L1 Renal functions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Functions of kidneys
Regulation of water and electrolyte balance
Vary output of water in urine to match intake
Independently vary output of different minerals (Na, K, Mg etc) depending on intake
Excretion of metabolic waste and bioactive susbtances
Excretion of urea (from protein), uric acid (from nucleic acids), creatubube (from muscle creatine).
Excretion of drugs and hormones
Regulation of arterial blood pressure
Regulation of blood volume
Renin production (Renin-angiotensin-Aldosterine System (RAAS)
Regulation of erythrocyte (red blood cell) production
Kidney major cite of Erythropoitein (EPO) production relased by fibroblast-like cells in the interstitium of the renal cortex and outer medulla
Regulation of Vitamin D production
Active form of Vit D (Calcitriol) is made in the kidneys
Promotes calcium and phosphate absorption from the gut
Rate of synthesis regulated by hormines that control calcium and phosphate balance.
Gluconeogensis (glucose synthesis)
Synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources
Occurs during periods of fasting
Renin production (Renin-angiotensin-Aldosterine System (RAAS)
A hormone system that regulates blood pressure and fluid balance, with renin, an enzyme released by the kidneys, playing a crucial role in its activation.
Erythropoitein (EPO)
A hormone primarily produced by the kidneys that stimulates red blood cell production in the bone marrow, crucial for maintaining adequate oxygen levels in the body.
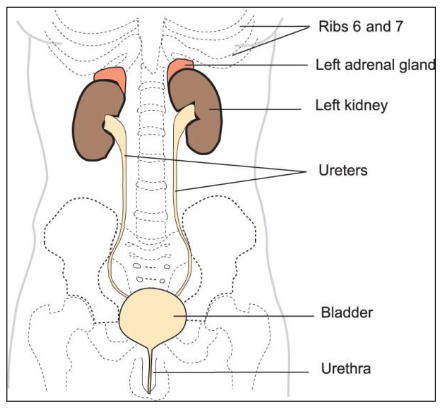
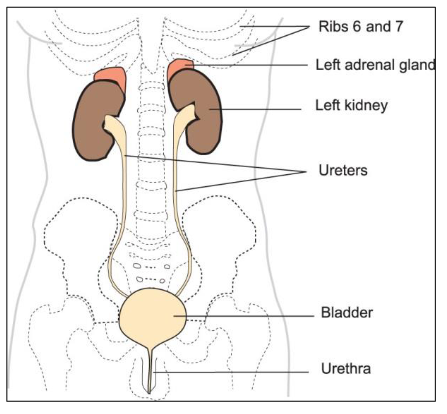
The urinary system
Kidneys (retroperitoneal)
Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
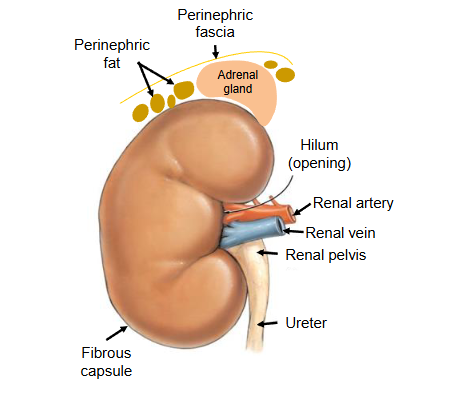
External structure of the Kidney
→ recreate with the notes on the diagram
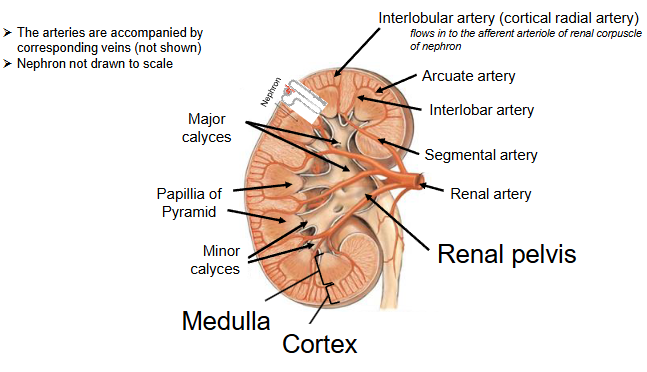
Internal structure of the Kidney
There are THREE distinct regions of the kidney:
Cortex (location of glomeruli of nephrons)
Medulla (predomianntly consists of nephron’s tubules)
Renal pelvis (major and minor calyces collect urine and empty into the renale pelvis).
Internal structure of the kidney
When identifying vessels, consider locations
Arcuate(shapes like a bow; curves) arteries and veins are the cotricomedullary boundary
Interlobular (situated between lobes) arteries and veins are in the cortex
HISTOLOGY → Internal structure of the kidney = Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining.
Boundary between the Cortex (contains the renal corpuscles) and the medulla is very clearly delineated.
Medulla is further divied into:
Outer medulla (adjacent to the cortex)
Innder medulla (adjacent to the pelvis)
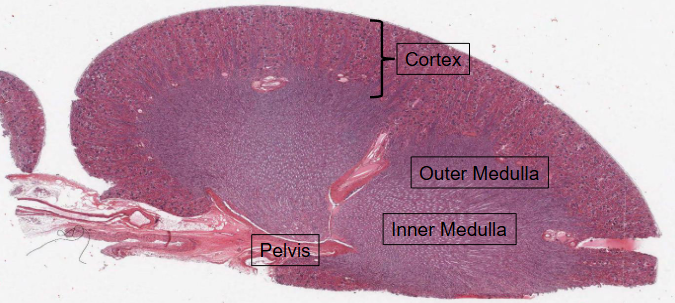
Hematoxylin
Has a deep blue-purple colour and stains NUCLEIC ACIDS.
In typical tissue, nuclei are stained blue.
Eosin
Pink and stains proteins nonsepcifically.
The cytoplasm and extracellular matrix have varyding degrees of pink staining.
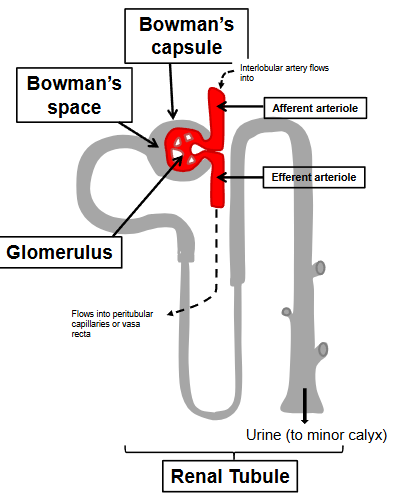
Structure of nephron
The nephrons (>1 million per kidney) are the functional units of the kidney.
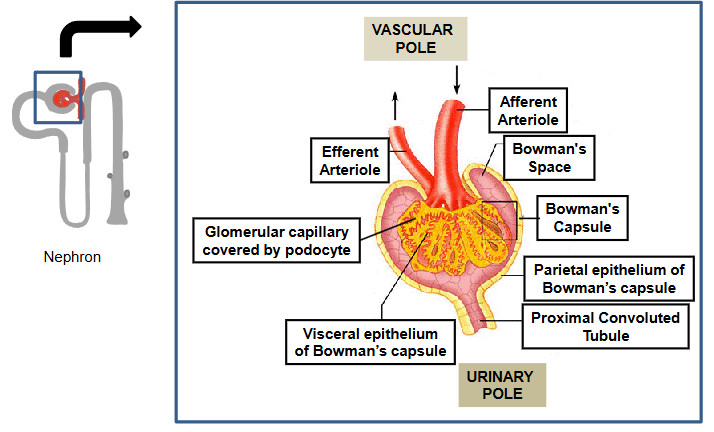
Renal corpuscle = site of filtration of the blood
(i) Bowman’s capsule
(ii) Glomerulus (tuft of capillaries)
Renal tubule
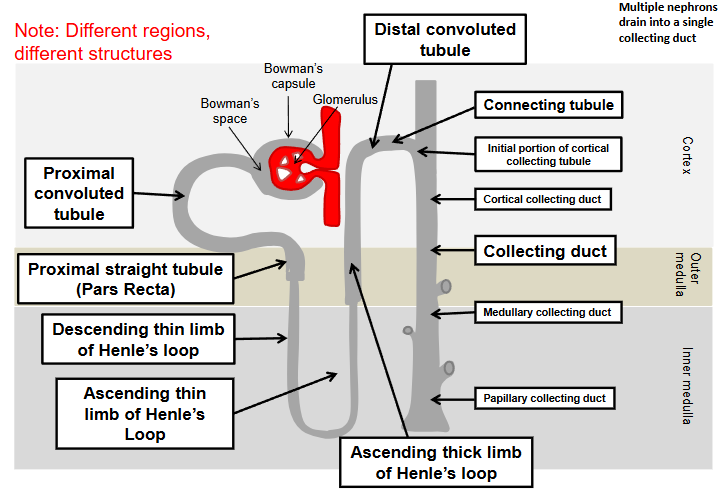
Nomenclature of the renal tubule
The Renal Corpuscle → Site of filtration of the blood
Two distinct types of nephrones in the kidney
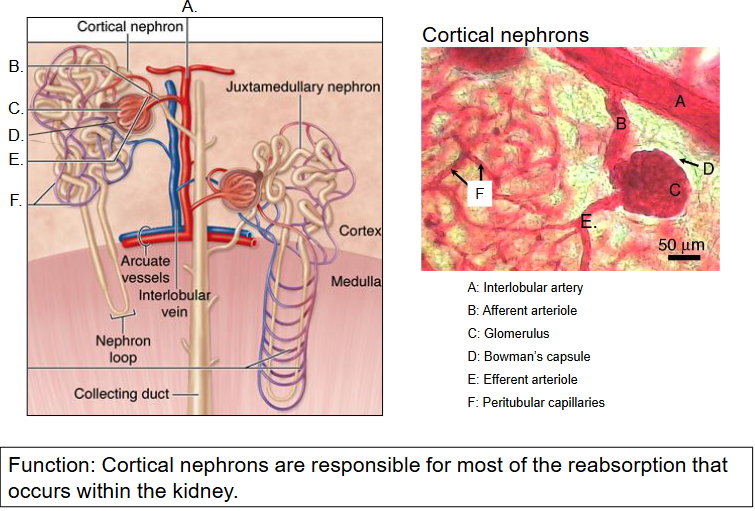
~85% of nephrons are cortical neprhones (also called superficial nephrons)
A. The corpusle lies IN THE OUTER CORTEX; short loops of Henle that barely penetrate the medulla.
B. Blood supply: the efferent arteriole taking blood away from the glomerulus enters a capillary netwrok called the peritubular capillaries that rejoin at the interlobular vein.
C. Function: These neprhores are responsible for the most reabsorption that occurs within the kidney.
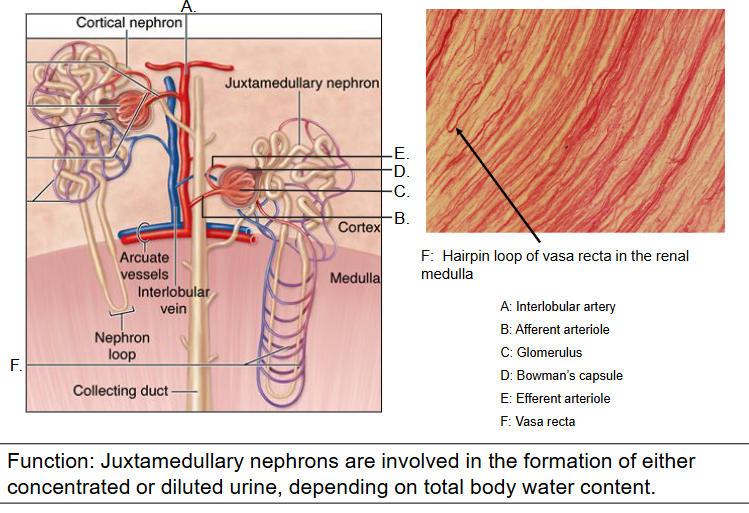
~15% of nephrons are juxtamedullary nephrons
A. The corpuscle lies IN THE INNER CORTEX; long loops of Henle that reach deep into the medulla
B. Blood supply: The efferent arteriole takeing blood away from the glomerulus follows the loop of Henle down into the medulla in a set of long loops (vasa recta) that rejoin at the interlobular vein.
C. Function: These nephrons are involved in the formation of both concentrated and diluted urine.
Cortical nephrons diagram
Juxtamedullary nephrons
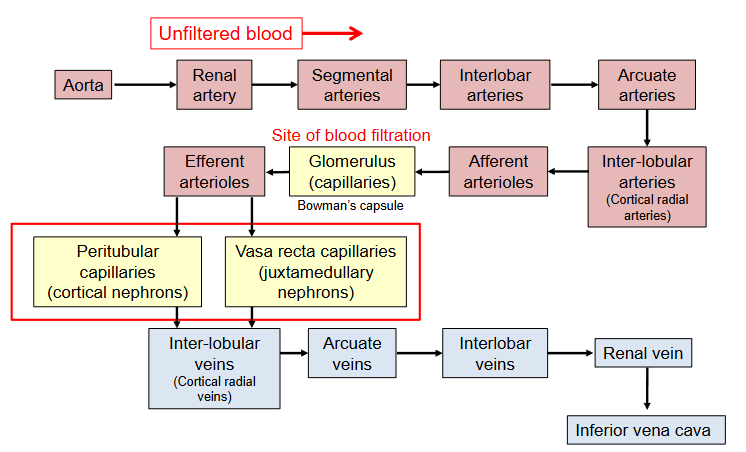
Renal blood supply
Blood flow is reduced from fortex to inner medulla
Prevents hyperosmolar gradent in medullary interstitium from being washed away.
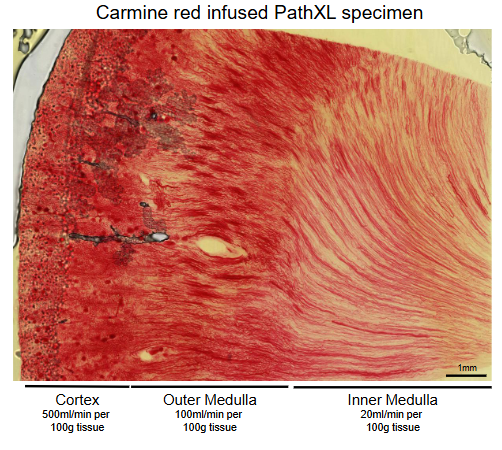
Summary slide of renal blood supply
Breakdown of how blood is being filtered, urea/urine being made etc.