Water cycle and climate change
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
How is electromagnetic radiation reflected?
Reflected by clouds, ice sheets and deserts.
How does radiation enter and leave the Earth?
Incoming short-wave radiation
Upwelling long-wave (terrestrial) radiation
Long-wave radiation absorbed by the atmosphere is the greenhouse gases e.g carbon dioxide and methane.
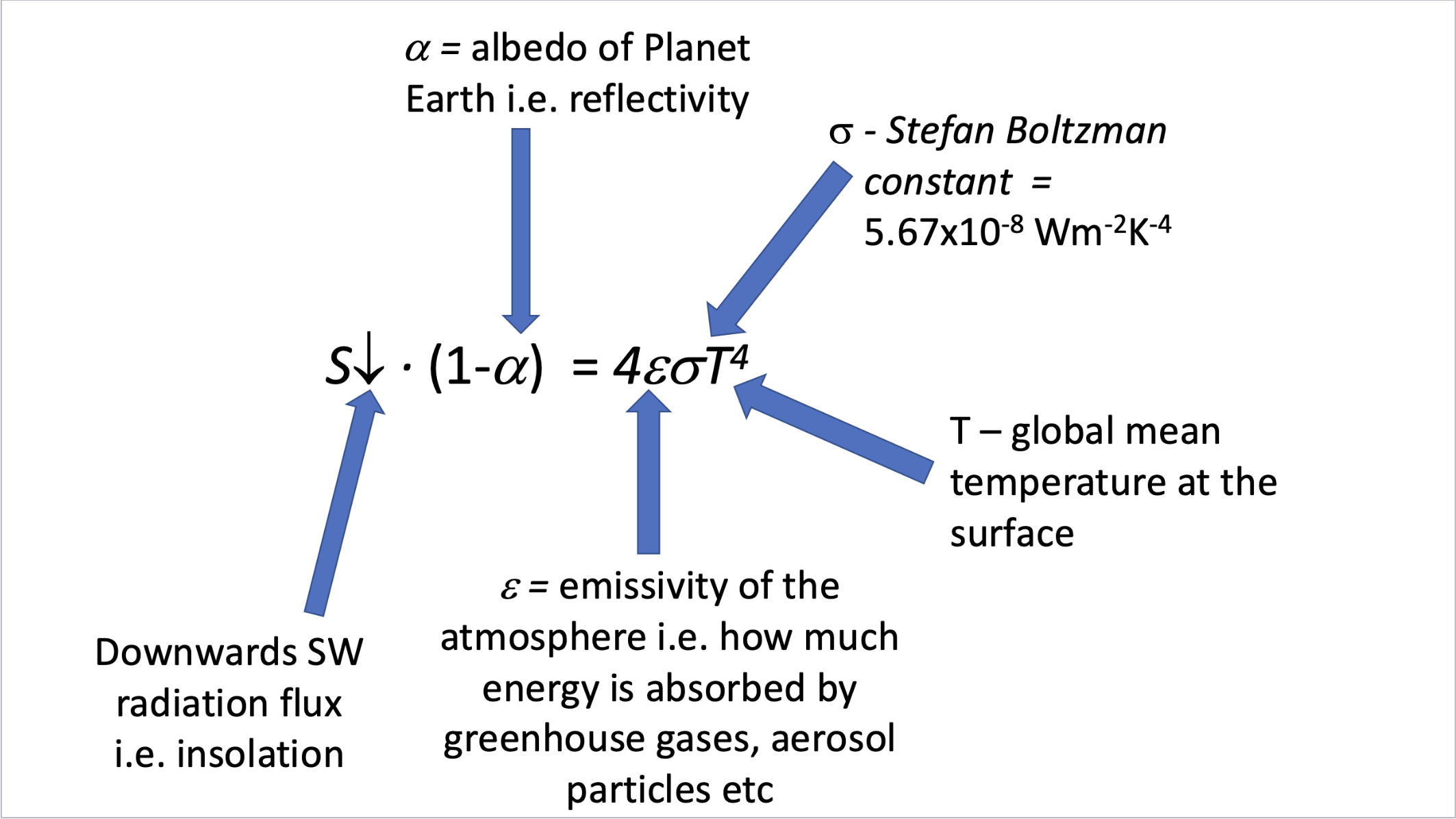
What is the equation for estimating global mean temperature?
At global equilibrium, absorbed solar energy equals emitted thermal energy.
emissivity = 0.6 - Earth’s natural greenhouse effect.
How is climate forcing related to change in global mean temperature?
Positive forcing - warming
Increased greenhouse gas emissions
Melting ice, decreases albedo.
Negative forcing - cooling
Volcanic aerosols
Increasing albedo, painting white.
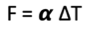
Can you name some feedback loops.
Climate cooling = Tundra = vegetation = high albedo = more reflected.
Increased precipitation = forest = increased water vapour.
Increased CO2 = warming = melting of ice and snow = decreased albedo more darker surface = warming.
How are clouds important feedbacks?
they reflect sunlight
high clouds - trap heat and act as a greenhouse gas
low clouds - reflect more sunlight
What is Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity (ECS) and what feedbacks is it largely determined by?
ECS is the long-term increase in global mean temperature resulting from a doubling of atmospheric CO2.
uses the climate forcing equation.
Determined by:
water vapour
snow and ice
clouds
How is Earth System sensitivity (ESS) different from ECS?
ESS considers slower feedbacks like
ice-sheet retreat
forest die-back
methane
How does water coming from the land surface play a role in climate change?
Energy not used to evaporate water goes into heating the land or air instead.
Stomata allows plants to absorb the CO2 and release water vapour and oxygen. Stomata open less often when CO2 is higher because they can grow without opening up.This means less water vapour is released and so more energy is used to heat the air than evaporate = high temps during day.
Less water vapour also means less clouds and so hotter as they are not reflecting radiation.
How are water fluxes in the climate system observed?
Primarily using satellites that measure reflected short-wave and emitted long-wave radiation to infer clouds, water vapour, snow/ice, and precipitation, supported by ground-based precipitation measurements.