Organisational Design
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is an organisational structure?
An organisation structure is the way in which a business is arranged to carry out its activities.
What does the organisational structure / design of a business define?
Roles of employees.
Route through which decisions are made.
Communication channels.
Relationship between positions.
Responsibility and accountability.
What is a hierarchy?
Refers to the ranking of the workforce in terms of importance and power, whereby people at the top of the organisational structure have the most power and those at the bottom have the least.
What is the chain of command?
The route through which information and authority pass through the levels of the hierarchy.
What is the span of control?
The number of subordinates directly answerable to a manager.
What are the types of organisational structures?
Traditional hierarchical structure
Matrix structure
What is a traditional hierarchal structure?
A series of levels within a business where each level has responsibility and authority over the levels below.
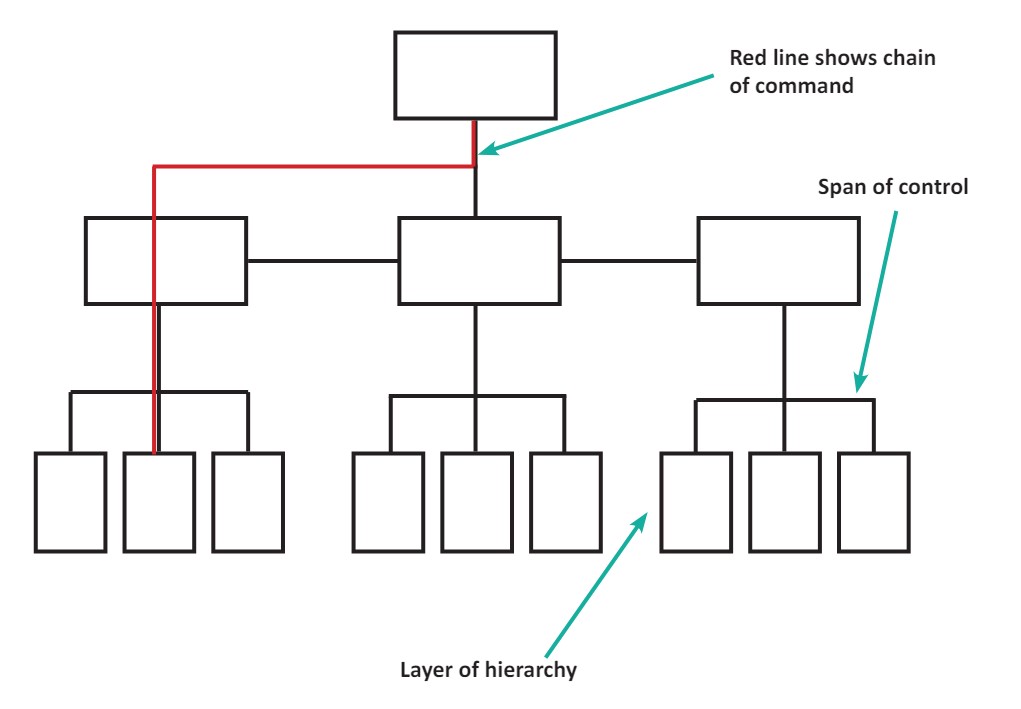
What are the 2 types of traditional hierarchical structures?
Tall organisational structure
Flat organisation structure
What are the features of a tall organisational structure?
Long chain of command
Many levels of hierarchy
Narrow span of control
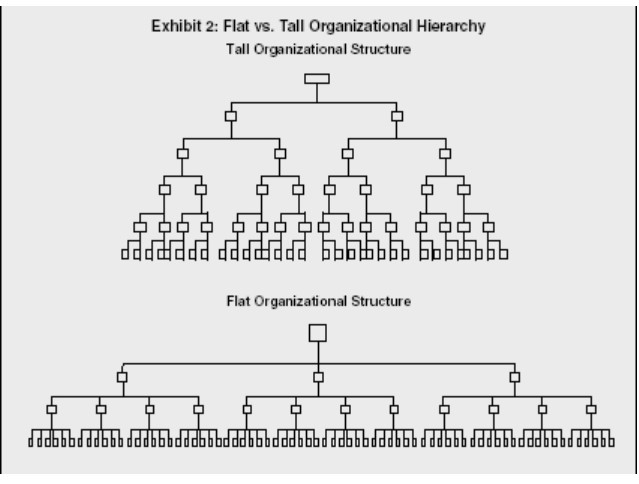
What are the advantages / disadvantages of a tall organisational structure?
Advantages:
Control is at the centre, and senior management fully understand exactly who does what, and what their responsibilities are.
Paths of communication and responsibility are clearly defined.
Departments understand their position in relation to other departments within the organisation.
Each worker knows how they fit into the organisational structure.
Disadvantages:
Vertical communication is difficult, with information that is received by management distorted by the layers it must pass through. Very long chains of communication could even mean that instructions are out of date by the time they are received.
Communication between different departments is hampered by the lack of direct contact between departments.
What are the features of a flat organisational structure?
Short chain of command
Few levels of hierarchy
Wider span of control
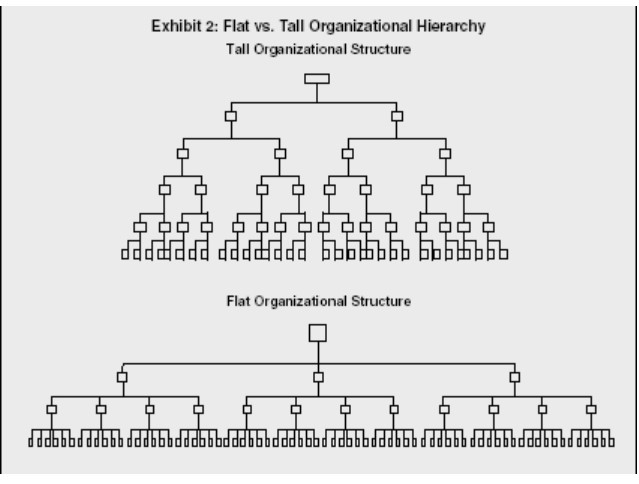
What are the advantages / disadvantages of having a flatter organisational structure?
Advantages:
Increased motivation as a result of the delegation of authority.
Decisions are made more quickly by those nearest the ‘ground’.
Communication is quicker and suffers less distortion.
Empowerment of workers.
Disadvantages:
Loss of control of the workforce.
What is delayering?
Involves removing one or more layer of management from the hierarchy leading to a flatter structure with wider spans of control.
What are the benefits of delayering?
Cut costs as fewer managers needed.
Shorten chain of command so communication is improved.
Leads to empowerment as wider spans of control will make delegation necessary.
What are the drawbacks of delayering?
Fewer opportunities for promotion may demotivate.
Greater workload on those with wider spans of control.
Initial cost may be high- business must pay redundancies.
May lose important talent.
What is a matrix organisational structure?
Emphasis on getting people with particular skills into project teams.
Workers work under a number of managers on different projects rather than in a fixed role in hierarchical structure.
Give some advantages / disadvantages of having a matrix structure.
Advantages:
It allows individuals with specific skills to contribute to a number of different projects.
It breaks down barriers to communication and ensures that projects can be better coordinated.
It helps ideas and innovation spread throughout the business.
Disadvantages:
Can require expensive support systems – extra secretarial and office staff.
Co-ordination and/or communication problems may occur as people are drawn from different departments. This can also slow down the decision making process.
Employees can have divided loyalties – conflict can occur between project and department managers.
What is delegation?
Involves the assignment of authority for particular functions/tasks/decisions to others within the organisational structure.
What is centralisation?
When decision making is kept to the top level of an organisational structure and there is little/no delegation to lower levels.
What is decentralisation?
When decision making is spread throughout the organisation and is delegated to lower levels of the hierarchy.
*Associated with a flat structure, with few layers and a wide span of control.
What is empowerment?
Refers to giving someone the power / responsibility to carry out specific duties and make certain decisions.