2. Evidence based medicine
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
True.
T/F: No research project or source of information is perfect.
clinical reasoning; evidence based medicine
Epidemiology is the basic tool of ____ and the root of ___
dogma
What term is defined as: Beliefs and explanations accepted by experts as truth, often without the support of strong and verifiable empirical evidence.
empirical evidence
What term is defined as: (Facts) obtained by analysis of unbiased objective data rather than reasoning or "feeling."
best evidence available
Through the philosophy of EBM, we should always base our recommendations on the .....
problem, patient or population
What does the P stand for in "PICO"
intervention
What does the I stand for in "PICO"
comparison
What does the C stand for in "PICO"
Outcome
What does the O stand for in "PICO"
F ( — strong papers that disagree are equally valuable.)
T/F: Through EBM, you should just look for papers that agree with your opinion or clinical preference.
F
T/F: Through EBM, finding papers with one or two p-values that agree is proof.
F
T/F: Through EBM, it is acceptable to use "expert opinion" or dogma as strong evidence.
F
T/F: Through EBM, when you rank evidence, you should delete the evidence that disagrees with you regardless of strength/value of paper
Formal systematic review
What am I describing?
- Tried to answer a specific question by collecting and analyzing evidence with pre-specified criteria and then a meta-analysis.
Narrative review
What am I describing?
- "what I want to teach you about / what I believe"; rarely peer reviewed.
no support (spanning 0); support (above 0)
What does it mean when it spans 0? What does it mean if its above 0?
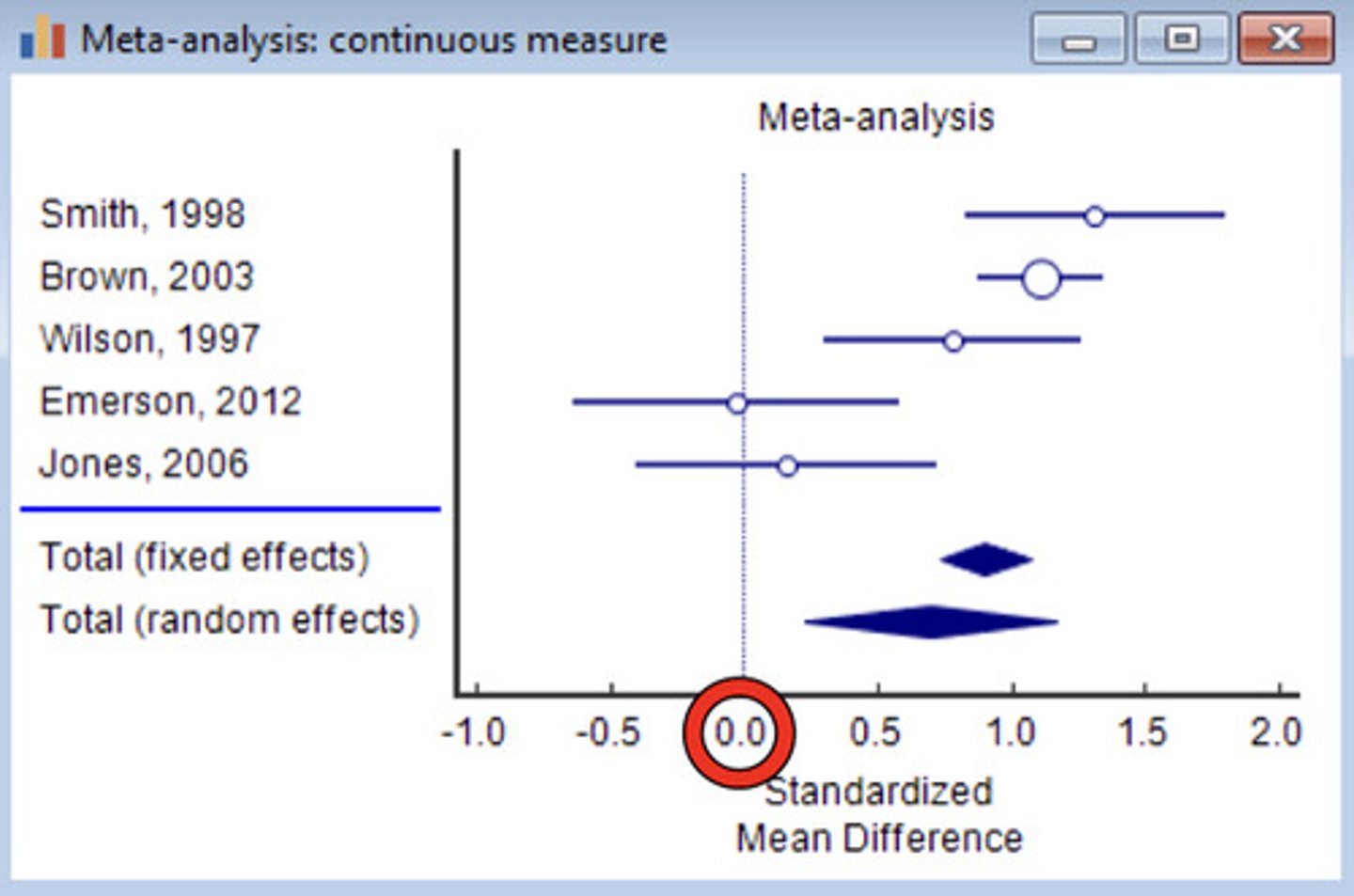
- Formulate the review question
- Define inclusion/exclusion criteria
- Locate studies and select studies
- Assess study quality
- Extract data
- Analyze and interpret results
- Disseminate findings
What are the steps of a systematic review? (7)