Chapter 19 - Respiratory Emergencies
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
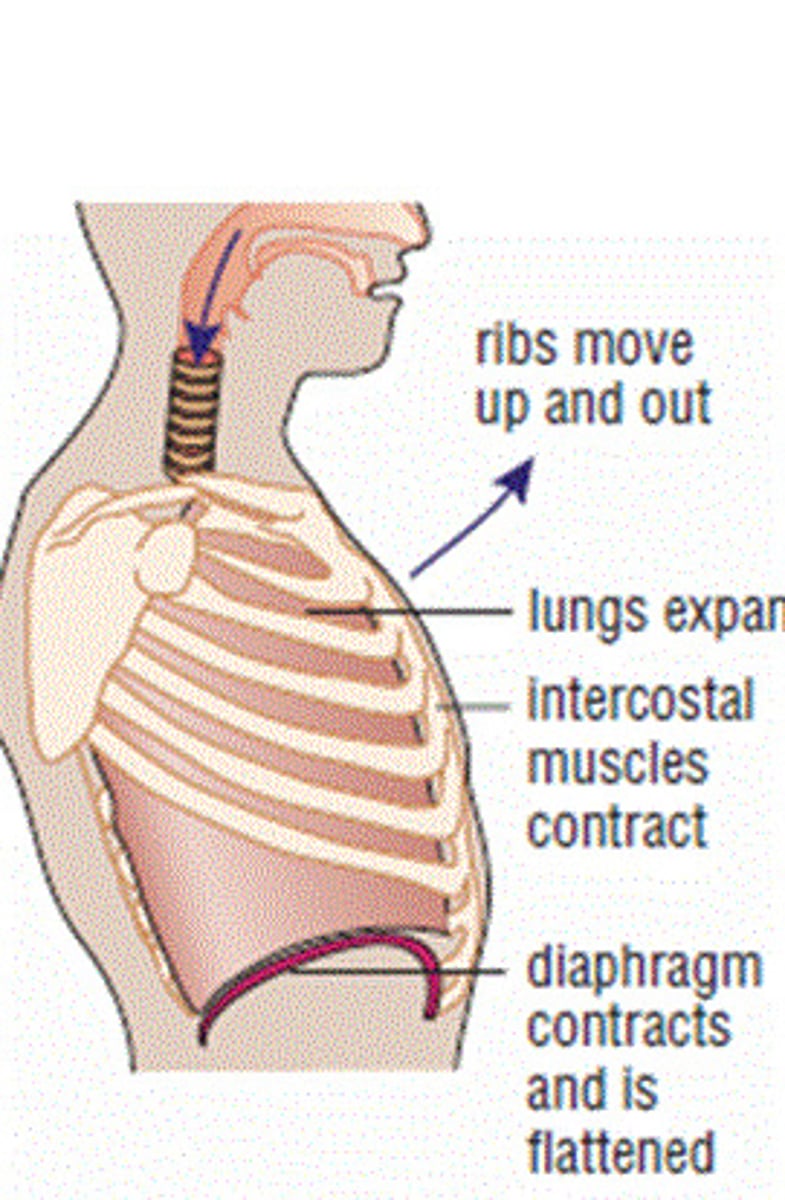
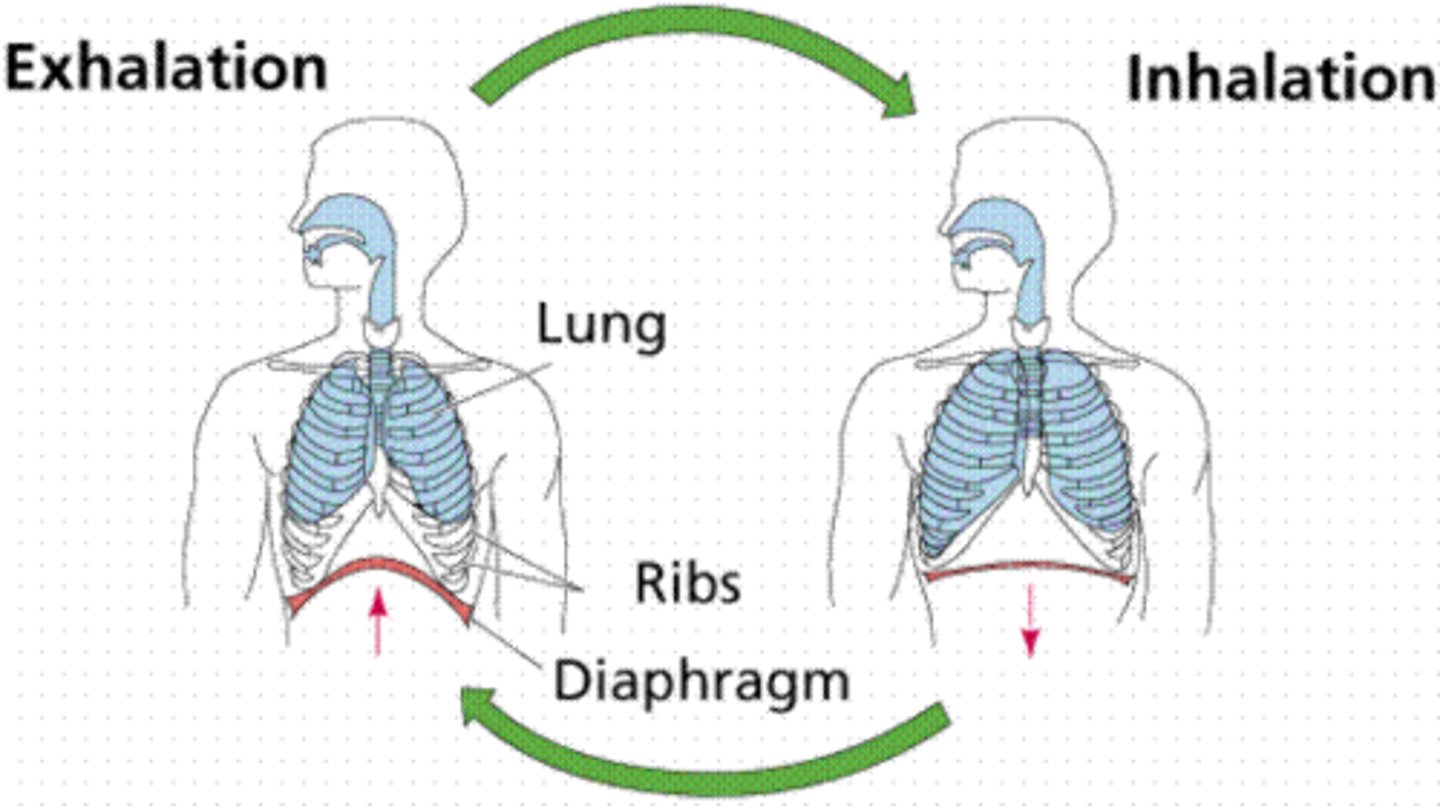
Inspiration/inhalation
breathing in
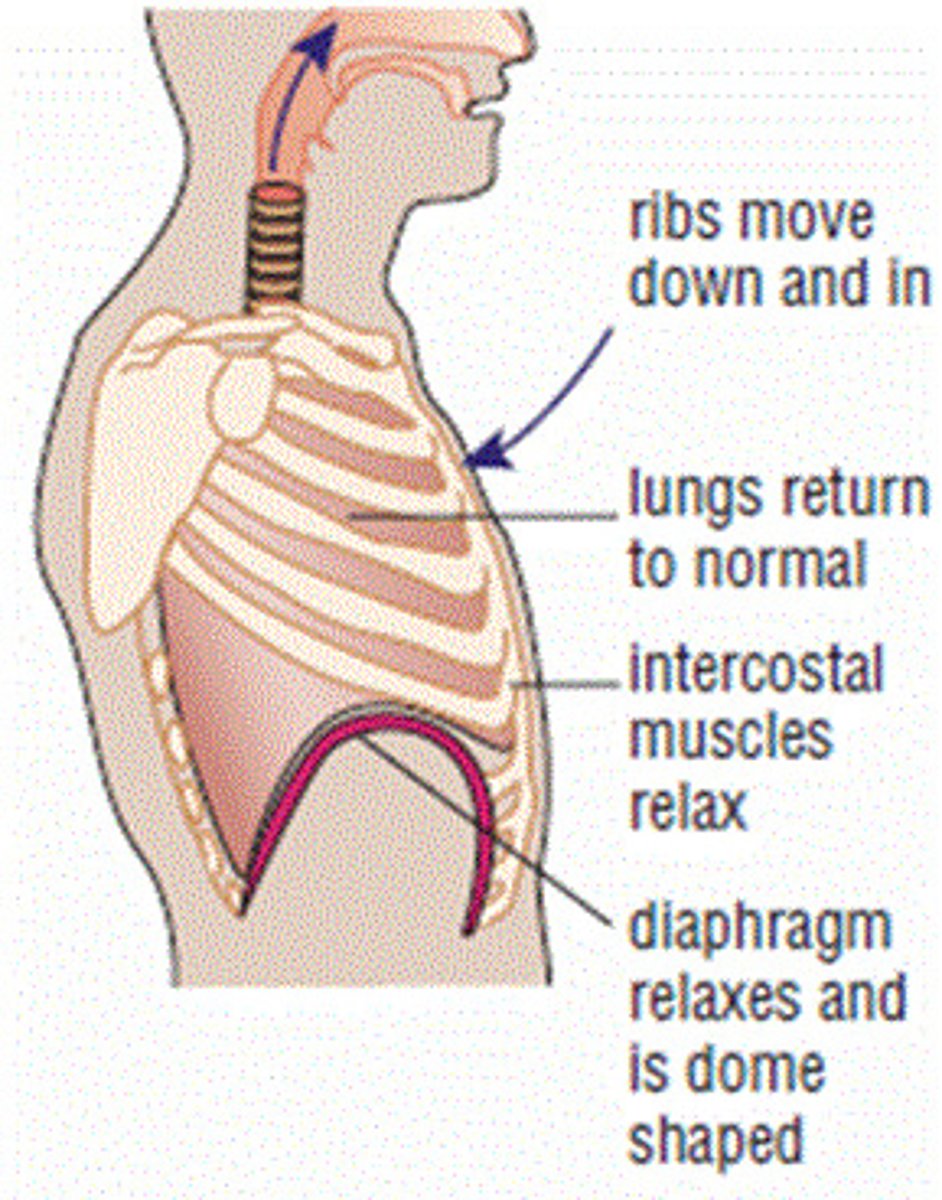
Expiration/exhalation
breathing out
Adequate breathing
-normal rate-12-20breaths/min
-regular pattern on inhale/exhale
-clear and equal lung sounds on both sides of the chest
-regular and equal chest rise and fall
adequate depth (tidal volume)
Inadequate breathing
breathing effort; increased use of accessory muscles especially in infants and children; cyanotic skin, cool, clammy; agonal respirations
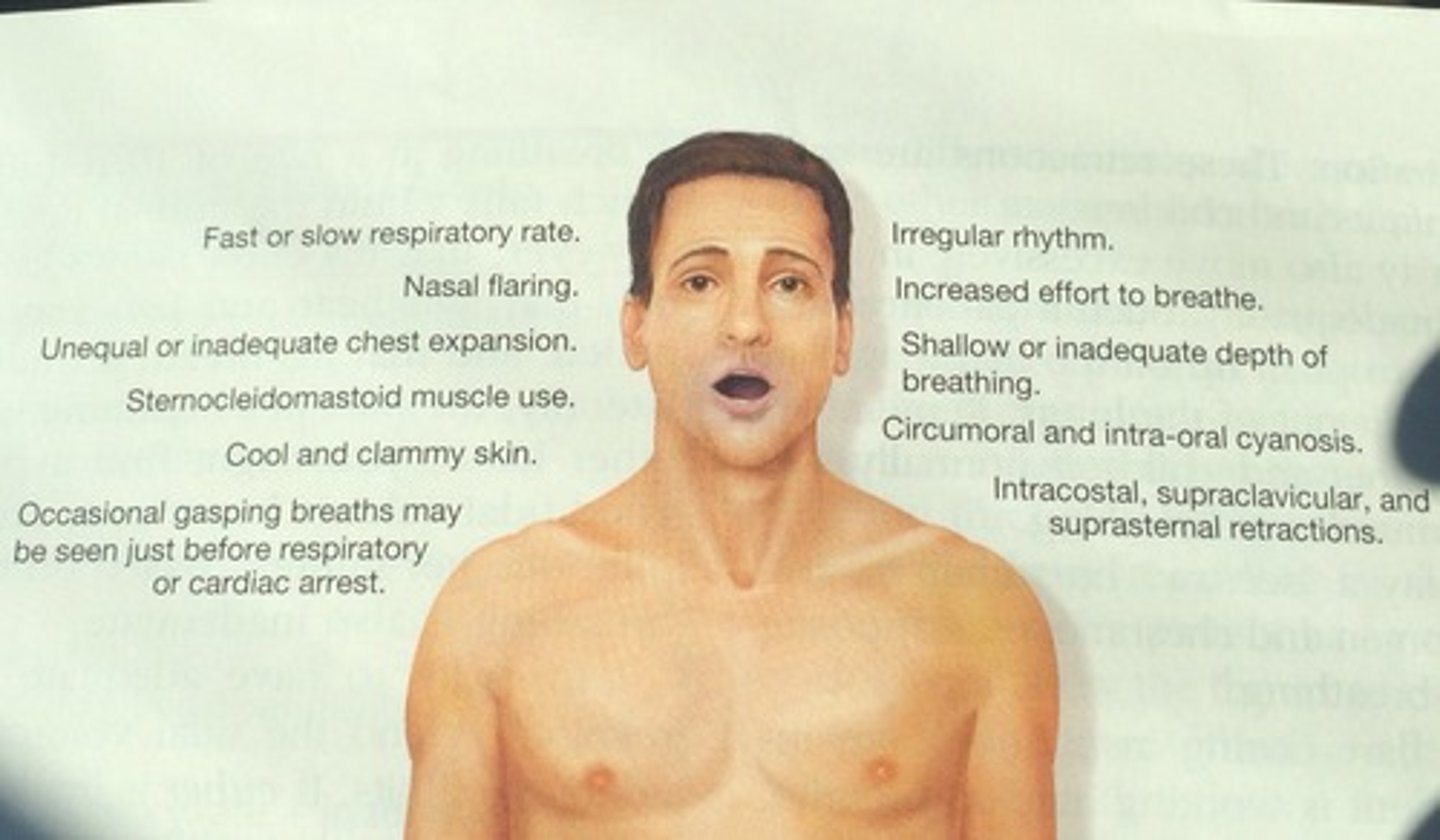
Signs of hypoxia
Blue or gray skin, decreased LOC, confusion, restlessness.
tachypnea
rapid breathing
irregular respiration
When the depth of breathing changes & the rate of the rise & fall of the chest is not steady, it is called?
Silent chest
no lung sounds
*sign of respiratory failure
agonal respirations
Slow, shallow, irregular respirations or occasional gasping breaths; sometimes seen in dying patients.

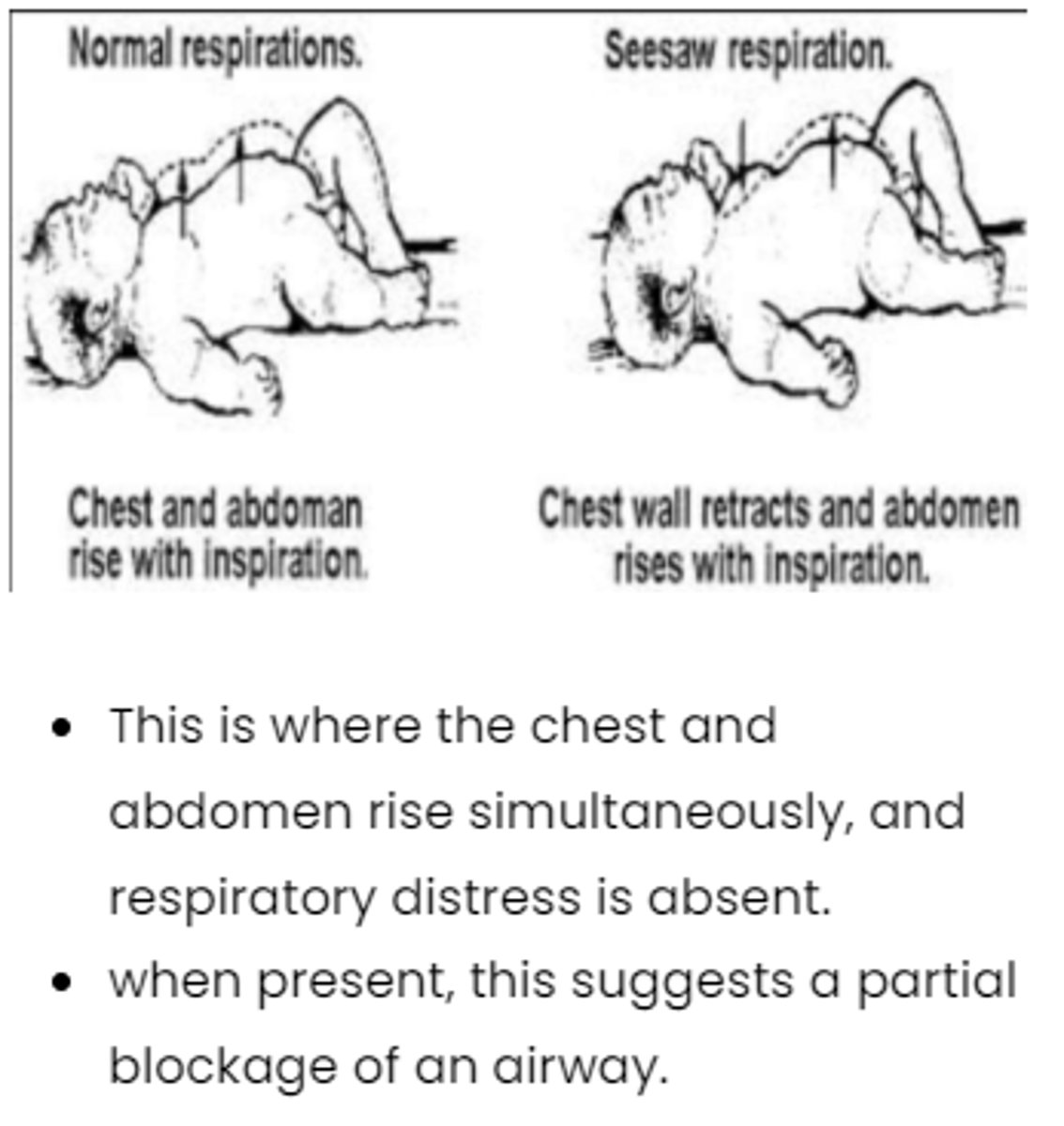
Seesaw breathing
chest and abdomen work in opposite directions
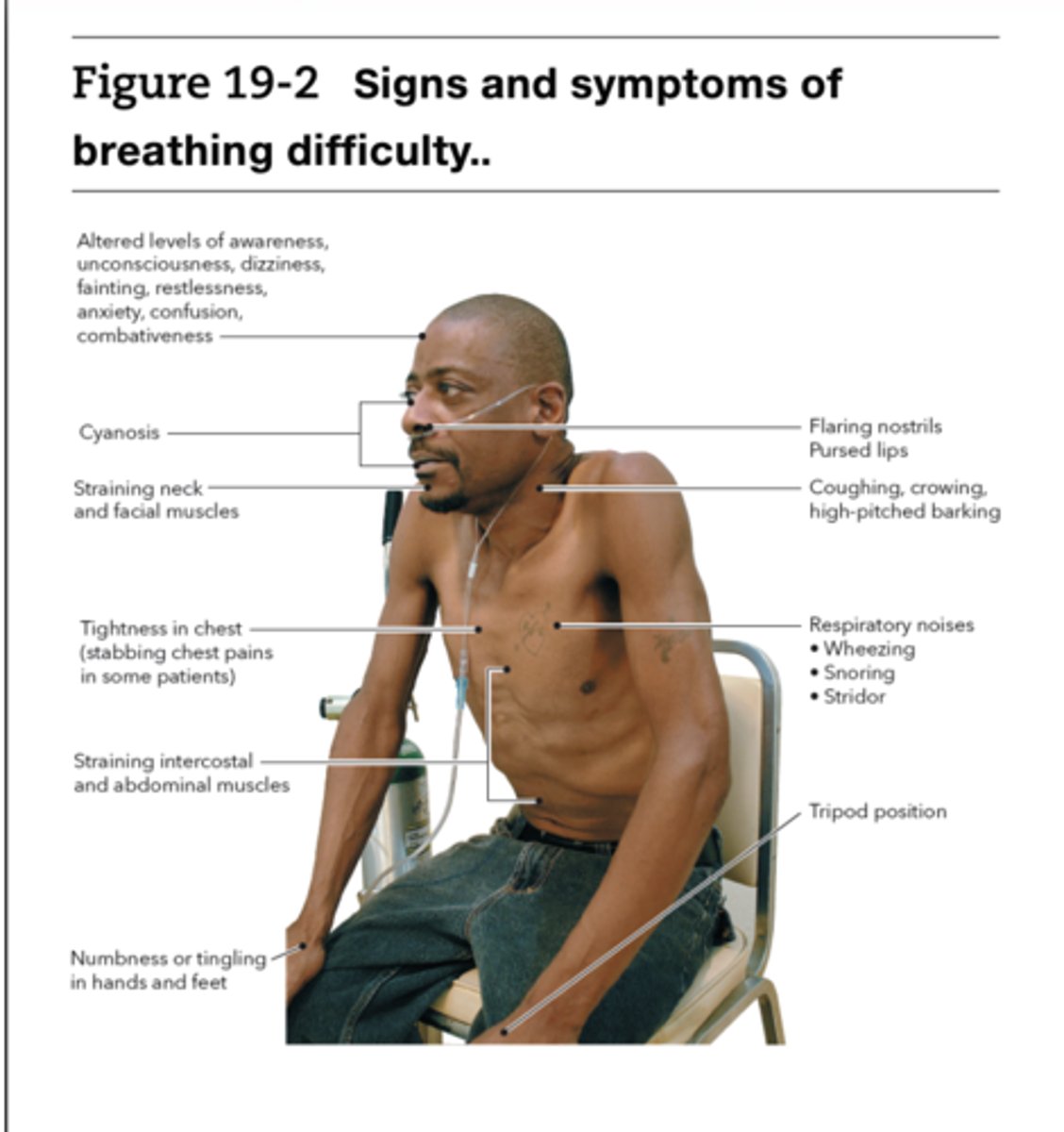
Signs and symptoms of difficulty breathing
altered mental status, anxious or restless, resp rate to fast or slow, irregular breathing, skin is pale cool or clammy, cyanosis, wheezing, coughing, decreased or noisy breath sounds , unequal chest rise,
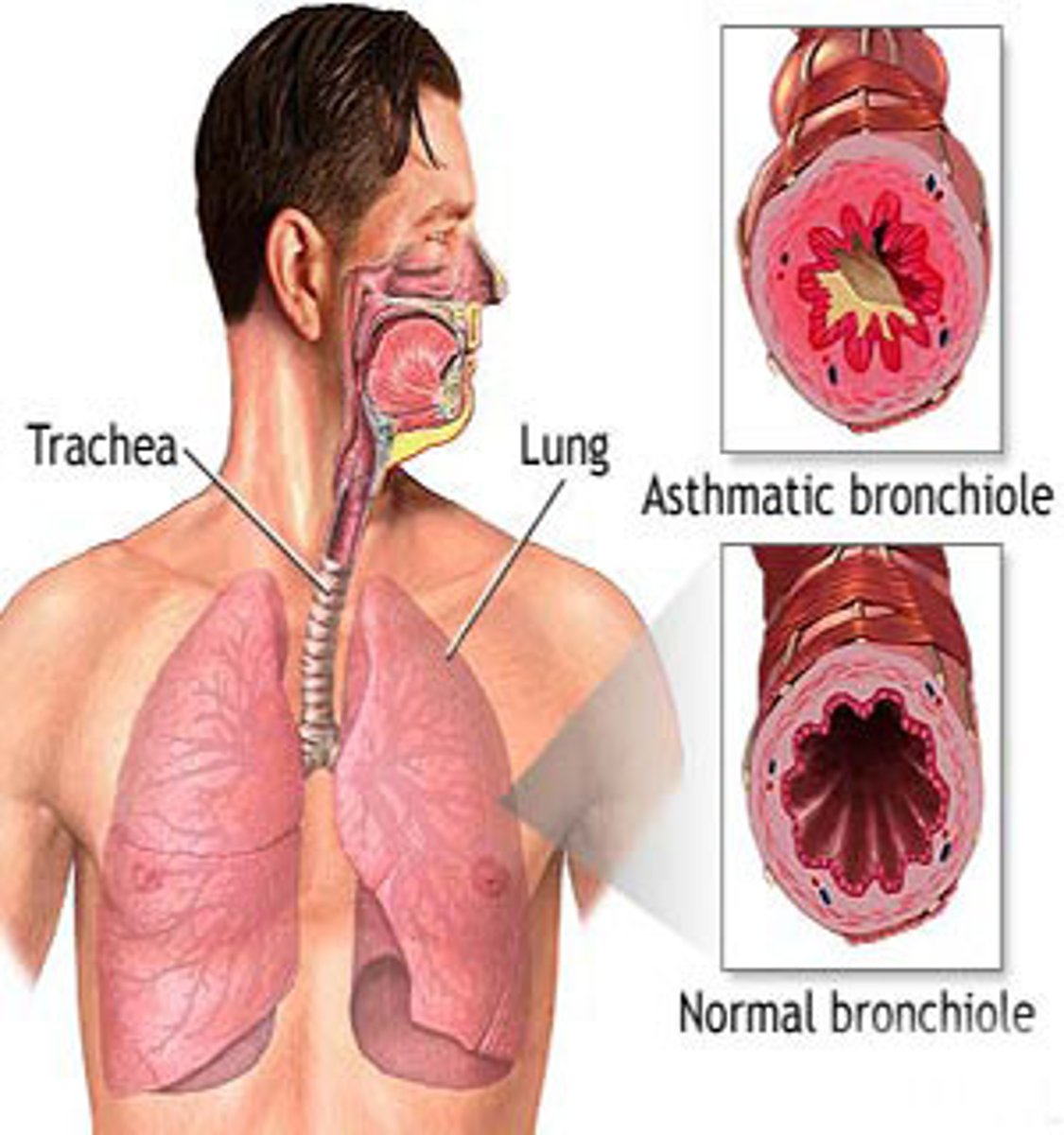
Wheezing
A high-pitched, whistling breath sound that is most prominent on expiration, and which suggests an obstruction or narrowing of the lower airways; occurs in asthma and bronchiolitis.
crackles (rales)
Short and intermittent clicking, rattling, or popping sounds heard during inhalation when air is forced through an airway narrowed by fluid.
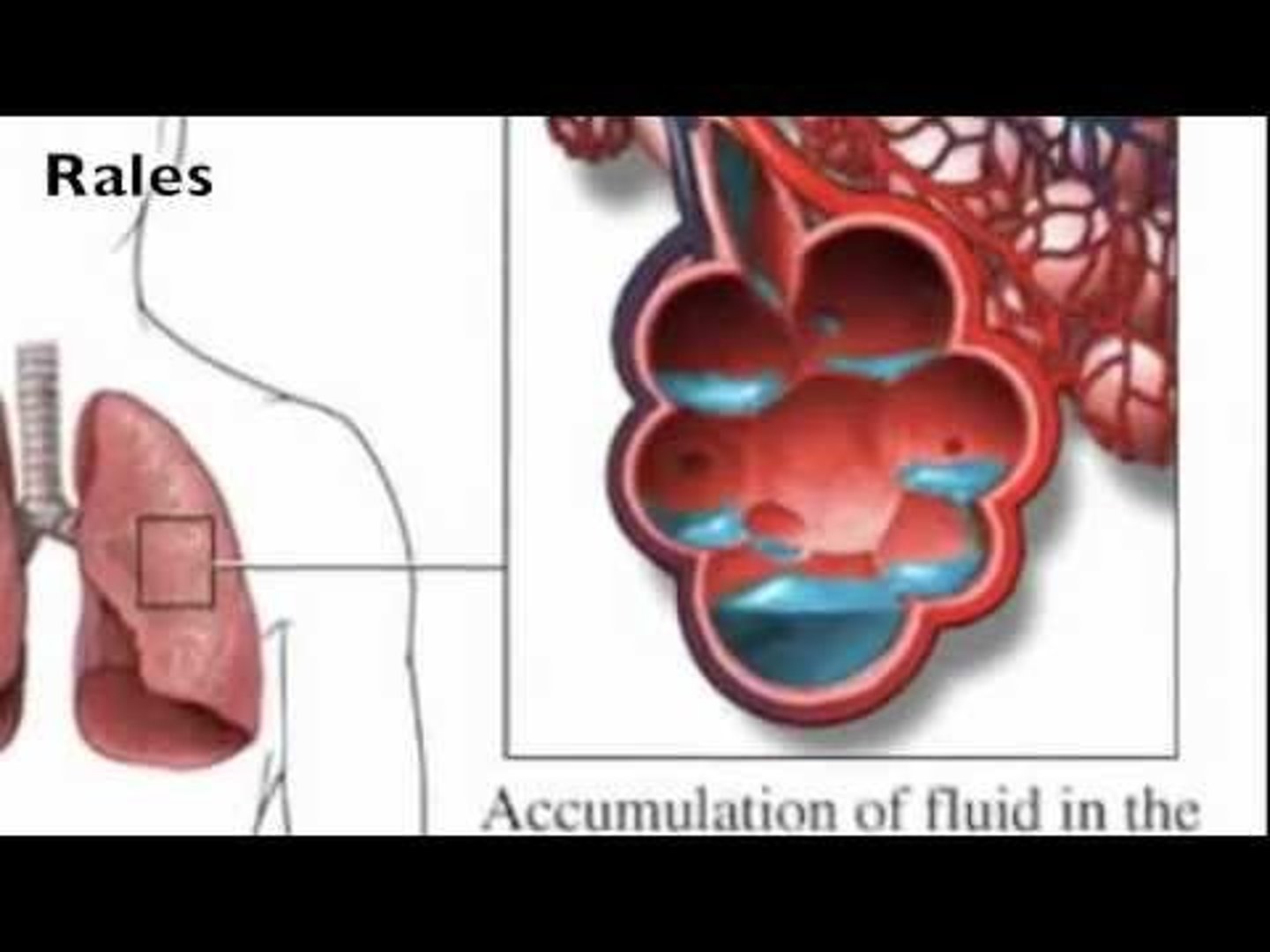
Rhonchi
Coarse, low-pitched breath sounds heard in patients with chronic mucus in the upper airways.
Stridor
A high pitched sound generated from partially obstructed air flow in the upper airway.
Where to listen to lung sounds
upper and lower chest, upper and lower back, and midaxillary line
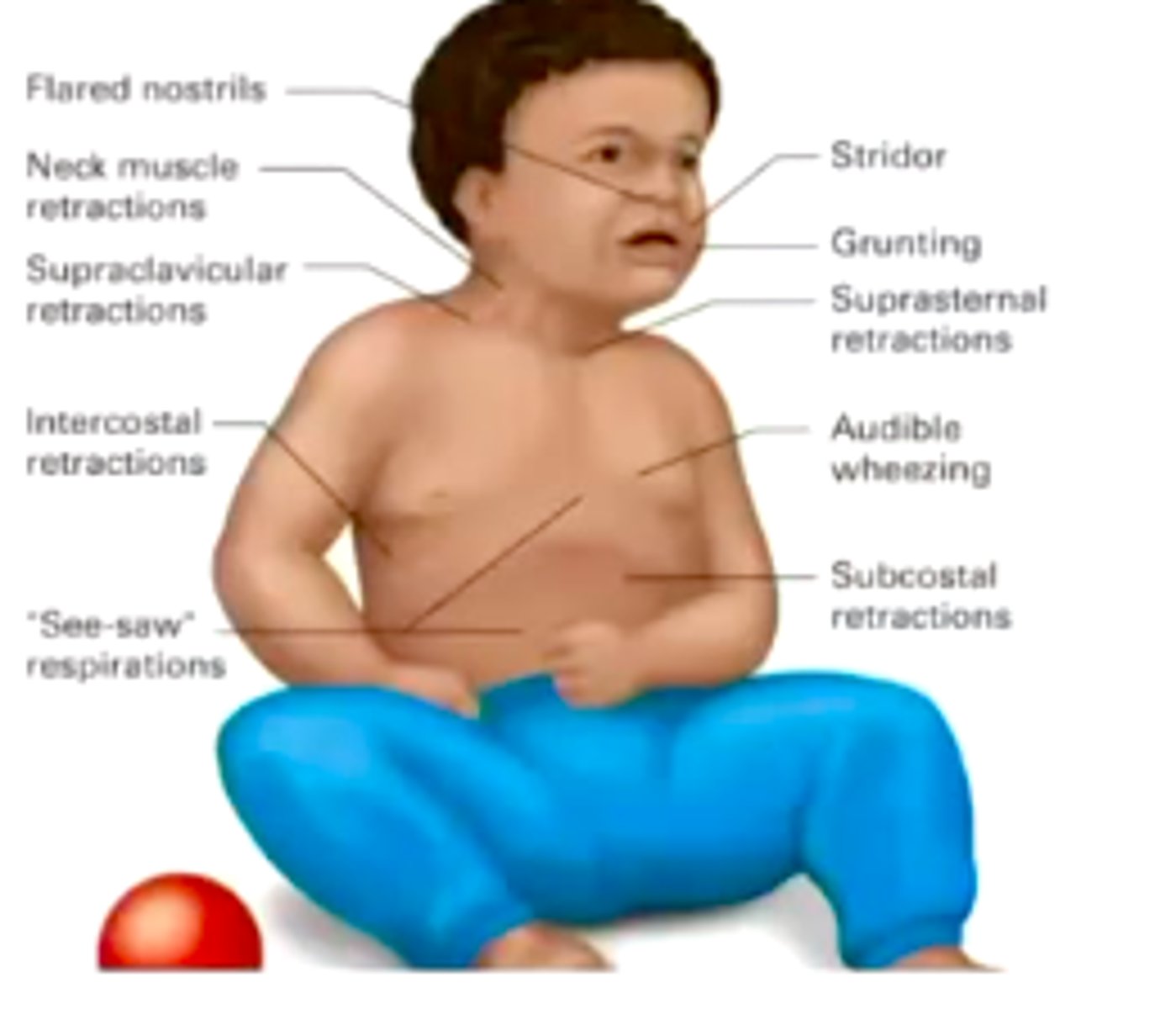
signs of respiratory distress in pediatric patients
nasal flaring, retractions, grunting, stridor, decreased muscle tone, altered mental status, decreased heart rate, decreased cap refill time
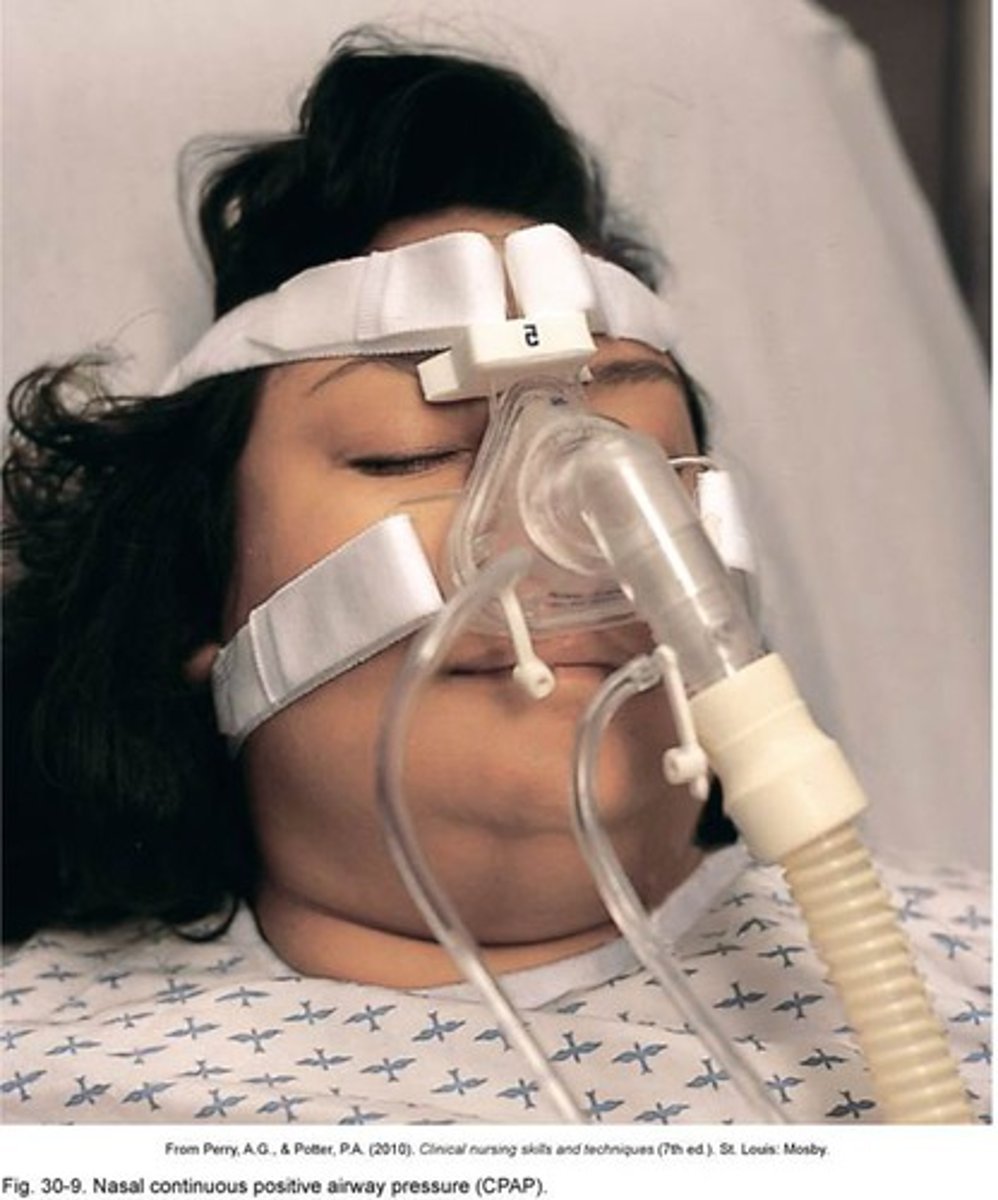
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure)
A method of ventilation used primarily in the treatment of critically ill patients with respiratory distress; can prevent the need for endotracheal intubation.
PEEP
positive end-expiratory pressure - common mechanical ventilator setting in which airway pressure is maintained above atmospheric pressure
Common uses for CPAP
- Pulmonary edema
- Drowning
- Asthma and COPD
- Respiratory failure in general

Contraindication of CPAP
Untreated pneumothorax
Hemodynamically unstable patient
Severely apneic patients
Systolic pressure of 90 or below
Inability to maintain mask seal
Recent GI bleed or surgery
Vomiting
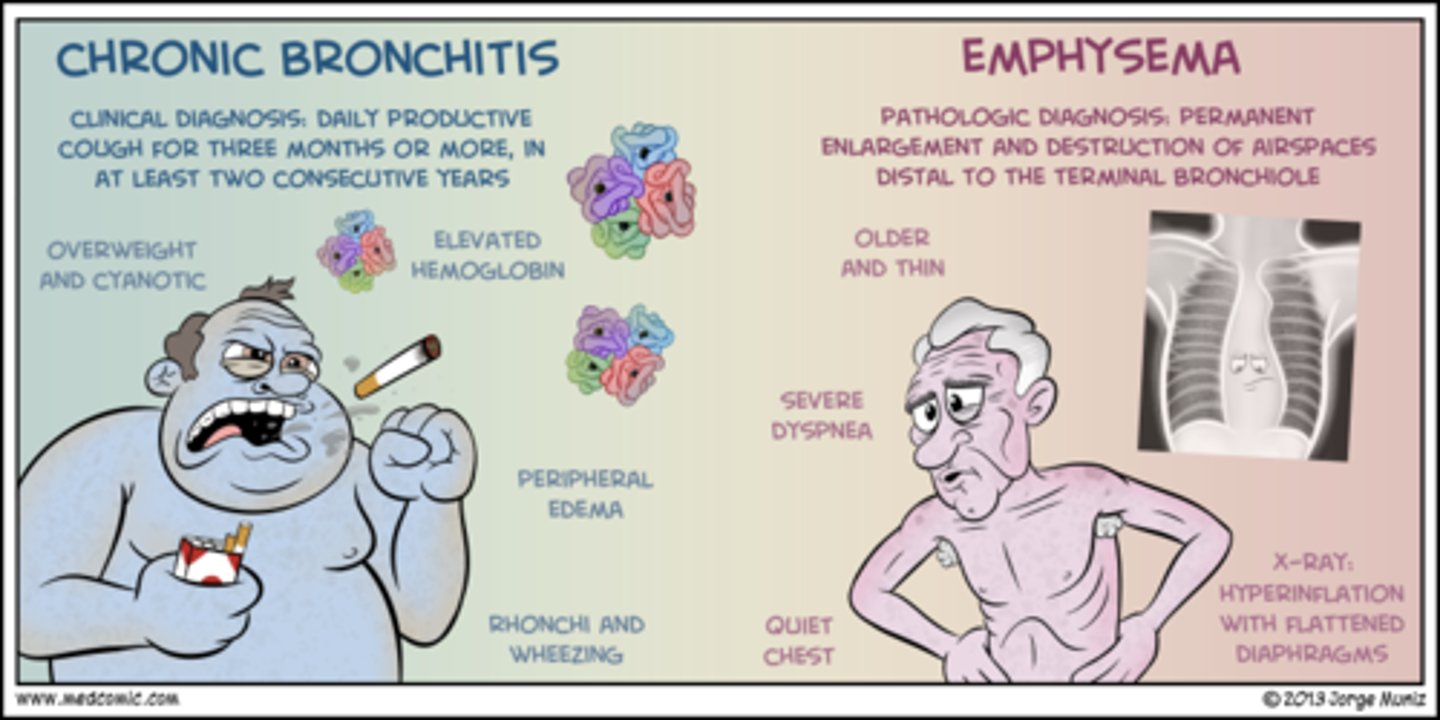
COPD
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
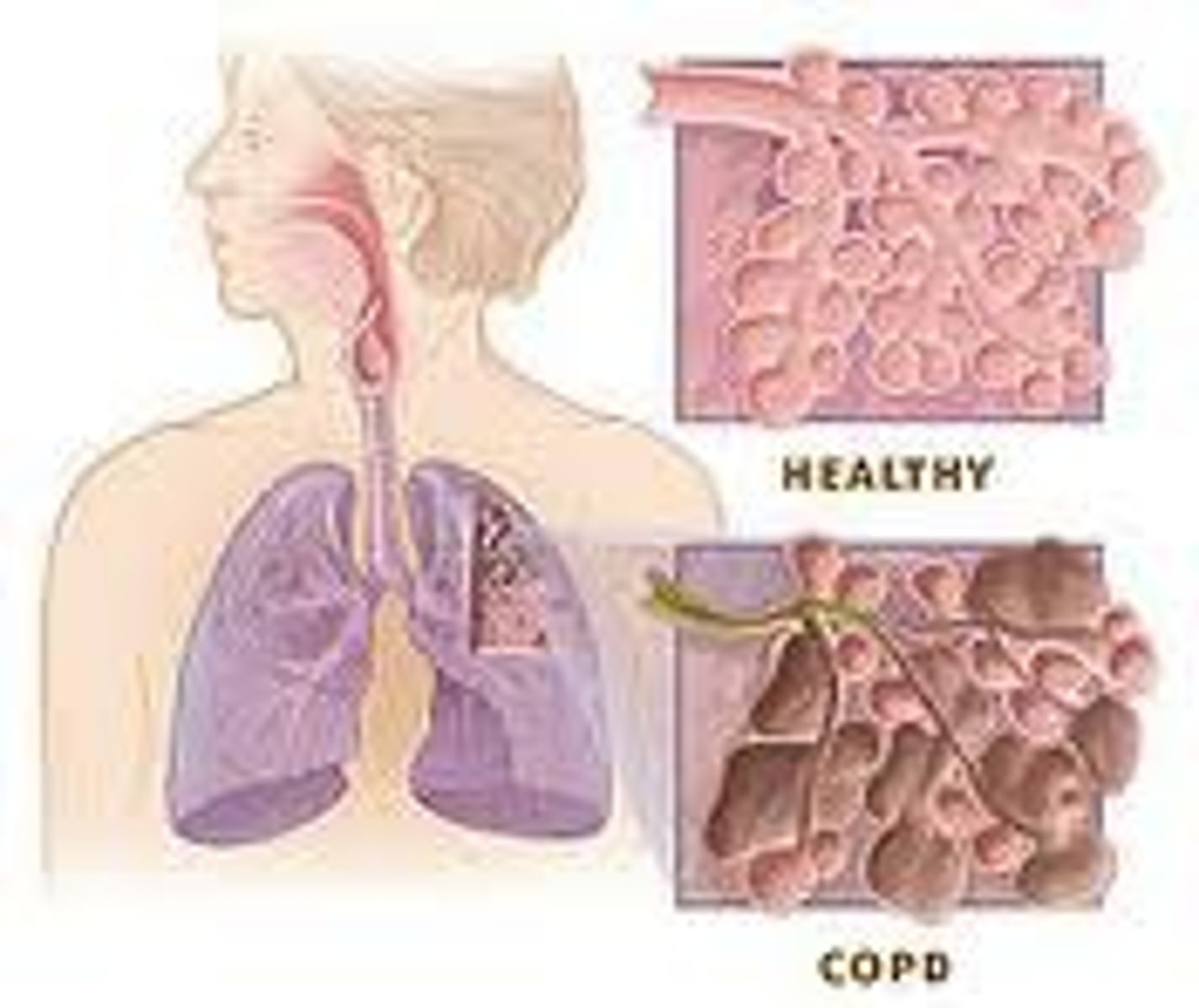
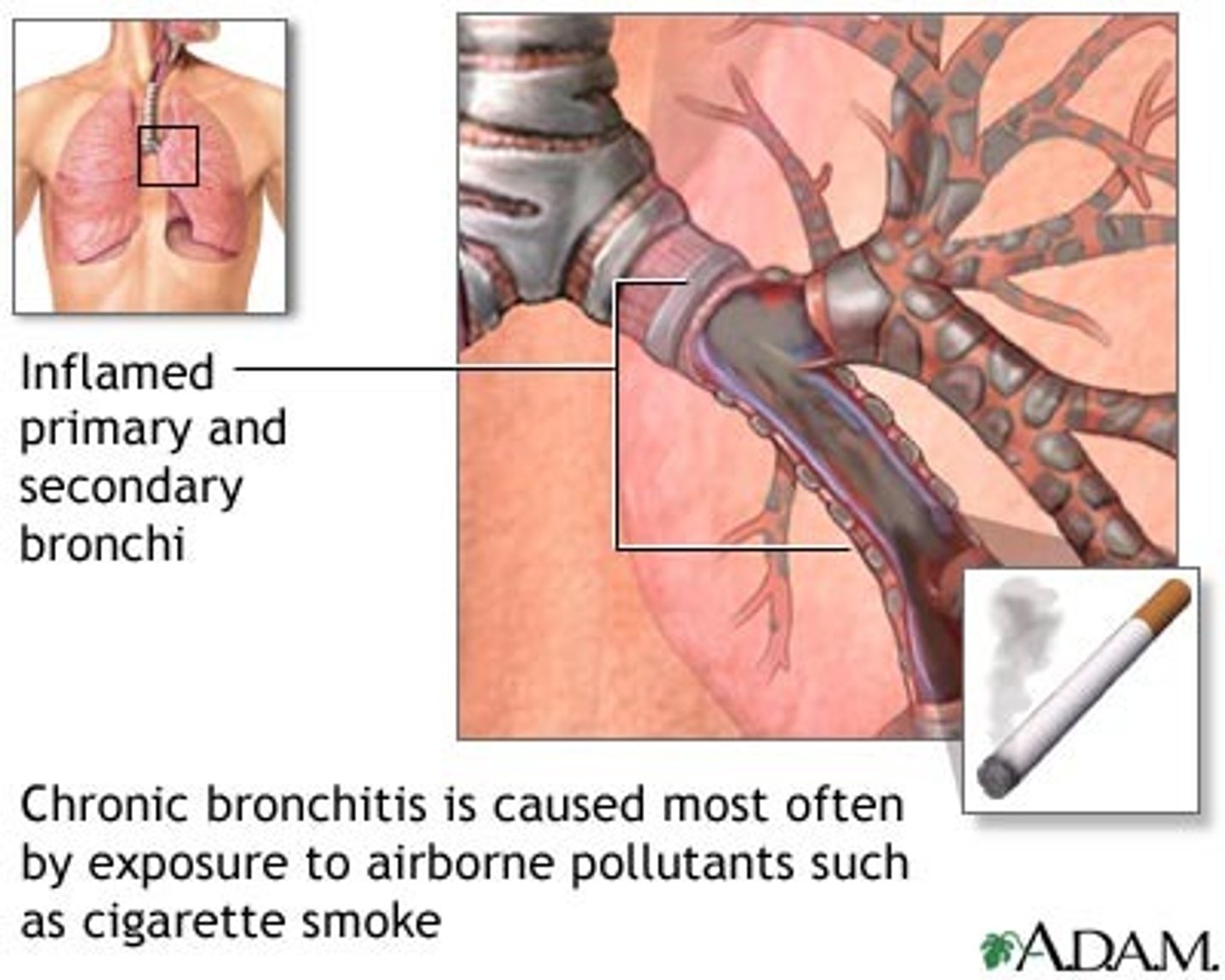
chronic bronchitis
inflammation of bronchi persisting over a long time; type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
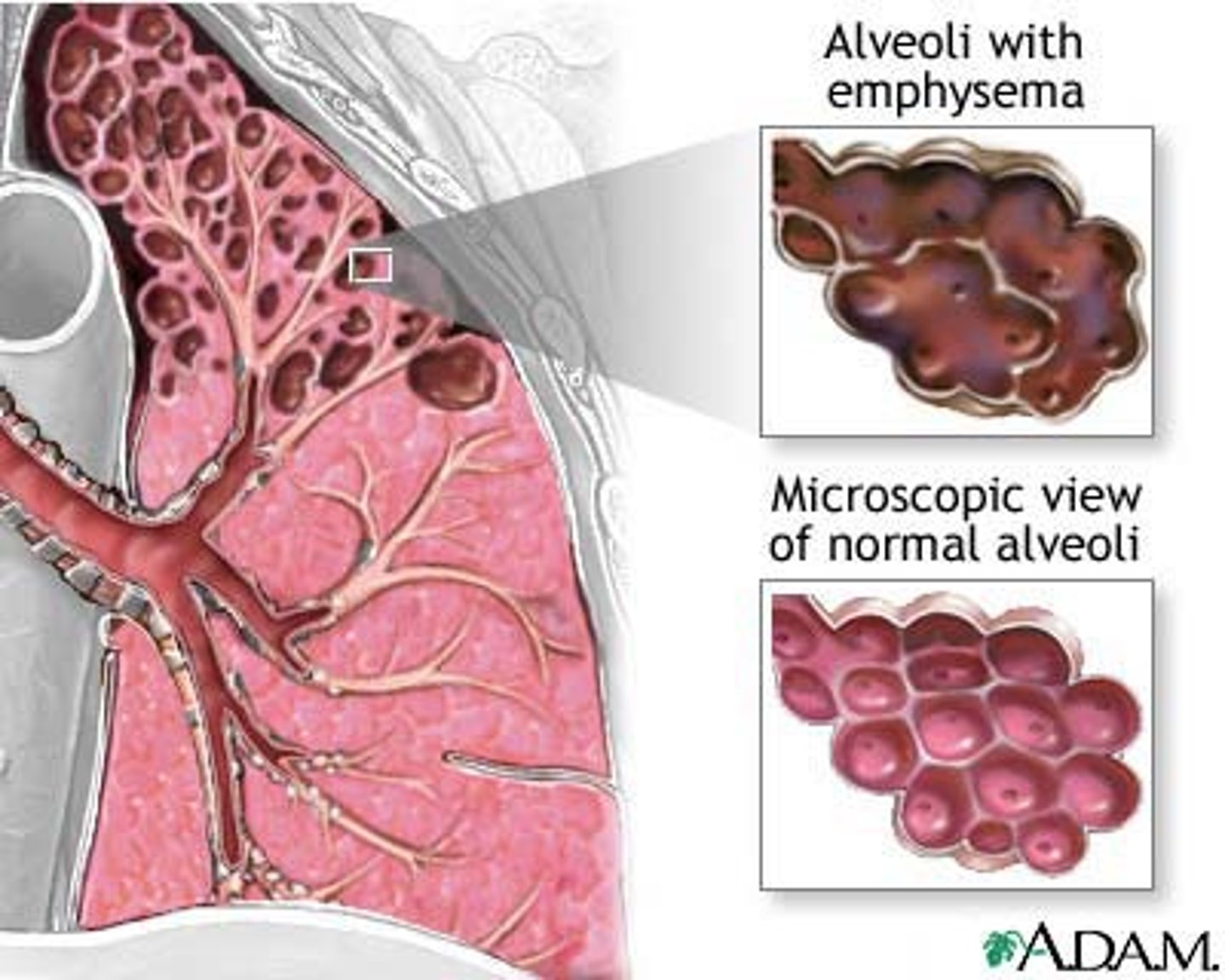
Emphysema
a condition in which the air sacs of the lungs are damaged and enlarged, causing breathlessness.
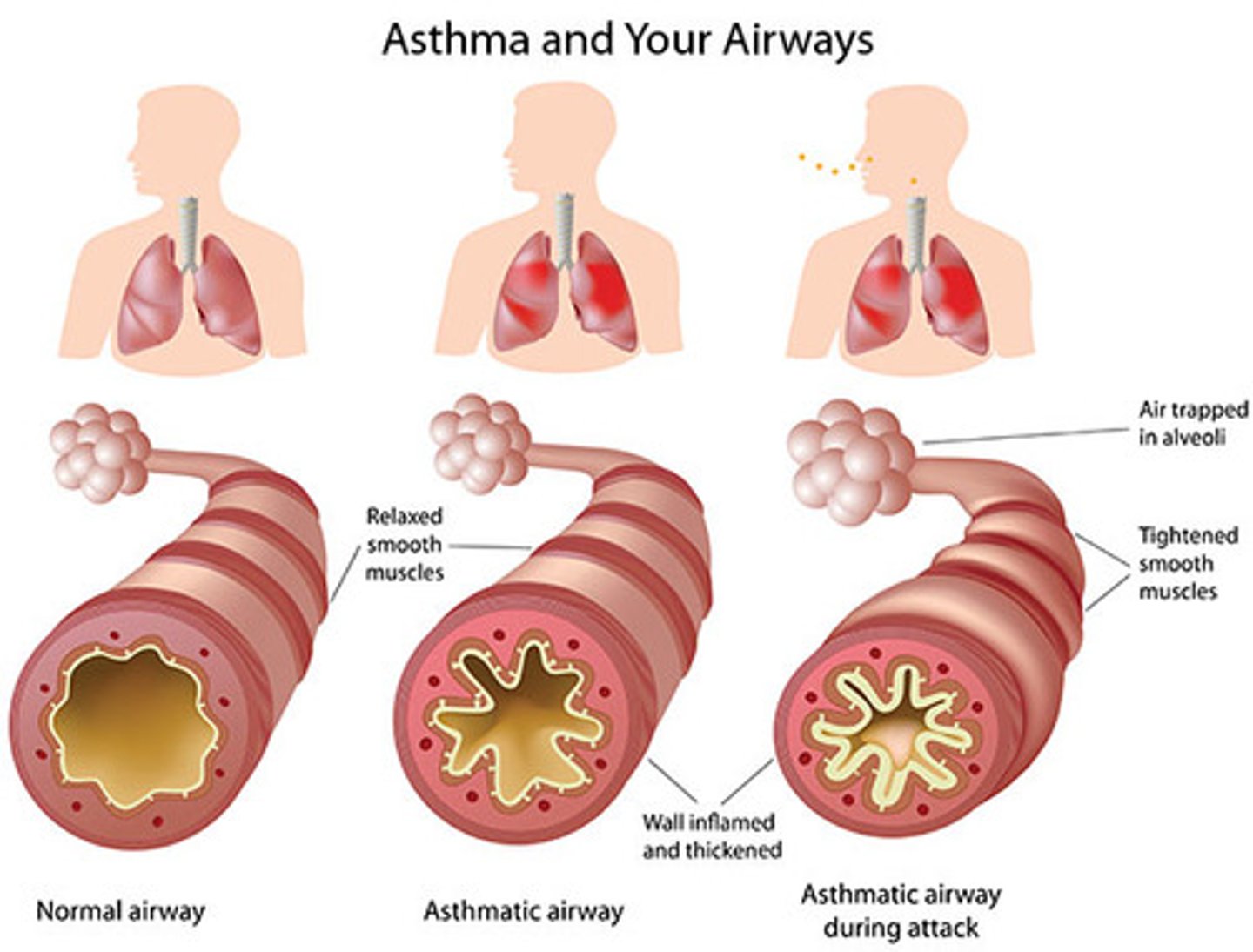
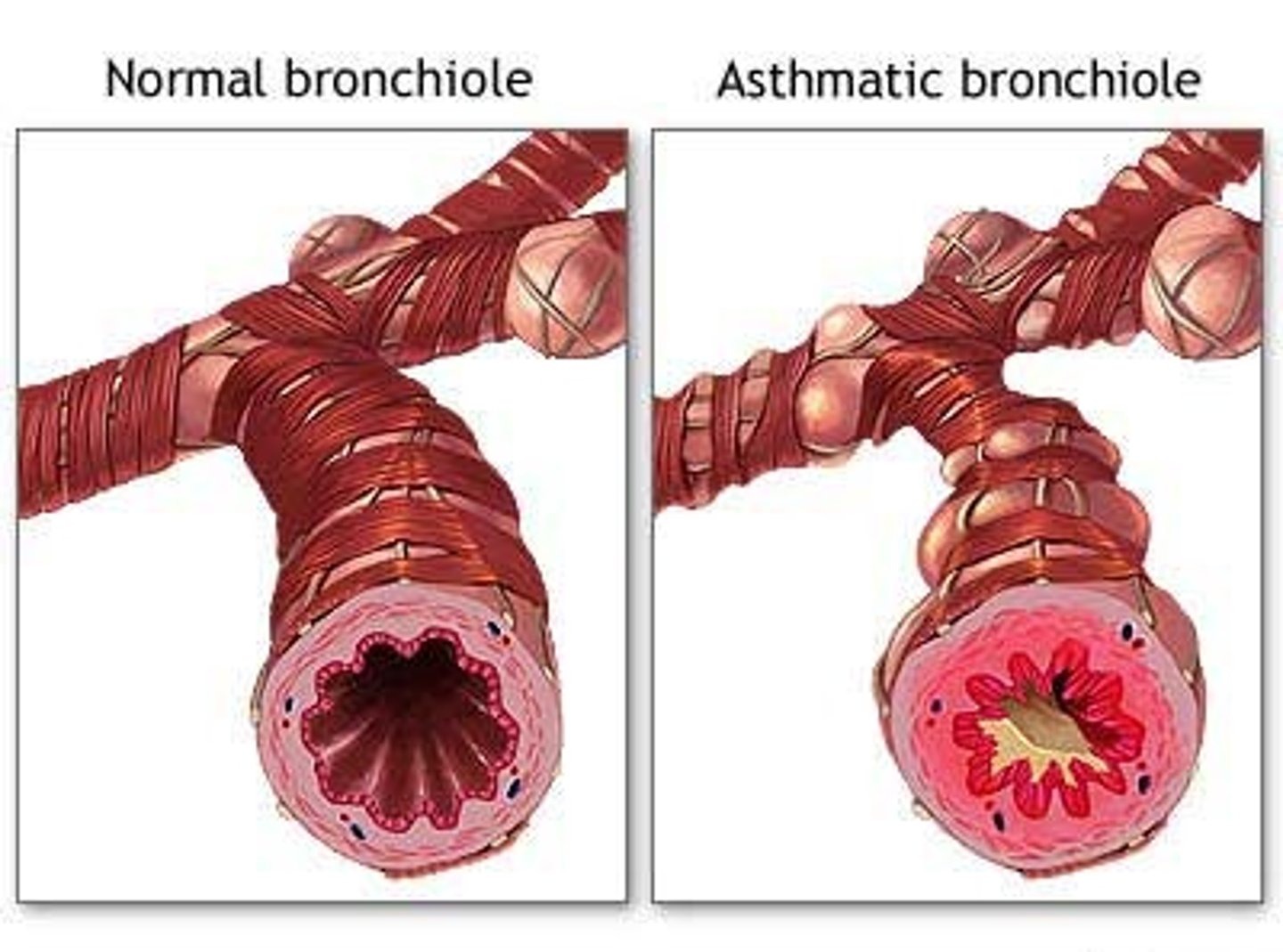
Asthma
A chronic allergic disorder characterized by episodes of severe breathing difficulty, coughing, and wheezing.
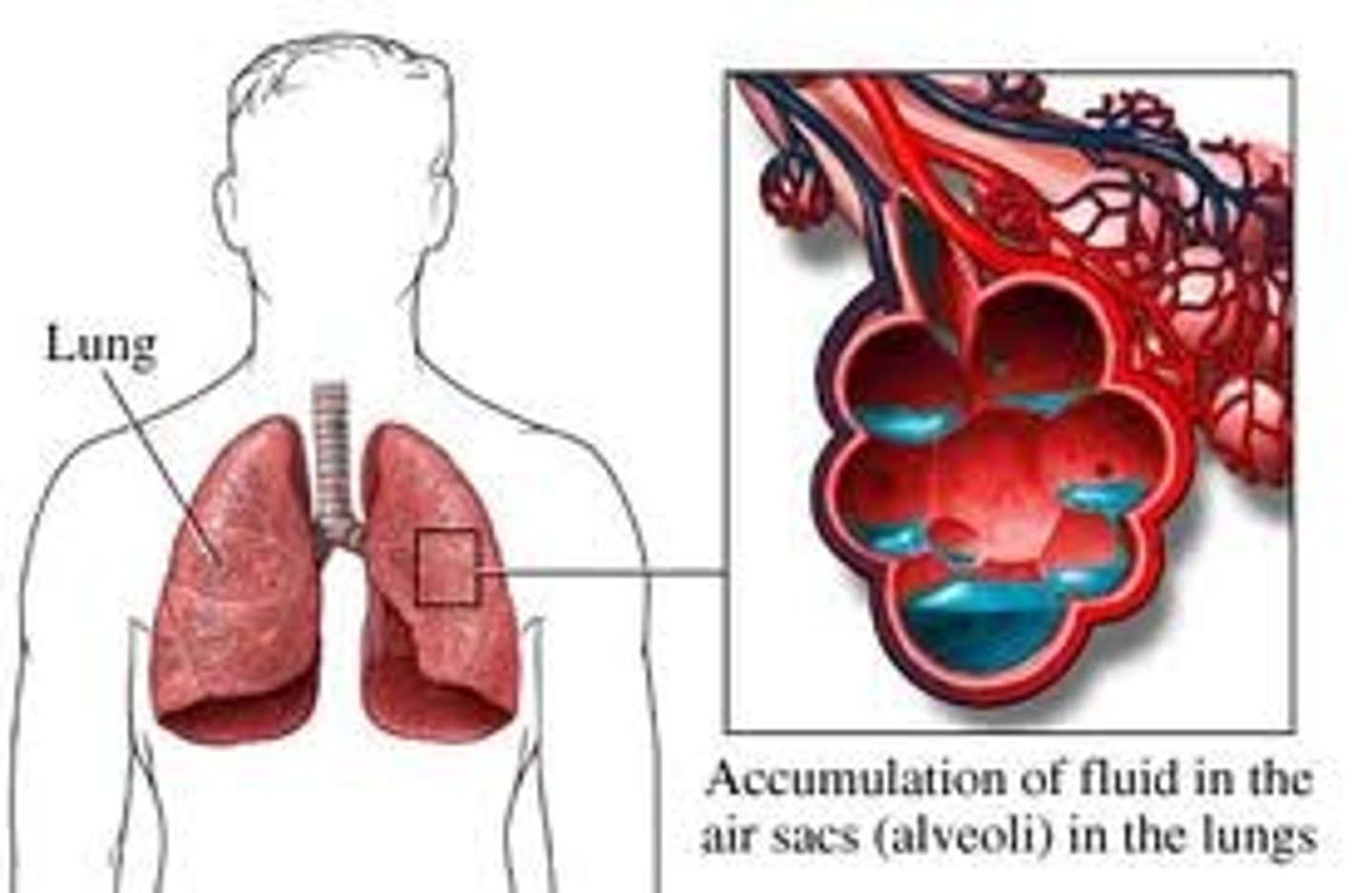
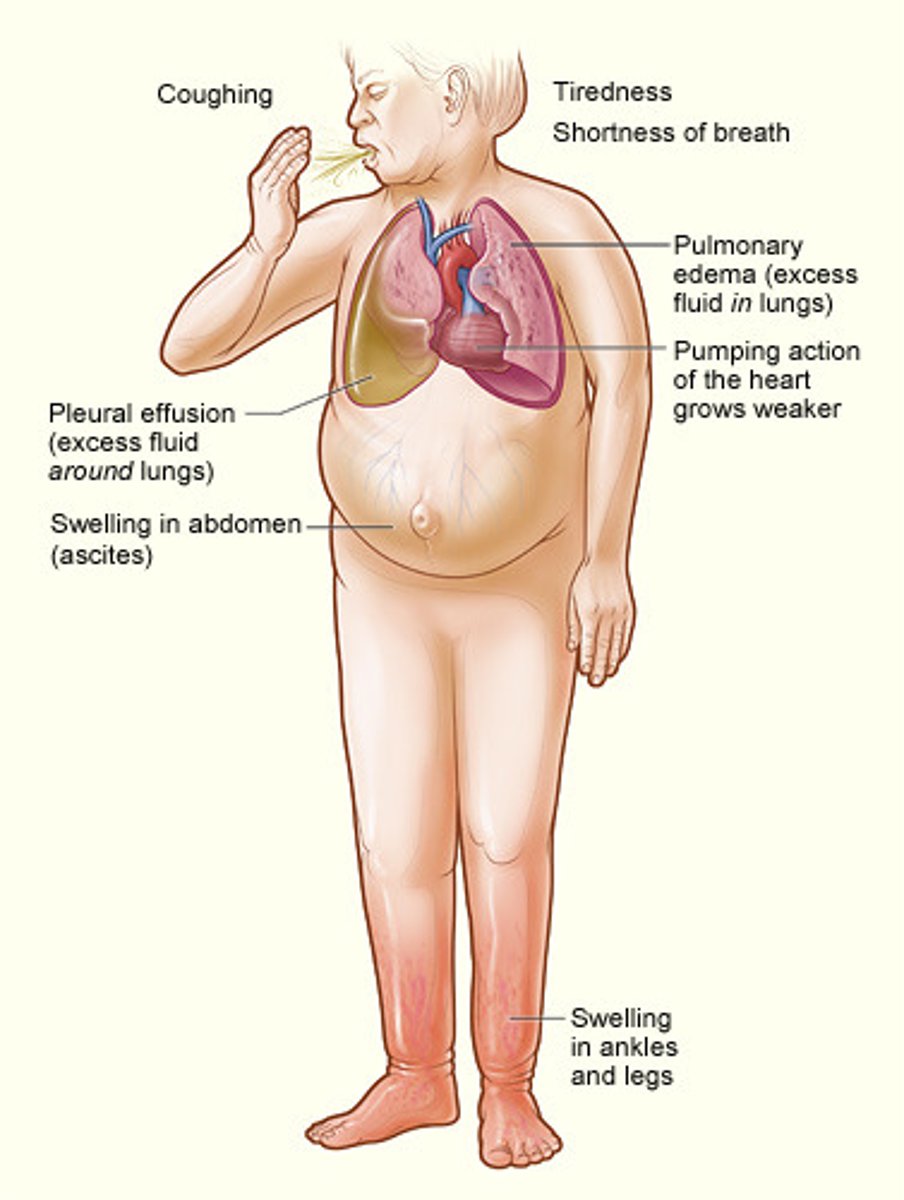
Pulmonary Edema
accumulation of fluid in the lungs
Left sided heart failure results in
pulmonary edema
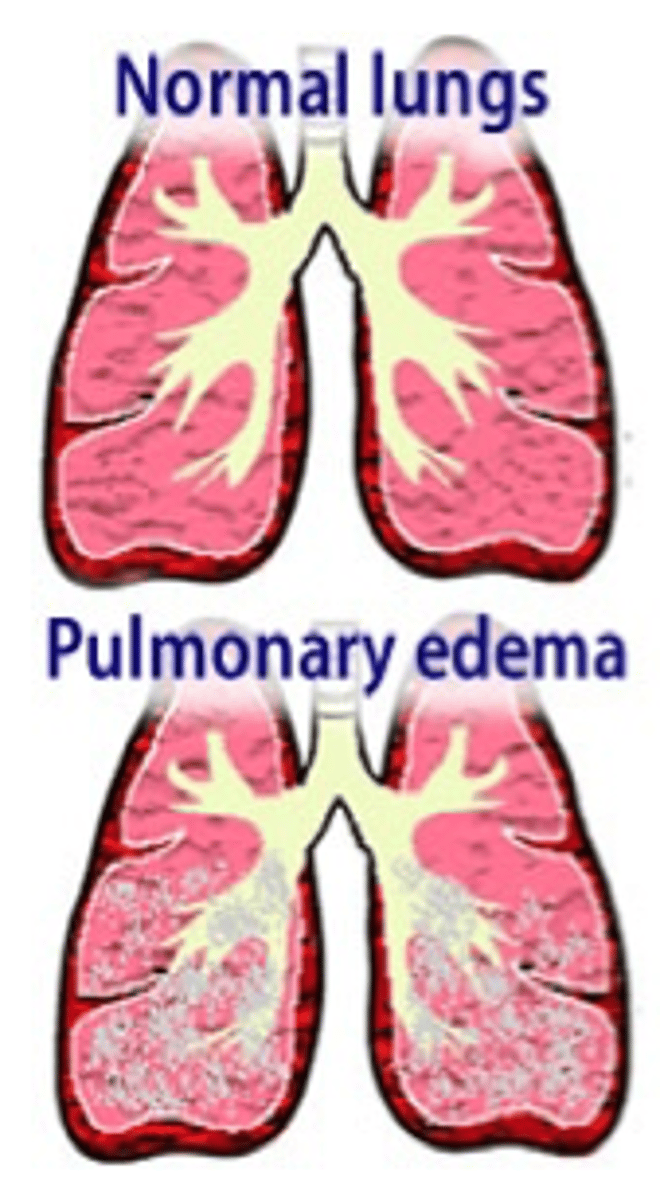
Right sided heart failure results in
peripheral edema

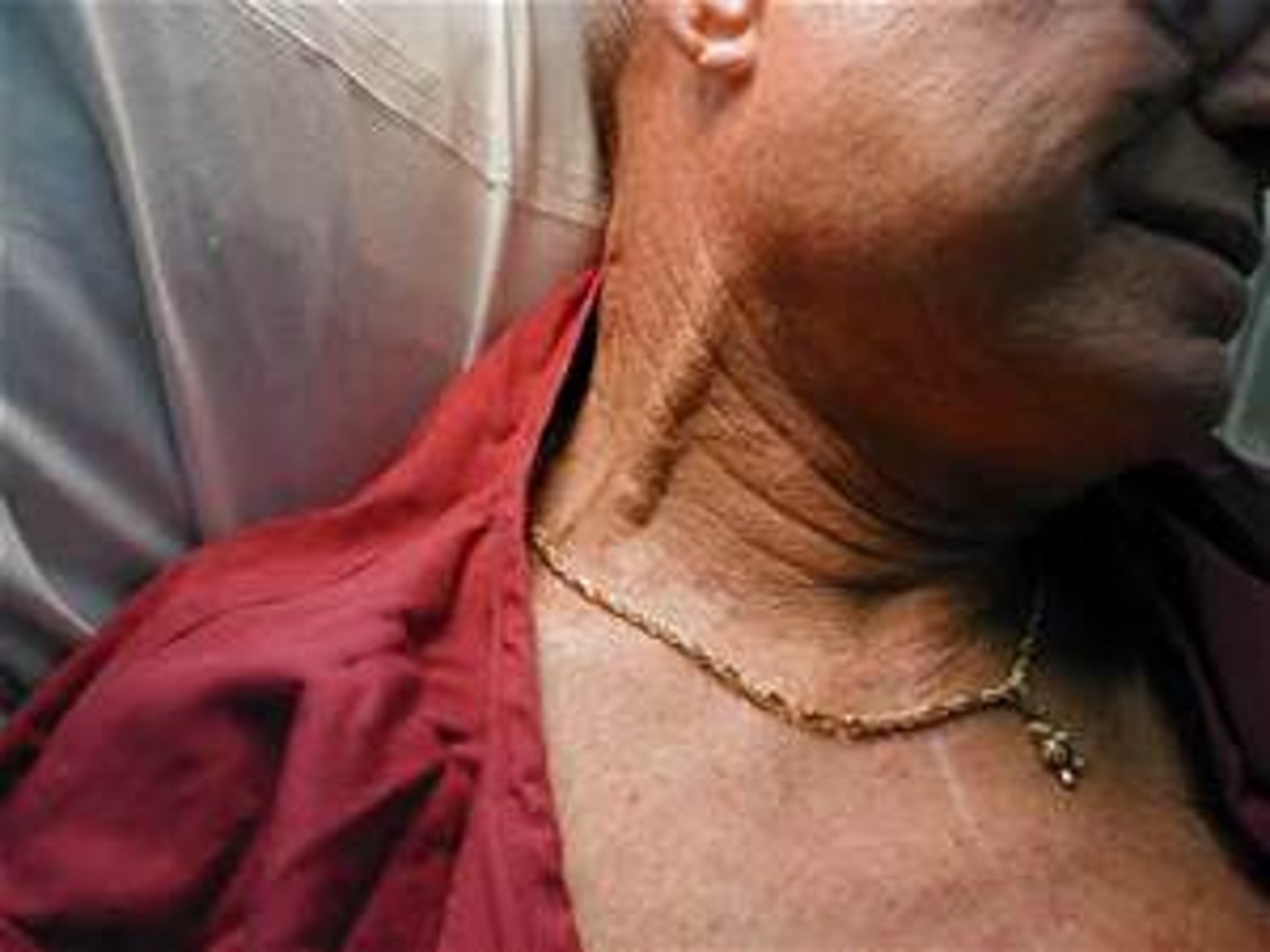
JVD (jugular vein distention)
bulging of blood veins on the sides of the neck
Dyspnea
difficult or labored breathing
Congestive heart failure
A condition resulting from the heart's inability to pump out all the blood that returns to it; blood backs up in the veins leading to the heart, causing an accumulation of fluid in various parts of the body
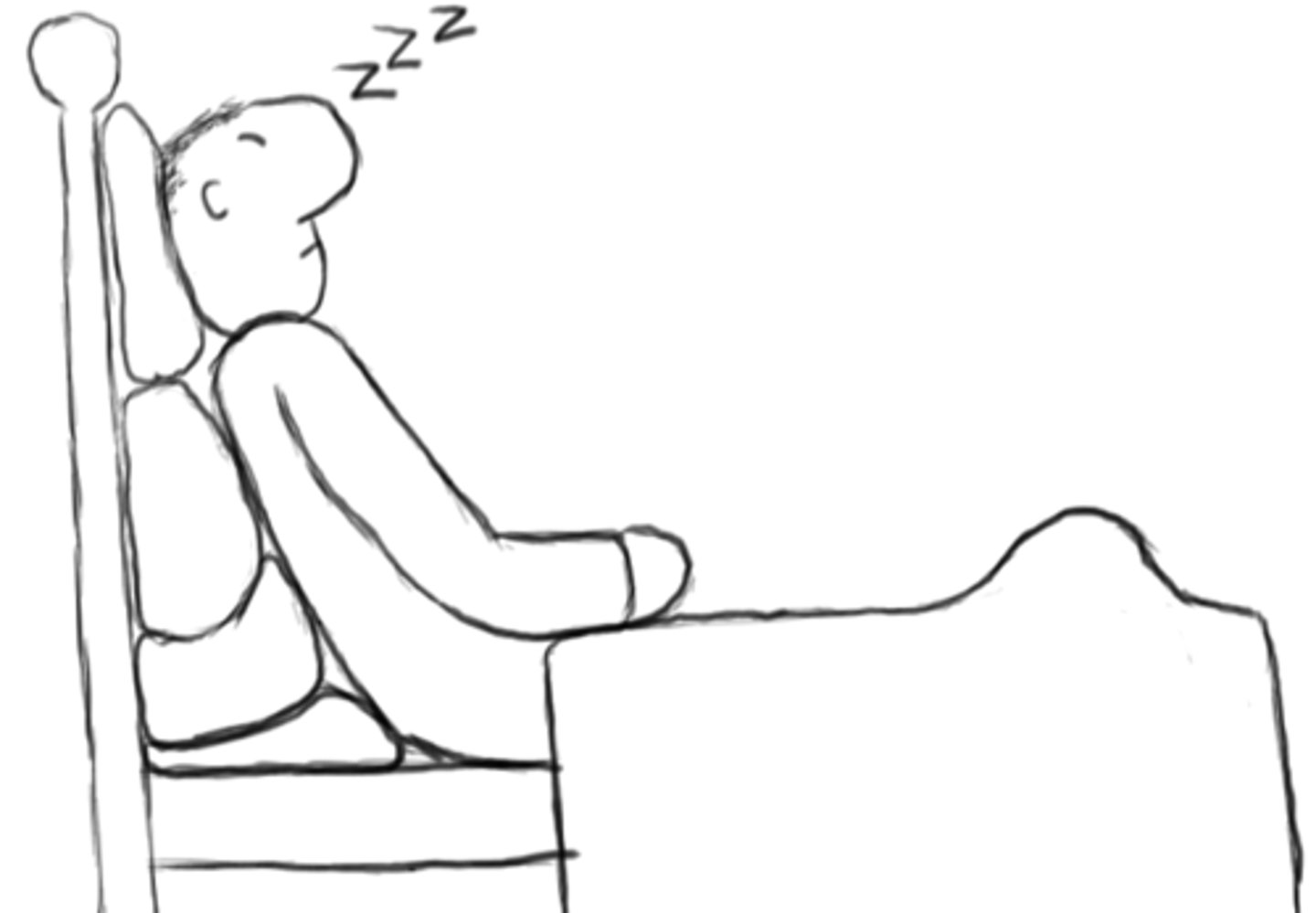
orthopnea
difficulty breathing when lying down
pneumonia
Bacterial infection of the lungs
signs of pneumonia
Pleuritic chest pain, productive cough with rust or green sputum, dyspnea, tachynea, fatigue, fever, generalized aches.
Spontaneous Pneumothorax
the rupture of a weakened area of the lung, which allows air to escape into the pleural space
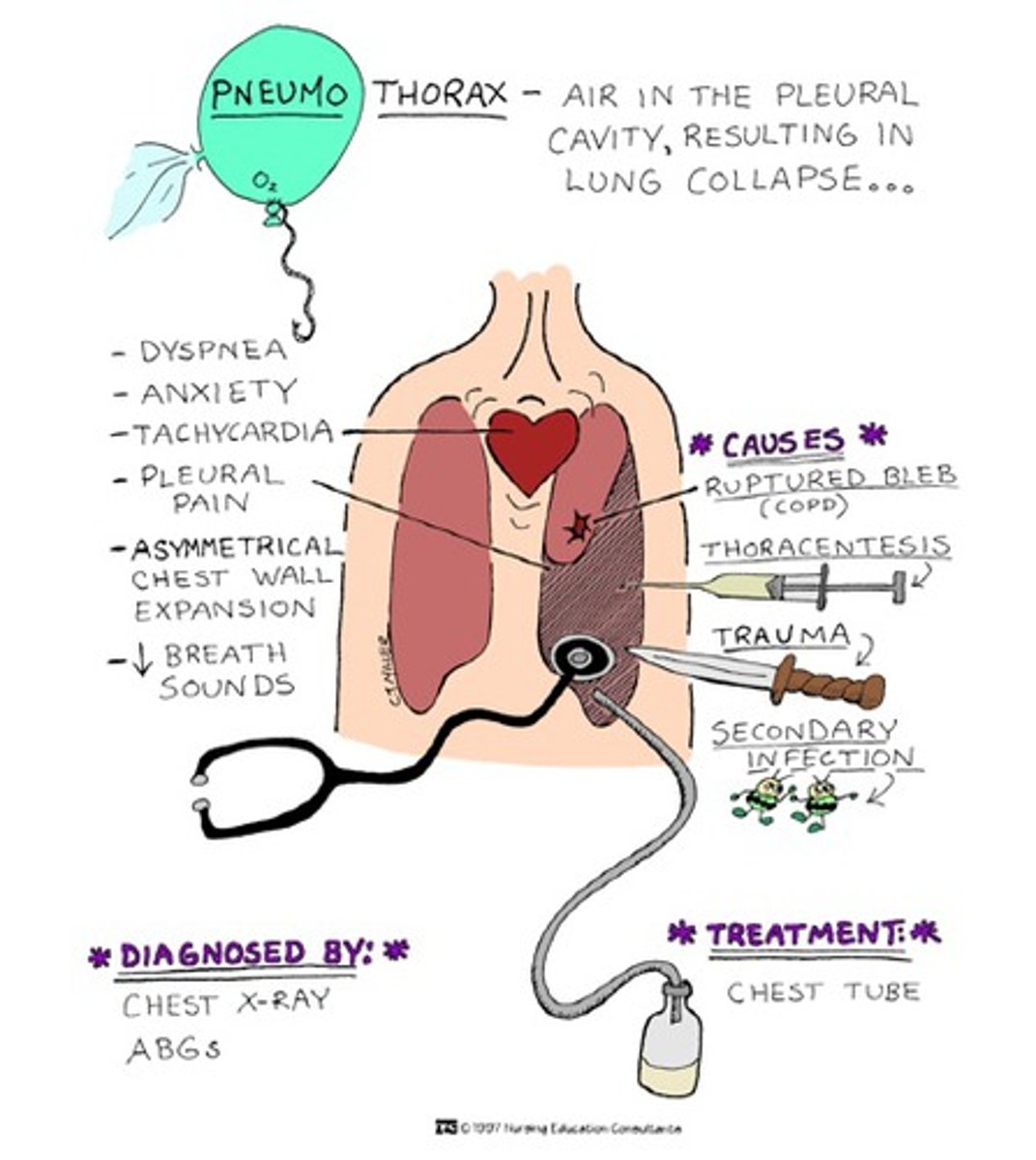
lung sounds with pneumothorax
diminished or absent
Late signs of pneumothorax
JVD and hypotension
Pulmonary Embolism
A blood clot that breaks off from a large vein and travels to the blood vessels of the lung, causing obstruction of blood flow.
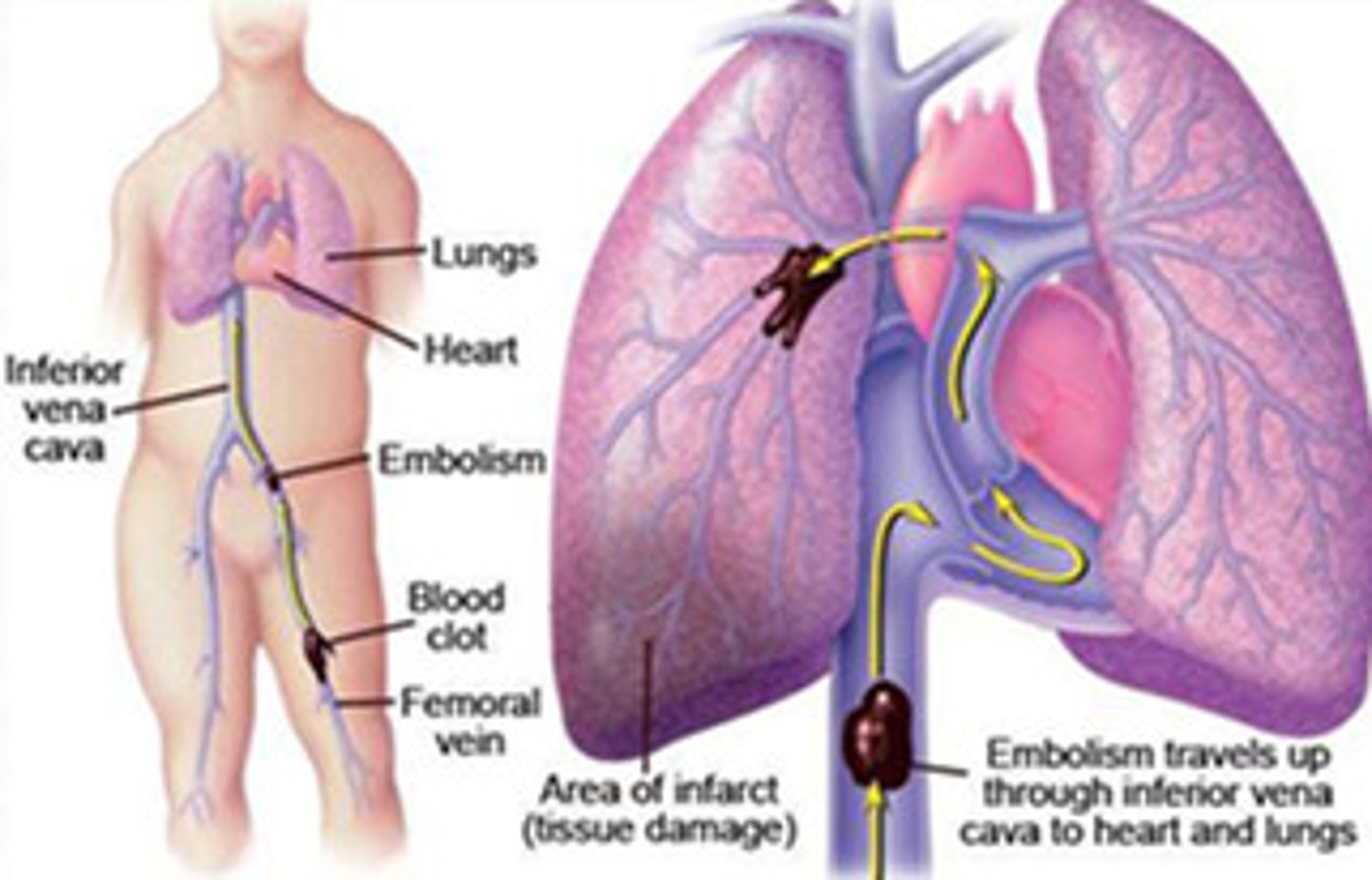
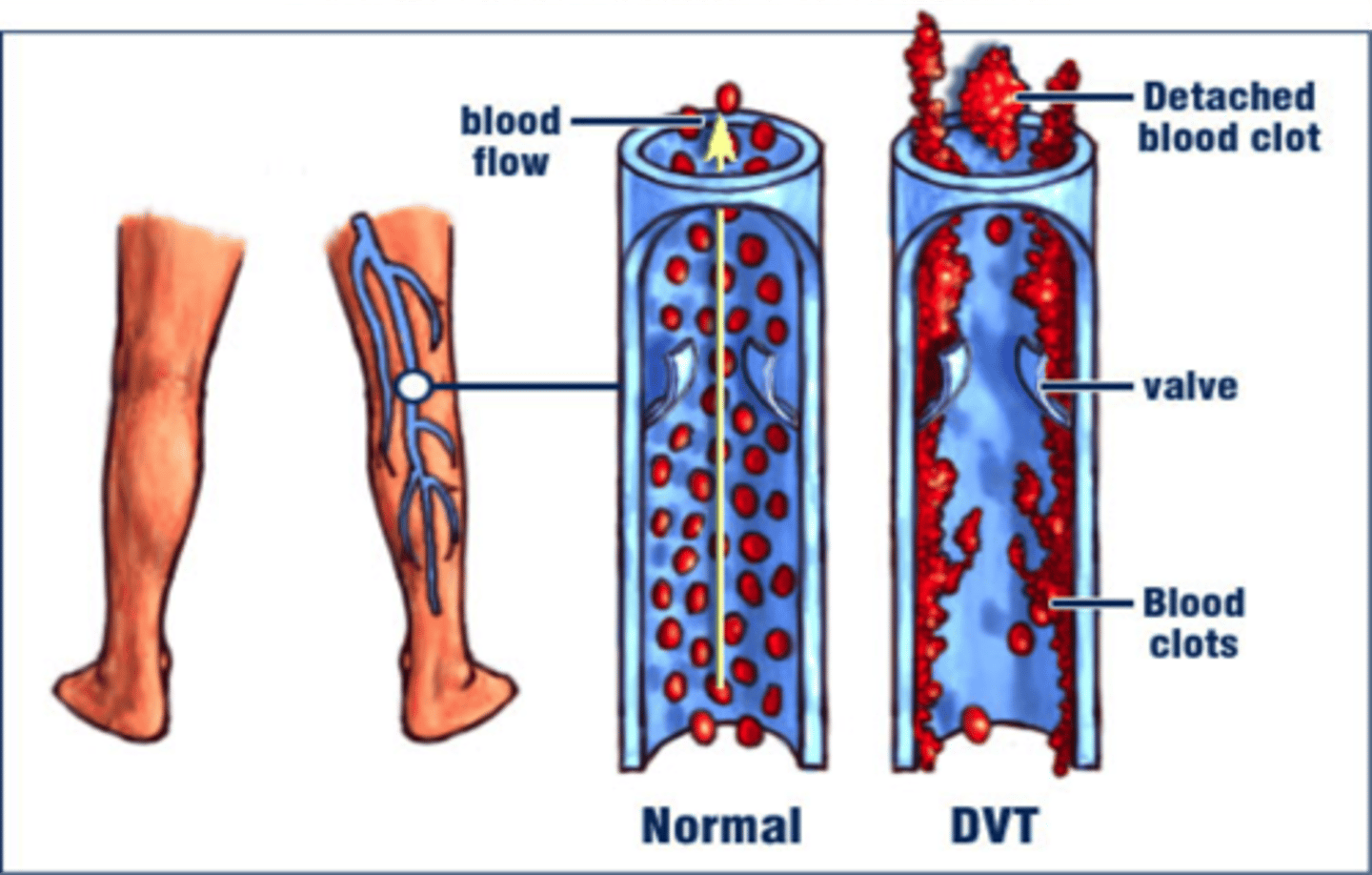
Deep Vein Thrombosis
blood clot forms in a large vein, usually in a lower limb
pleuritic chest pain
Sharp, stabbing pain in the chest that is worsened by a deep breath or other chest wall movement; often caused by inflammation or irritation of the pleura.
tachypnea
rapid breathing
tachycardia
fast heart rate
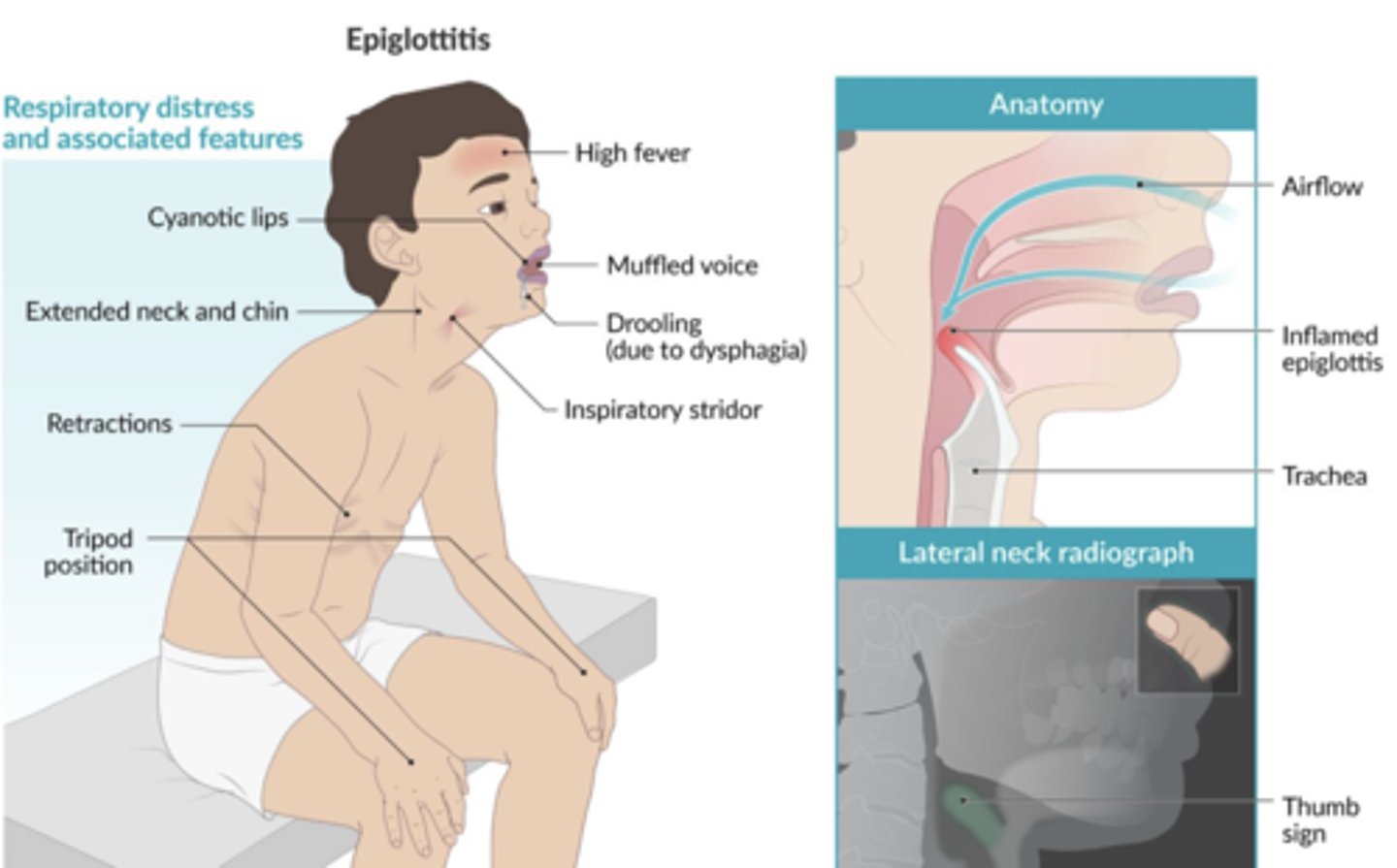
epiglottitis
severe, life-threatening infection of the epiglottis and supraglottic structures that occurs most commonly in children between 2 and 12 years of age
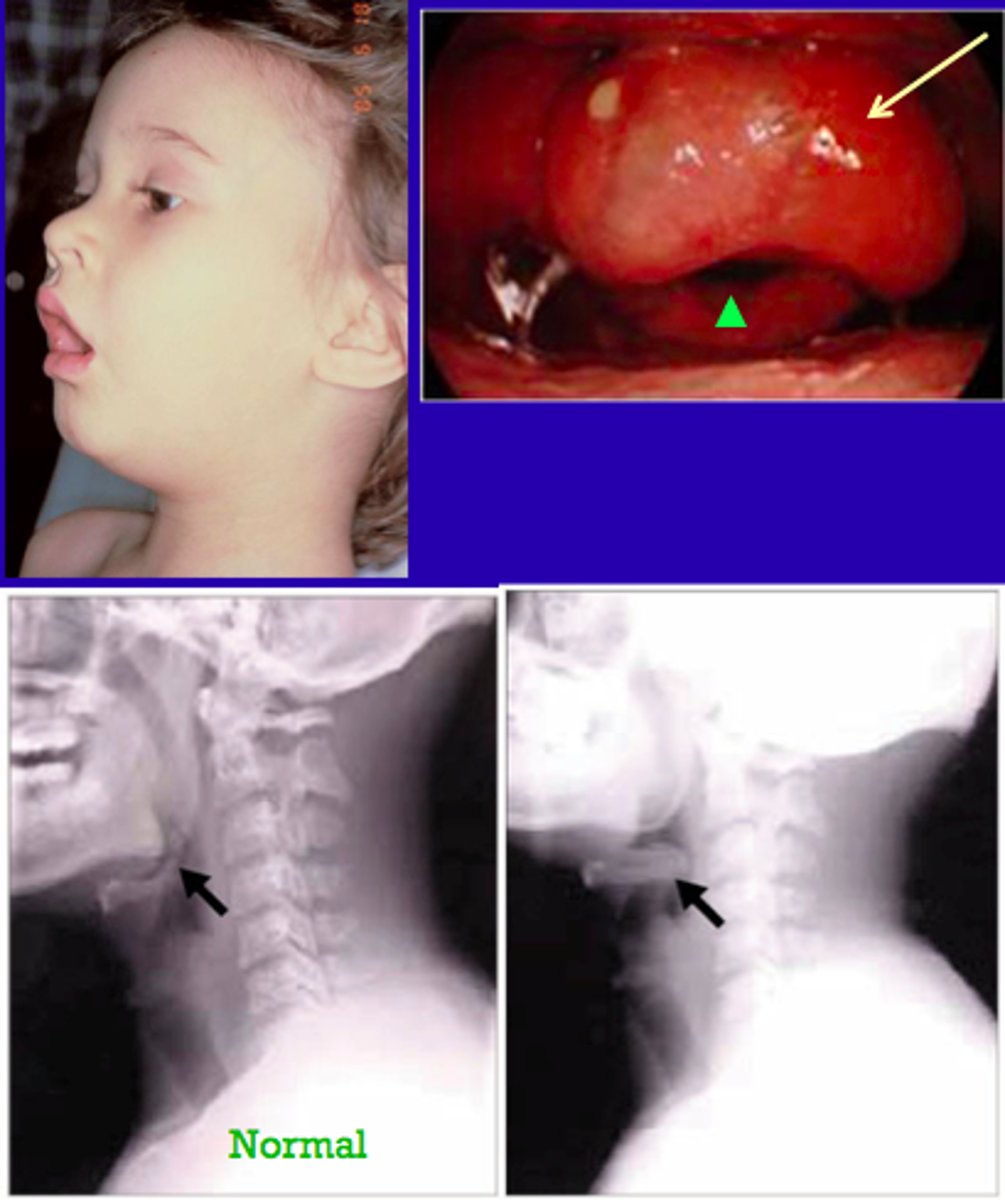
Presentation of epiglottitis
Dysphagia, drooling, respiratory distress
Tripod position
Stridor
Croup
acute viral infection of infants and children with obstruction of the larynx, accompanied by barking cough and stridor
Brochiolitis
inflammation of the small bronchioles
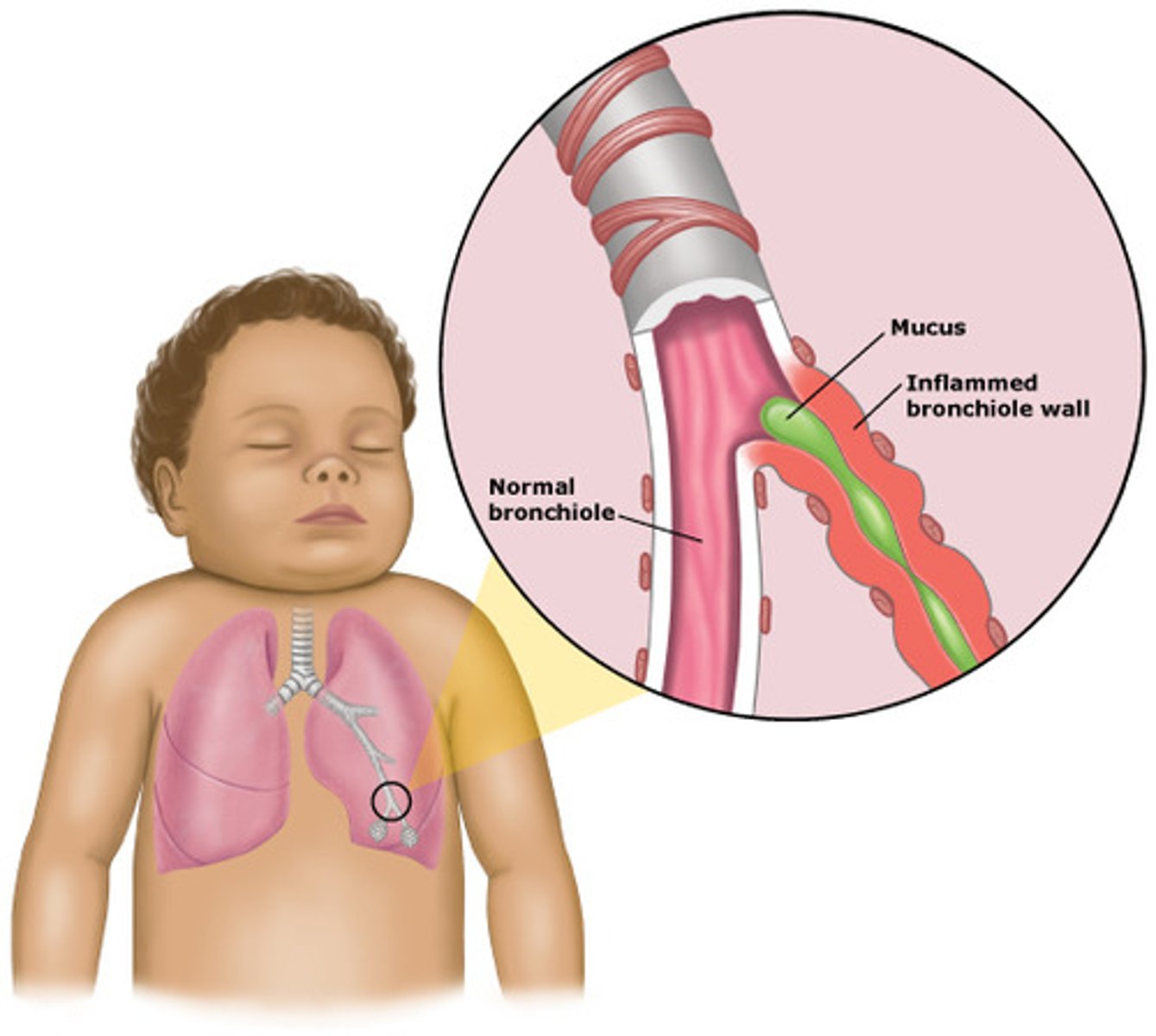
Most common cause of bronchiolitis
RSV (respiratory syncytial virus)
Cystic Fibrosis
A genetic disorder that is present at birth and affects both the respiratory and digestive systems.
Bronchoconstriction
reduction in diameter of a bronchus
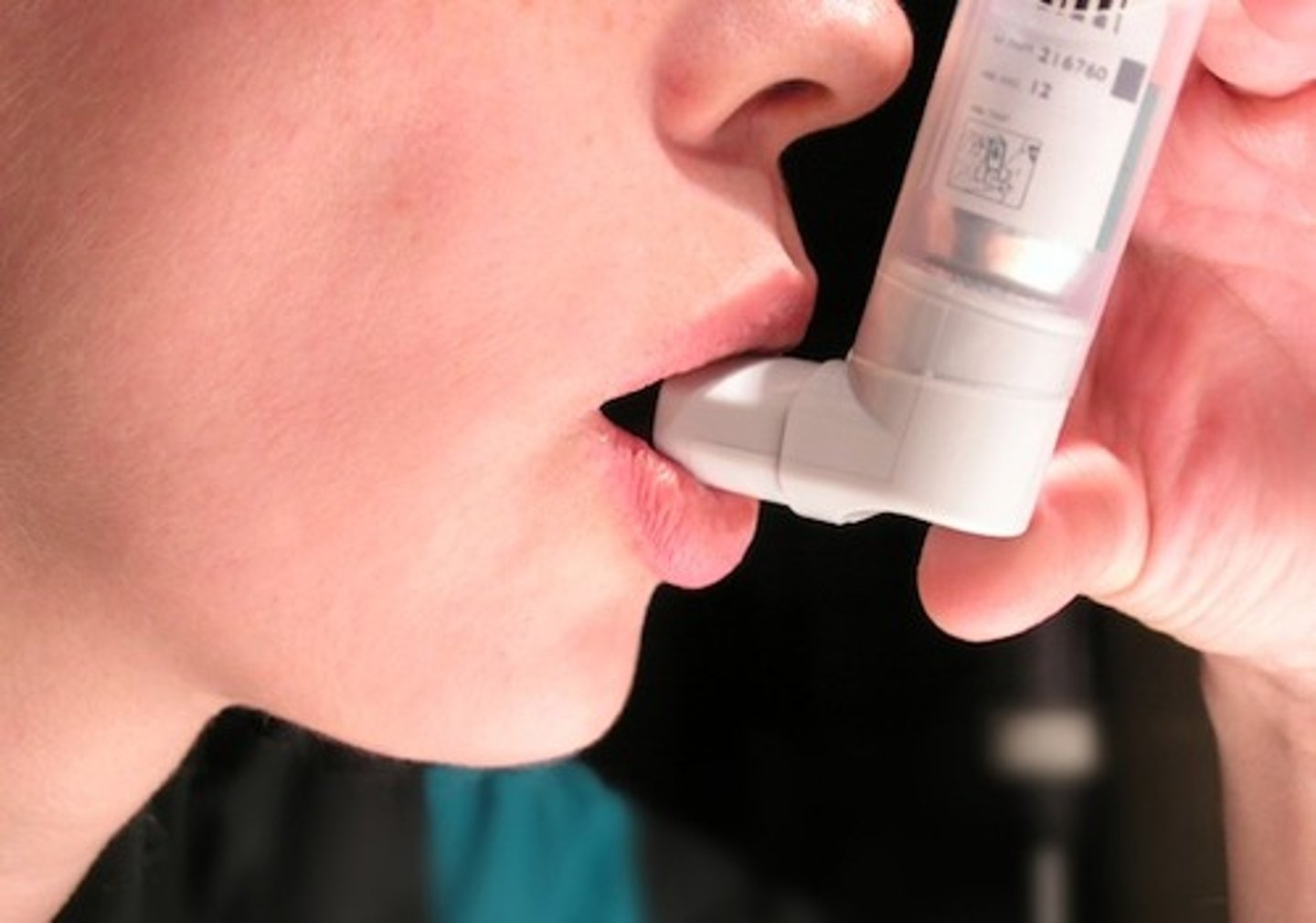
Inhaler
A spray device with a mouthpiece that contains an aerosol form of a medication that a patient can spray into his airway.
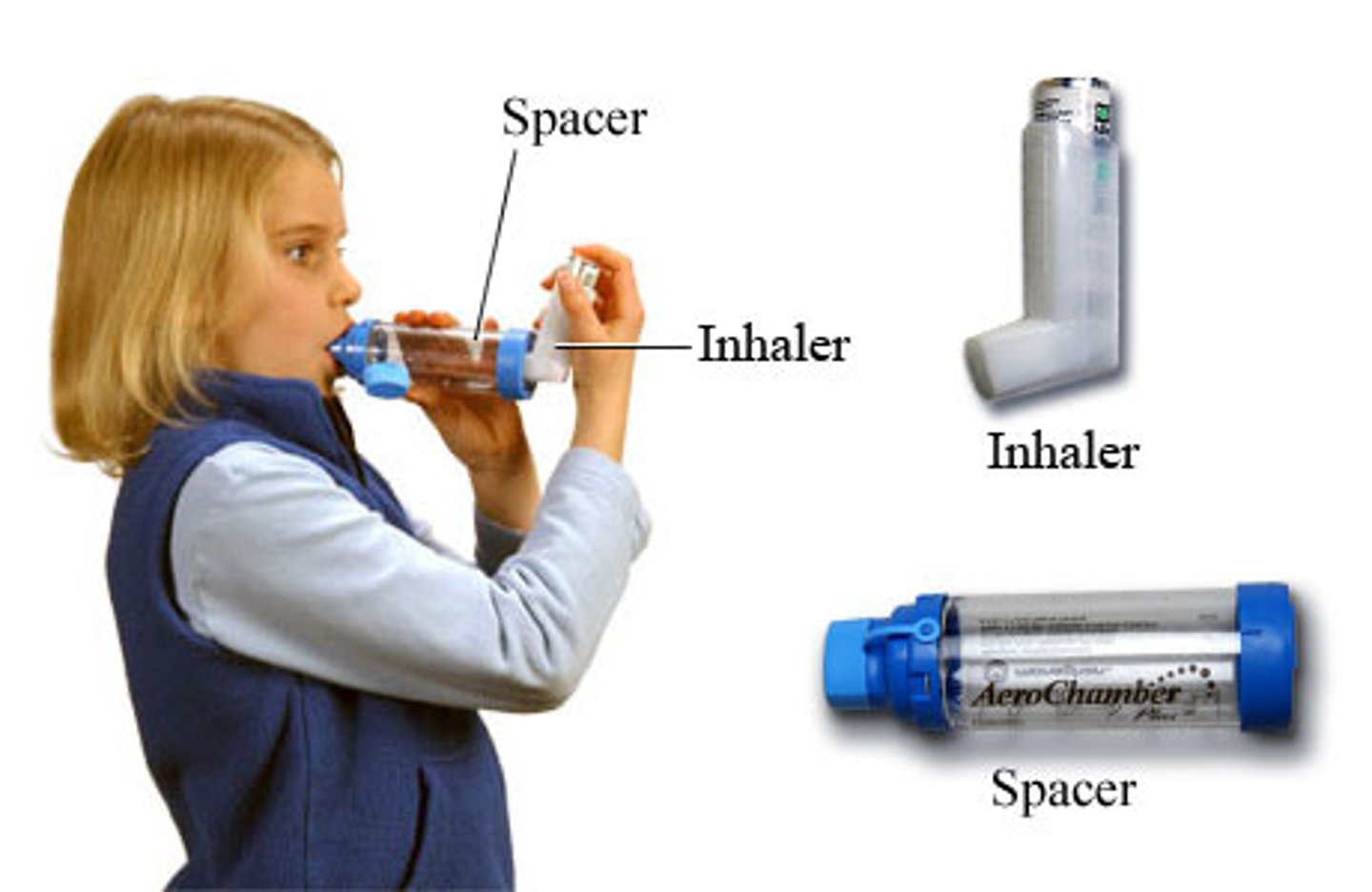
Spacer
a chamber that is connected to the metered-dose inhaler to collect the medication until it is inhaled

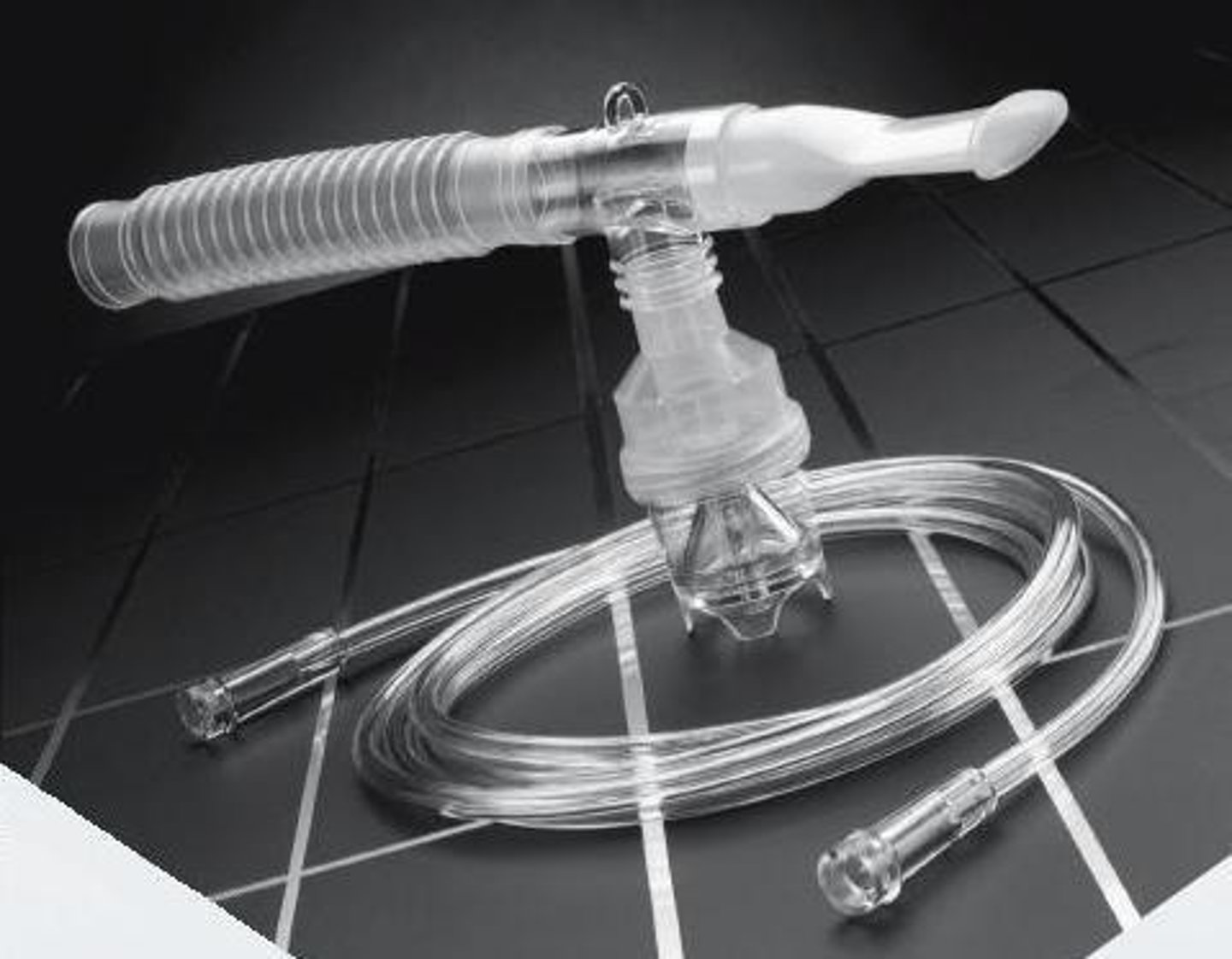
Small Volume nebulizer
-can be used to deliver respiratory meds through a fine mist that patient inhales
-albuterol usually (bronchodilator)
-can treat asthma and COPD
Albuterol
Bronchodilator
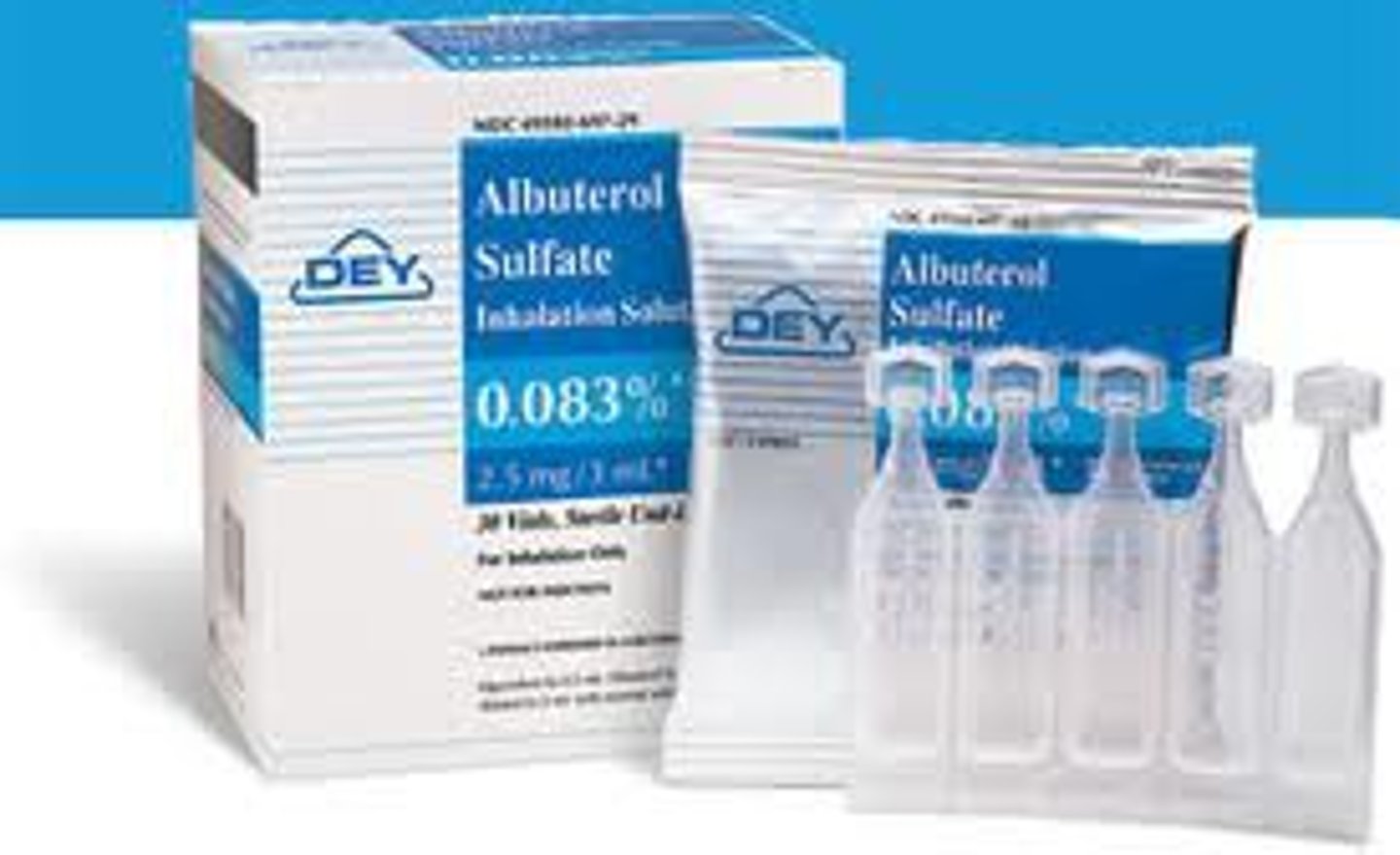
Albuterol Dose
2.5-5mg Neb

Xopenex (Levalbuterol)
Bronchodilator
Xopenex dose
1.25 mg Neb
Side effect of albuterol
tremors and tachycardia
Nebulizer
device that creates a mist used to deliver medication for giving respiratory treatment
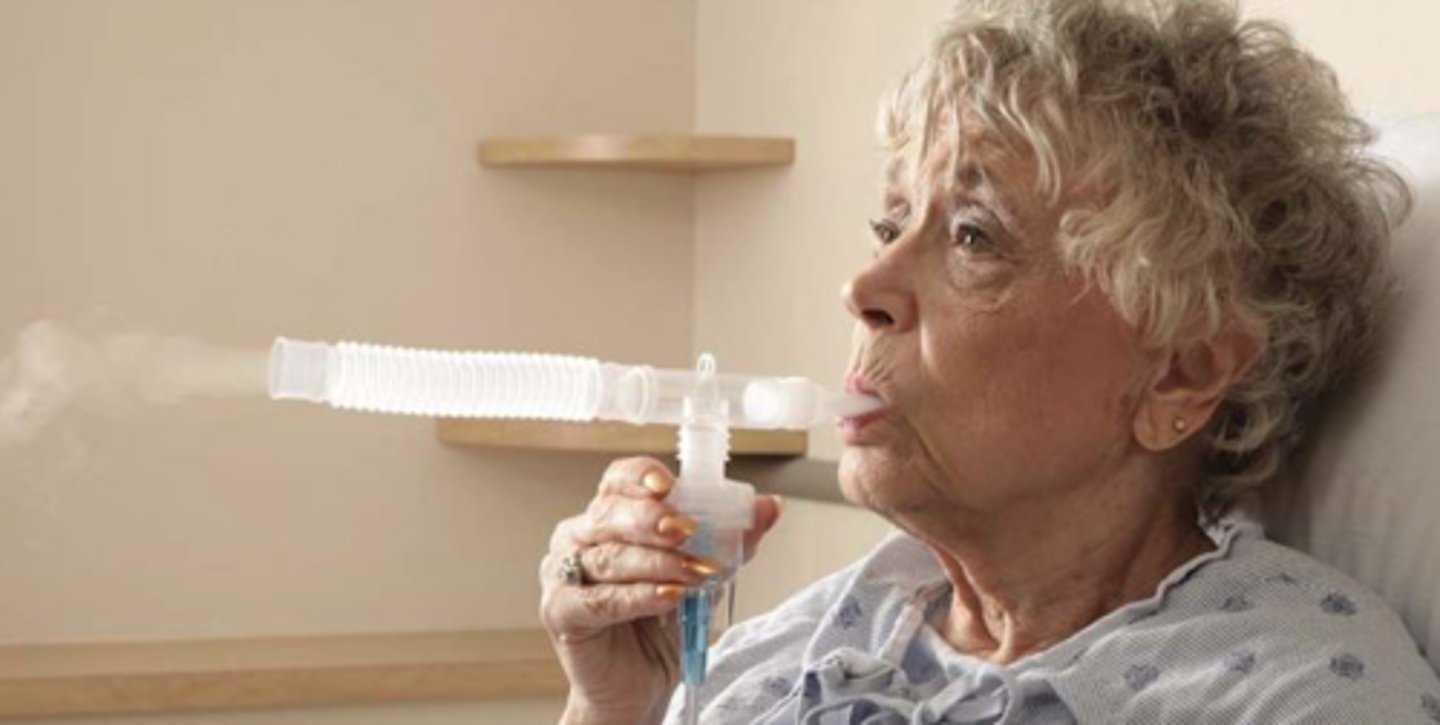

Nebulizer flow rate
6-8 lpm
Nasal Cannula
An oxygen-delivery device in which oxygen flows through two small, tubelike prongs that fit into the patient's nostrils; delivers 24% to 44% supplemental oxygen, depending on the flow rate.
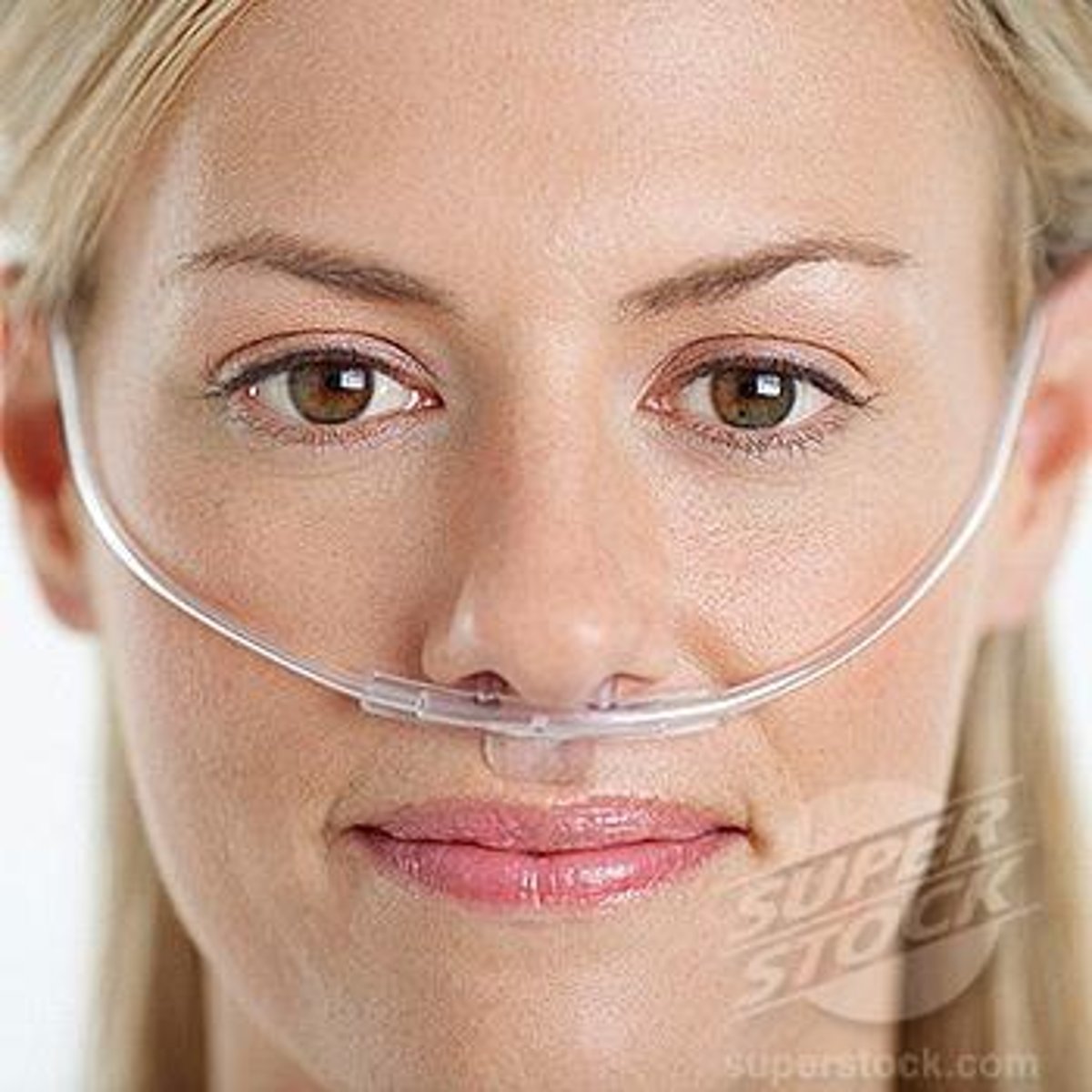

Nasal cannula flow rate
1-6 lpm

Nonrebreather Mask
A face mask and reservoir bag device that delivers high concentrations of oxygen. The patient's exhaled air escapes through a valve and is not rebreathed.
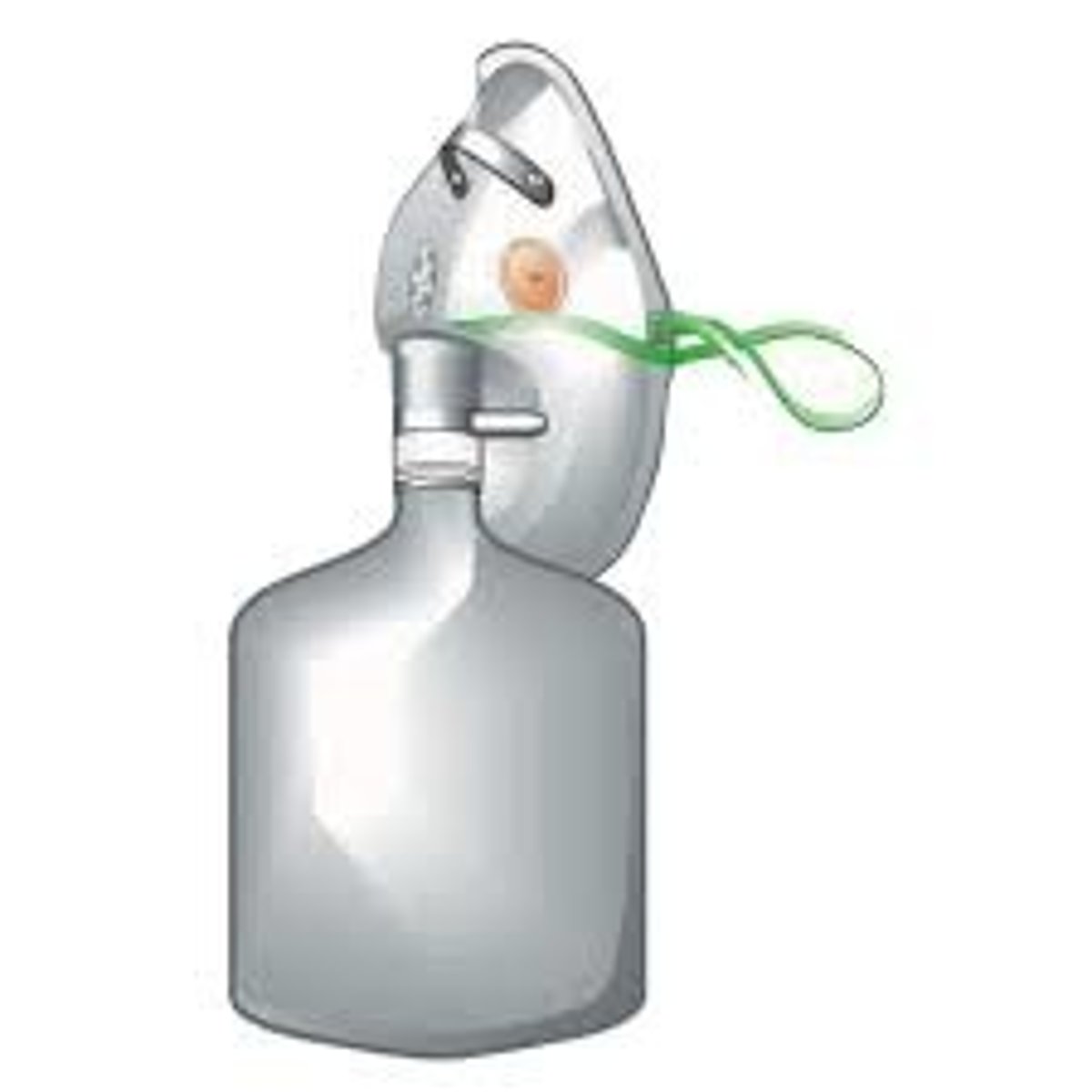

Flow rate for a nonrebreather mask
10-15 LPM

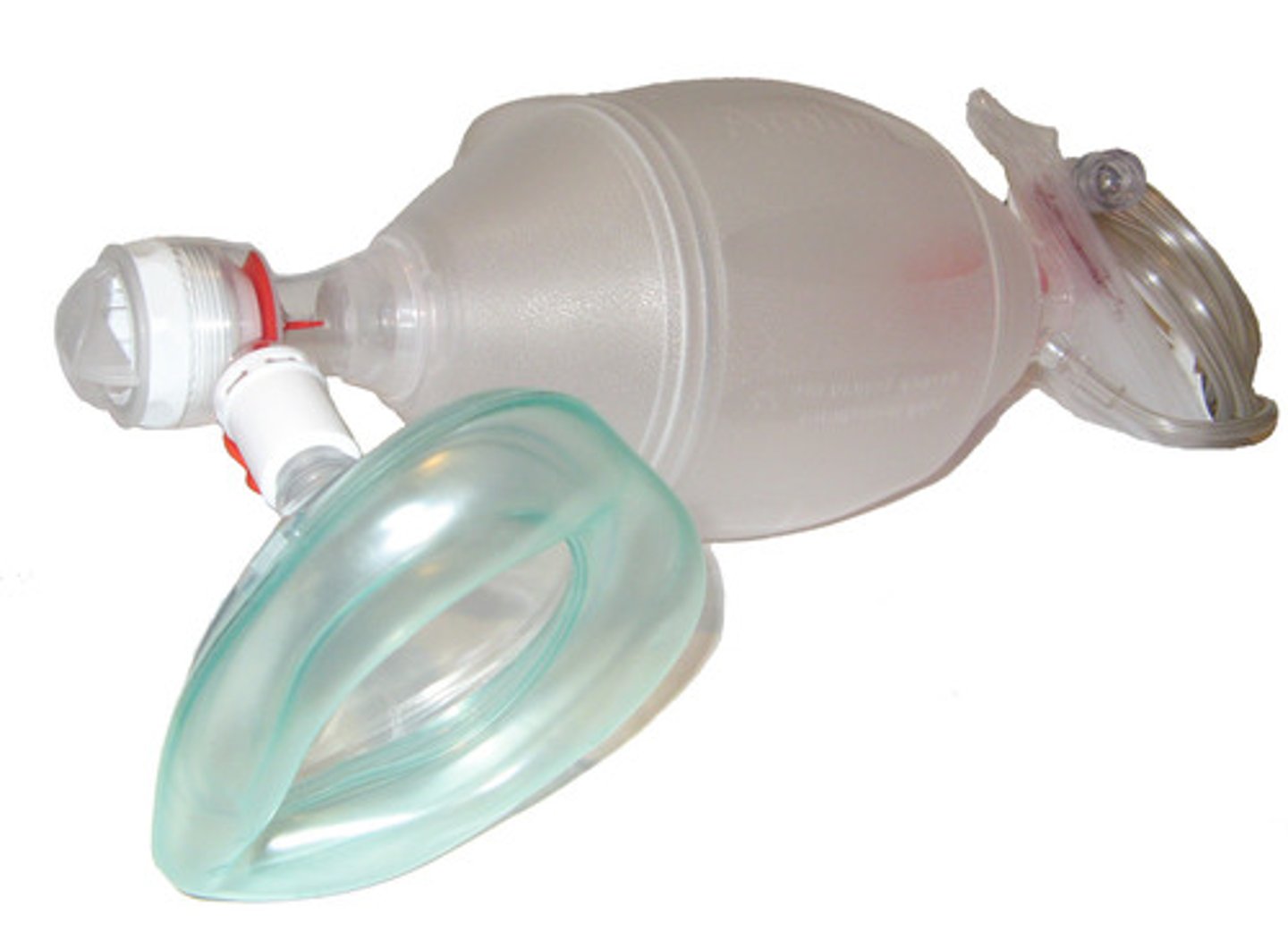
BVM
Bag-Valve-Mask Resuscitator
hand held device attached to a resuscitation mask that is used to ventilate a victim in respiratory arrest or when performing CPR. It requires two rescuers: one to maintain a tight seal for the mask, one to squeeze the bag
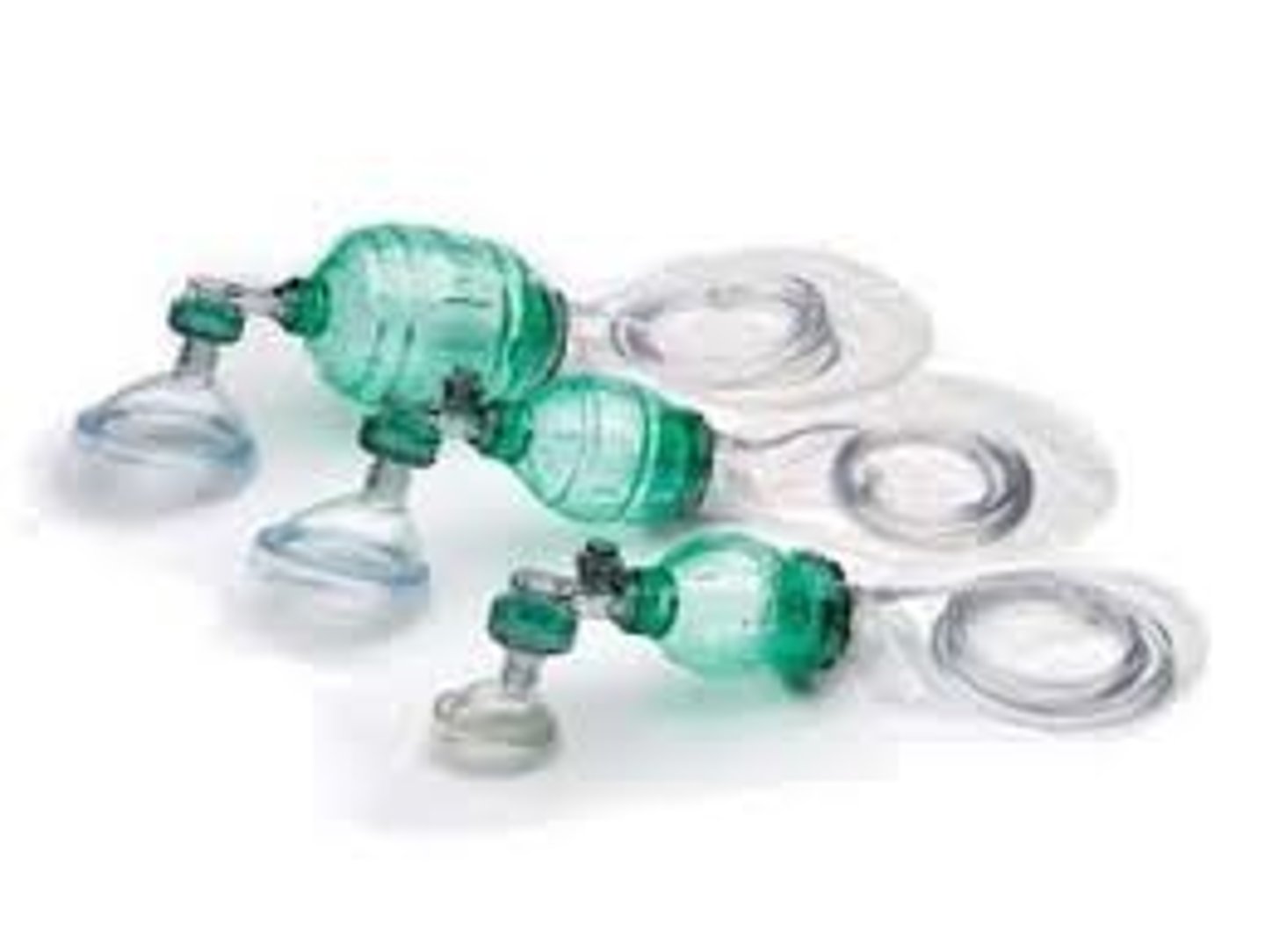

Flow rate for BVM
15-25 LPM