bone tissue
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
bone tissue, hematopoietic tissue, adipose tissue, cartilage tissue, lymphatic tissue
what are the types of specialized connective tissue?
connective
bone is a type of ____ tissue
matrix and cells and connective tissue
similar to cartilage, bone tissue is surrounded by _____
matrix is calcified, so it is harder and less flexible, and blocks diffusion, so it is very vascular
how is bone tissue different than cartilage tissue?
yes, very
is bone tissue vascular?
no
does diffusion of nutrients occur in bone tissue?
protection of vital organs, support of soft tissues, locomotion- attachment site of muscles and tendons, houses bone marrow, involved in the metabolism of calcium
functions of bone tissue:
it is where muscles and tendons attach
why is bone tissue responsible for locomotion?
calcium
bone tissue is involved in the metabolism of ____
1. reticulated spongy/cancellous bone
2. compact bone
what are the two types of bone tissue at a macroscopical level?
reticulated spongy/cancellous bone
what type of bone tissue houses the bone marrow?
reticulated spongy/cancellous
the epiphysis of long bones is made of ______ bone tissue
reticulated spongy/cancellous
what type of bone tissue makes up short and flat bones?
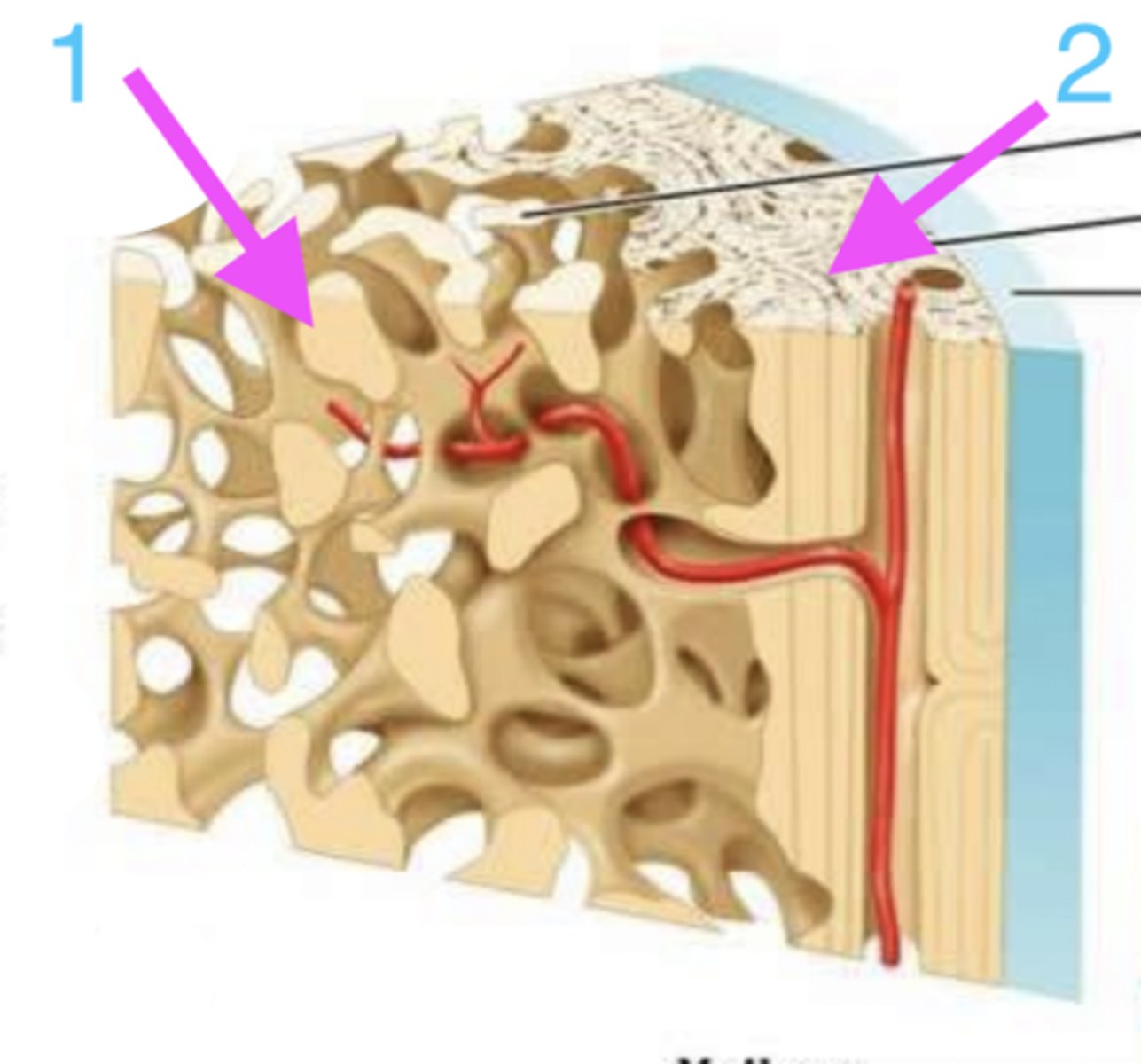
coating reticulated spongy/cancellous bone, surrounding central canal
where is compact bone found?
reticulated spongy/cancellous
what type of bone is this?

compact
_____ bone surrounds the central canal with bone marrow
2
which is compact bone?
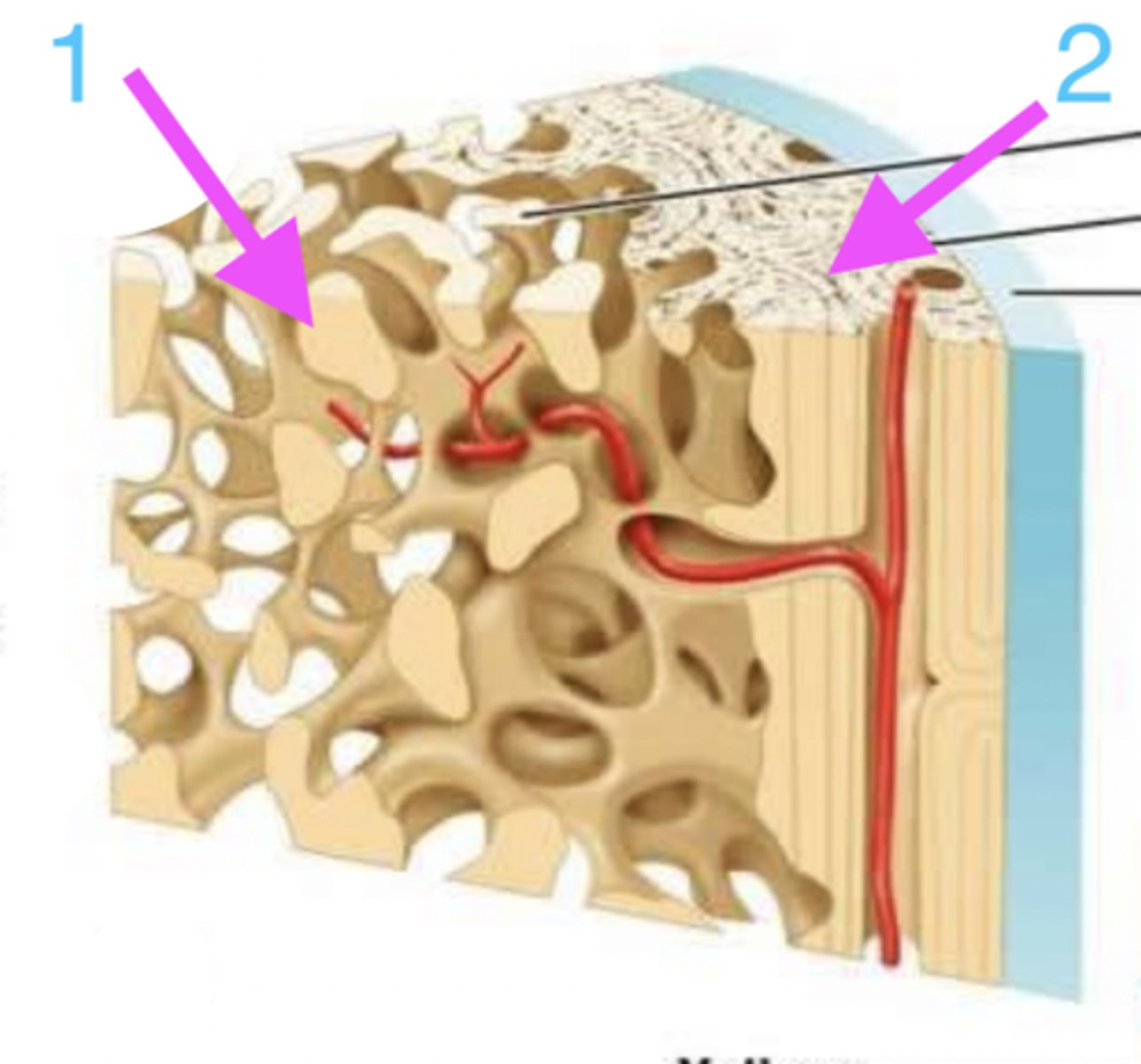
1
which is reticulated spongy/cancellous bone?
wearing
what technique is sued to study the inorganic matrix of bone tissue?
removes the matrix, the cells and matrix can be studied
what does de-calcification do? what can you study with this method?
H-E, Schmorl staining
what two stains are most common to see bone tissue?
not very different
how do compact and reticulated spongy/cancellous bone differ microscopically?
canaliculi and lamellae in compact bone sections
what does a Schmorl staining stain?
calcium phosphate, organized around collaged fibers
small amount of magnesium, sodium, potassium, citrate and carbonates
what is the inorganic bone matrix composed of?
an inorganic matrix without calcium phosphate
what is an osteoide?
75%
how much of the matrix is inorganic?
collagen I
proteoglycans
ECM proteins (osteocalcin, osteopontin, osteonectin,..)
cytokine and growth factors
what composes the organic bone matrix?
inorganic
if the matrix contains calcium phosphate, it is.....
osteogenic cells
osteoblasts
osteocytes
osteoclasts
what four types of cells would you find in bone tissue?
no
do osteocytes and osteoblasts divide?
mesenchymal stem cells that differentiate into bone cells
what are osteogenic cells?
fusiform
what shape are osteogenic cells?
in the deeper layer of the periosteum and endosteum covered by the Havers conducts
where are osteogenic cells located?
cubic rounded, excentric nucleus, small cytoplasmic extensions connected by gap junctions
describe the appearance of osteoblasts
in areas of matrix synthesis
where would you find osteoblasts?
to synthesize the bone matrix
what is the function of osteoblasts?
osteoblasts
what type of bone cell?
osteoblasts
which bone cell has the role of synthesizing the bone matrix?
osteocyte
a osteoblast that is surrounded by bone matrix is now called a _______
basophilic, purple
the cytoplasm of an osteocyte is ______, so it is dyed ______ with the H-E stain
osteocyte
which bone cell has long cytoplasmic extensions that goes into the calciferous conducts?
maintains the bone matrix, stores calcium
what does an osteocyte do?
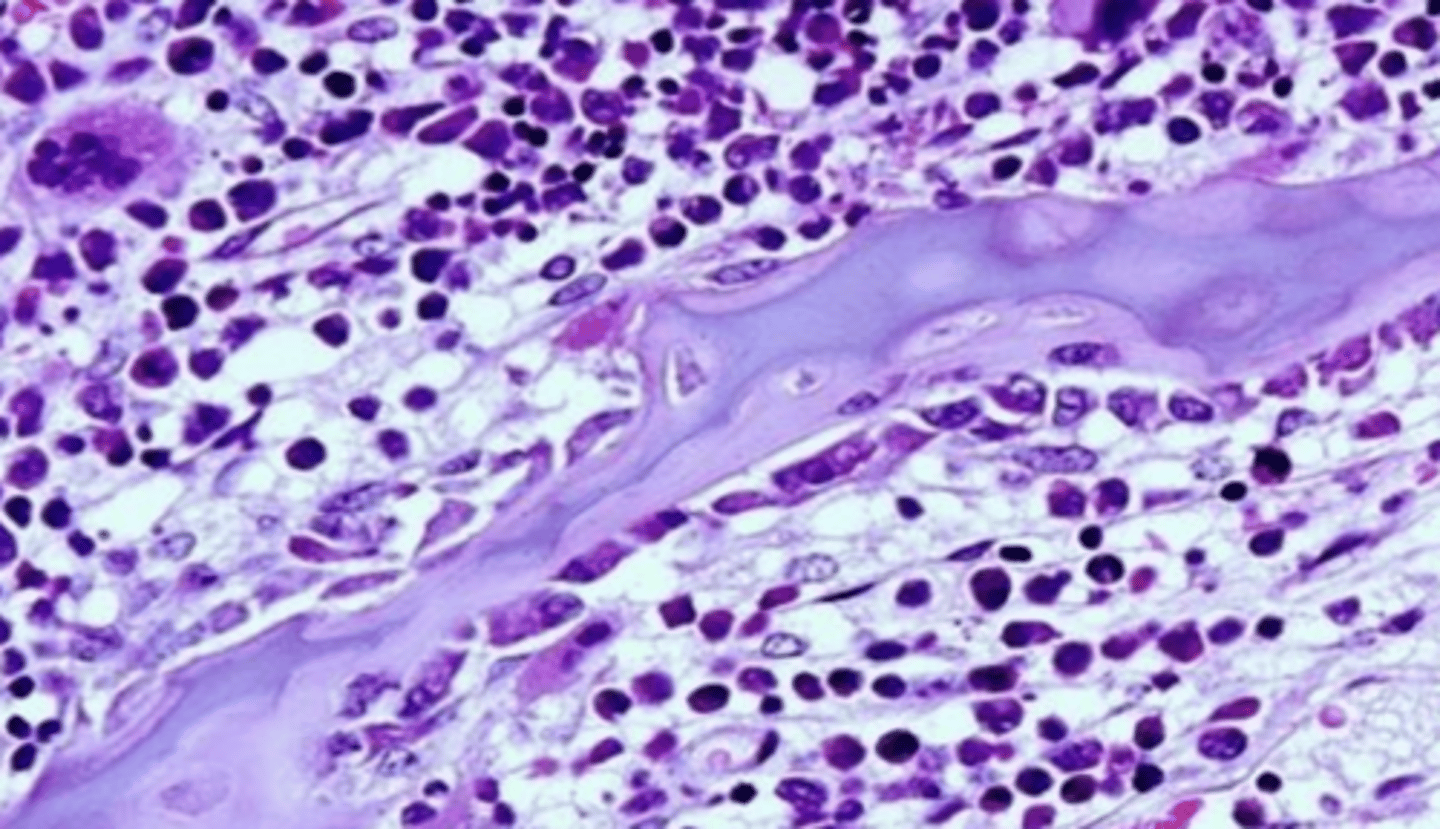
osteocytes
what are these bone cells?
monocytes
osteoclasts originate from______
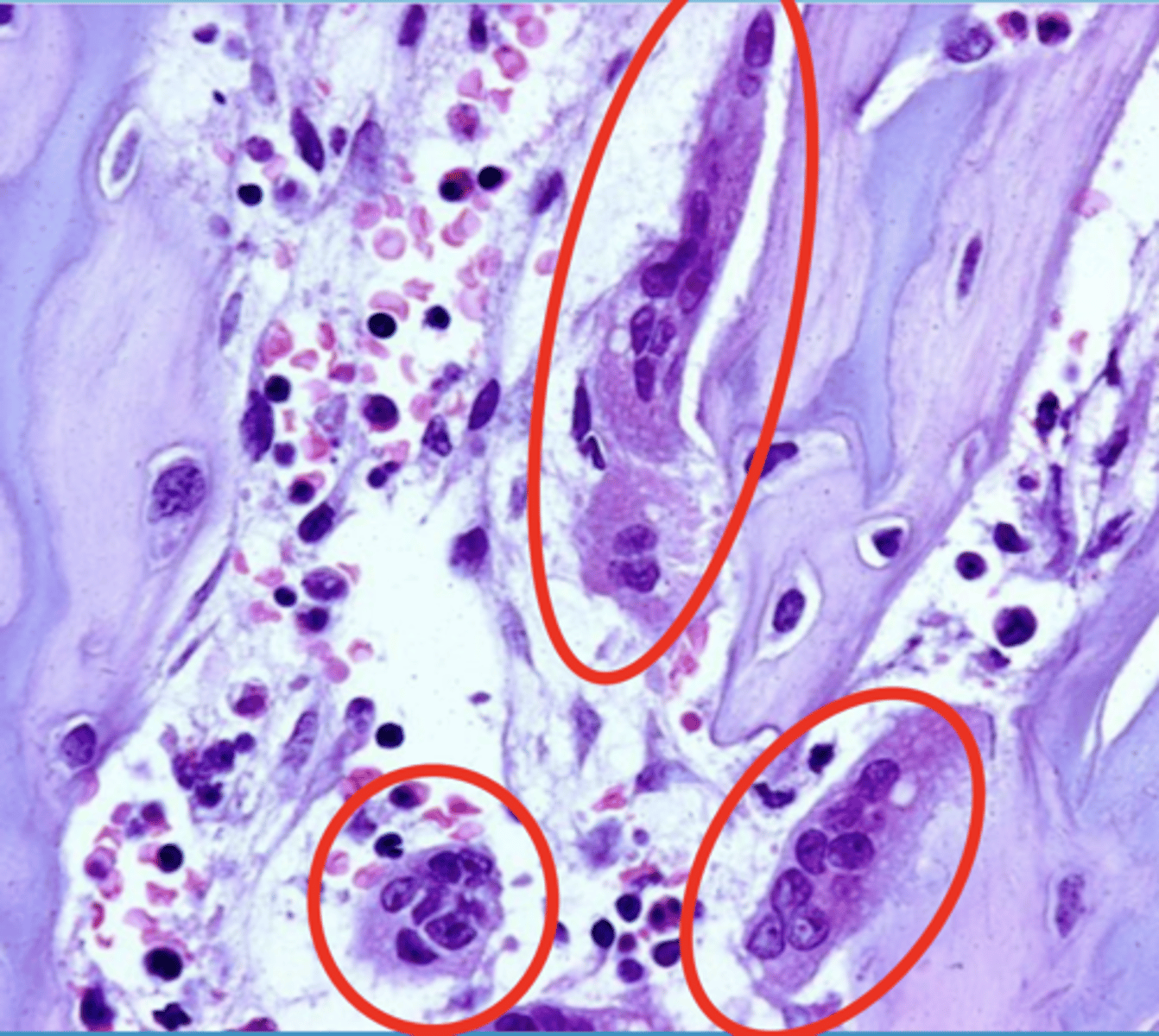
osteoclasts
which bone cell is big and multinucleated?
bone reabsorption
what is the function of osteoclasts?
Howship lacunas or resorption bay, areas of bone remodeling
where would you find osteoclasts?
osteoclasts, they are multinucleated
what type of bone cell?
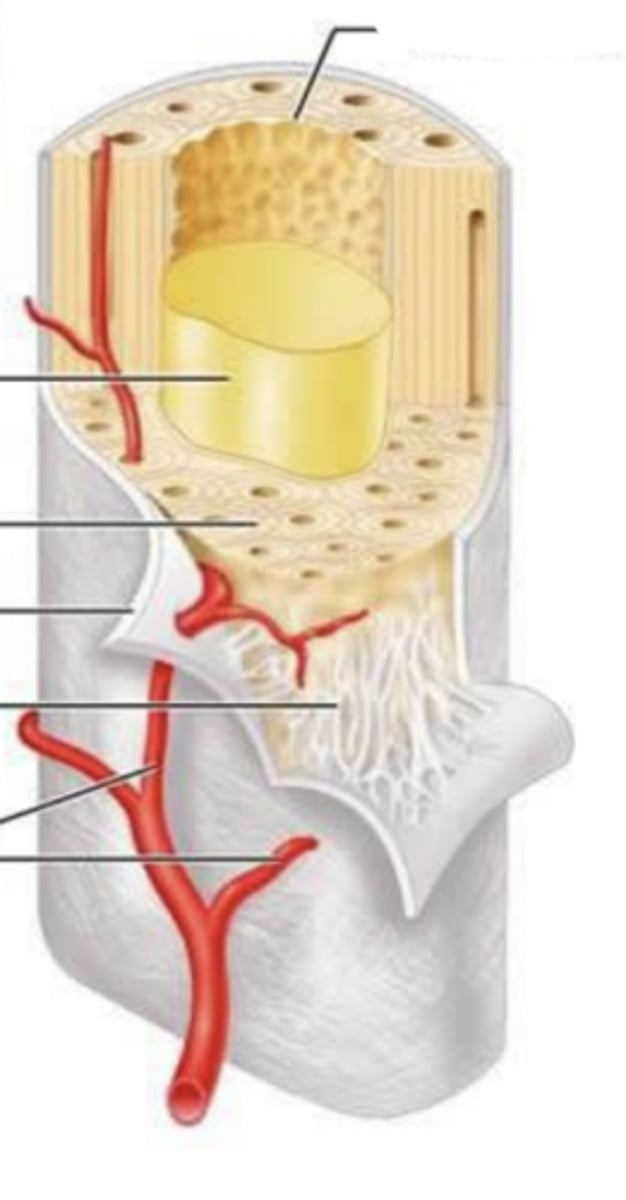
dense, irregular CT
what type of CT makes up the periosteum?
yes, very
is the periosteum vascularized?
the external layer
what part of the periosteum is fibrous?
osteogenic cells
the internal layer of the periosteum is made of_____
the whole bone except articular surfaces
the periosteum covers _____
loose
the endosteum is made of ____ CT
osteogenic cells and osteoblasts
what type of bone cells make up the endosteum?
endosteum
which lining covers the medulla canal. spongy cavities, and the Havers and Volkmann conducts?
both periosteum and endosteum
which lining functions to repair bone fractures?
periosteum
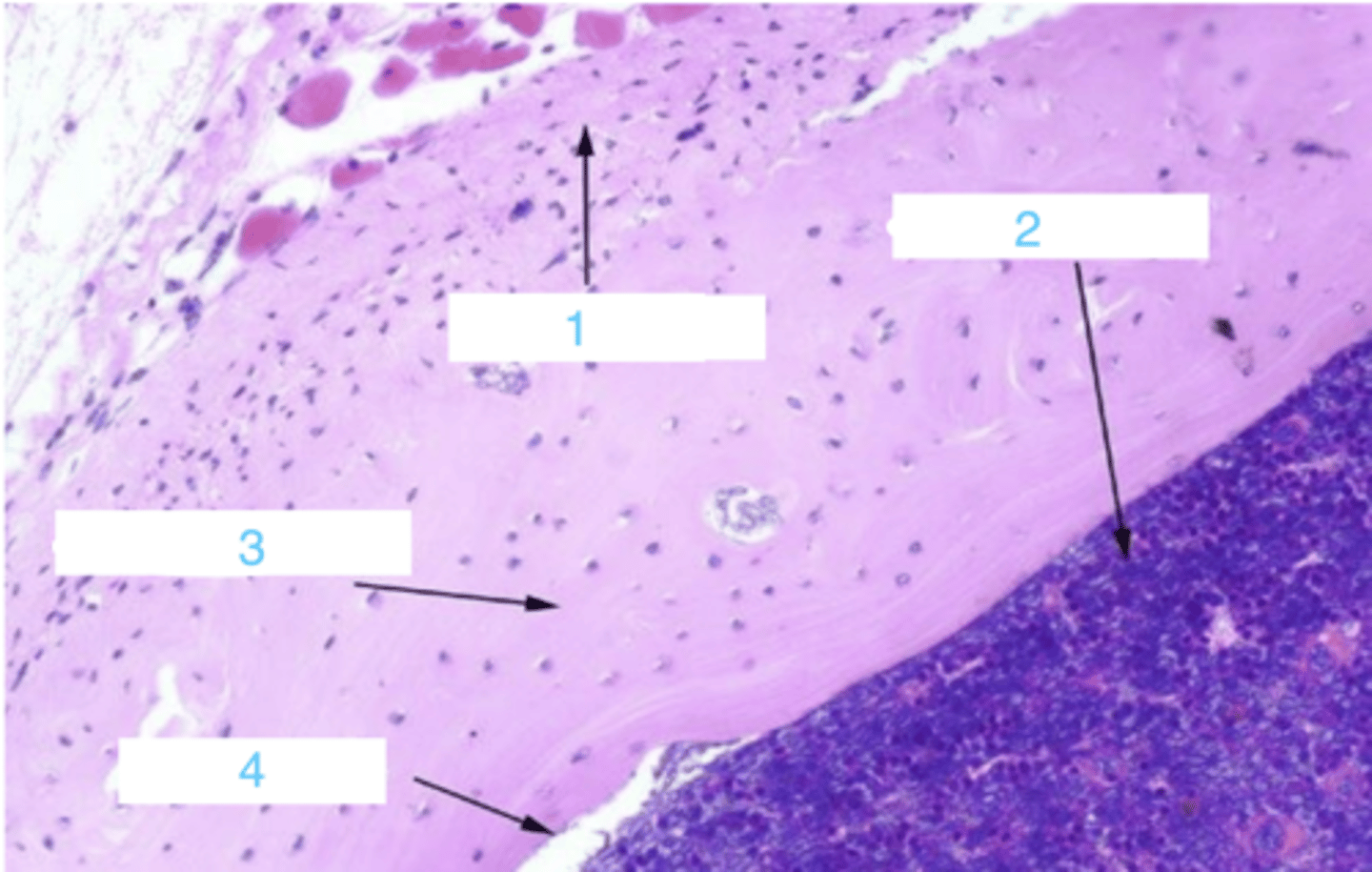
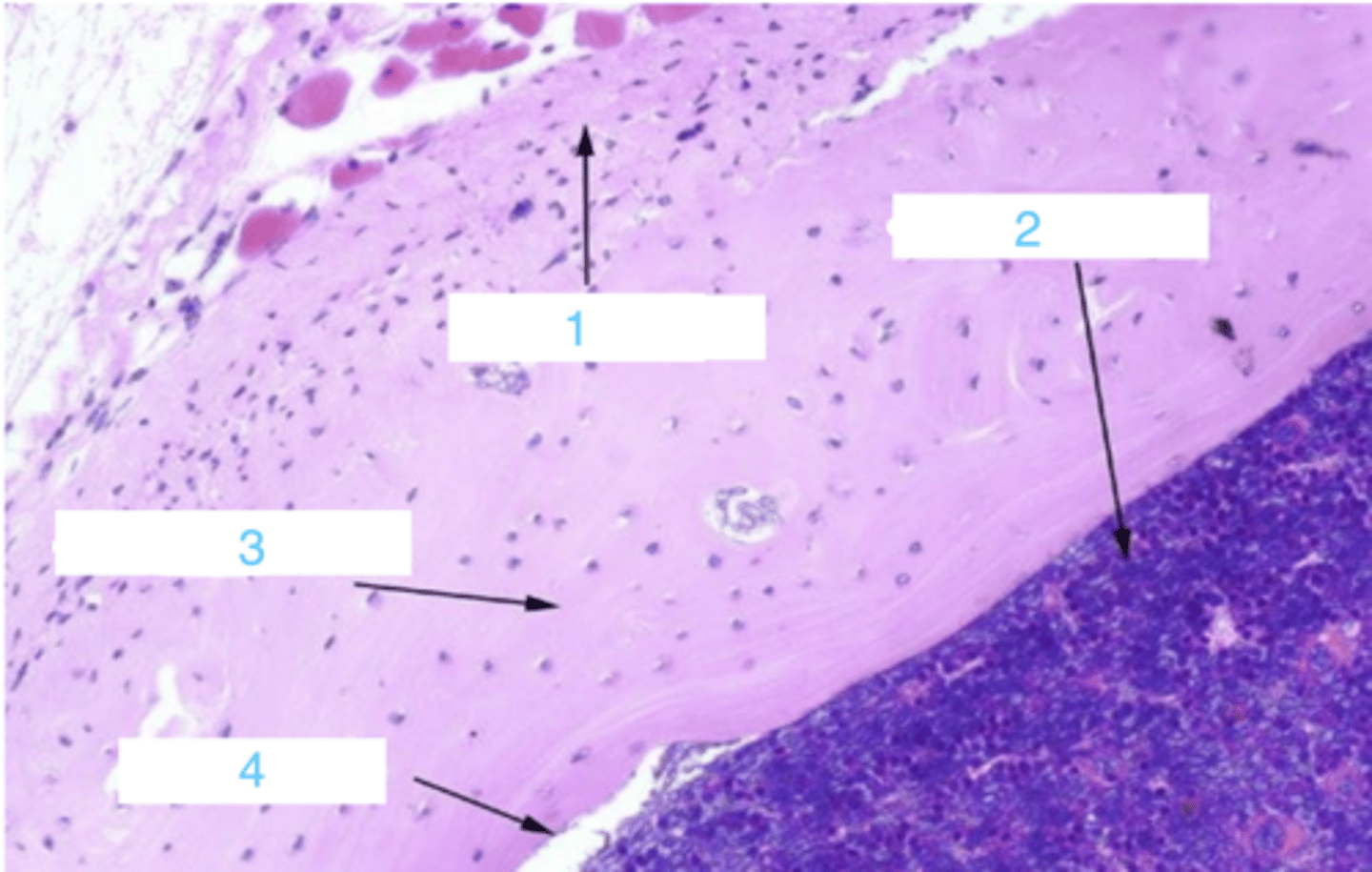
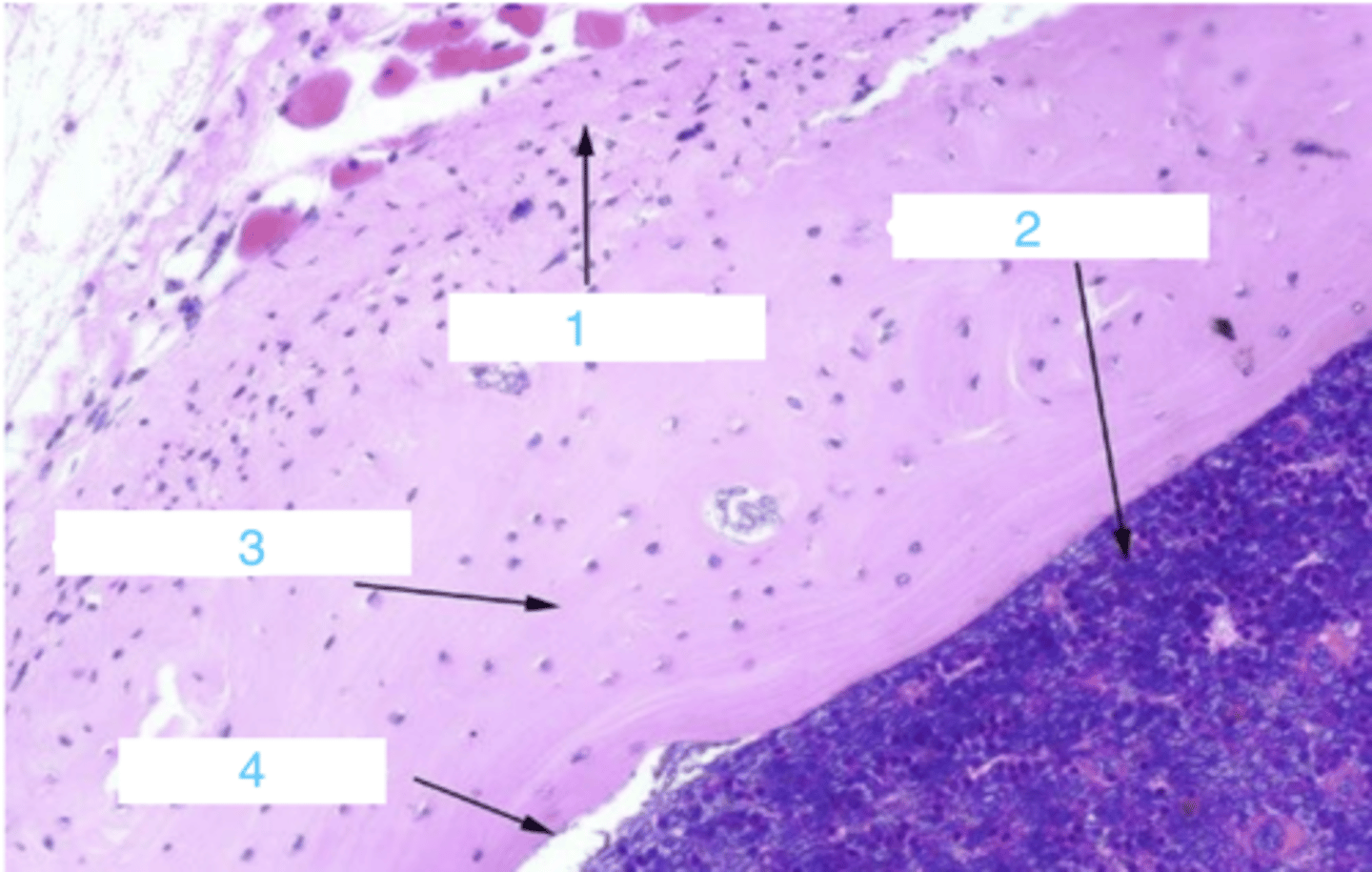
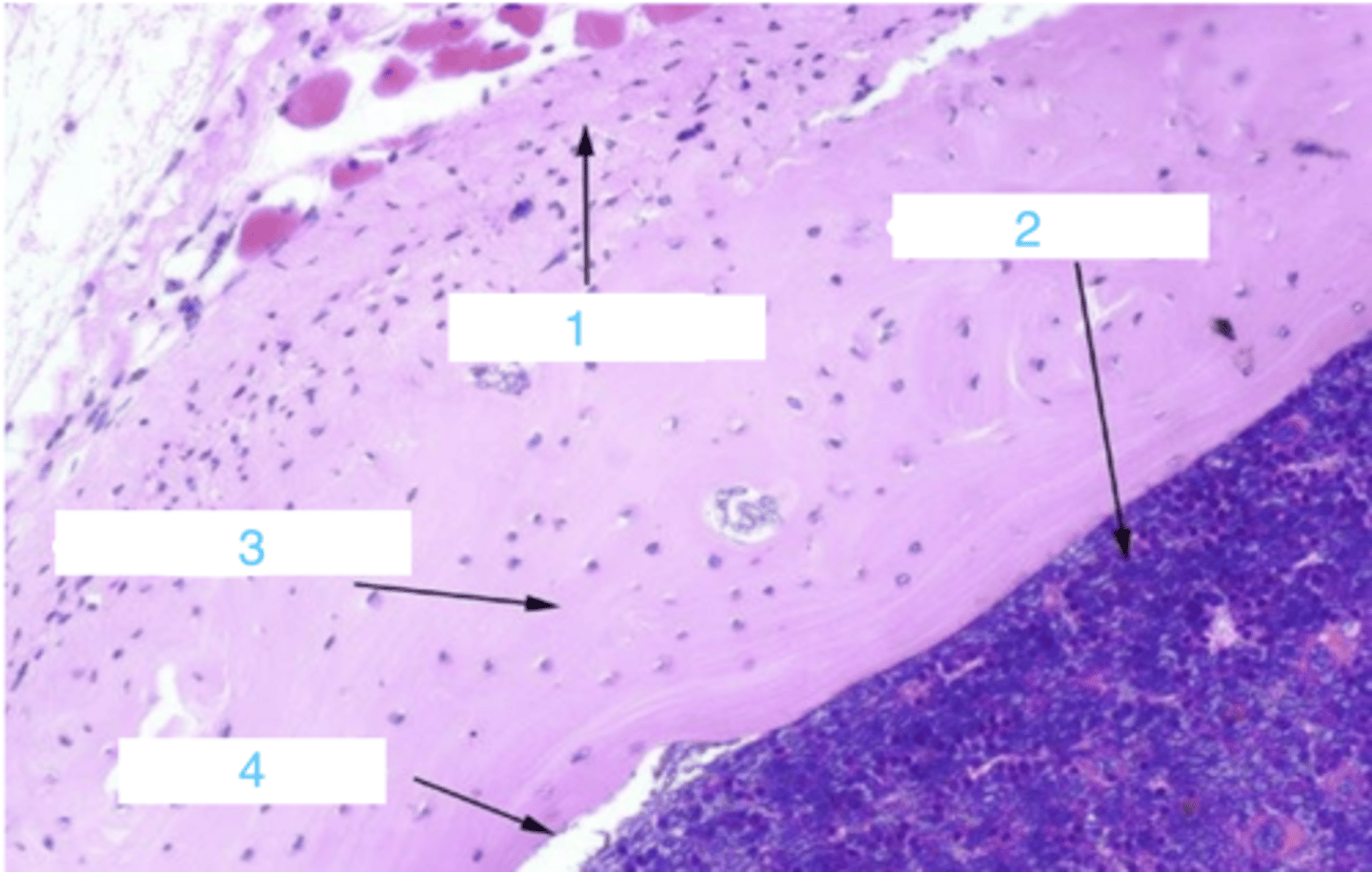
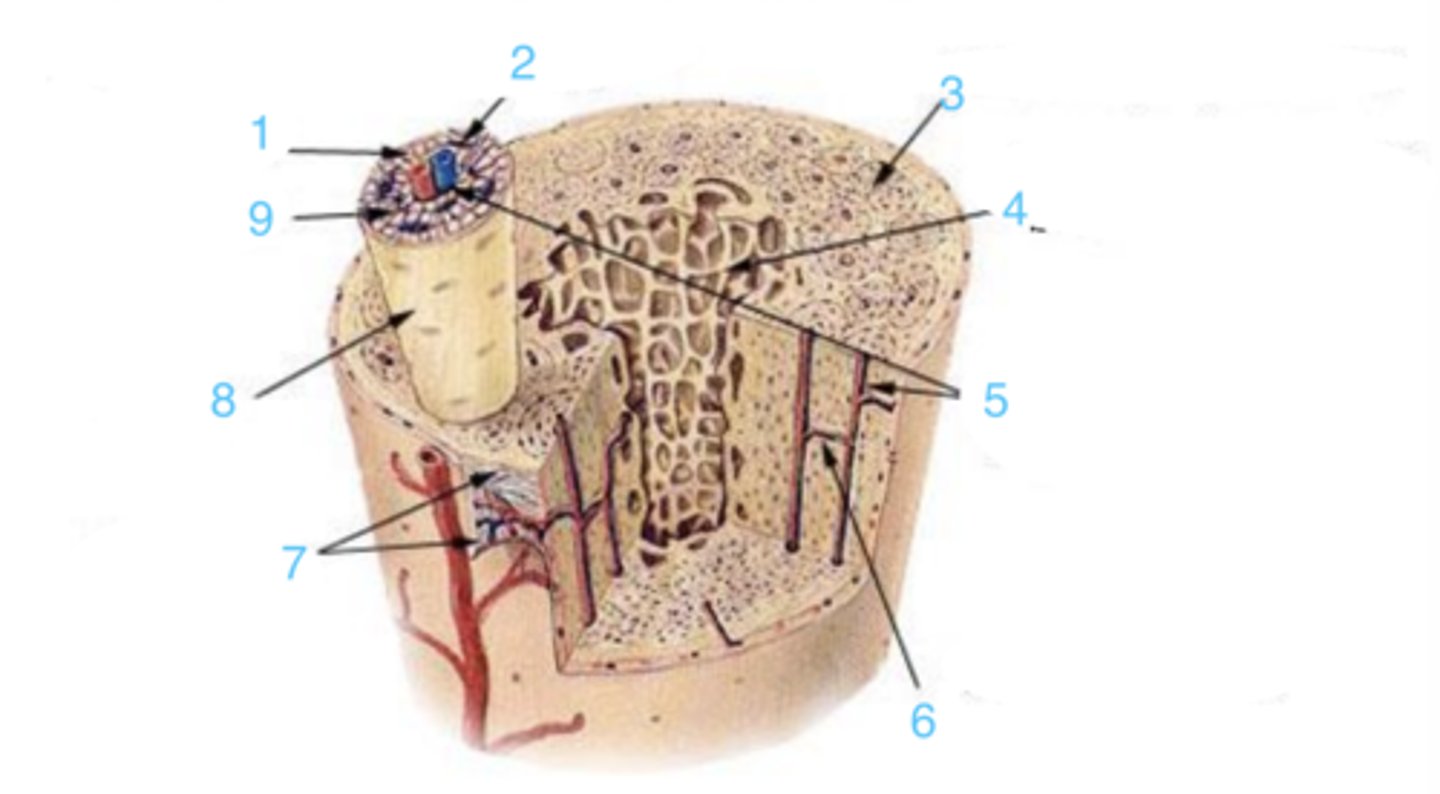
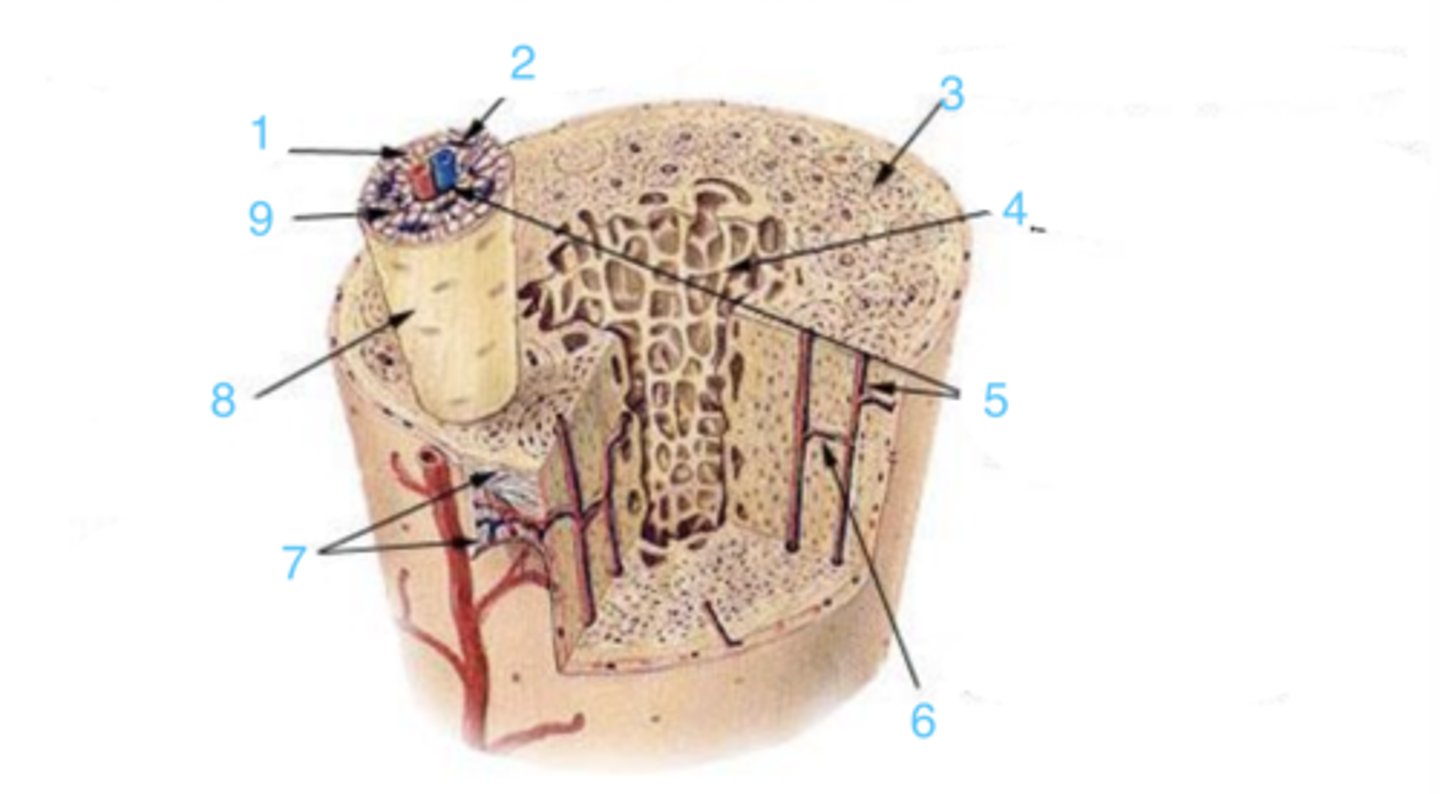
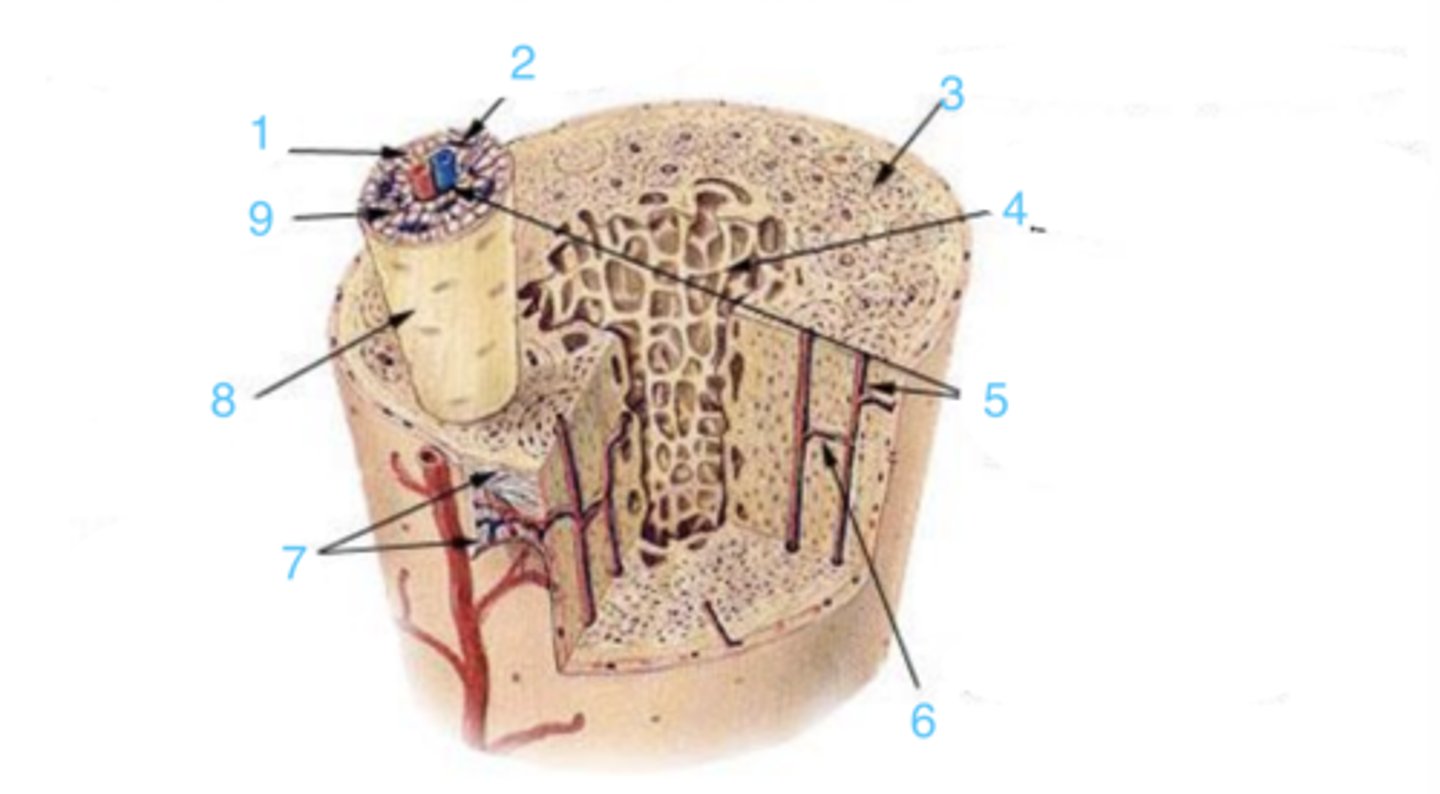
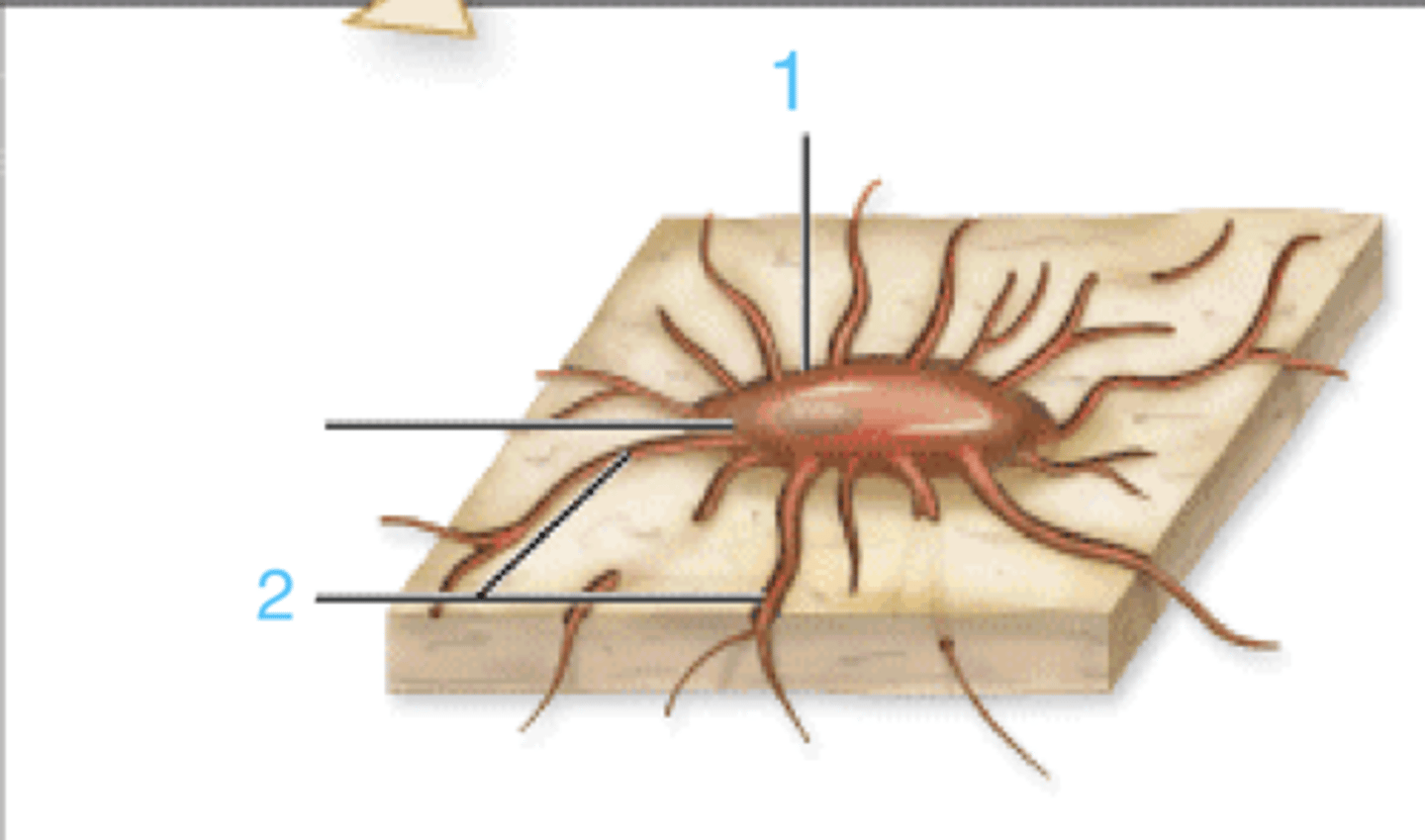
what is at 1?
4
where is the endosteum?
bone marrow
what is 2?
compact bone
3 is ____
fetus
primary/immature bone tissue is found in the ____
irregular collagen fibers, less minerals, more osteoblasts and osteocytes
describe primary/immature bone tissue
adults
where is secondary bone tissue found?
organized collagen, laminated system (lamellae), compact or spongy, network of nutritional conducts, lacunas and canaliculi
describe the characteristics of secondary bone tissue
secondary
which, primary or secondary bone tissue, has organized collagen fibers?
primary
which, primary or secondary bone tissue, has more osteocytes and osteoblasts?
Haversian canal
which canals run parallel to the bone axis?
perpendicular, Haversian conducts
Volkmann canals run ____ to the bone axis and bind ____
diffusion
how do spongy bones get nutrition?
lacunae
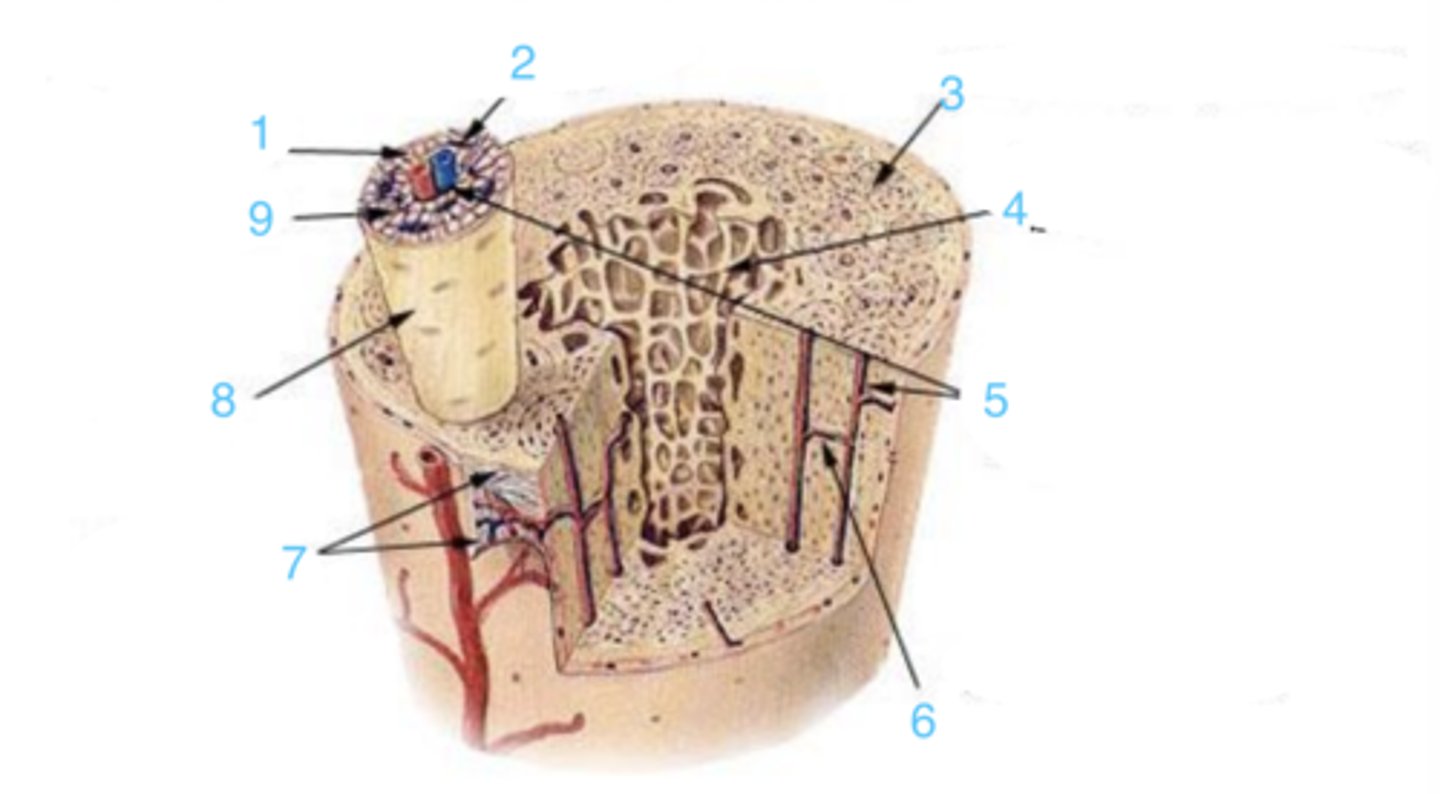
what structure is at 2?
compact
3 represents ___ bone
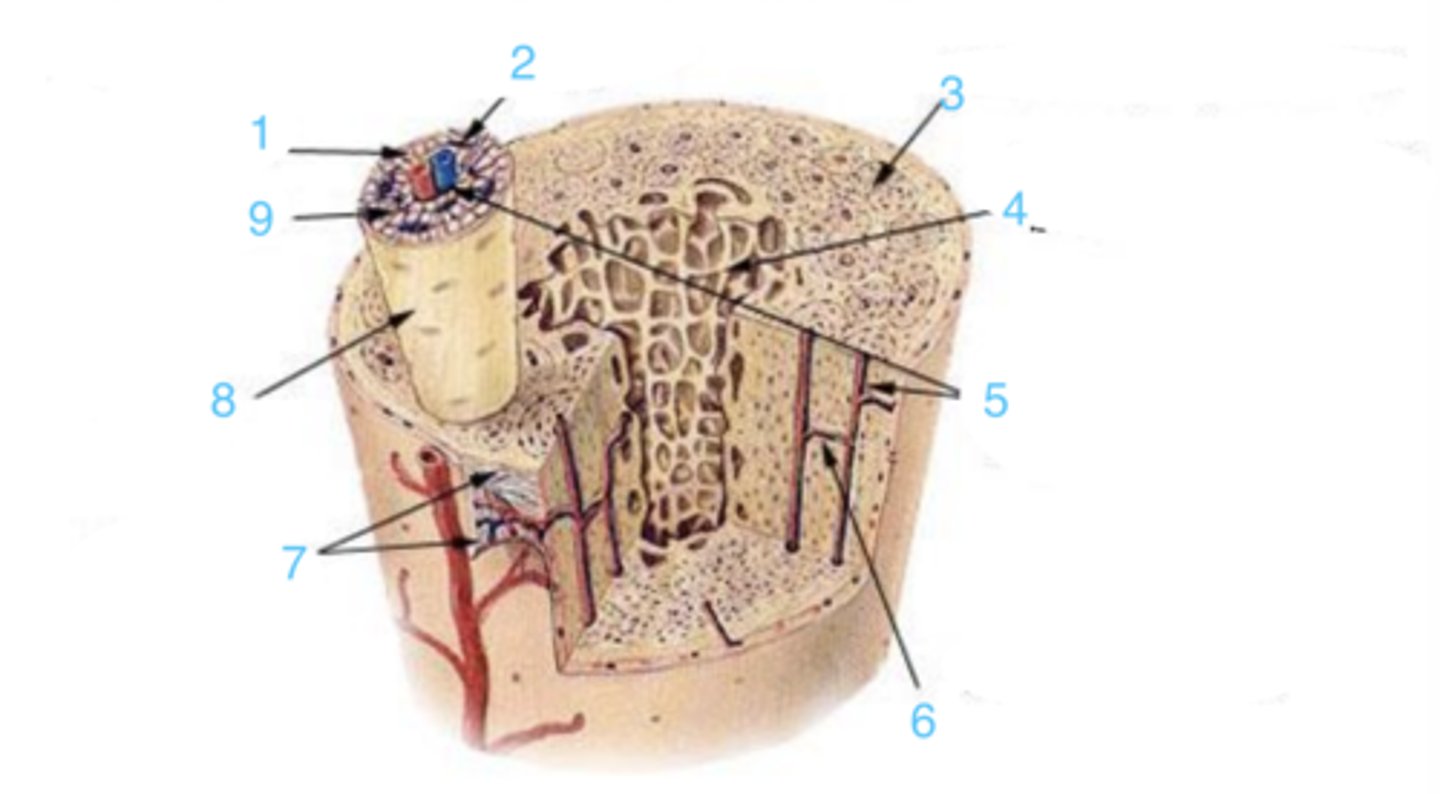
spongy
4 represents _____ bone
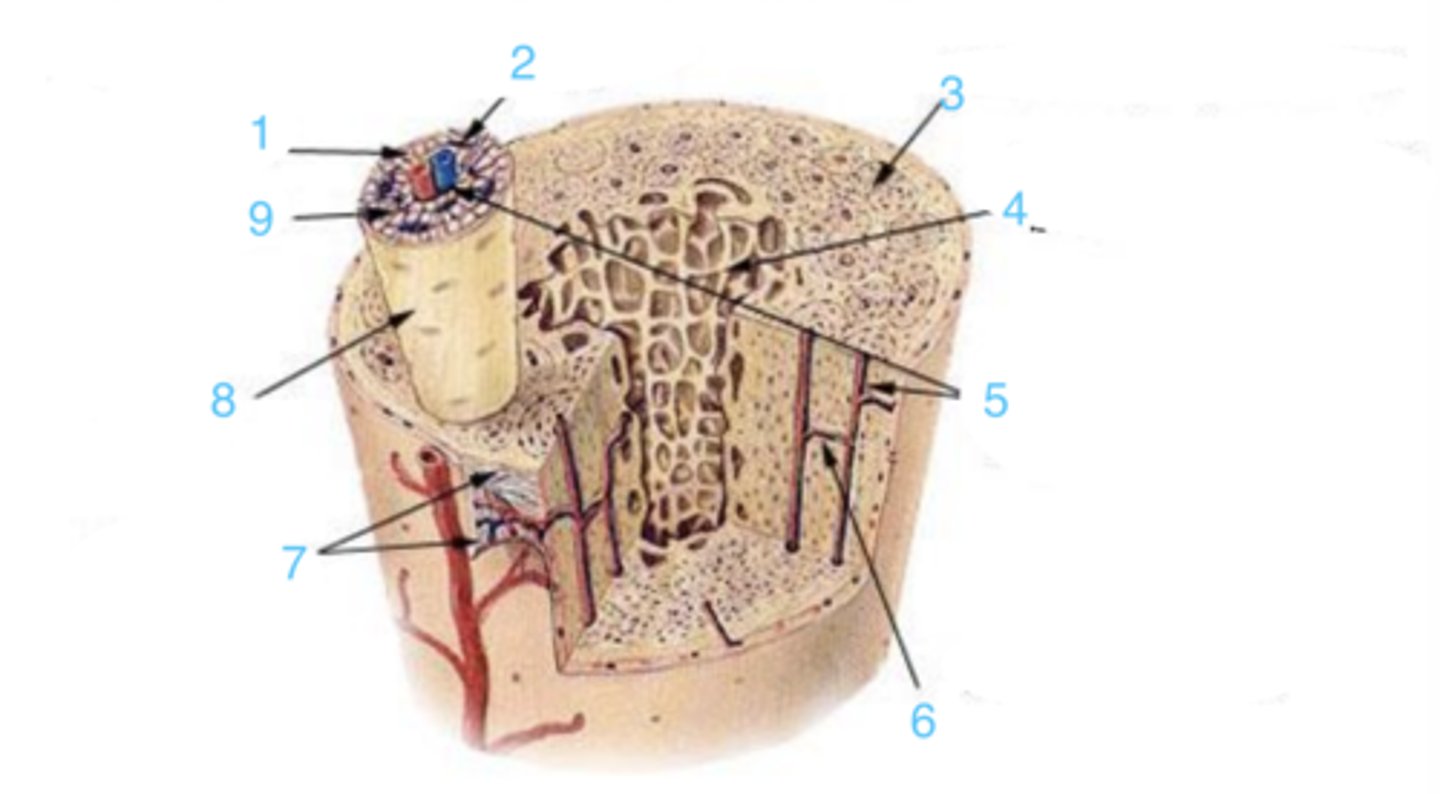
5
where is the Haversian canal?
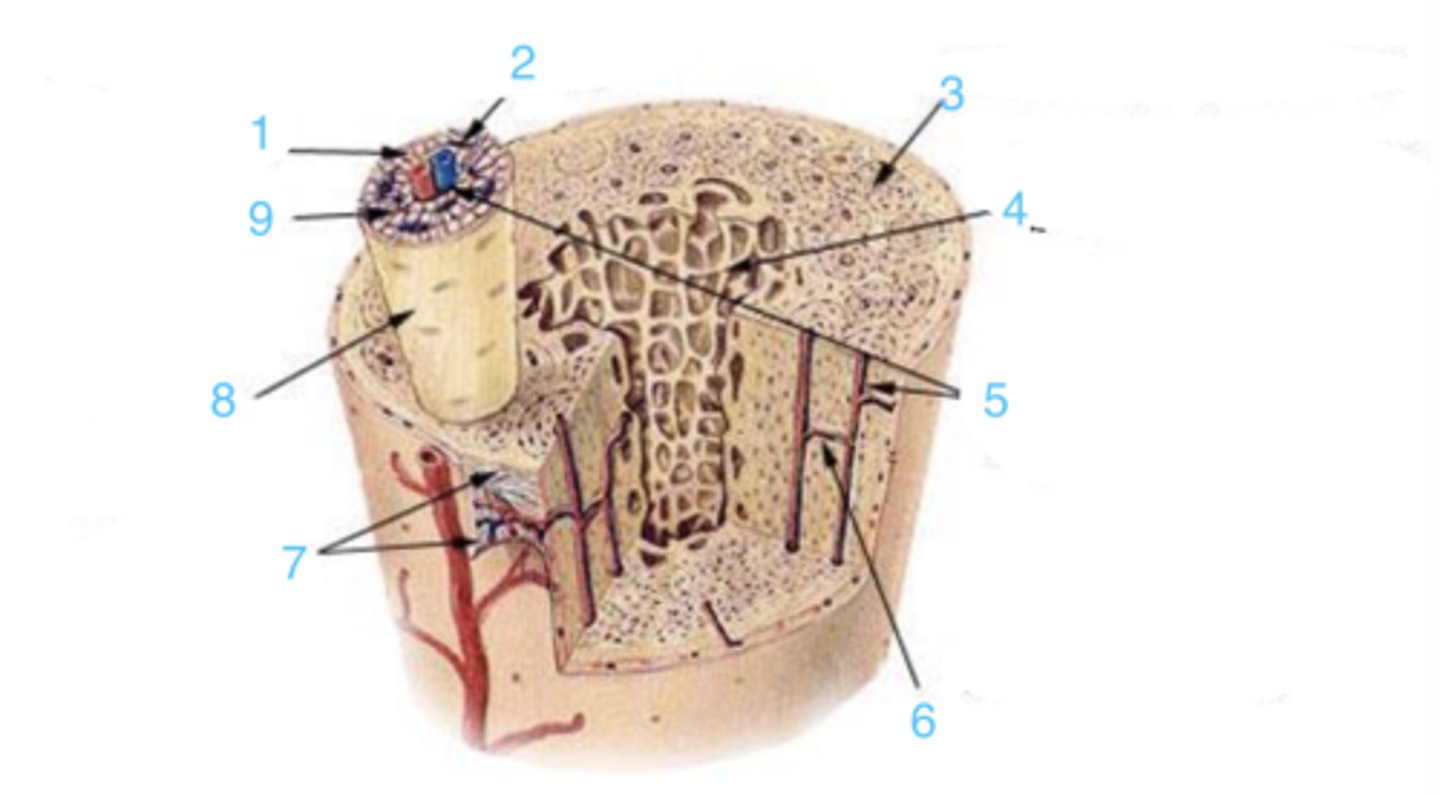
lamellae
what is the structure at 1?

Volkmann's canal
what is at 6?
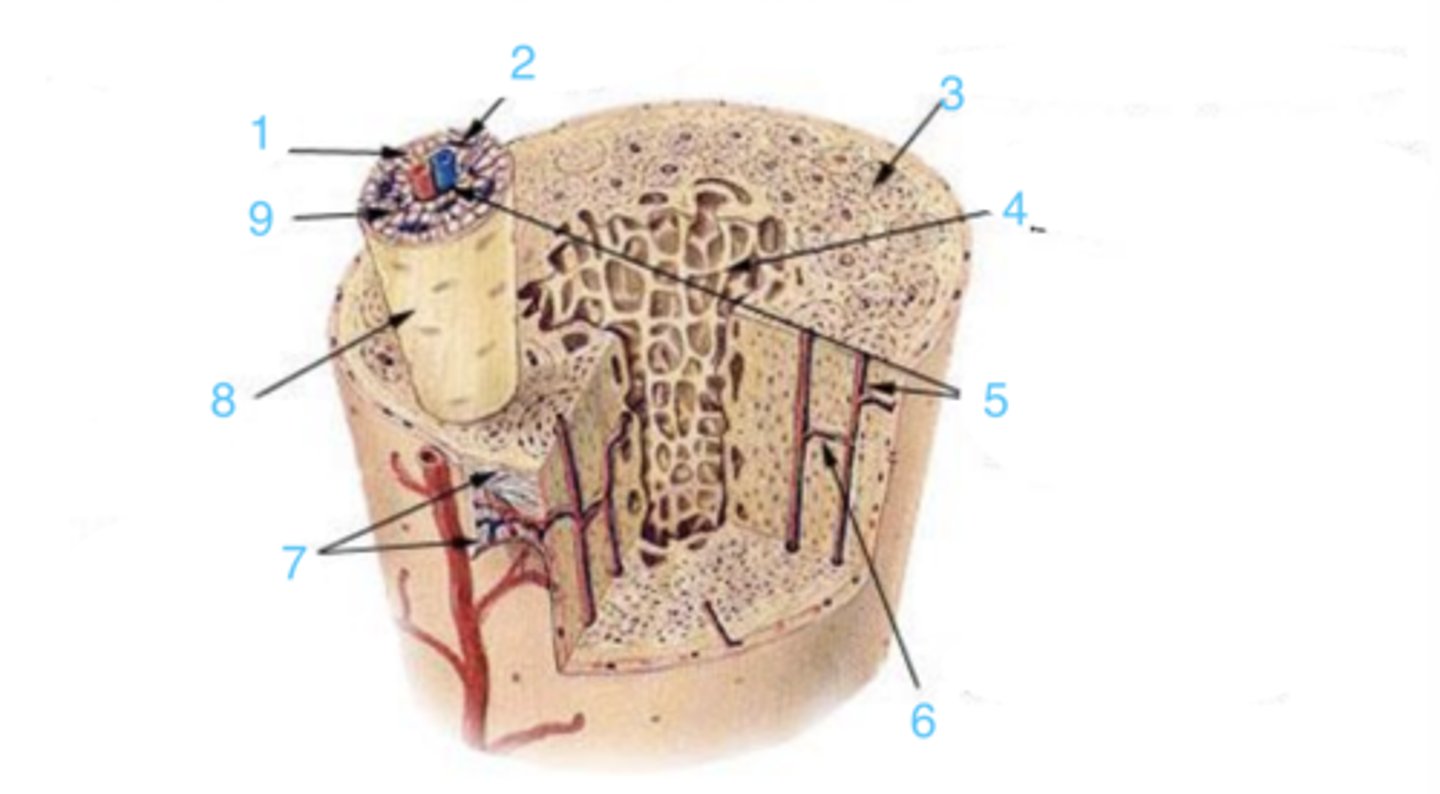
periosteum
what lining is at 7?
8
where is the osteon?
canaliculi
9 is ___
circumferential
secondary bone tissue has a ______ laminated system
cavities with osteocytes
what are lacunae?
canals to communicate with lacunaes
canaliculi or lamellar boundaries are ____
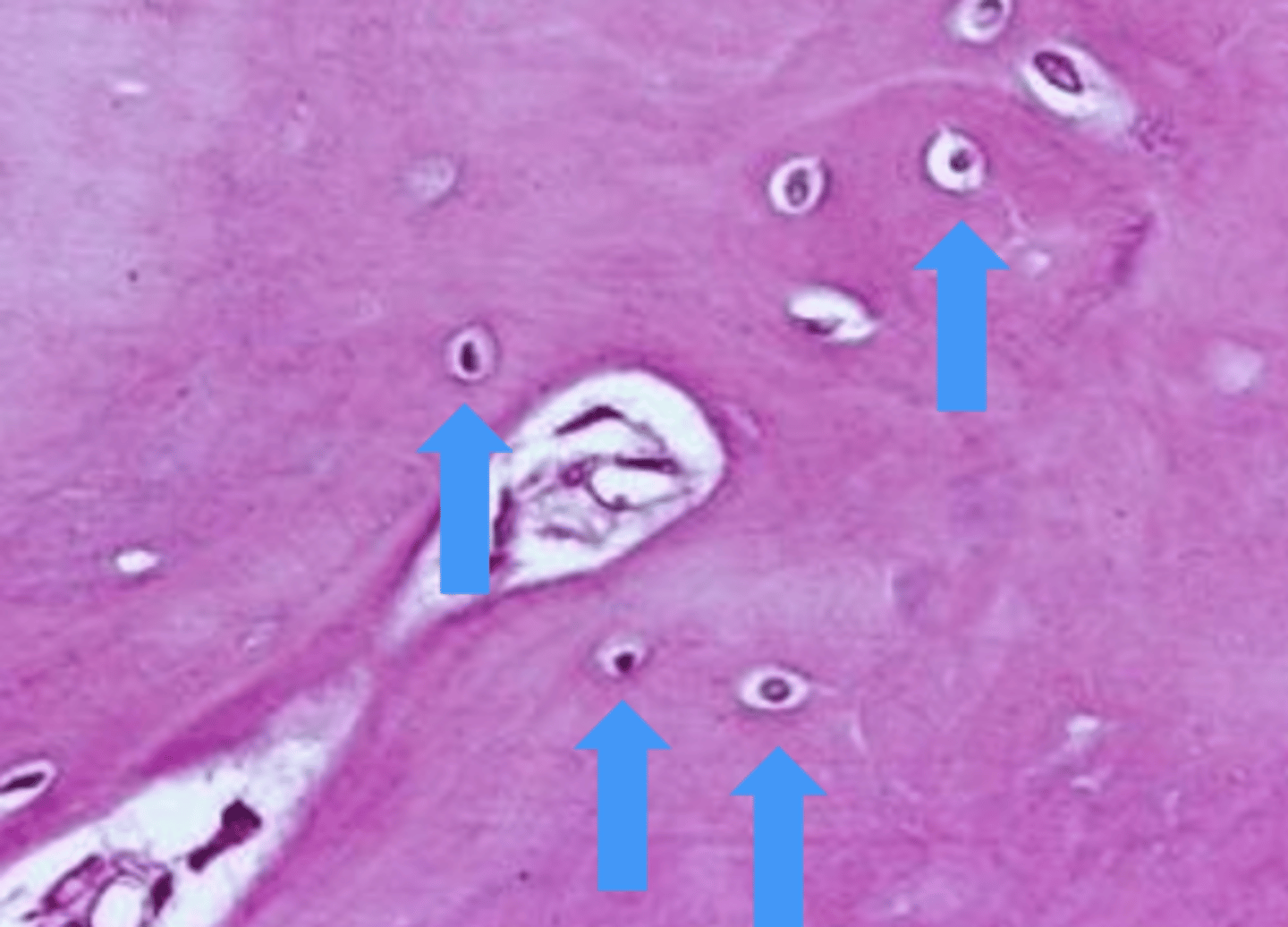
canaliculi
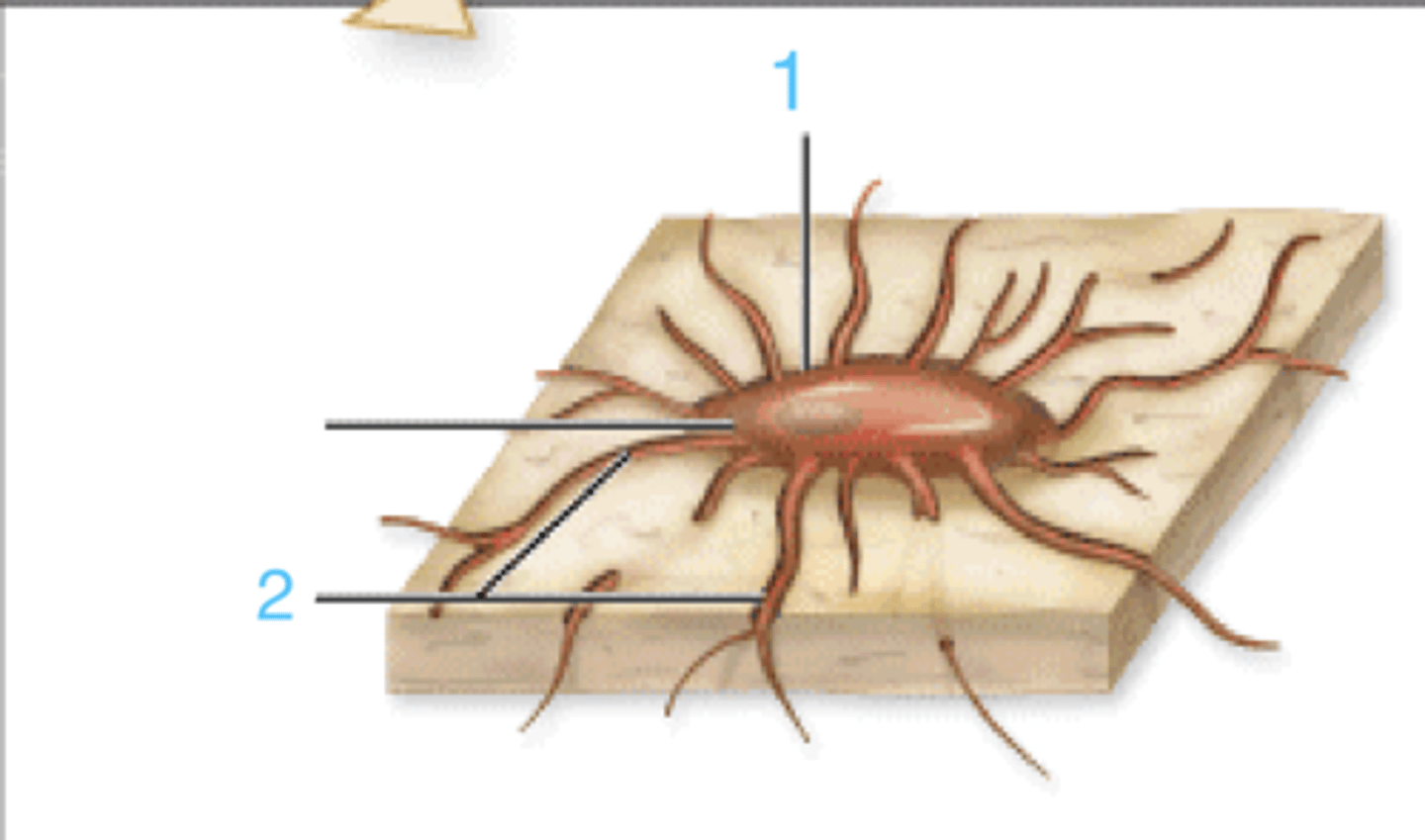
this is an osteocyte. what is at 2?
lacunae
this is an osteocyte. what is at 1?
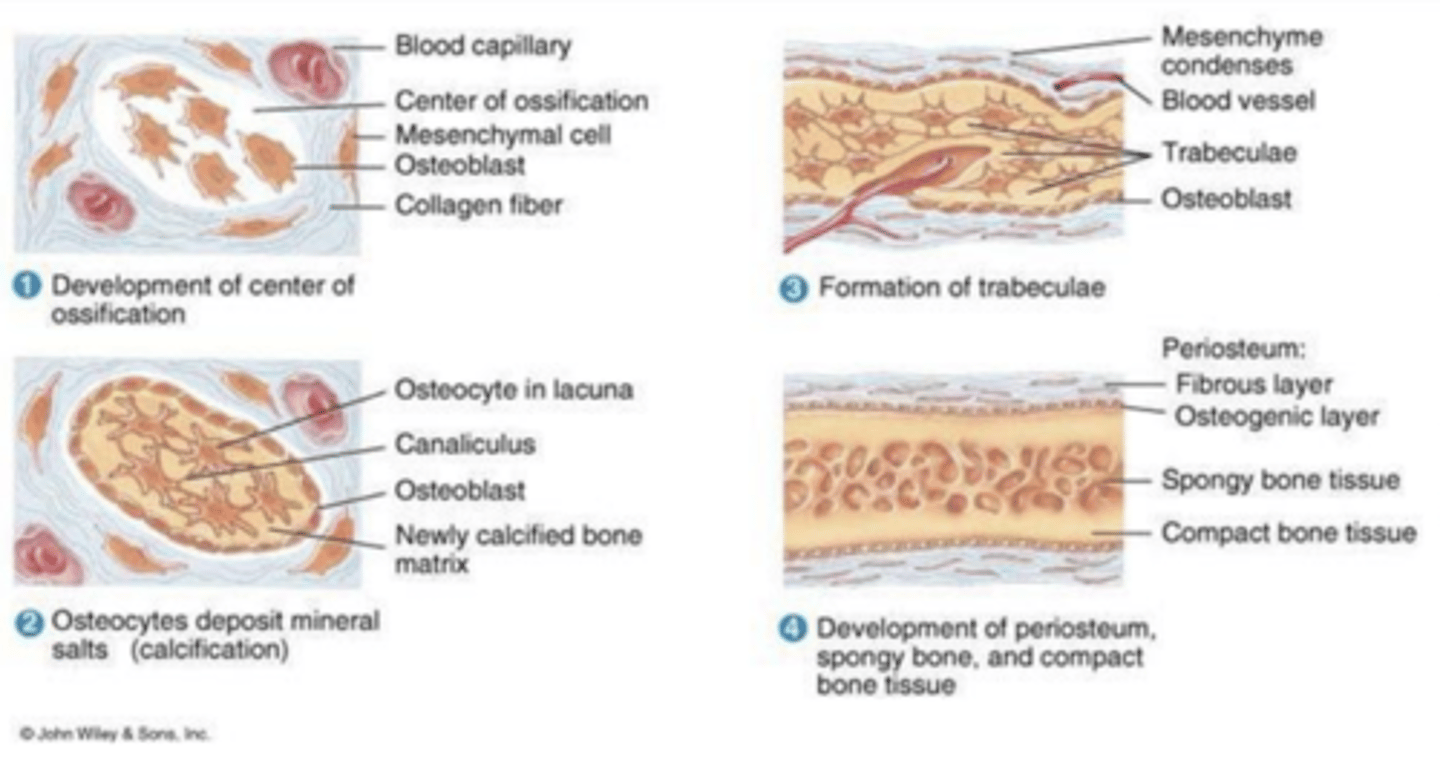
the process of bone formation
what is ossification?
non-organized laminated tissue
primary ossification results in _____
an organized laminated system
secondary ossification results in _____
reabsorption remodeling
what process occurs between primary and secondary ossification?
1. direct/intramembranous
2. indirect/endochondral
what are the two types of bone ossification?
direct
what type of ossification occurs in flat bones?
indirect
what type of ossification occurs in long bones?
-calcification of matrix
-radial growth
-osteocyte maturation into lacunas
-neoformation of vessels, migration of mesenchymal stem cells undifferentiated into the bone marrow
-remodeling resorption balance by osteoclast
describe direct ossification
-forms hyaline cartilage first in the diaphysis
-growth in length
-osteoblasts form bone
-the epiphyseal growth plate is the limit between primary and secondary ossification
-the calcified cartilage matrix is replaced by the synthesized bone
-formation of medullary canal
describe indirect ossification
indirect
direct or indirect ossification?
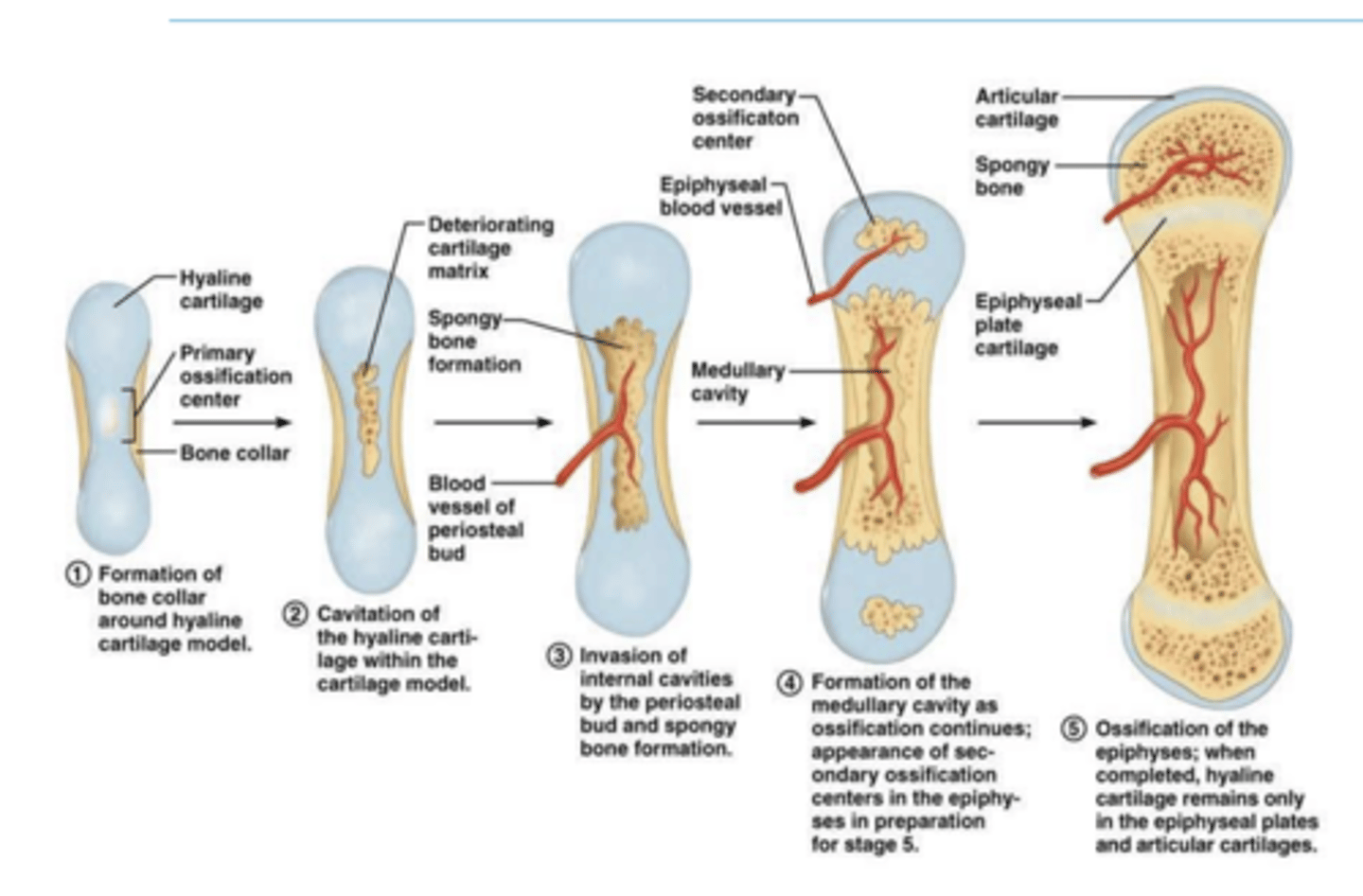
direct
direct or indirect ossification?