APES SUPER STUDY SET
3.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/688
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A 99% complete study guide for the APES exam
Last updated 4:06 PM on 11/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
689 Terms
1
New cards
Biomes
a broad, regional type of ecosystem characterized by distinctive climate and soil conditions and a distinctive kind of biological community adapted to those conditions.
2
New cards
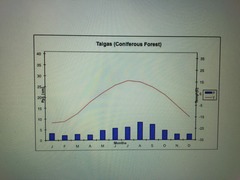
Boreal Forest (Taiga)
located in high latitudes, 50-60 N
low percipitation, low species diveristy and richness, low annual temperatures that promote permafrost, poor soil quality
evergreen coniferous trees and medium/small animals
Biggest threat is logging, lesser but still threatening is mining for natural gas and oil
low percipitation, low species diveristy and richness, low annual temperatures that promote permafrost, poor soil quality
evergreen coniferous trees and medium/small animals
Biggest threat is logging, lesser but still threatening is mining for natural gas and oil
3
New cards
Temperate Rainforest
warm summers, cool winters, adequate rainfall, much more species rich and diverse than taiga, poor soil
Biggest threat is logging of old growth trees
Biggest threat is logging of old growth trees
4
New cards
Temperate Seasonal (Deciduous) Forest
strong species richness, low percipitation, on the warmer side with warm summer and cooler winters, fertile soil
deciduos trees: trees that drop their leaves every year
Logging, clearing land for agriculture, and urbanization
deciduos trees: trees that drop their leaves every year
Logging, clearing land for agriculture, and urbanization
5
New cards
Tropical Rainforest
high productivity, high rainfall, nutrient poor soil, close to the equator, most biodiverse biome, VERY productive (NPP)
Agriculture (slash and burn), logging, grazing land
Agriculture (slash and burn), logging, grazing land

6
New cards
Shrubland (Chaparral)
Found in coastal regions with hot dry summers and cool (mild) moist winters
very prone to frequent natural fires, relatively unfertile soil
Human development and livestock grazing
very prone to frequent natural fires, relatively unfertile soil
Human development and livestock grazing
7
New cards
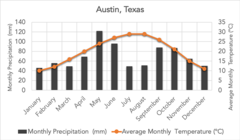
Temperate Grassland
found in the north, large seasonal variability in teperatures, relatively low percipitation, mostly grasses with few/no trees
8
New cards
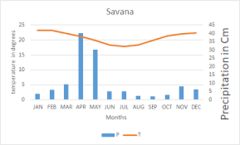
Savanna
found in the south, warm temperatures and seasonal rainfall,mixture of grasses and sparse trees
9
New cards
Desert
hot and dry, low species richness, poor soil
10
New cards
Tundra
low NPP, low species richness, cold and dry, disturbances have a severe affect due to slow growth, permafrost freezes green house gases
oil and natural gas exploration
oil and natural gas exploration
11
New cards
threats to water biomes
eutrophication, acid mine drainage, sediment pollution, diversion of water for human use, construction of dams, wastewater release, sewage, overfishing
12
New cards
coastal zone (saltwater biome)
shallow, close to shore, light rich, nutrient poor,
13
New cards
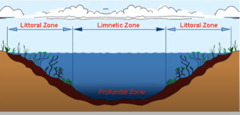
lakes and ponds (freshwater)
littoral: shallow ends of lake with rooted vegetation, lots of productivity and biodiversity
limnetic: open water
profundal: where light cannot penetrate
limnetic: open water
profundal: where light cannot penetrate
14
New cards
What factors define a flowing freshwater biome
upstream vs downstream
amount of canopy cover (temperature)
depth, velocity, volume
turbidity (cloudiness)
salinity
amount of canopy cover (temperature)
depth, velocity, volume
turbidity (cloudiness)
salinity
15
New cards
Floodplain
the area on either side of a river that will flood on a regular or occasional basis
usually more fertile- water goes up, leaves nutrient rich sediemnt
usually more fertile- water goes up, leaves nutrient rich sediemnt
16
New cards
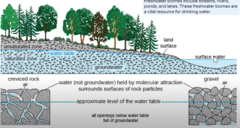
water table
the upper surface of underground water
17
New cards
what factors define a saltwater marine biome
depth, light, nutrient availability, salinity, communities present (open ocean vs tidal)
18
New cards
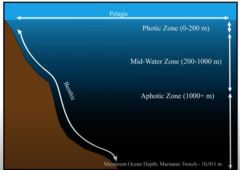
ocean zones
pelagic: open water
photic: where light reaches
batheal: less light
abyssal: no light
benthic: the bottom/sea floor regardless of depth
coastal: on the coast
photic: where light reaches
batheal: less light
abyssal: no light
benthic: the bottom/sea floor regardless of depth
coastal: on the coast
19
New cards
Marshland
coastal wetland, brackish (A mixture of fresh and salt water, typically found where rivers enter the oceans), soil saturated with water most of the year, orgnaisms are adapted to rising and falling tides, dominated by grasses
helps clean the water, filtering water before it reaches the ocean
helps clean the water, filtering water before it reaches the ocean
20
New cards
Estuaries
where a flowing freshwater stream/river meets the ocean, brackish water, tidal cycles affect depth and salinity, EXTREMELY fertile, high NPP and species richness, known as "nature's nursery"
21
New cards
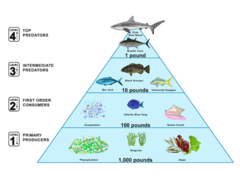
basic organisms in marine biome
plankton: producers
nekton: free swimming fish, consumers
benthos: bottom dwellers, scavengers/decomposers
nekton: free swimming fish, consumers
benthos: bottom dwellers, scavengers/decomposers
22
New cards
eutrophic lake
Lake with a large or excessive supply of plant nutrients, mostly nitrates and phosphates
dense fish populations, shallow, gentle sloped shores
dense fish populations, shallow, gentle sloped shores
23
New cards
ogliotrophic lake
nutrient poor, deep, steep sloped shore, low fish/plankton concenrations
24
New cards
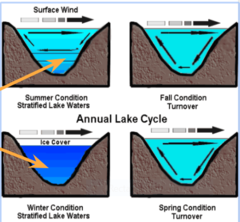
lake circulation
nutrients up, oxygen down
thermocline: uneven temperature distribution in lake
thermocline: uneven temperature distribution in lake
25
New cards
watershed
an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas, that will all end up in the same location, like a funnel
watersheds are divided by divides and can differ depending on their area, length, slope, soil, vegetation types, and divides with adjoining watersheds
watersheds are divided by divides and can differ depending on their area, length, slope, soil, vegetation types, and divides with adjoining watersheds
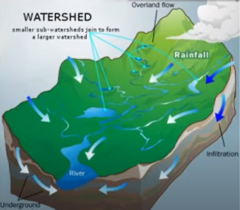
26
New cards
drainage basin
area in which water pools together at single point before entering another body of water
27
New cards
river delta
a triangular area of sediment deposited at the mouth of a river
28
New cards
abiotic factors
Temperature/sunlight
Salinity of soil/water
pH of soil/water
Precipitation
Salinity of soil/water
pH of soil/water
Precipitation
29
New cards
limiting factor
Any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence, numbers, reproduction, or distribution of organisms.
30
New cards
resource/niche partitioning
using reosurces in different ways, places, or times
reduces the negative impact of competition on survival
reduces the negative impact of competition on survival
31
New cards
symbiosis
different species living in close association with one another
32
New cards
parasitism
+/-
33
New cards
mutualism
+/+
34
New cards
commensalism
+/0
35
New cards
amensalism
-/0
36
New cards
barrier islands
thin strips of sediment running parallel to the shore, protect mainland from floods
37
New cards
ecotone
a transitional zone from one ecosystem to another
High biodiversity, high productivity
Contains mixture of species from both ecosystems
High biodiversity, high productivity
Contains mixture of species from both ecosystems
38
New cards
gross primary productivity
rate at which an ecosystem's producers convert solar energy to chemical energy and biomass (via photosynthesis)
39
New cards
net primary productivity
rate of photosynthesis MINUS rate of energy use via respiration
NPP= GPP-R
NPP= GPP-R
40
New cards
first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
41
New cards
second law of thermodynamics
whenever energy is transferred, some of it will be lossed through heat
42
New cards
phosphorus cycle
a phosporus containing rock is weathered down and releases its P into the soil. Plants take up the P and assimilate, using it to build plant tissues. Animal eats the plant and consumes the P inside the plant. The animal excretes and P returns to the soil. Water runs ALOT of it off into the ocean.
happens very slowly, no atmospheric component
-phosporus soluble in water
- phosphate containing fertilizers disturbs the cycle
happens very slowly, no atmospheric component
-phosporus soluble in water
- phosphate containing fertilizers disturbs the cycle
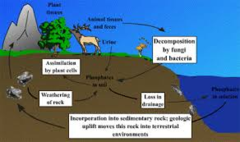
43
New cards
nitrogen cycle
nitrogen fixation: microbes in the soil convert N2 into NH3 (ammonia)
nitrification: bacteria turns NH3 into NO3 (nitrates)
assimilation: plant absorbs the nitrates
ammonification: animal waste/humus is broken down into NH3
denitrification: NO3 is turned into N2 and released back into the atmosphere
nitrification: bacteria turns NH3 into NO3 (nitrates)
assimilation: plant absorbs the nitrates
ammonification: animal waste/humus is broken down into NH3
denitrification: NO3 is turned into N2 and released back into the atmosphere
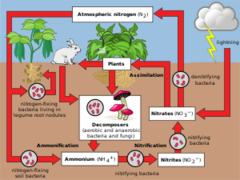
44
New cards
carbon cycle
the healhier the ecosystem, the more carbon will be absorbed instead of emitted
carbon sinks: plants, ocean, soil
carbon sinks: plants, ocean, soil
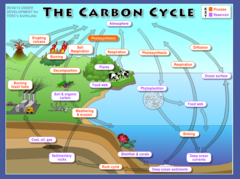
45
New cards
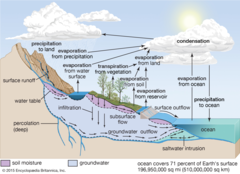
hydrologic cycle
powered by the sun
Evaporation, condensation, percipitation, percolation (movement of water through the soil), transpiration
Evaporation, condensation, percipitation, percolation (movement of water through the soil), transpiration
46
New cards
human threats to biodiversity
habitatat destruction
invasive species
pollution
population
overharvesting
invasive species
pollution
population
overharvesting
47
New cards
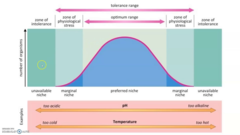
ecological tolerance
the specific range of abiotic conditions in which a species can survive.
48
New cards
biodiversity
the variety of life
species, ecosystem, genetic
more diveristy = more resilience
species, ecosystem, genetic
more diveristy = more resilience
49
New cards
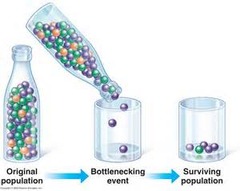
bottleneck affect
a decrease in population size will lead to a decrease in the gene pool, and a decrease in alleles
50
New cards
ecosystem services (benefits of biodiversity)
provisioning: provide for us, any type of benefit for people that can be extracted from nature, ex. food, drinking water, lumber, medicine, minerals, etc
regulating: processes that moderate natural phenomena, making eocsystemns resilient to change, ex. carbon storage, pollination, water/air filtration, erosion prevention, local climate regulation
cultural: spiritual, aesthetic, educational, ex. hikes, retreats, etc.
supporting: perform underlying processes, ex. photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, soil formation
regulating: processes that moderate natural phenomena, making eocsystemns resilient to change, ex. carbon storage, pollination, water/air filtration, erosion prevention, local climate regulation
cultural: spiritual, aesthetic, educational, ex. hikes, retreats, etc.
supporting: perform underlying processes, ex. photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, soil formation
51
New cards
island biogeography
the number of species on any island reflects a balance between the rate at which new species colonize it and the rate at which populations of established species become extinct
smaller islands wil have lower species diveristy, lower immigration rate, and higher extinction rates than bigger islands. Islands closer to the mainland will have higher rates of biodiversity and immigration
smaller islands wil have lower species diveristy, lower immigration rate, and higher extinction rates than bigger islands. Islands closer to the mainland will have higher rates of biodiversity and immigration
52
New cards
Natural disruptions
periodic: occur at some what of a regular frequency (annual rainy or dry seasons)
episodic: occasional with no regular frequency (hurricanes)
random: no partcular frequency (volcanic eruption)
episodic: occasional with no regular frequency (hurricanes)
random: no partcular frequency (volcanic eruption)
53
New cards
adaptations
random genetic mutations -> natural selection
54
New cards
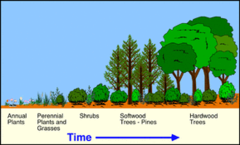
ecological succession
primary: no soil left (volcanic erruptions, glacier movement)
secondary: soil already there (fires, hurricane)
secondary: soil already there (fires, hurricane)
55
New cards
pioneer species
First species to populate an area during primary succession
ex. lichen, bacteria, moss
Lichen secrete acid that chemically weathers the rock, they then ide, decompose, and add organic material to the weathered rock thus creating soil
ex. lichen, bacteria, moss
Lichen secrete acid that chemically weathers the rock, they then ide, decompose, and add organic material to the weathered rock thus creating soil
56
New cards
keystone species
a species on which other species in an ecosystem largely depend, such that if it were removed the ecosystem would change drastically.
57
New cards
trophic cascade
when one organism has a 'cascade' like affect on the rest of the ecosystem

58
New cards
indicator species
organism whose presence, absence or abundance reflects a specific environmental condition, gives information about overall helath/state of an ecosystem, usually an organism that is countabel/visible/detectable
59
New cards
predator-prey relationship
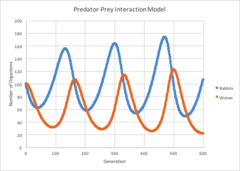
60
New cards
density independepent factors
factors that affect a population regardless of size
natural disasters, weather
natural disasters, weather
61
New cards
density dependent factors
factors that affect a population depending on its size
predation, disease,
predation, disease,
62
New cards
intraspecific competition
competition between members of the same species
63
New cards
interspecific competition
competition between members of different species
64
New cards
negative feedback loop
a balanced system
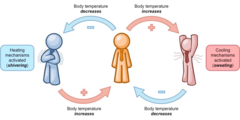
65
New cards
positive feedback loop
exponential growth or decline
ex. cancer and global warming
ex. cancer and global warming
66
New cards
directional selection
a shift in the organisms' phenotype and genotype to one extreme due to a stressor
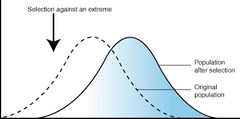
67
New cards
stabilizing selection
Shift that favors the mean.
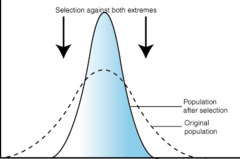
68
New cards
disruptive selection
high reproduction at both extremes
69
New cards
speciation
Formation of new species
70
New cards
adaptive radiation
species founds a new place, takes up all available niches
71
New cards
fundamental niche
full range of resources and conditions a species could occupy
ex. ANY position on the team
ex. ANY position on the team
72
New cards
realized niche
the resources of the fundamental niche a species TENDS to use
ex. Point guard
ex. Point guard
73
New cards
generalist species
Species with a broad ecological niche. They can live in many different places, eat a variety of foods, and tolerate a wide range of environmental conditions. Examples are flies, cockroaches, mice, and rats
74
New cards
specialist species
Species with a narrow ecological niche. They may be able to live in only one type of habitat, tolerate only a narrow range of climatic and other environmental conditions, or use only one type or a few types of food
less tolerant = less likely to survive
less tolerant = less likely to survive
75
New cards
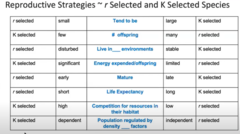
r vs k selected species
most organisms do not fit into the box of r or k startegists
r strategists= high growth rate
k strategists= slowly increasing populations that hover around carrying capacity (k)
r strategists= high growth rate
k strategists= slowly increasing populations that hover around carrying capacity (k)
76
New cards
fecundity
reproductive potential, describes reproductive charactarestics
77
New cards
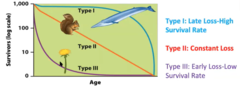
survivorhsip curves
type 1 and 2 = k-strategists
type 3 = r-strategists
type 3 = r-strategists
78
New cards
biotic potential
the maximum rate at which a populatioin could grow under ideal conditions
Growth factors: Favorable environment/space, Few competitors/defense mechanisms, Generalist/genetic diversity, Food supply, Disease/parasite resistant
Growth factors: Favorable environment/space, Few competitors/defense mechanisms, Generalist/genetic diversity, Food supply, Disease/parasite resistant
79
New cards
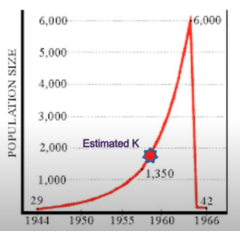
population overshoot
there is a lag time between reproduction rate and reosurce consumption
80
New cards
factors that influence birth rate
Education Level, Child Labor Importance, Urbanization, Medical Advancements/helathcare availability, Employment, Marriage Age, Income, Development, CULTURAL NORMS, laws/policies (ex. China's one child policy), access to family planning, access to prenatal care, nutrition
81
New cards
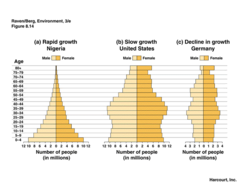
age structure diagrams
0-14 years = pre-reproductive age
15-44 years=reproductive age
45-85+ years = post reproductive age
15-44 years=reproductive age
45-85+ years = post reproductive age
82
New cards
total fertility rate
the number of children an average woman will have
83
New cards
replacement level
2 children to replace 2 parents
84
New cards
crude birth rate
number of babies born per 1000 people in a single given year
85
New cards
Most populous countries
China, India, U.S.
86
New cards
affects Sudden Population Rises have on a Country
Increased unemployment
Increased pollution
Increased mortality rates (even with medical advances)
Lower survival rates
Decreased quality of life
Increased pollution
Increased mortality rates (even with medical advances)
Lower survival rates
Decreased quality of life
87
New cards
infant mortality rate
number of children that die under 1 year old per 1000 births
88
New cards
Malthusian Theory
Starvation is the inevitable result of population growth, because the population increases at an exponential rate while food supply increases linear
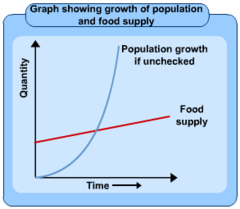
89
New cards
demographic transition
'mechanization' also known as 'transitional'
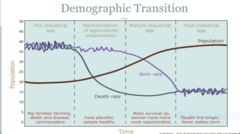
90
New cards
developed vs developing countries
- levels of industrialization and income, nutrition, sanitation, eductaion, helath care, and clean water access will all be greater in developed countries
- TFR and IMF rates, population growth rates, and number of children in the workforce will be higher in developing countries
- TFR and IMF rates, population growth rates, and number of children in the workforce will be higher in developing countries
91
New cards
divergent plate boundary
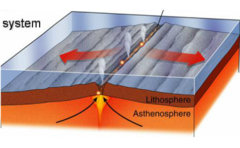
92
New cards
Lithosphere and Asthenosphere
-rigid upper mantle and crust, where the tectonic plates are
- molten upper mantle where magma is found
-lithosphere moves over asthenosphere
- molten upper mantle where magma is found
-lithosphere moves over asthenosphere
93
New cards
plate tectonics
movement of giant rock plates (tectonic plates)
94
New cards
convergent plate boudary
->
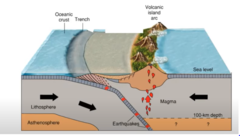
95
New cards
island arcs
long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries (such as the Ring of Fire). Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle along the subduction zone
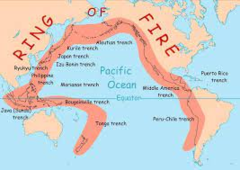
96
New cards
transform/strike slip plate boundary
plates grind past eachother in opposite directions
97
New cards
plate boundaries
boundary and plate types determine the geologic features of the area
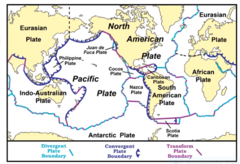
98
New cards
eathquakes
tectonic plates lock up, building up pressure and energy. When this pressure and energy is released, an earthquake occurs
99
New cards
tsunamis
a long and powerful sea wave caused by earthquakes or underwater landslides
destroy habitats, drowns species, uproots trees, contaminates water with saltwater and debris
destroy habitats, drowns species, uproots trees, contaminates water with saltwater and debris
100
New cards
fissure
hole between tectonic plates