occlusion
centric stop
The occlusal contact point in centric occlusion where opposing teeth meet and provide stability
lingual of upper/buccal of lower teeth
Supporting/functional Cusps
Buccal of upper/LIngual of lower
non-supporting/non-functional cusps
tripods
ideal for cusp-fossae contacts
dipods
ideal for cusp-marginal ridge contacts
Tooth-to-two-tooth MI Contacts
cusp-fossae and cusp-marginal ridge relationships
tooth to tooth MI contacts
all cusp-fossae relationships
occlusal stability and max-mand distance (vertical dimension of occlusion)
importance of contacts
working side
side toward which mandible moves in lateral excursion, affecting occlusal contacts.
non-working side
the side opposite to the working side during lateral excursion
protrusive movement
mandibular forward movement anterior to centric relation
canine guidance
A type of occlusal scheme where the canines separate the opposing teeth during lateral movements, promoting stability and reducing wear.
group function
An occlusal scheme where multiple teeth on the working side contact during lateral movements, distributing forces and providing stability.
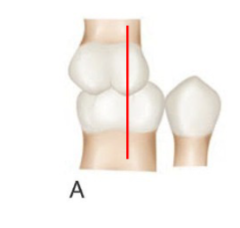
class I
classify
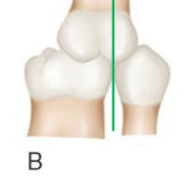
class II
classify
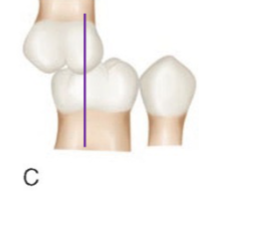
class III
classify
Class I articulator
a simple holding instrument capable of accepting a single
static registration; vertical motion is possible (NON-ADJUSTABLE)

class II articulator
instrument that permits horizontal as well as vertical
motion but does not orient the motion to the temporomandibular joints
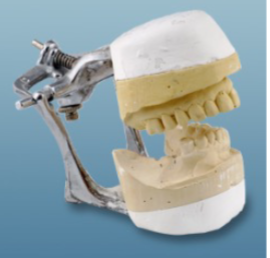
class III articulator
allow for orientation of the casts relative to the joints and may be
arcon or non-arcon instruments (SEMI-ADJUSTABLE)
class IV articulator
allow for orientation of the casts to the temporomandibular joints and simulation of mandibular movements (FULLY ADJUSTABLE)
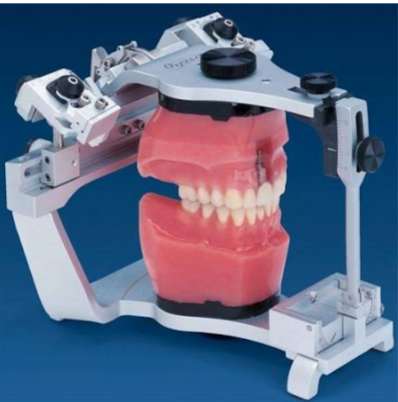
facebow
Records the spatial relationship of the maxillary arch to some anatomic reference point or points
earbow
registers the relation of the maxillary dental arch to the
external auditory meatus and a horizontal reference plane
register anterioposterior and vertical relationship of maxilla to transverse horizontal axis
GOAL of facebow/earbow registration