Biomed Pregnancy
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Pre-eclampsia/ eclampsia
unpredictable onset of convulsion during pregnancy or postpartum unrelated to cerebral pathological conditions
significant cause of maternal death
incurable except for removal of fetus (balance between fetus being viable and mums health)
risk factors = genetic predisposition, maternal characteristics, comorbidities, placental disease, immune factors and multifetal pregnancy
Eclampsia Characteristics
increase in BP >15mHg diastolic or >30 mmHg systolic (pregnancy increase BP naturally)
protein uria (0.3g/24hr) when it is sustained
and/ or edema
HELLP (H-haemolysis, EL - elevated liver enzyme activitym LP - Low platelets)
Eclampsia Clinical Manifestations
suspected in absence of proteinuria when patient has headache, blurred vision, abdominal/ epigastric pain, altered biochemistry (low platelets and abdominal liver enzymes: ALT, AST and GGT)
2 types
middle of pregnancy (more serious)
later stages of pregancy (less serious)
eclampsia pathological changes if not managed
brain - haemorrhage
liver - haemorrhage and necrosis
heart - subendocardial necrosis
kidney - endothelial glomeruloendotheliosis
decidual vessels - decreased limunal diameter
pre-eclampsia superimposed on hypertentsion (women that have hypertension previous to pregnancy)
may occur in women with pre-existing hypertension <20 weeks gestation who develops
new proteinuria >0.3g / 24 hr
sudden increase in pre-existing hypertension and proteinuria
thrombocytopenia (platelet count < 100 × 10 ^9/L)
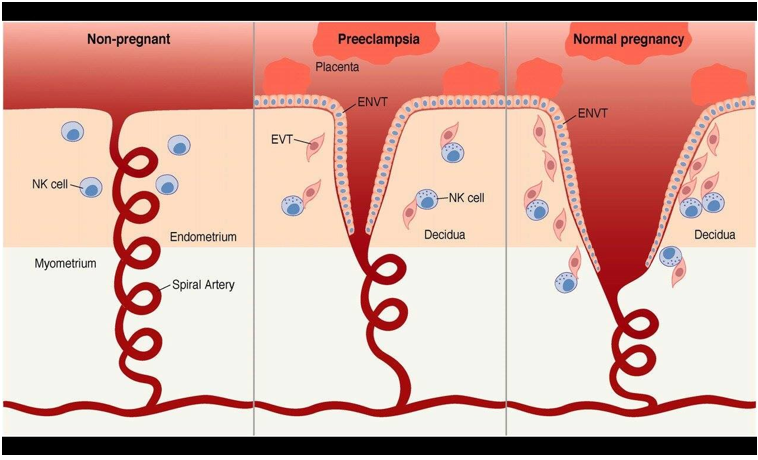
Placentae of pre-eclamptic women
Due to smaller cleft it is poorly perfused, abnormally implanted and excessively large in size
Need broad opening for pulsatile blood flow in pre-eclamptic women there is a small trickling of blood
ENVT = extravillous trophoblasts (placental cells) that grow into endometrial and myometrial layer
Pre-eclampsia pathophysiology
inadequate invasion of the spiral arteries by the trophoblastic cells
decreased uteroplacental perfusion occurs
vasoconstriction and decreased plasma volume, haemoconcentration and edema
vasoconstriction and DIC
what are sFlt-1 and sEND
2 hallmark antigens in ciruclation, if increased then increases chance lady develops pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia: pathology - blood
hypertension and endothelial damage affects capillary permeability
plasma leaks from damaged blood vessels = decrease in colloid osmotic BP and edema in the intracellular spaces
produced hypovolemia nd haemoconcentration reflected in increase in haematocrit
severe cases the lungs become congested as consequence of pulmonary edema (impaired oxygenation & cyanosis)
Pre-eclampsia: pathology - Coagulation
increase platelet consumption - thrombocytopenia
may be responsible for disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
characterised by —> low platelets, prolonged prothrombin time and low fibrinogen levels
fibrin and platelets subsequently laid down occludes (damages) blood flow to kidneys, liver, brain and placenta
Pre-eclampsia: pathology - kidneys
Vasospasm of afferent arterioles leads to decrease renal blood flow = hypoxia and edema
Glomerular-endotheliosis allows plasma proteins in the form albumin to fitler into the urine - proteinuria
renal damage is reflected by reduce creatinine clearance and increase serum creatinine and uris acid levels
oliguria ensures (increase volume of urine)
Pre-eclampsia: pathology - liver
vasoconstriction of the hepatic vascular bed
leads to hypoxia and edema of liver cells
extreme swelling of the liver may lead to epigastric pain and rupture
falling albumin
increase in liver enzymes - ALT, AST, GGT
Pre-eclampsia: pathology - brain
hypertension with cerebrovascular endothelial dysfunction leads to increase in permeability of blood brain barrier
lead to edema and microhaemorrhage
headaches, visual disturbances and CONVULSIONS (if this occurs tipping over into eclampsia)
hypertensive encephalopathy autoregualtion of cerebral blood flow impaired leading to cerebral vasospasm, cerebral edema and blood cot formation)
Pre-eclampsia; pathology - feta placental unit (baby and placenta)
hypertension induced vasoconstriction decrease uterine blood flow
decrease blood flow to choriodecidual spaces diminished amount of O2 that diffuses
ischemia of placental tissues ensures
capillaries in choronic villi thrombose, infarction occurs and baby born small
hormonal output is impeded (e.g., leptin)
Pre-eclampsia affect Brain
Symptoms - headaches and visual disturbances
Signs - brisk reflexes and clonus (involuntary, rhythmic, and jerking muscle contraction)
Investigations - N/A
Complications - Eclampsia, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, and intracranial haemorrhage
Pre-eclampsia affect Renal (Kidneys)
Symptoms - N/A
Signs - N/A
Investigations - proteinuria and raised serum creatinine
Complications - Acute kidney injury
Pre-eclampsia affect hepatological (Liver)
Symptoms - epigastric pain
Signs - right upper quadrant tenderness
Investigations - elevated serum liver enzymes (ALT, AST, GGT)
Complications - hepatic haematoma or rupture
Pre-eclampsia affect Haematological (Blood)
Symptoms - N/A
Signs - dark brown urine and petechiae
investigations - low platelets, abnormal clotting tests and haemolysis
Complications - coagulopathy
Pre-eclampsia affect uteroplacental and fetal
symptoms - vaginal bleeding and reduced fetal movements
signs - hard uterus and reduced fundal height
investigations - fetal growth restriction
complications - placental abruption and intrauterine fetal death
pre-eclampsia affect cardiorespiratory
symptoms - breathless, chest pain, and confusion
signs - tachypnoea (rapid breathing)
investigations - decreased oxygen saturation and diastolic dysfunction
complications - pulmonary edema
Pre-eclampsia treatment
aim to prolong pregnancy till fetus is mature to survive (deciding when to deliver baby depends on materal conditions vs fetal maturity)
antihypertensives assist in protecting against cerebrovascular accident
theories that are looking at viagra (increases blood flow)
Affect on Mother
miRNA 21-23 nucleotides dont get reduced —> go from placenta to mothers circulation target and stops transcription —> downregulated causes order expression of gene
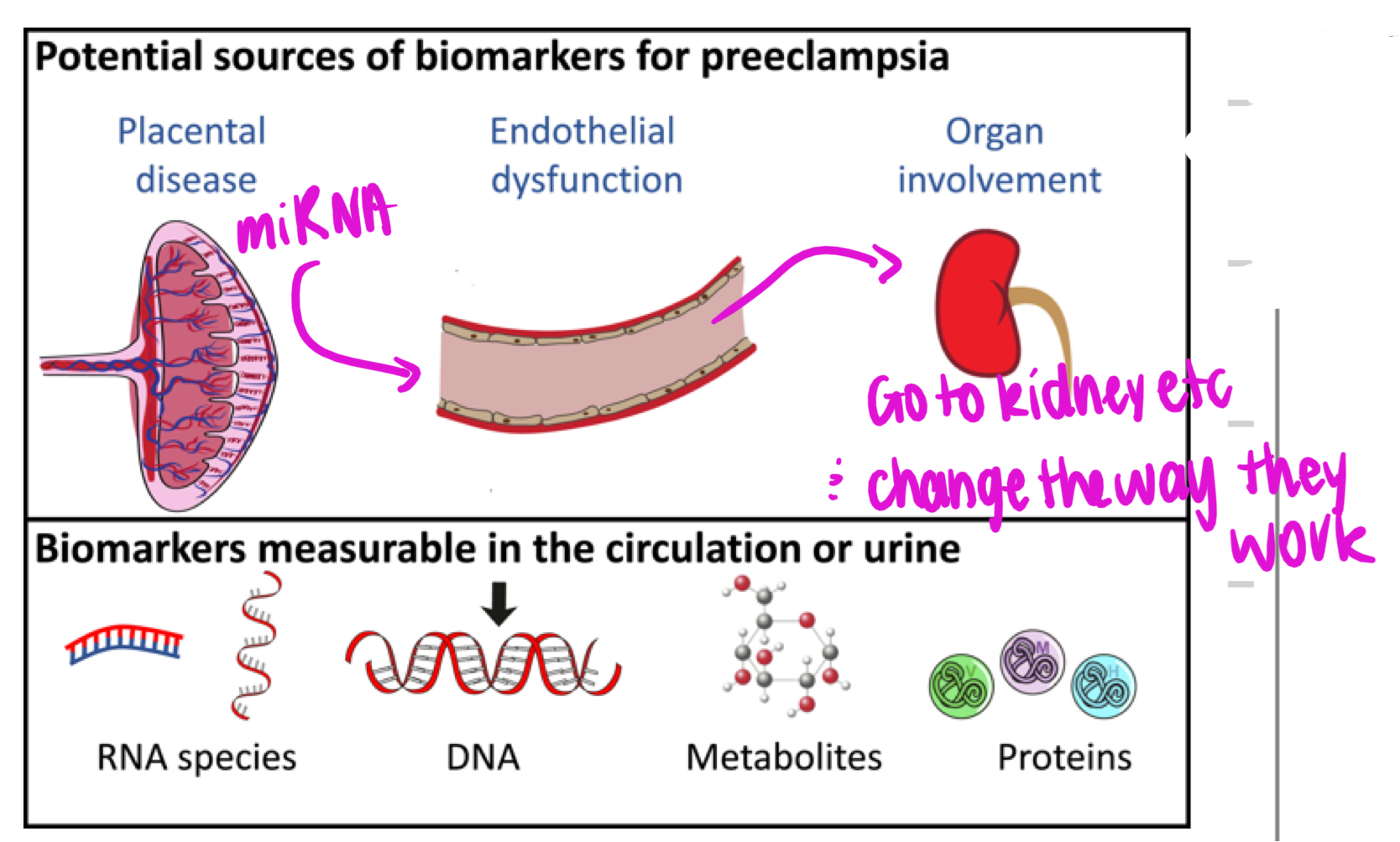
Development of pre-eclampsia
Mix of genetic, environmental, immunological and metabolic factors
abnormal trophoblast invasion and differentiation
placental ischemia/ hypoxia
angiogenic factor imbalance (decreased PIGF absence (sFlt) and increase VEGF and PIGF
endothelial dysfunction = hypertension proteinuria edema, hepatic ischemia, activated coagulation system and cerebral edema
Ectopic Pregnancy
implantation of enbryo within fallopian tube, ovary wall, cervix or peritoneal cavity
termination of pregnancy or rupture of structure = haemorrhage
typically non viable
Ectopic pregnancy symptoms
severe abdominal pain
spotting
amenorrhea
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
diabetes 1st identified during pregnancy (if mum already had diabetes not GDM)
OGTT @ 24-28 weeks
fasting blood sugar already higher
GDM Risk Factors
previous GDM/ family history of GDM
enthnicity —> when mother in utero has insuffiecient nutrients therefore pancreas not developed fully therefore when come to Aus pancreas cant handle food therefore increases change of GDM
Age >40 years
obesity, especially BMI > 35 kg/m2
previous macrosomia ( baby birth weight >4 500g or >90th percentile
PCOS
medications (e.g., corticosteroids)
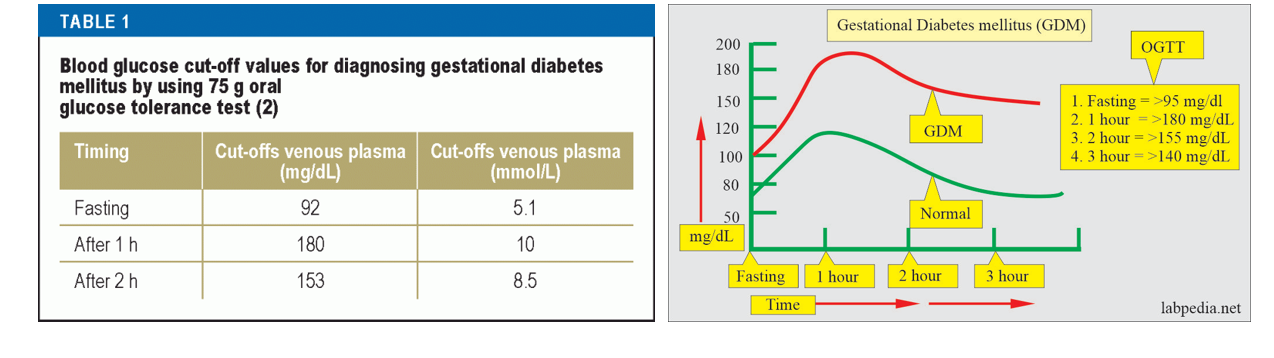
GDM Diagnostic Values
All women undergo OGTT (75g) 24-28 weeks gestation
other evaluations may be required if Hx indicated
Fasting PG: (>5.1 mmol/L)
1 hour PG: (>10.0mmol/L)
2 hour PG: (>8.5mmol/L)
GDM symptoms
GDM symptoms usually uncommon, however if blood sugar levels to high
polydipsia (excessive thirst)
polyurea (increase in the frequency of urination)
xerostomia (dry mouth)
gential itching
blurred vision
general malaise
Effects of GDM
high blood glycose caused hyperglycemia
hyperglycemia stimualted B cells to secrete more insulin
insulin targets cells in maternal tissue to uptake more glucose = insulin resistance
placenta secreted various hormones that inhibit the functioning of insulin
insulin resistance occurs due to blood glucose not being taken efficiently = hyperglycermia
increase in blood glucose circulated in fetal blood which leads the fetal pancreas to secrete its own insulin
fetus tissue uptake of more glucose causes fetal macrosomia (baby born big = increase illnesses later in life, trauma @ birth, hip dislocation
what id DoHAD
Development Origin of Health & Disease
fetal programming: 1st introduced by David Barker
correlation between maternal condition and development of disease in adult life
Role of placenta in fetal programming
decrease utero placental blood flow impairs supply to fetus therefore impair development (increase change for fetus to develop disease later in life)
placental weight/ birthweight ratio = better representation than birthweight
Programming of Adult Diseases
cardiovascular disease
renal disease
metabolic disease and obesity
osteoporosis
PCOS
neuroendocrine dysfunction
respiratory dysfunction
sarcopenia
behavioural —> schizophrenia
Effect of Stress on boy and girl placentas
Generally boys tend to be worse off
Female
slow growth trajectory
increases feto-placental adaptability
increases placental reserve capacity
Increased survival
slows down growth so impacted as much
Male
increase growth trajectory
decreases feto-placental adaptability
decrease placental reserve capacity
increased intrauterine morbidity and mortality risk
keeps growing at full rate
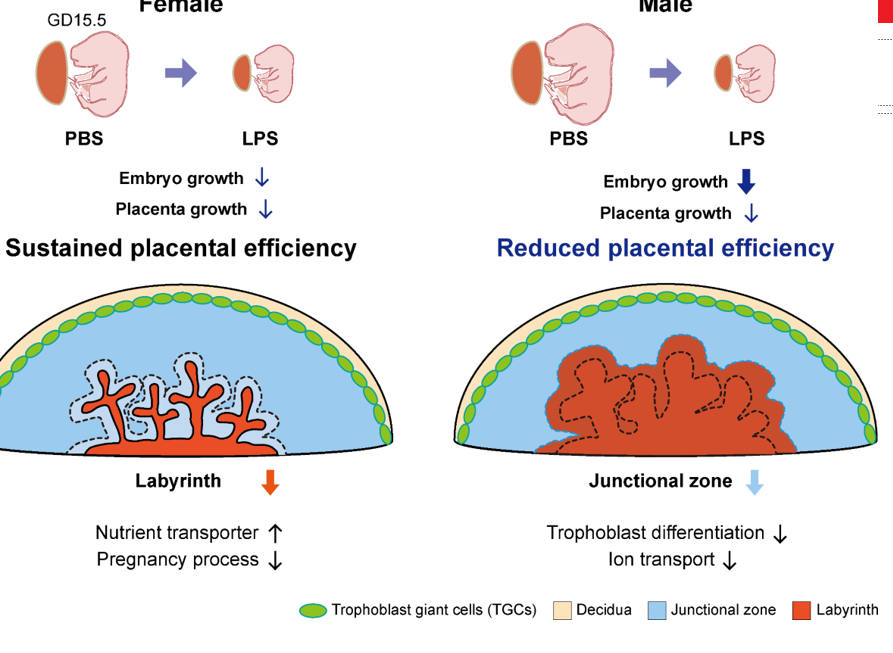
Example of DoHAD: Cannabus Research
Maternal Obesity
Effect on Mother
inflammation
pregnancy related complications
altered gut microbiota
Effect on Placenta
altered morphology
altered nutrient transport
inflammation (reduced IL6, Tnf in female placenta)
lipid accumulation
oxidative stress
Effect on Offspring
Male
compromised mitochondrial respiration
increase adipocyte area
impaired glucose tolerance
Female
increased insulin secretion
developed hypertension
increased anxiety
Pre-eclampsia pathophysiology (2 stages)
Stage 1
impaired spiral artery transformation
placental oxidative stress and ischemia
disrupted devlopment of placental villi
Stage 2
release of placental factors into maternal circulation
pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic imbalance (decrease PIGF, increase sFlt-1 & increase sENG)
systemic maternal endothelial activation
vascular injury and hypertension